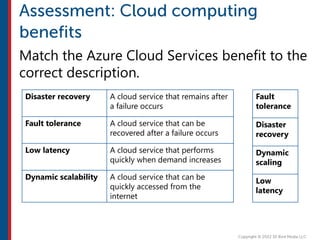
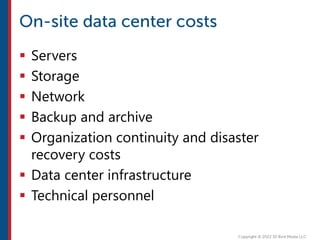
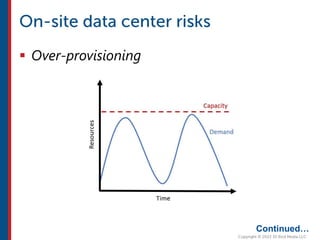
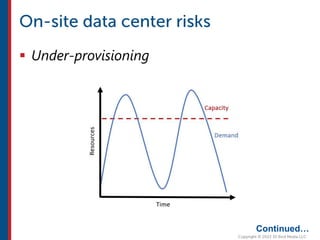
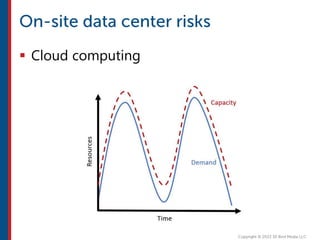
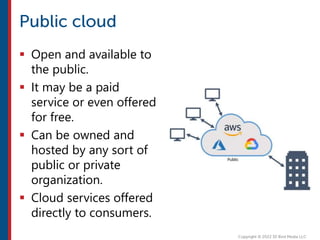
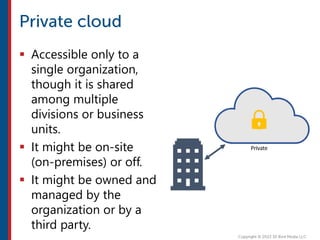
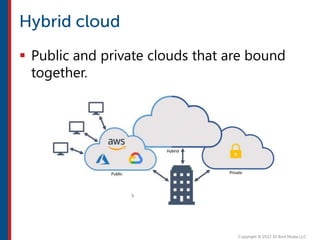
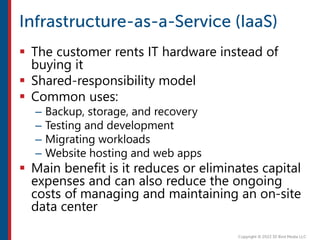
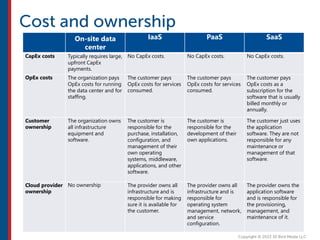
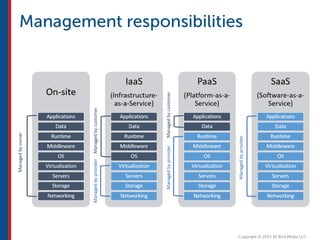
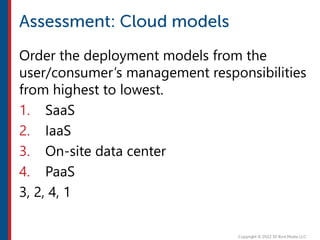
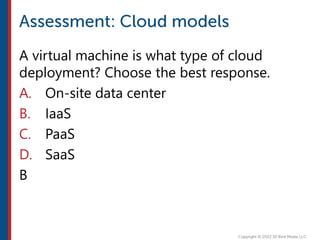
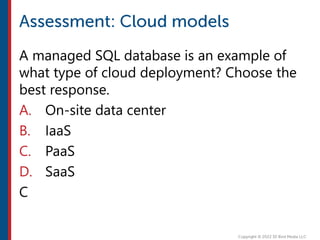
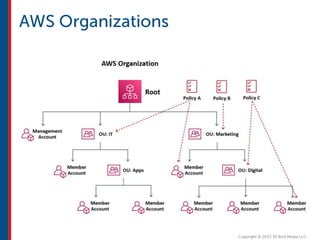
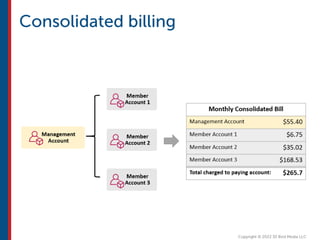
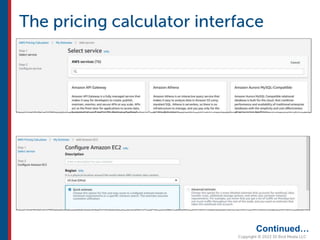
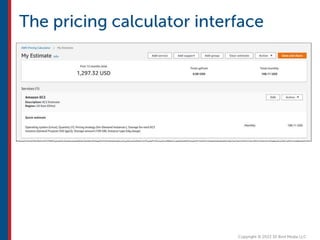
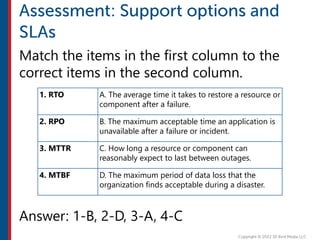
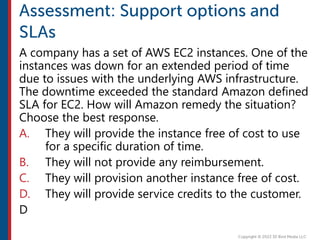
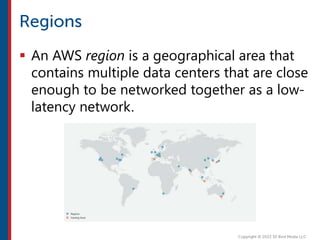
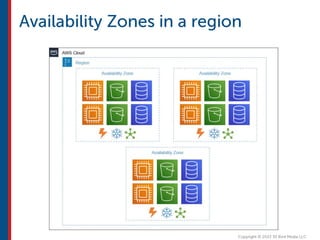
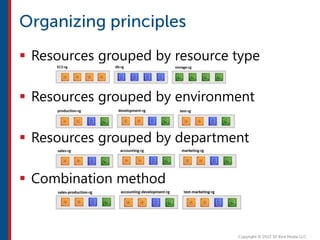
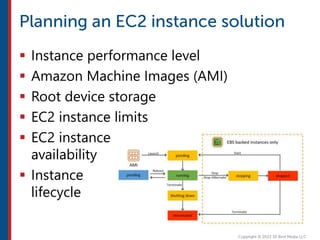
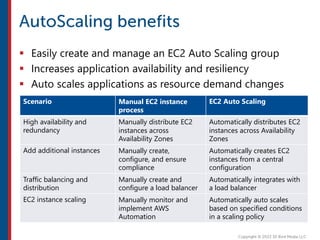
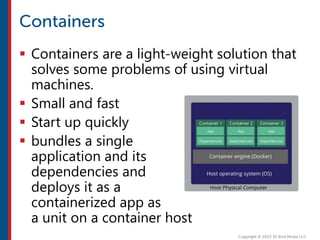
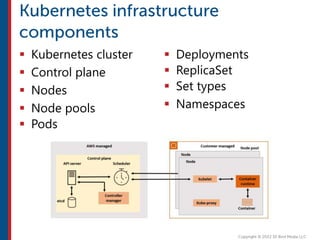
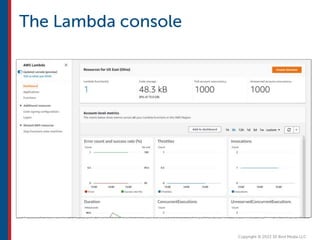
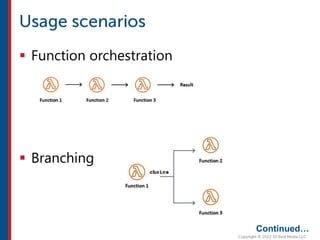
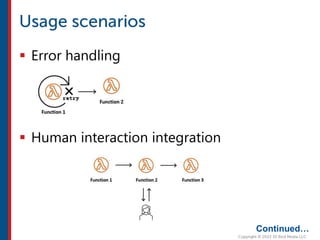
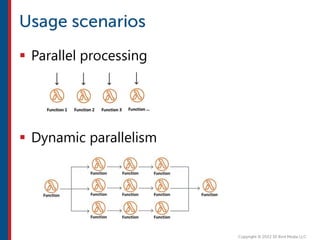
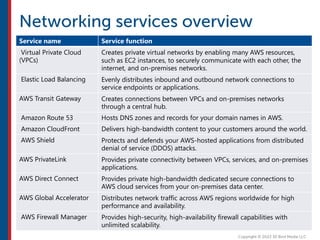
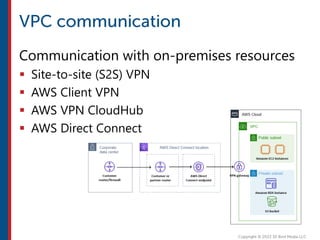
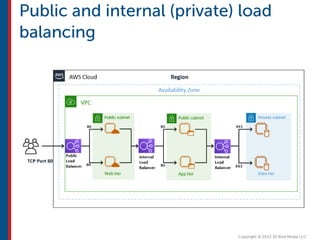
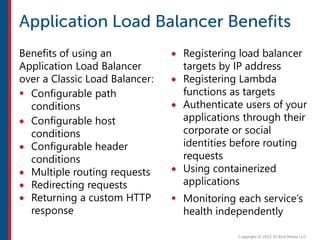
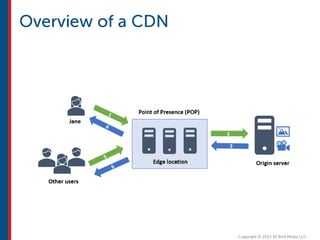
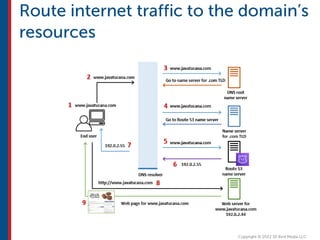
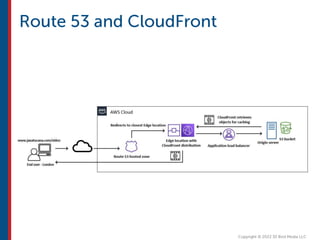
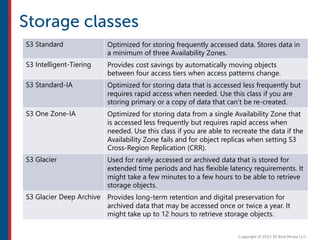
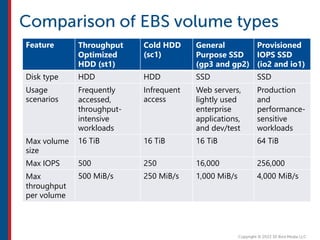
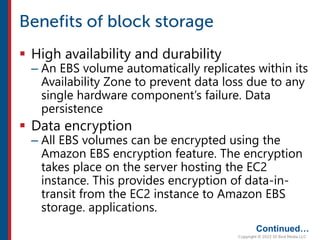
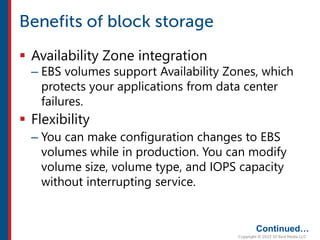
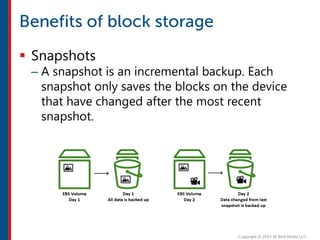
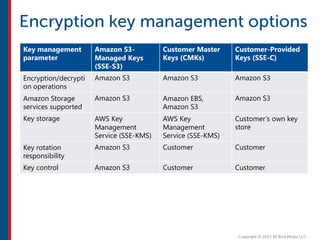
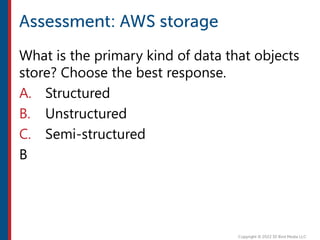
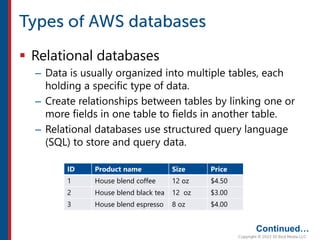
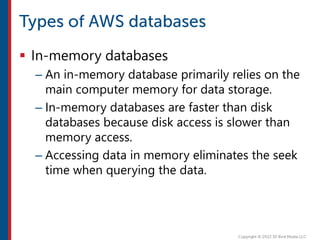
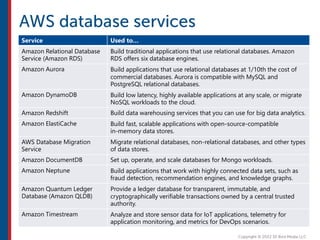
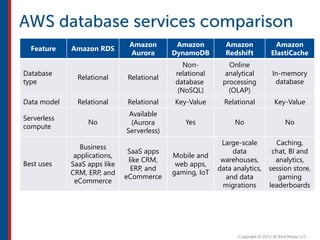
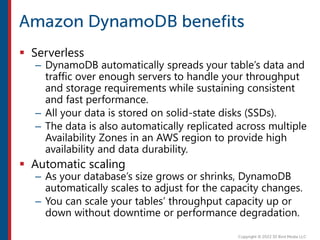
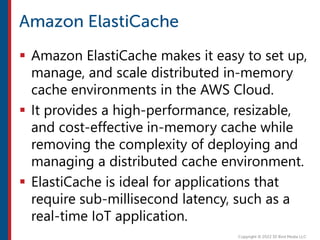
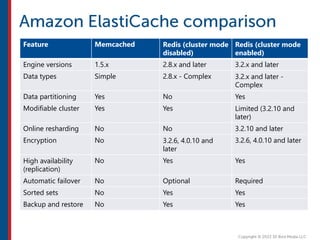
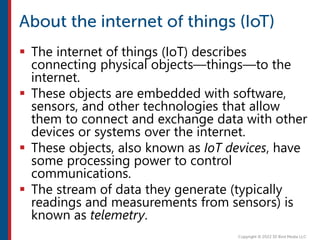
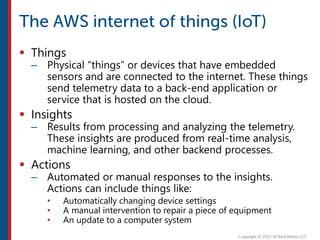
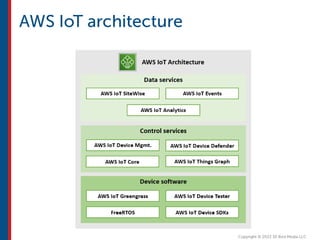
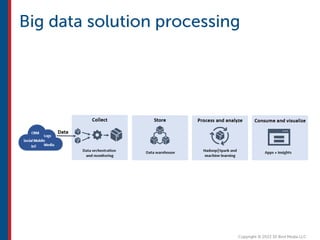
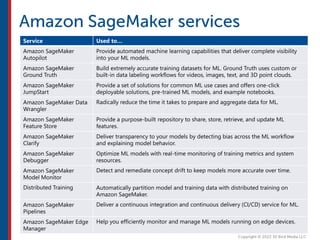
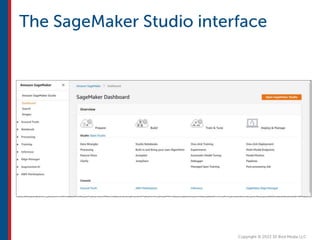
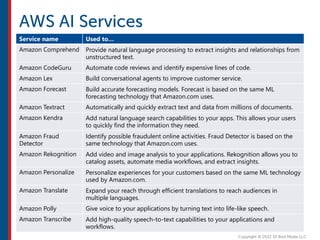
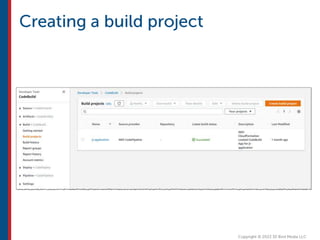
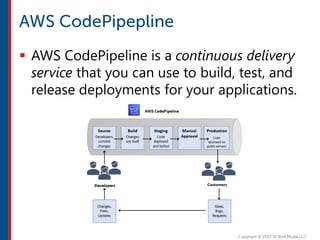
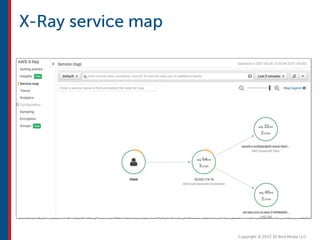
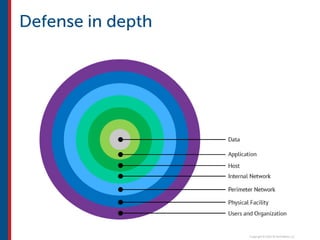
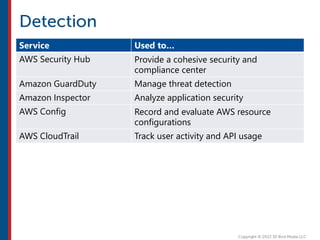
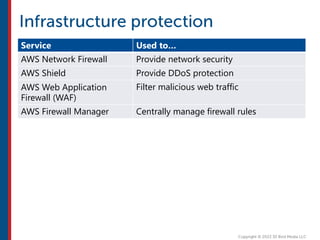
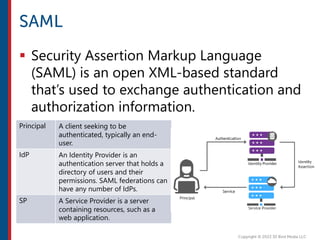
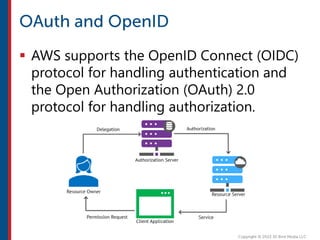
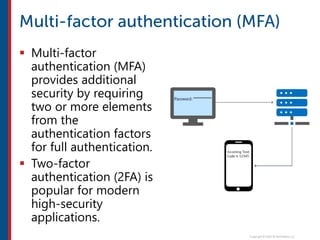
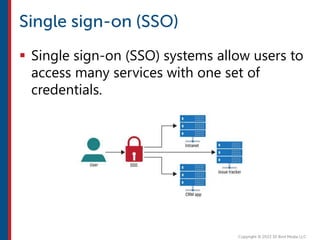
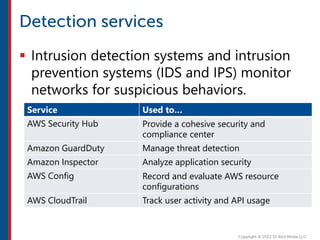
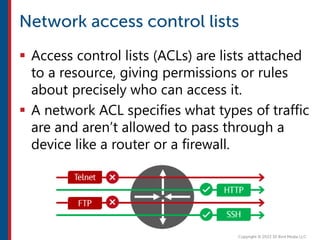
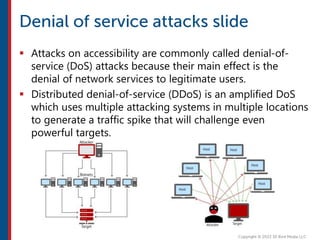
After completing this course, learners will understand core cloud computing concepts including scalability, elasticity, deployment models, service models, and the shared responsibility model. They will also learn about AWS services for compute, storage, networking, databases, analytics, security, and governance. The course covers how to use AWS tools and services to build reliable, secure, high-performing applications in the cloud.