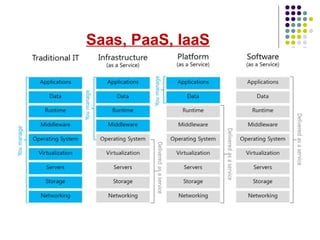
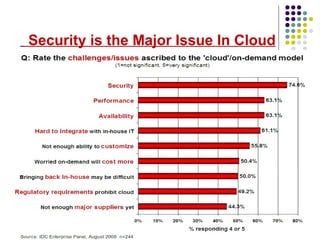
Cloud computing is a model that provides on-demand access to shared computing resources like networks, servers, storage, applications and services. Key characteristics include elasticity, on-demand usage, pay-per-use access, and multi-tenancy. The three main cloud service models are SaaS, PaaS and IaaS. Cloud computing offers advantages like scalability, low costs and location independence but also risks like security issues, lack of control and potential downtime. Its future scope includes improved support for medical data, weather forecasting and unlimited entertainment options.