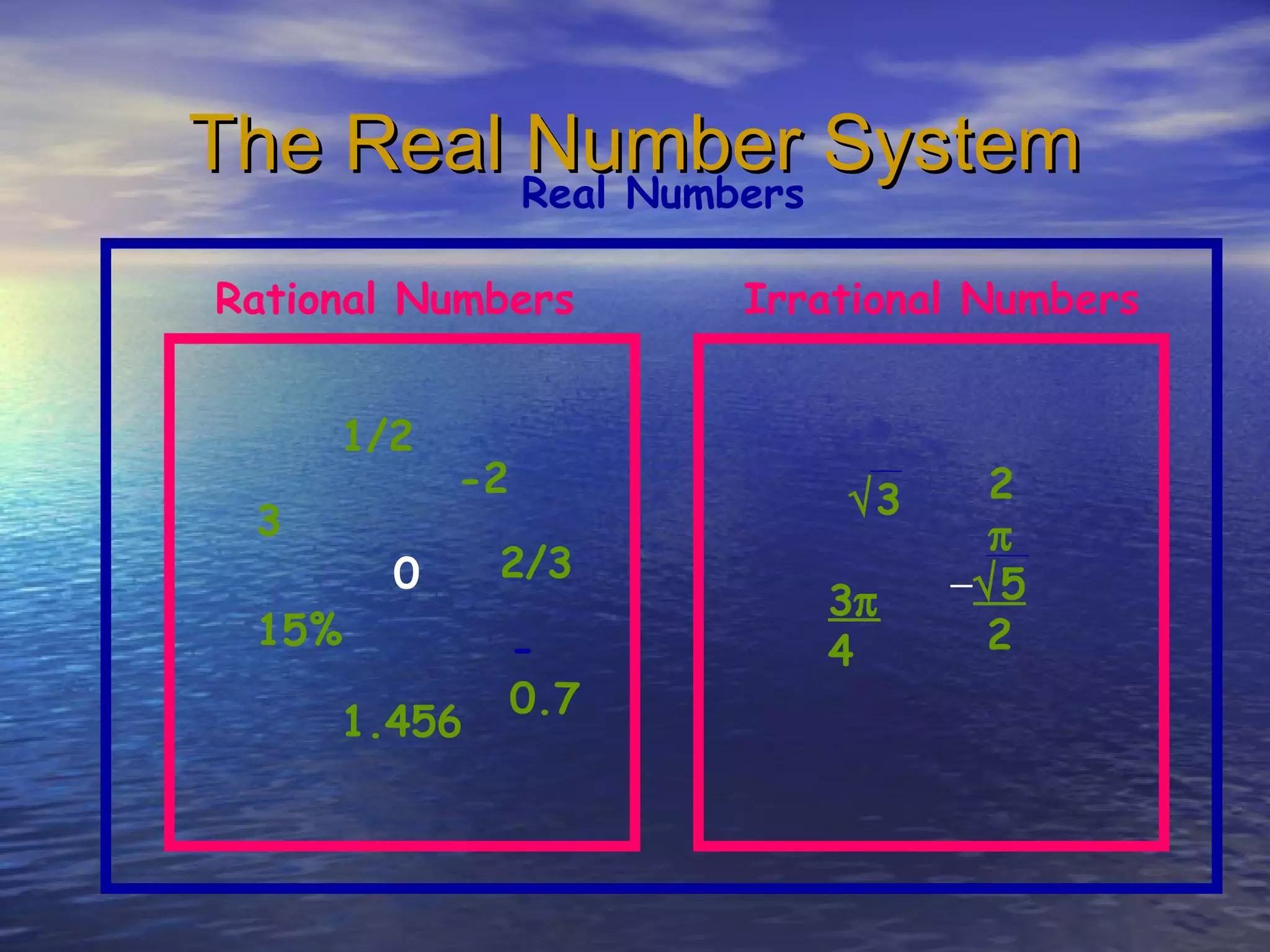
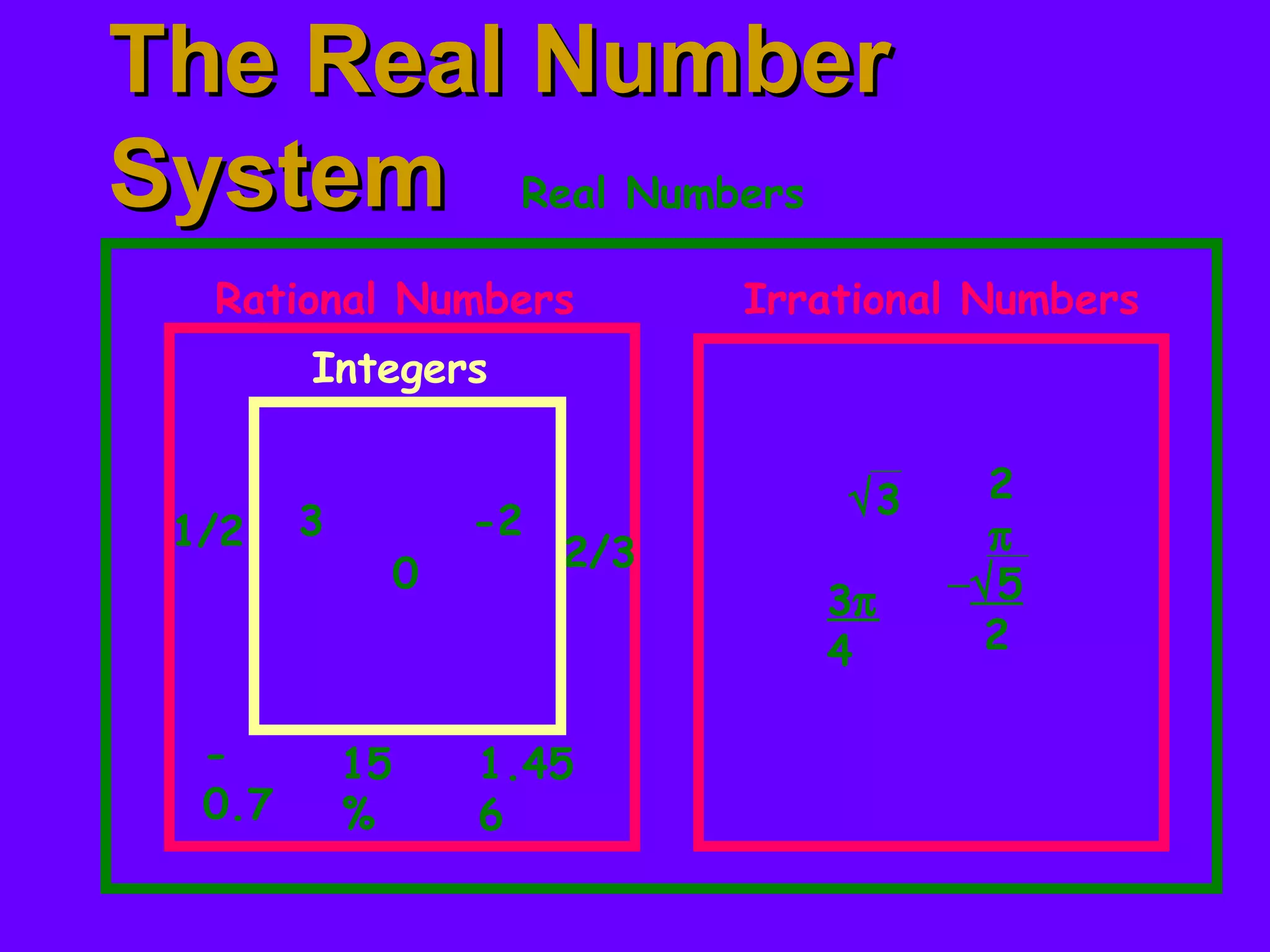
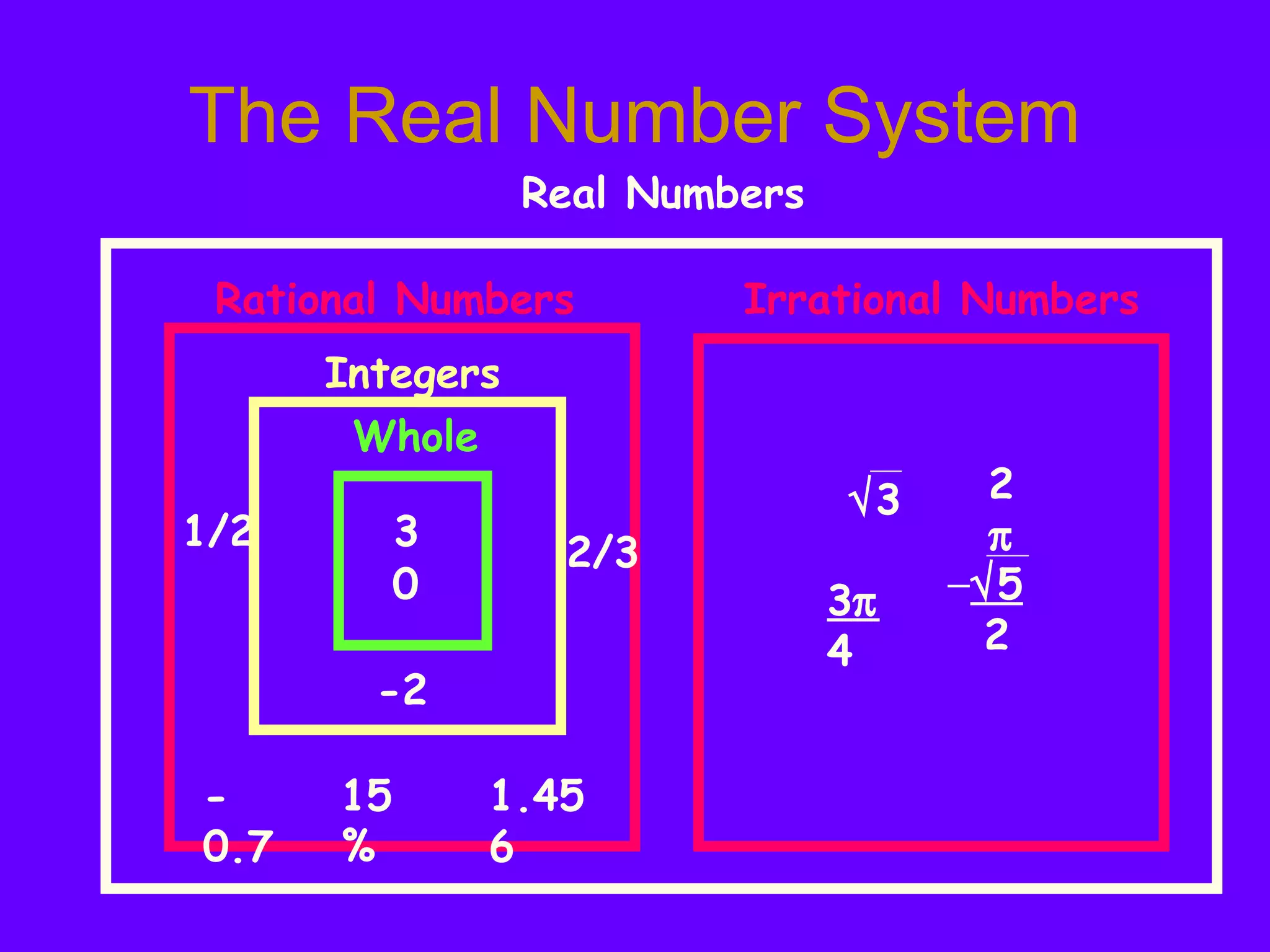
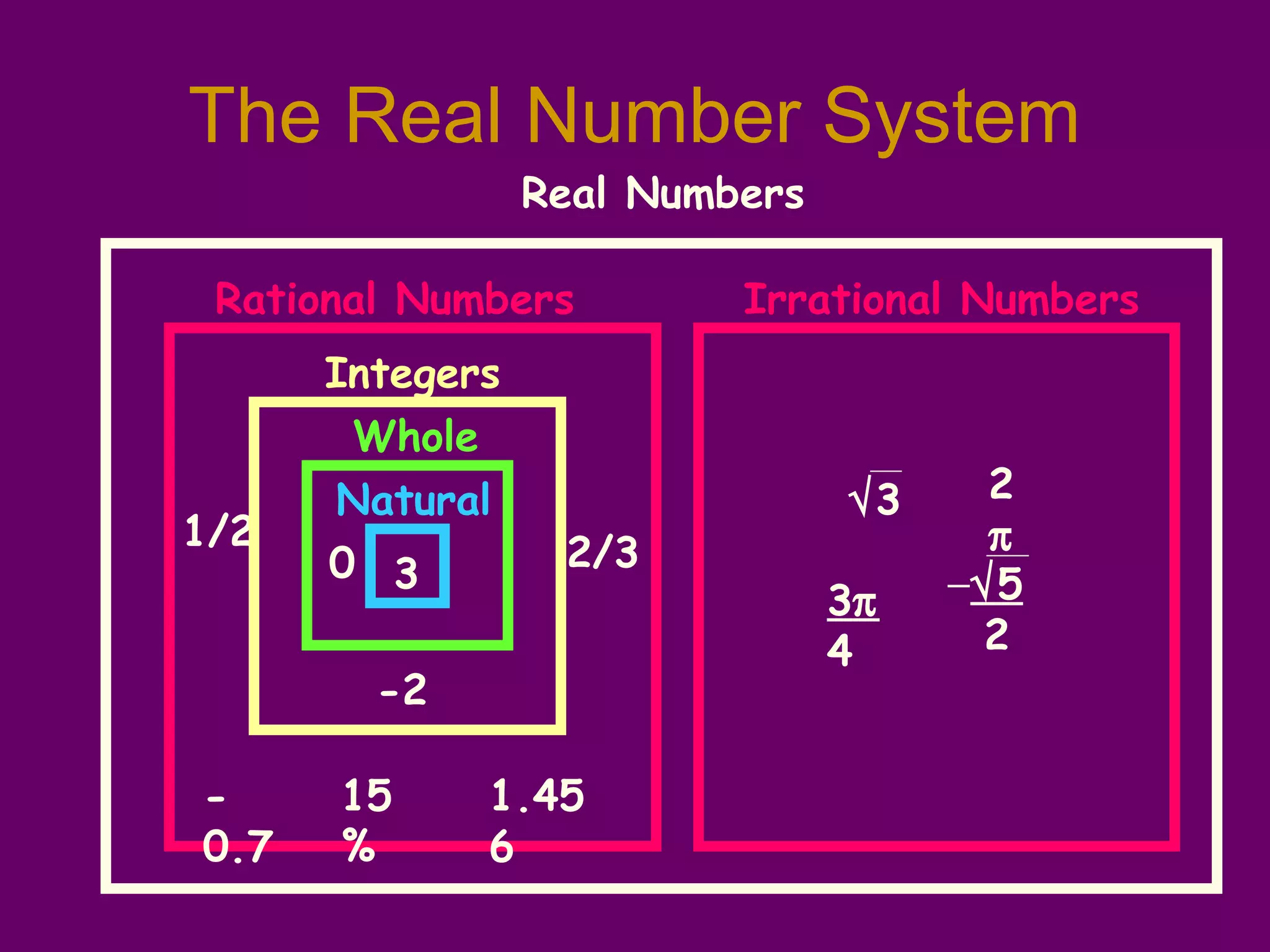
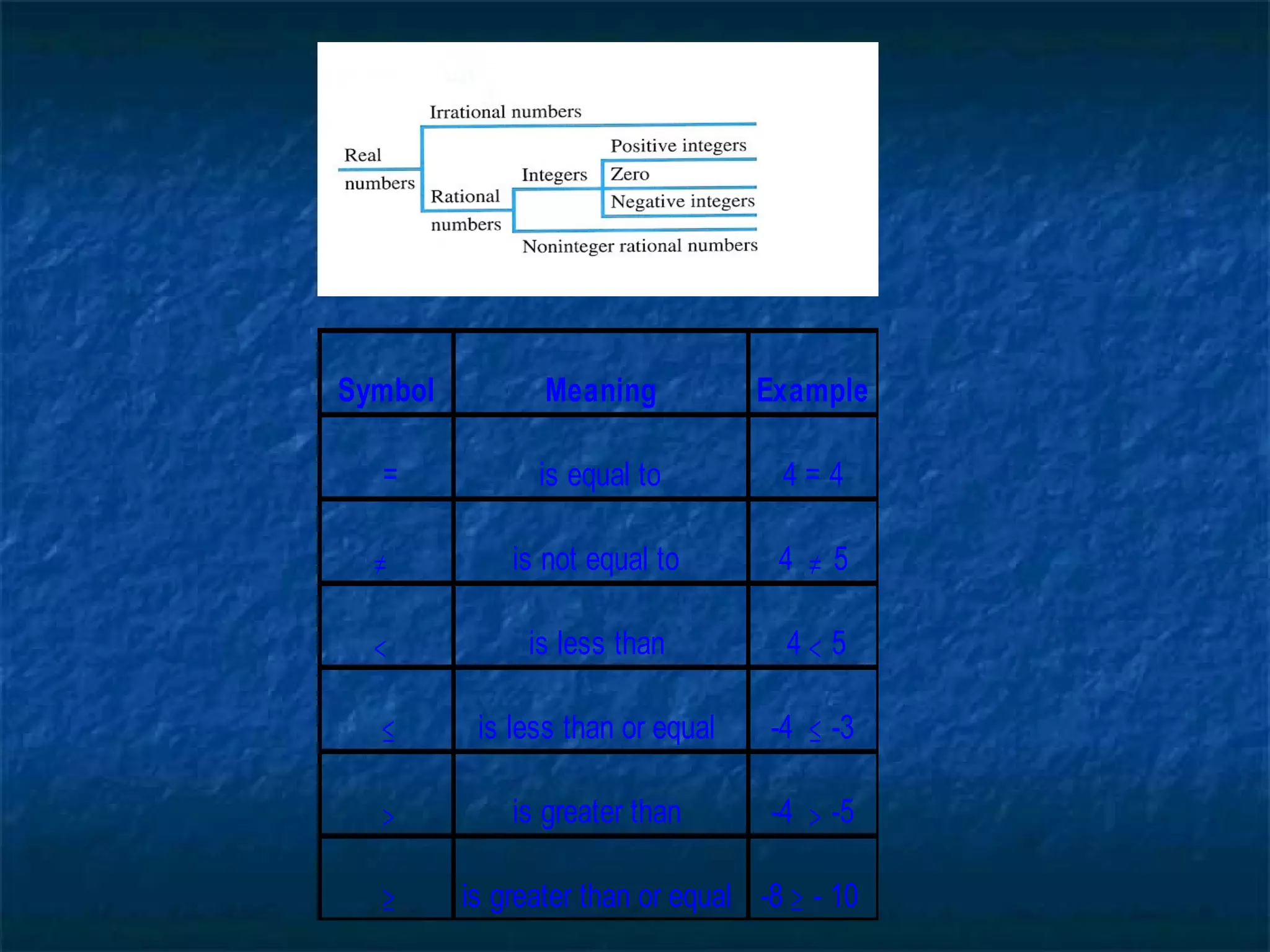
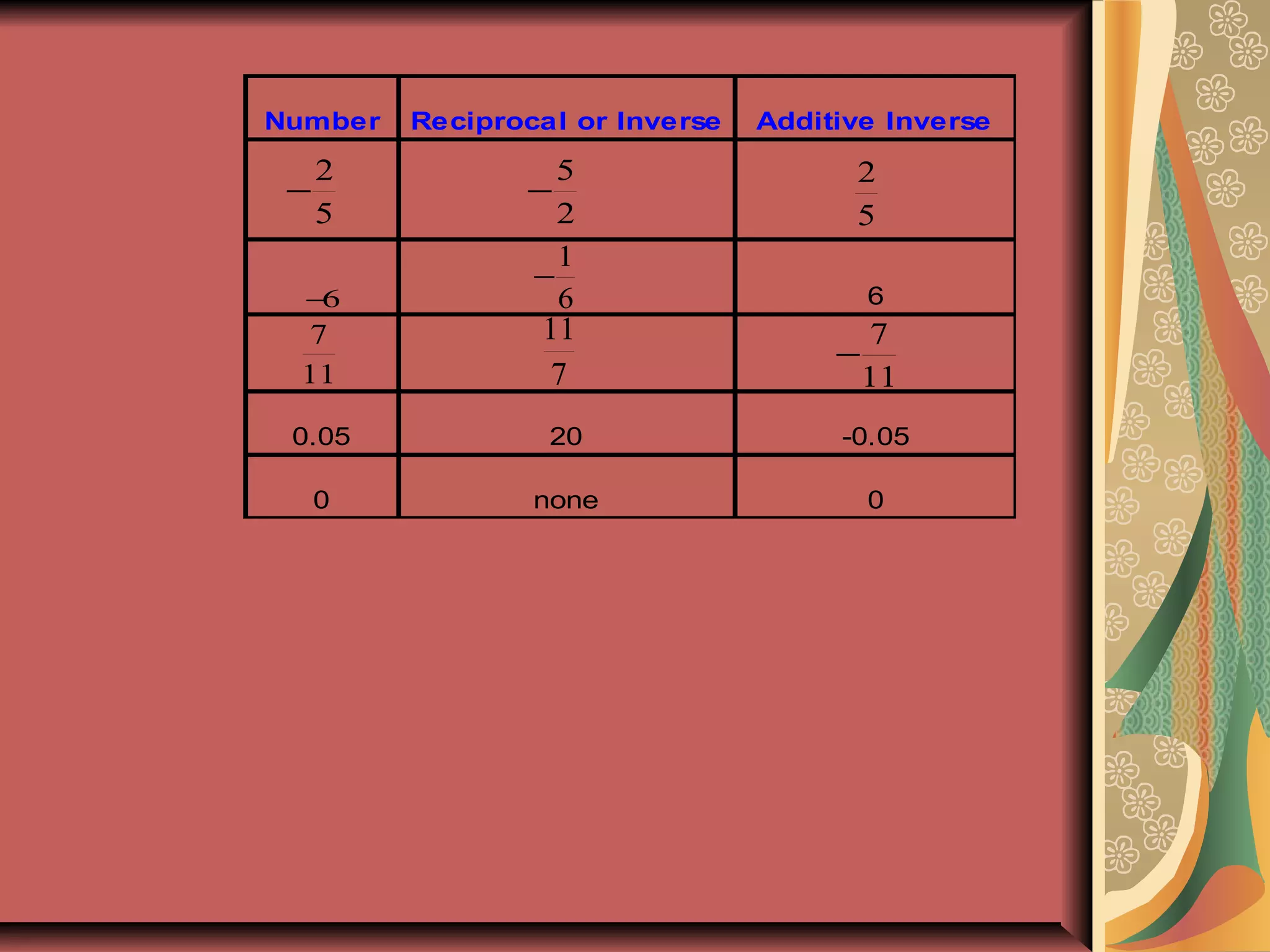
This document introduces real numbers and their properties. It discusses that real numbers can be divided into two kinds: rational numbers, which can be written as a ratio of integers, and irrational numbers, which cannot. It provides examples of rational numbers like fractions and decimals, as well as irrational numbers like square roots and pi. The document also defines integers, explains operations like exponents and identities, and illustrates the real number system.