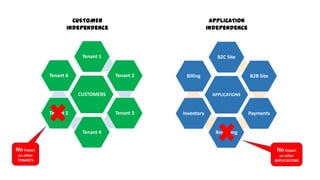
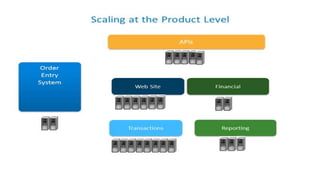
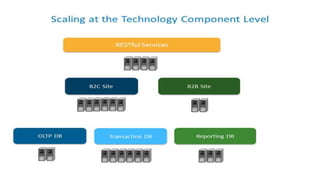
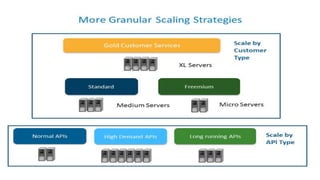
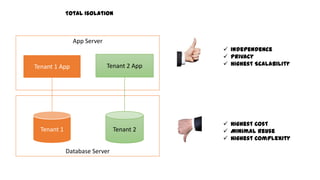
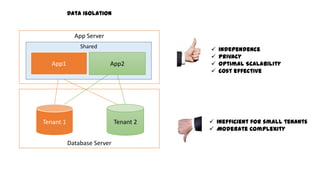
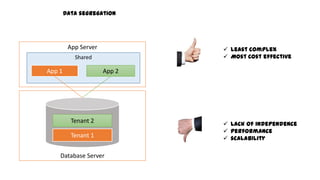
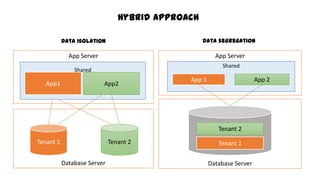
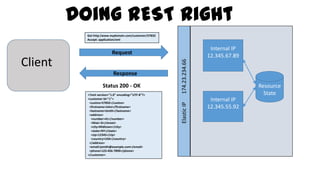
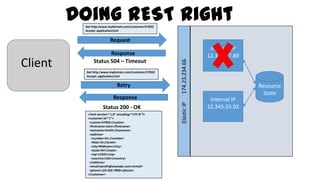
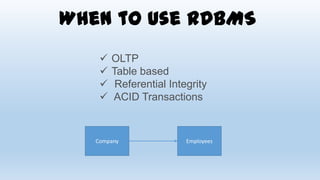
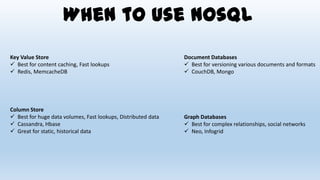
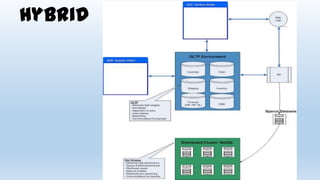
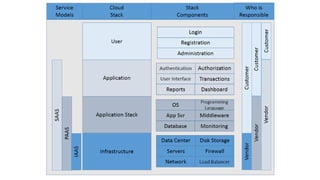
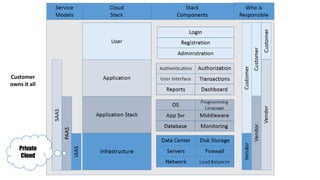
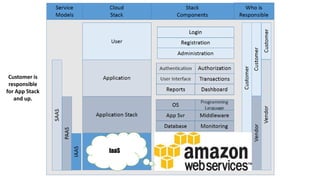
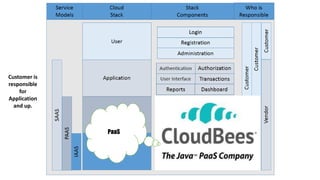
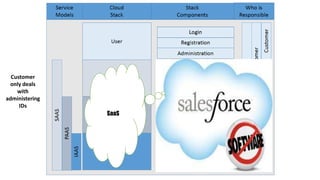
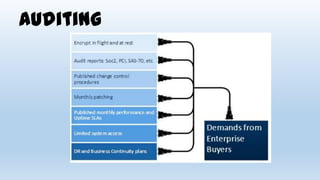
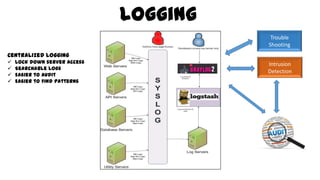
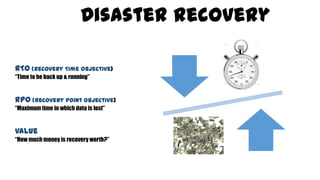
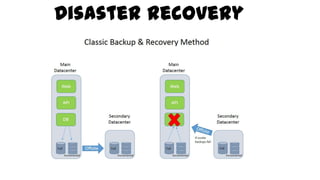
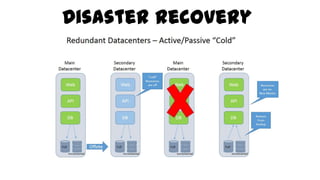
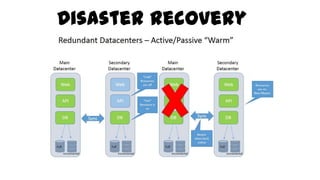
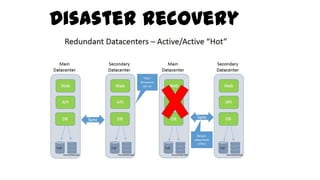
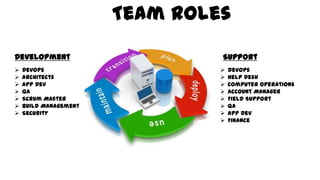
This document discusses design considerations for cloud computing. It covers topics like multi-tenancy approaches, data storage options, security, monitoring, disaster recovery and the roles of DevOps teams. Specifically, it analyzes different multi-tenancy architectures for isolating tenants and applications. It also outlines factors to consider when choosing between relational databases and NoSQL options. Lastly, it discusses disaster recovery objectives and strategies for the cloud.