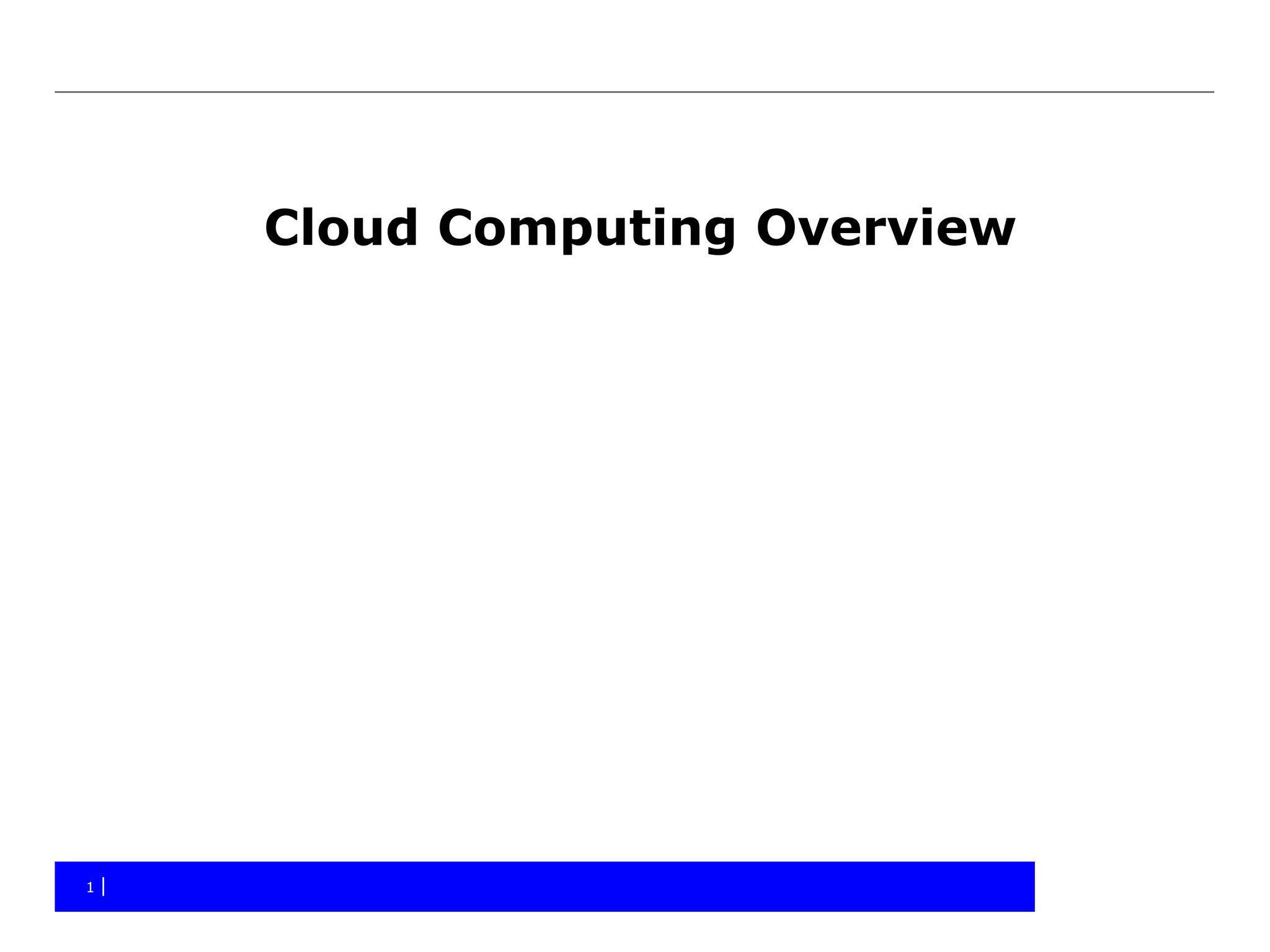
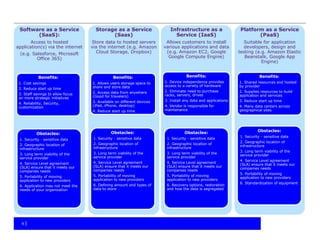
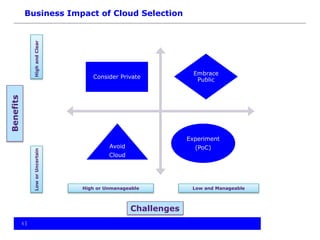
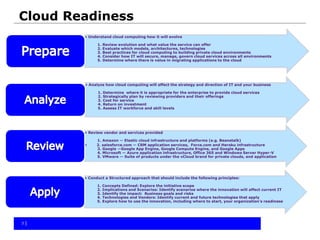
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including the different types of cloud services (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS), benefits and obstacles. It discusses security and privacy risks, as well as considerations for assessing an organization's cloud readiness. Recommendations include performing due diligence on options and risks, reviewing contracts and SLAs, determining data classification, staff training, and taking a staged approach to migrating data to the cloud.