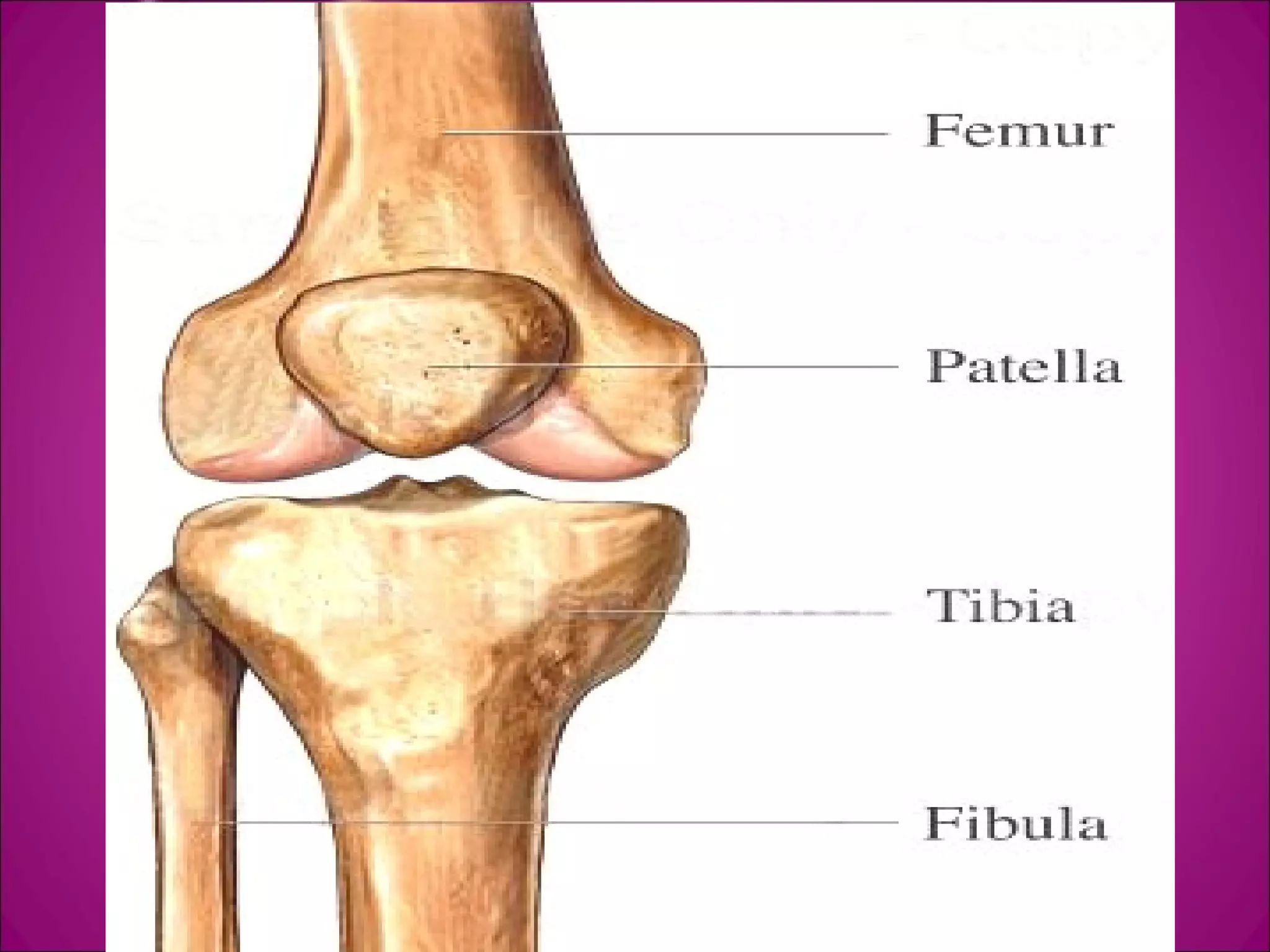
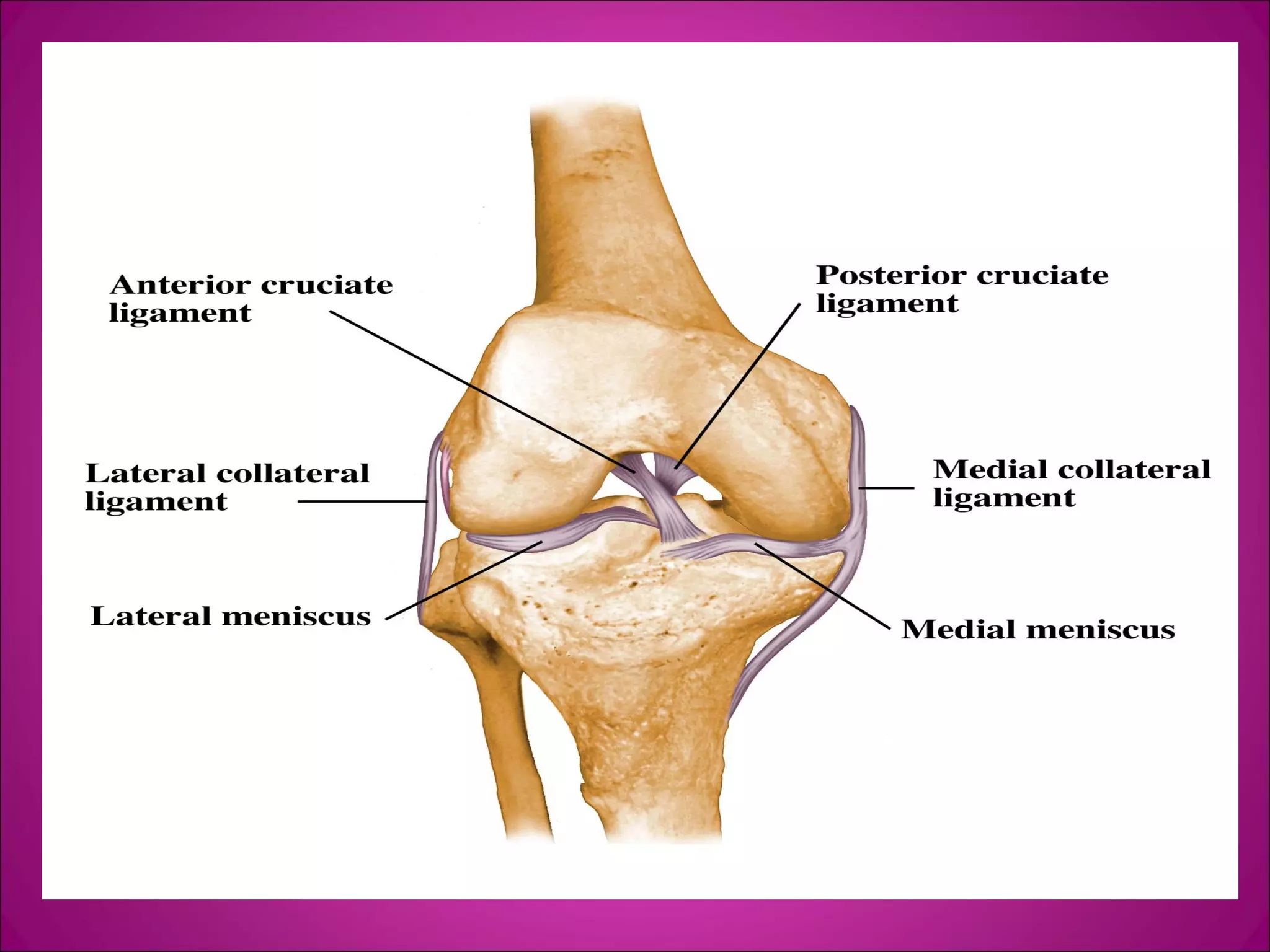
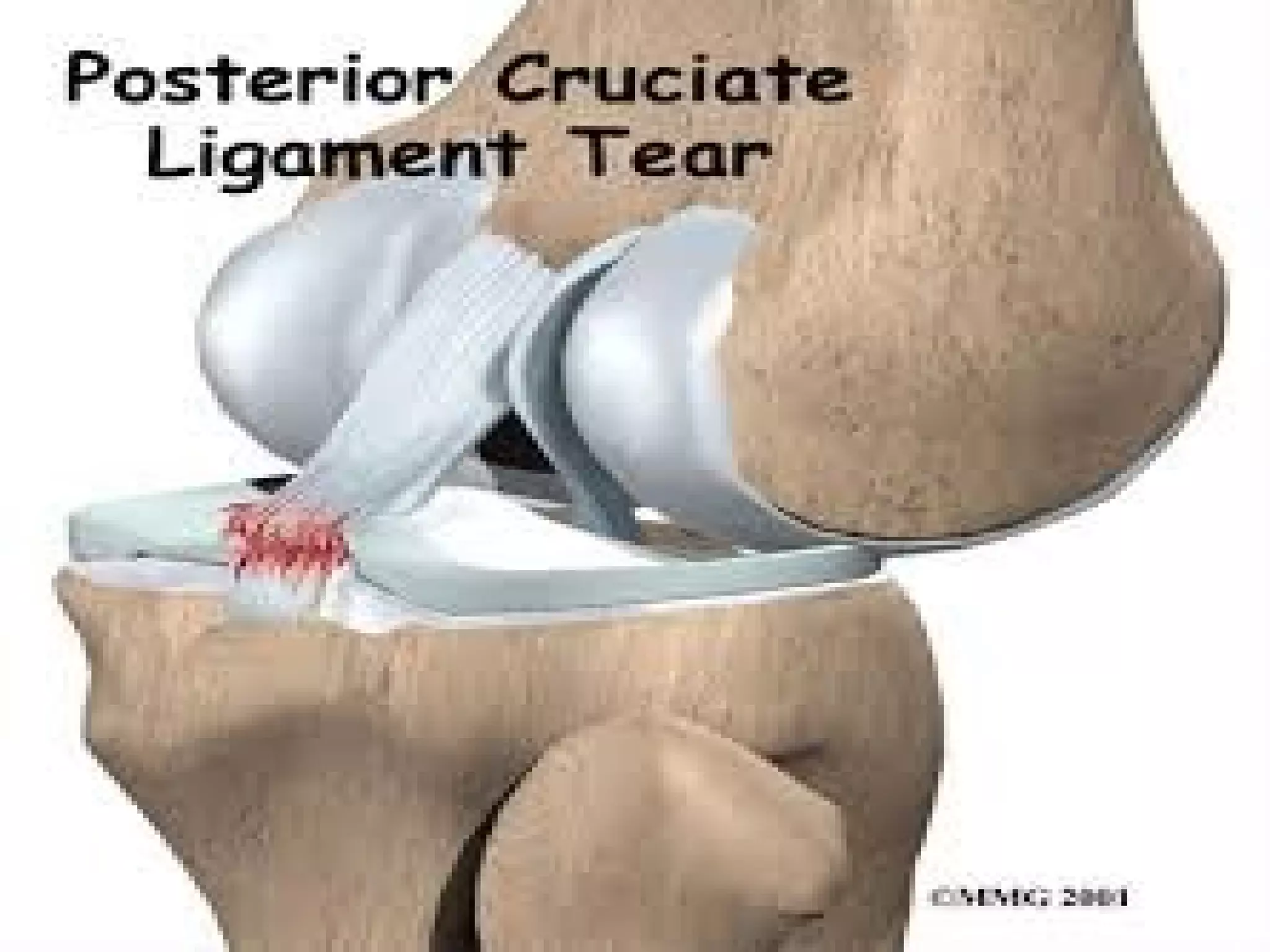
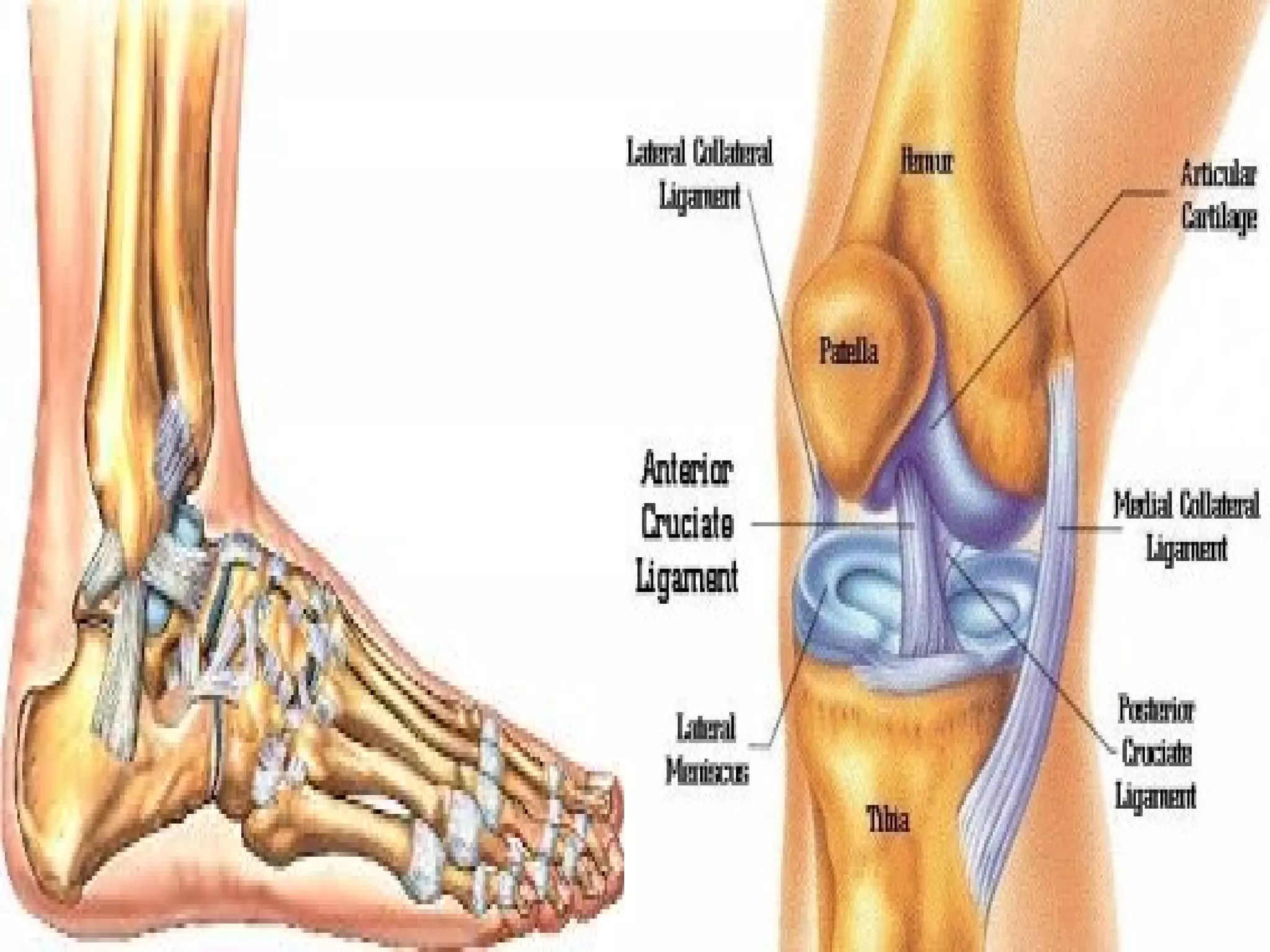
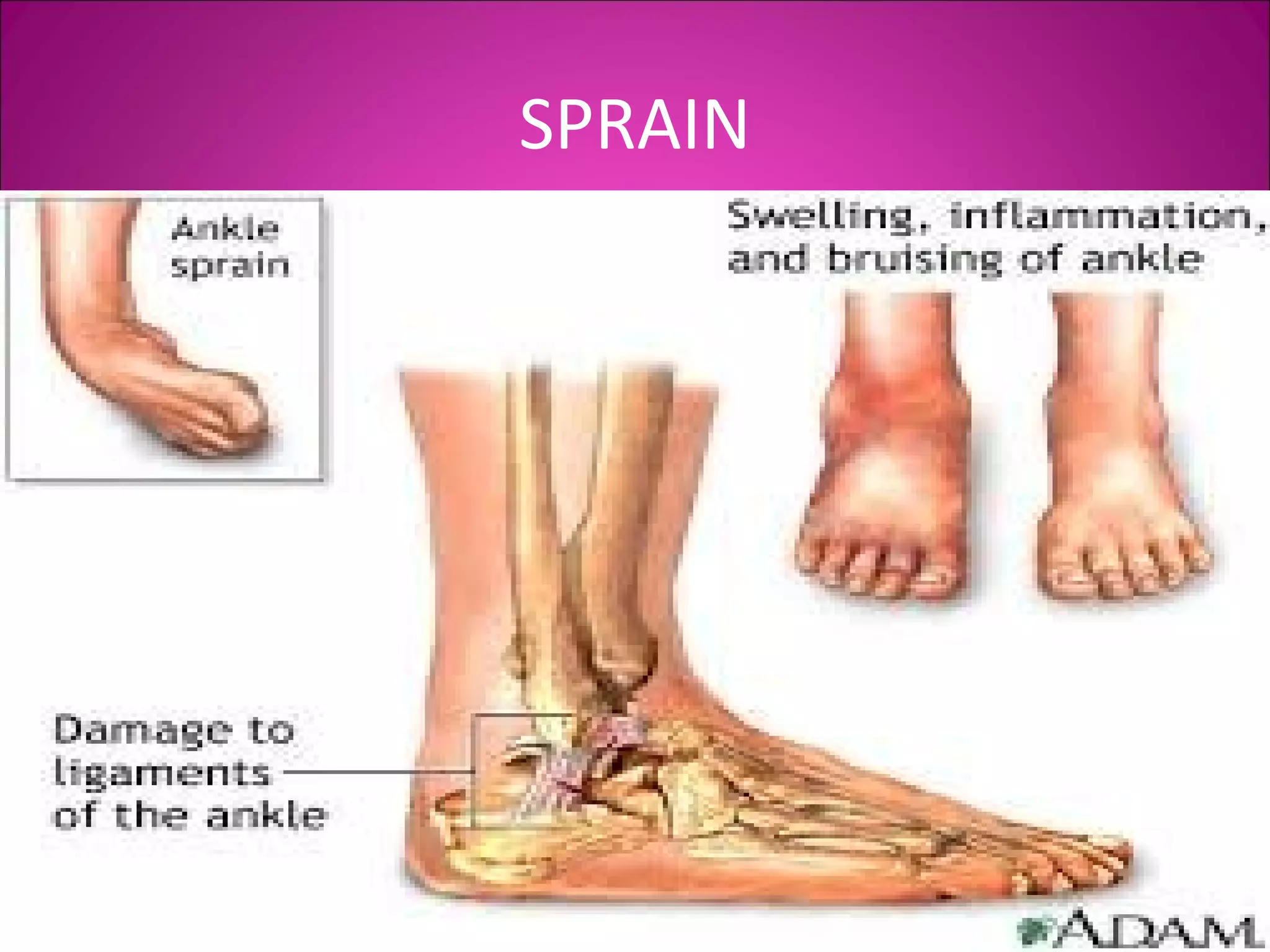
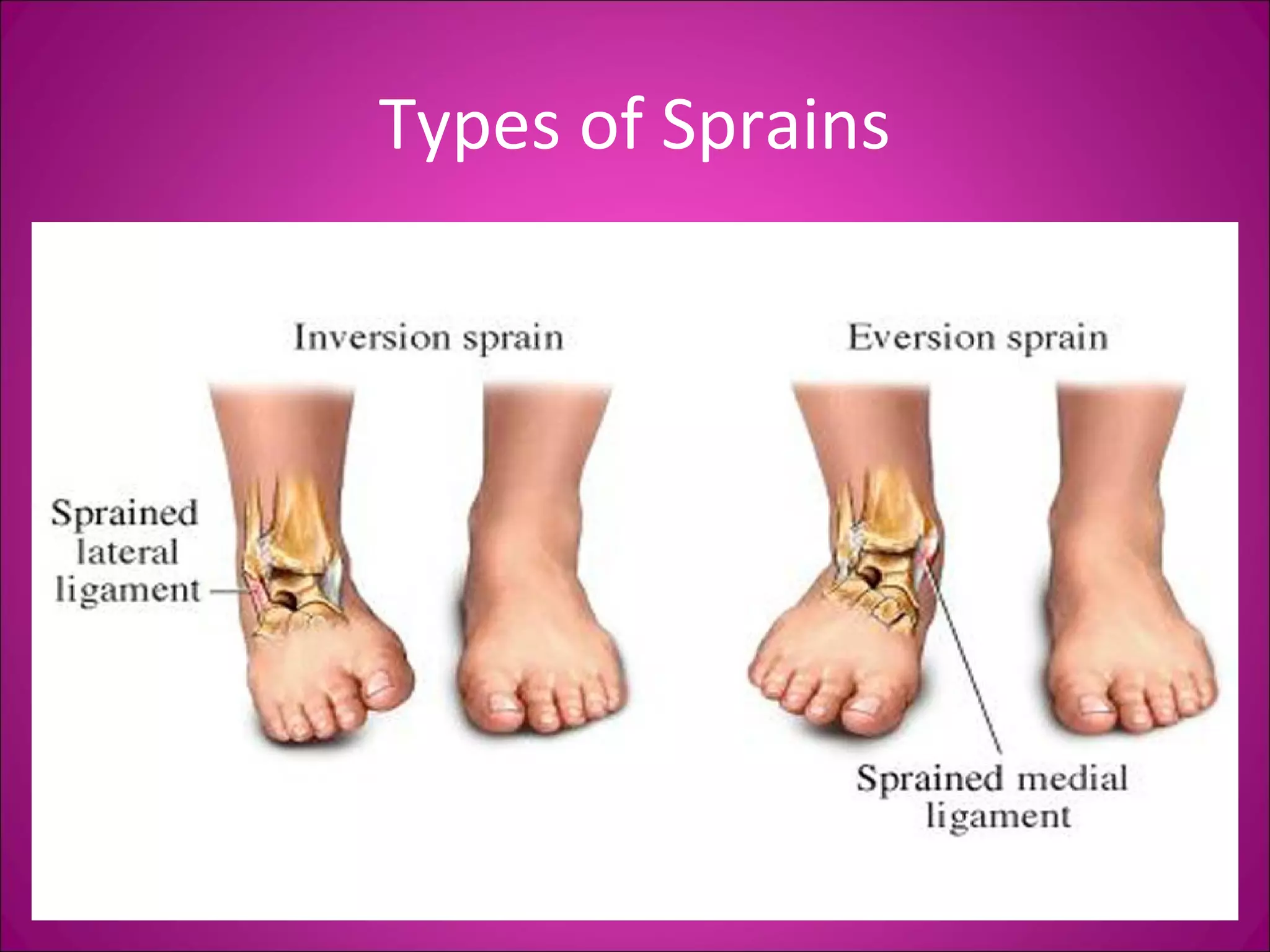
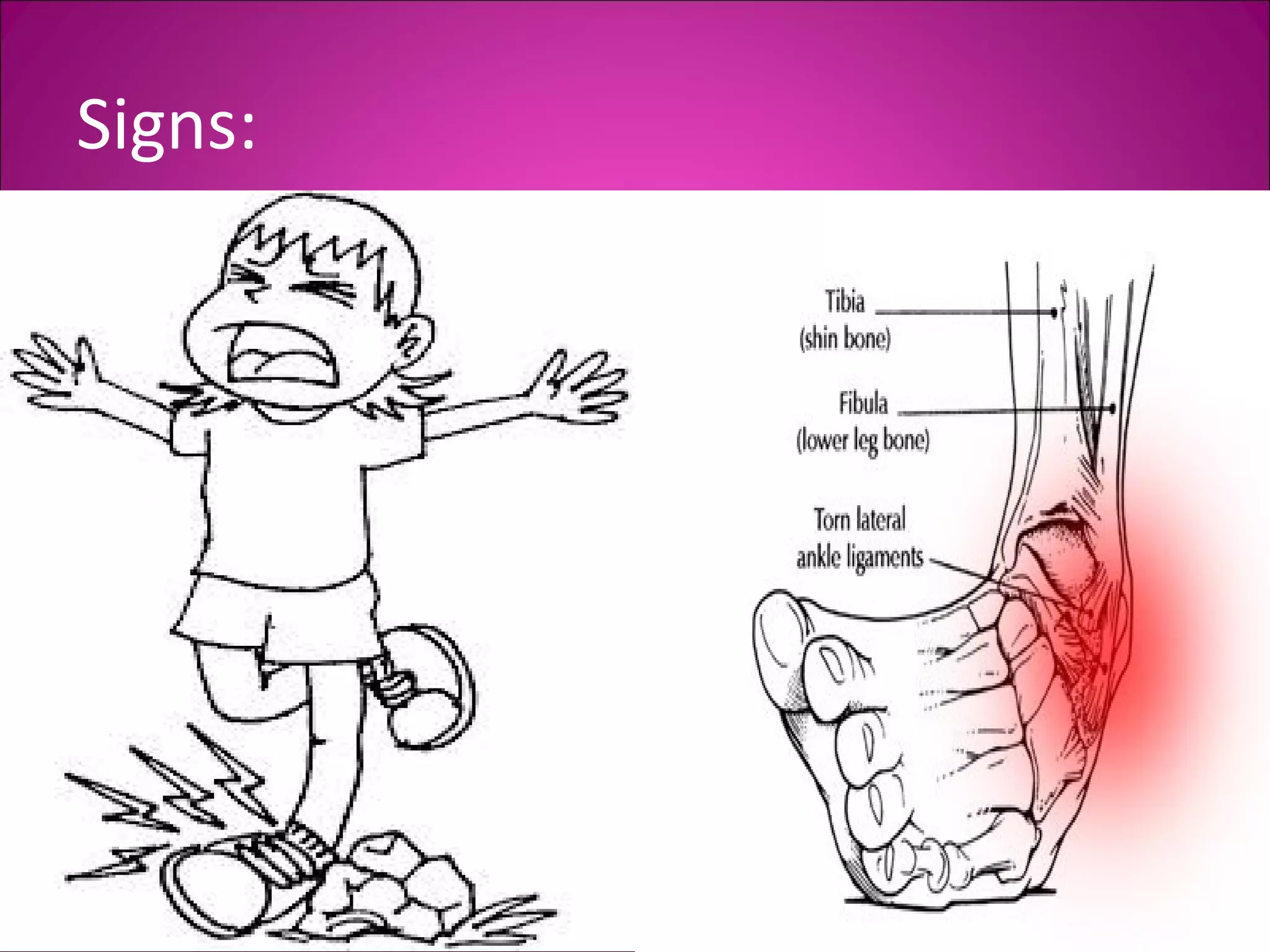
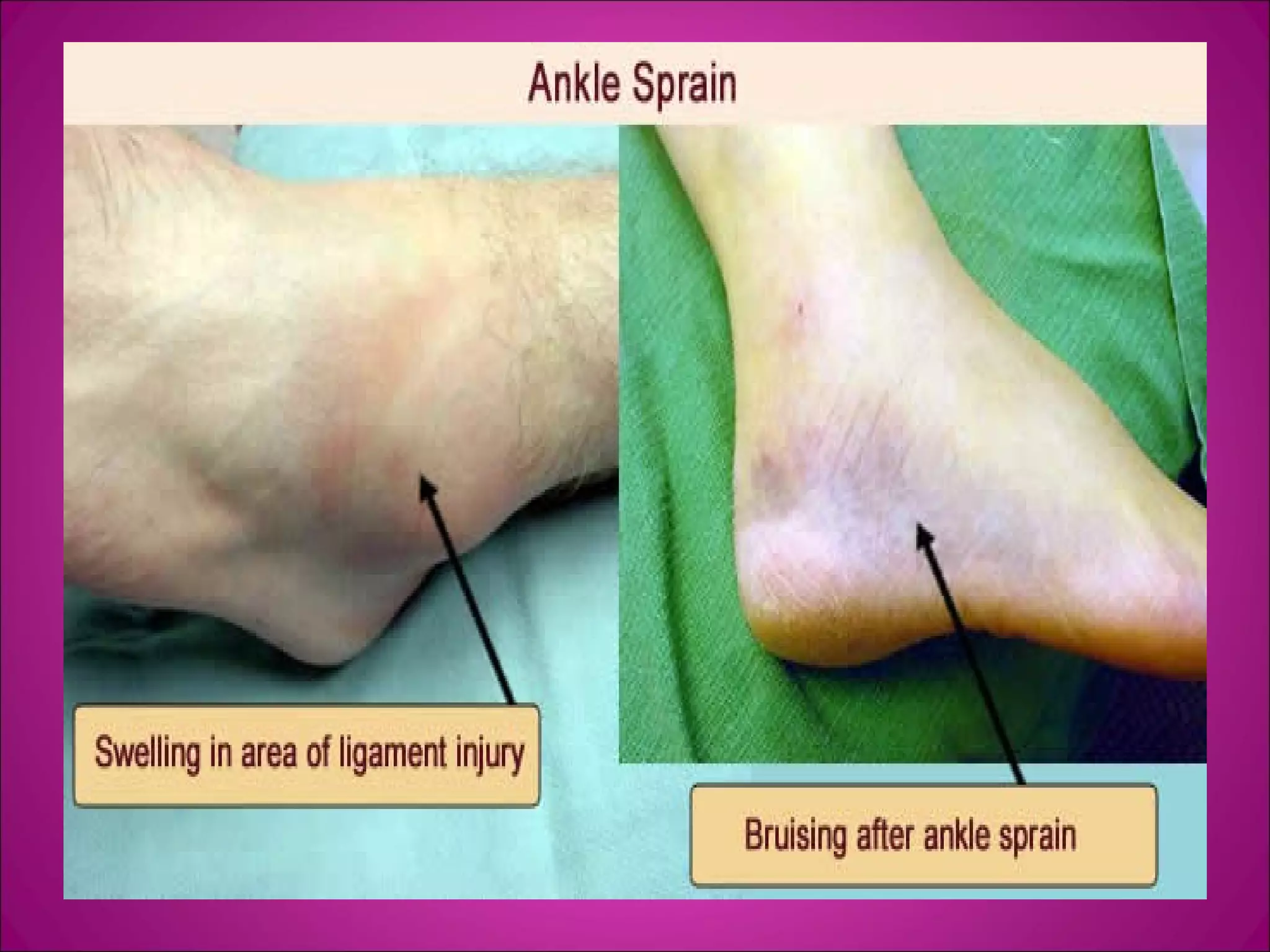
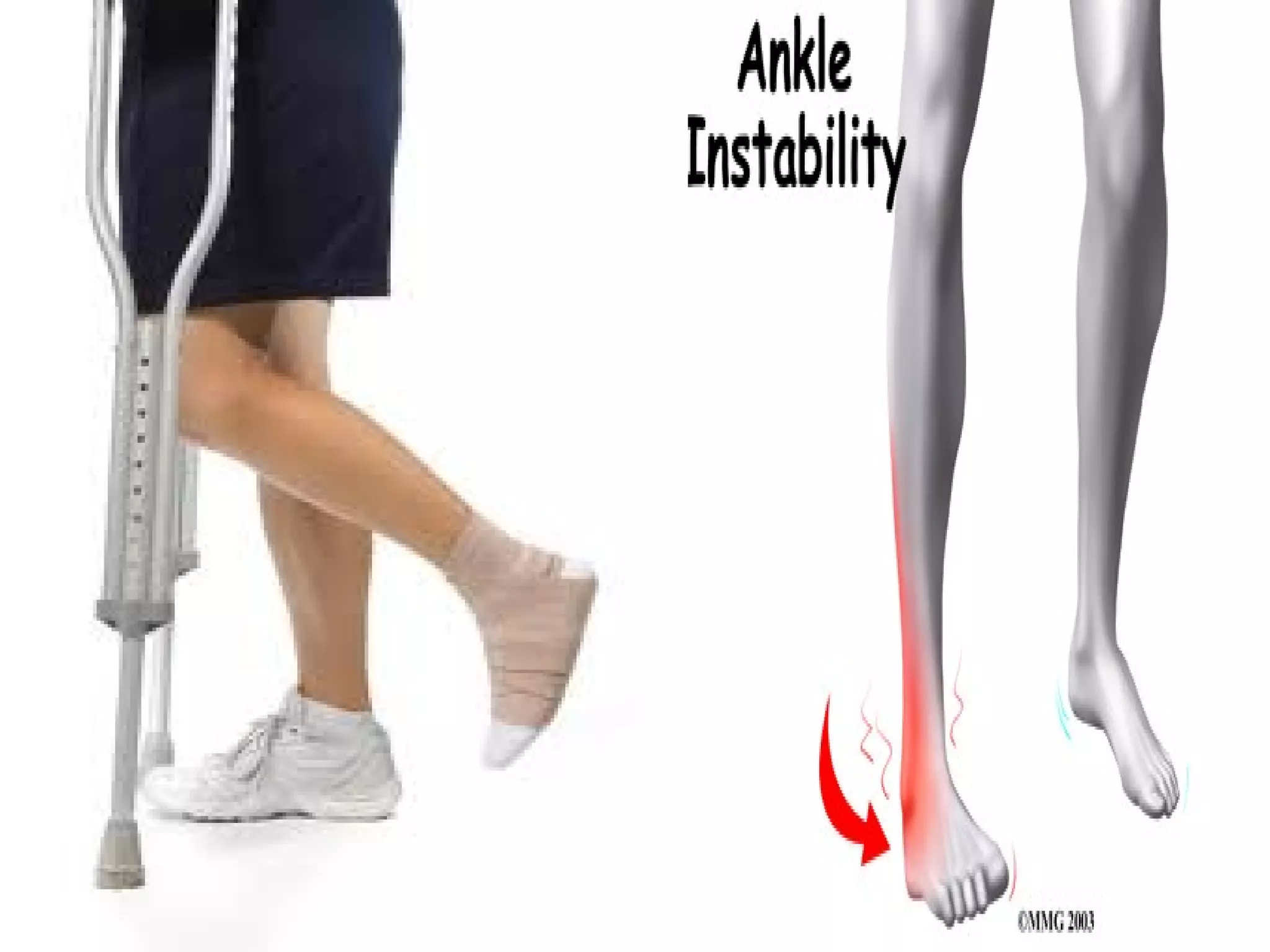
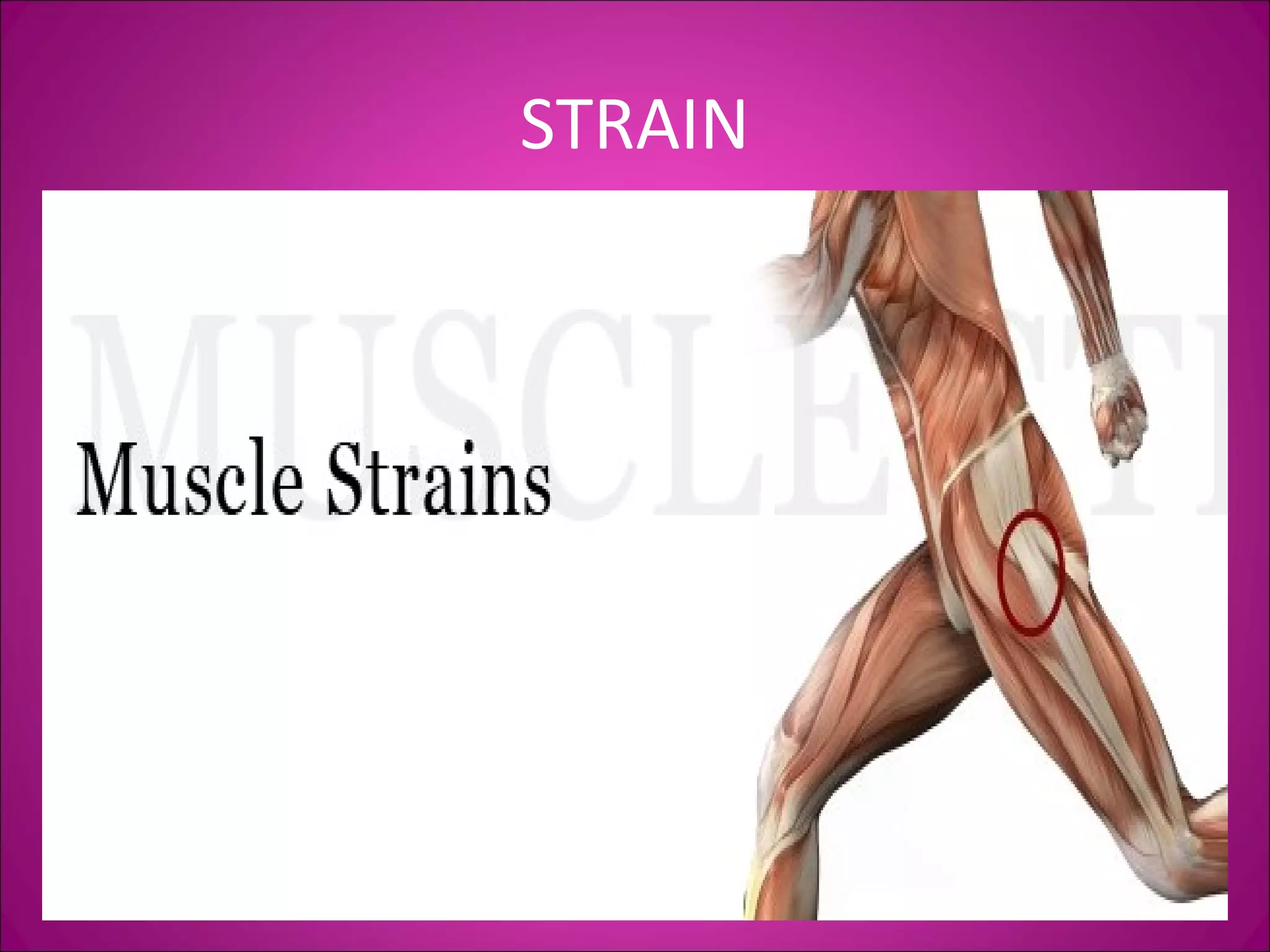
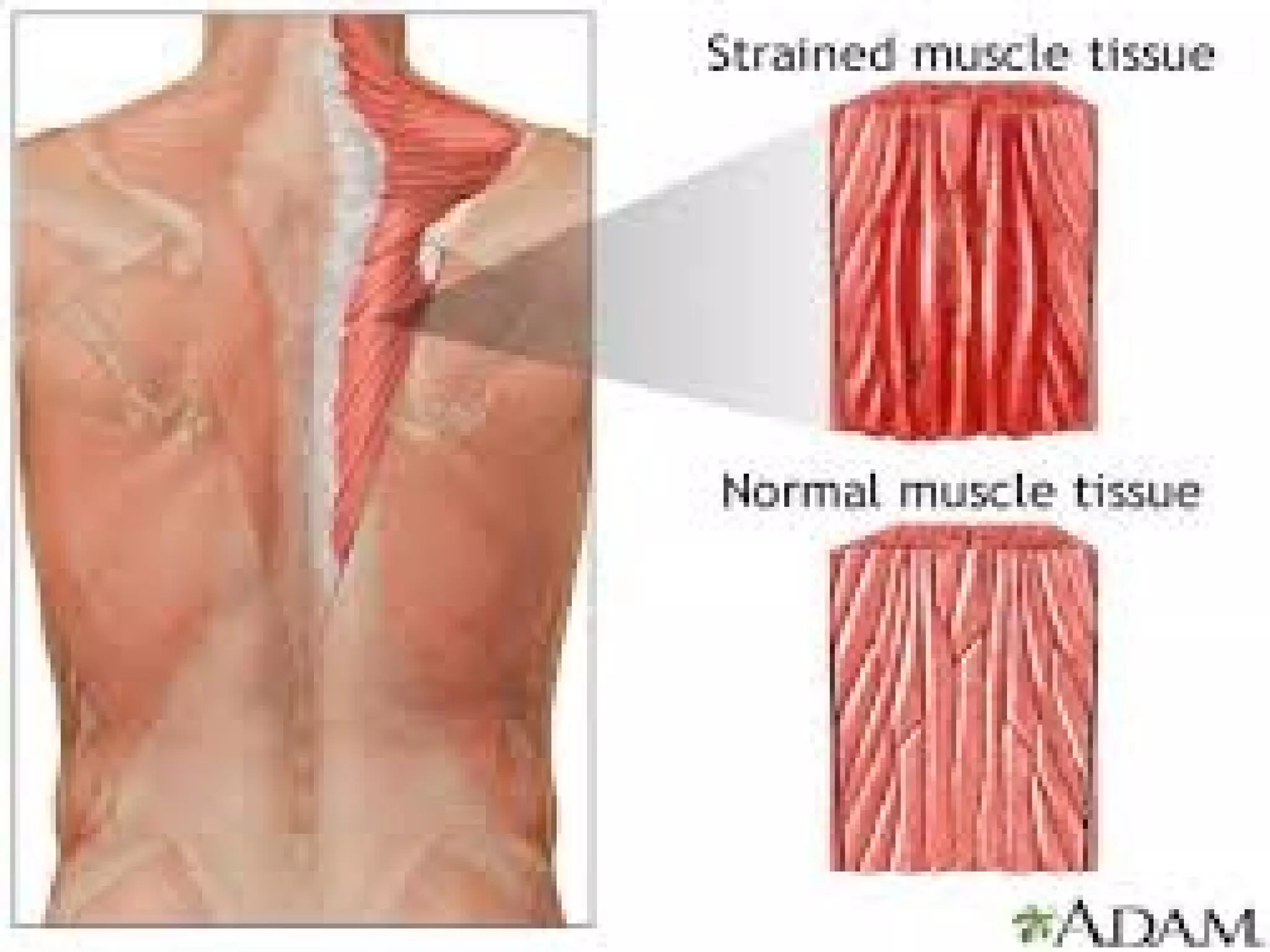
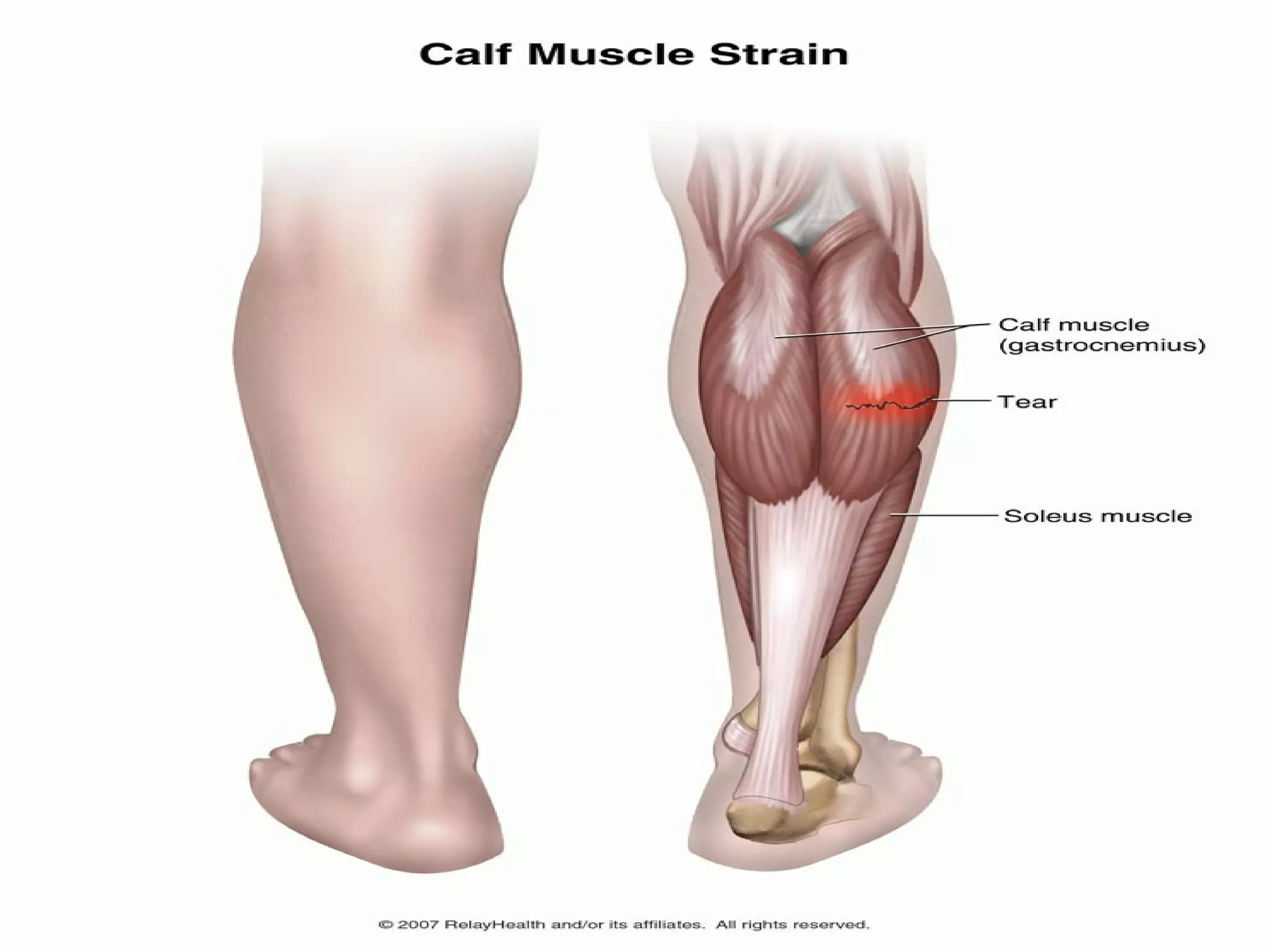
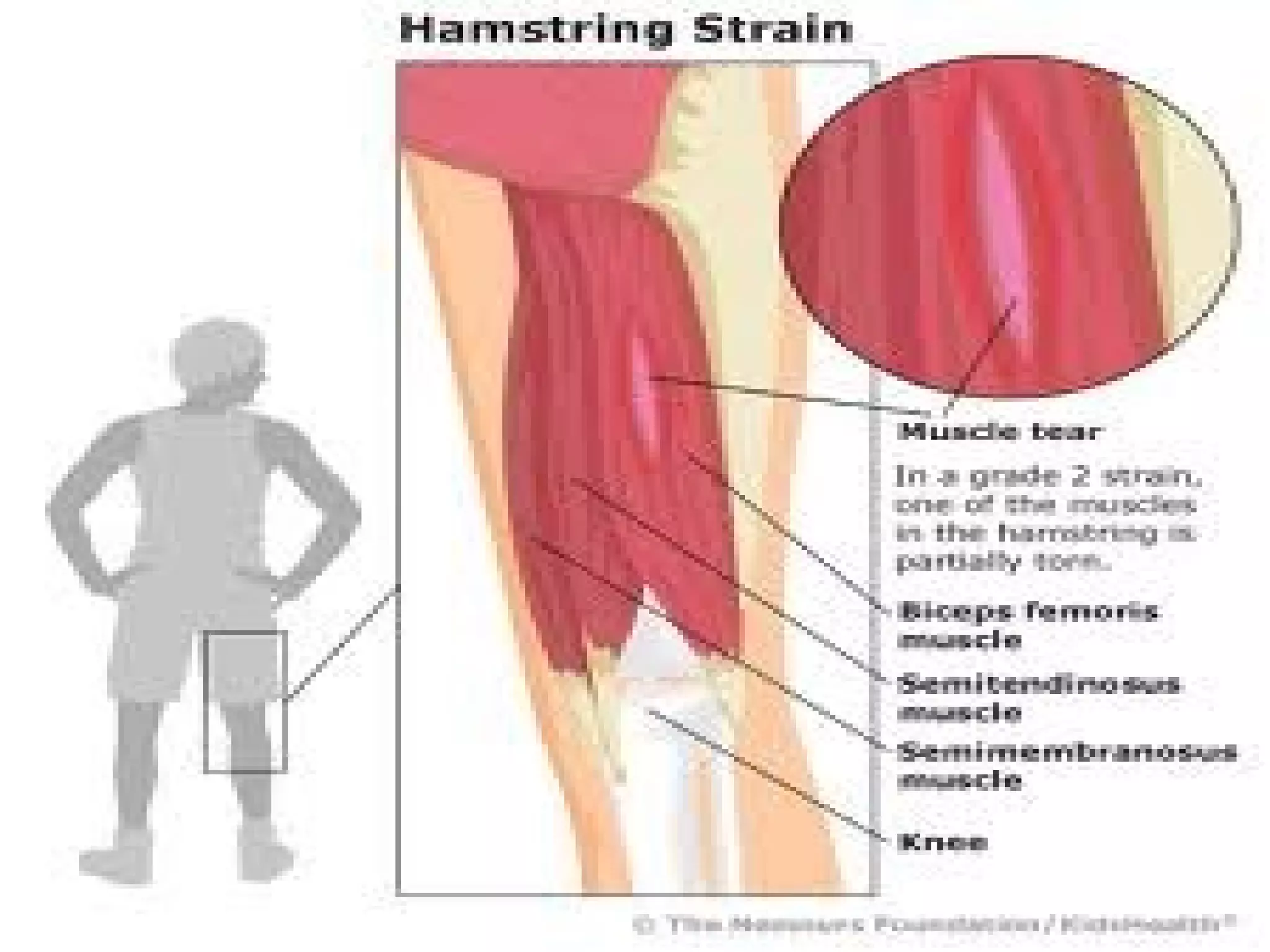
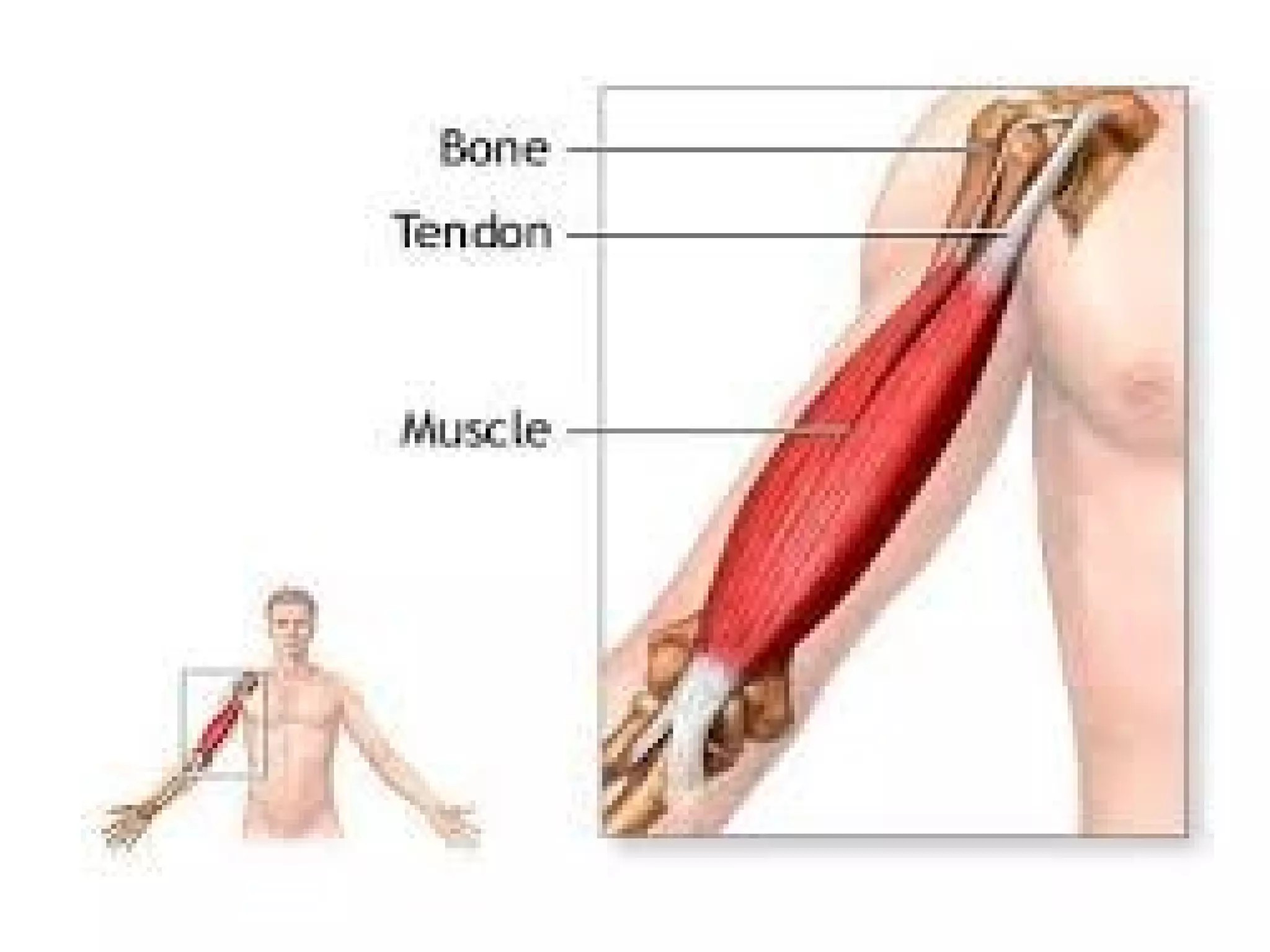
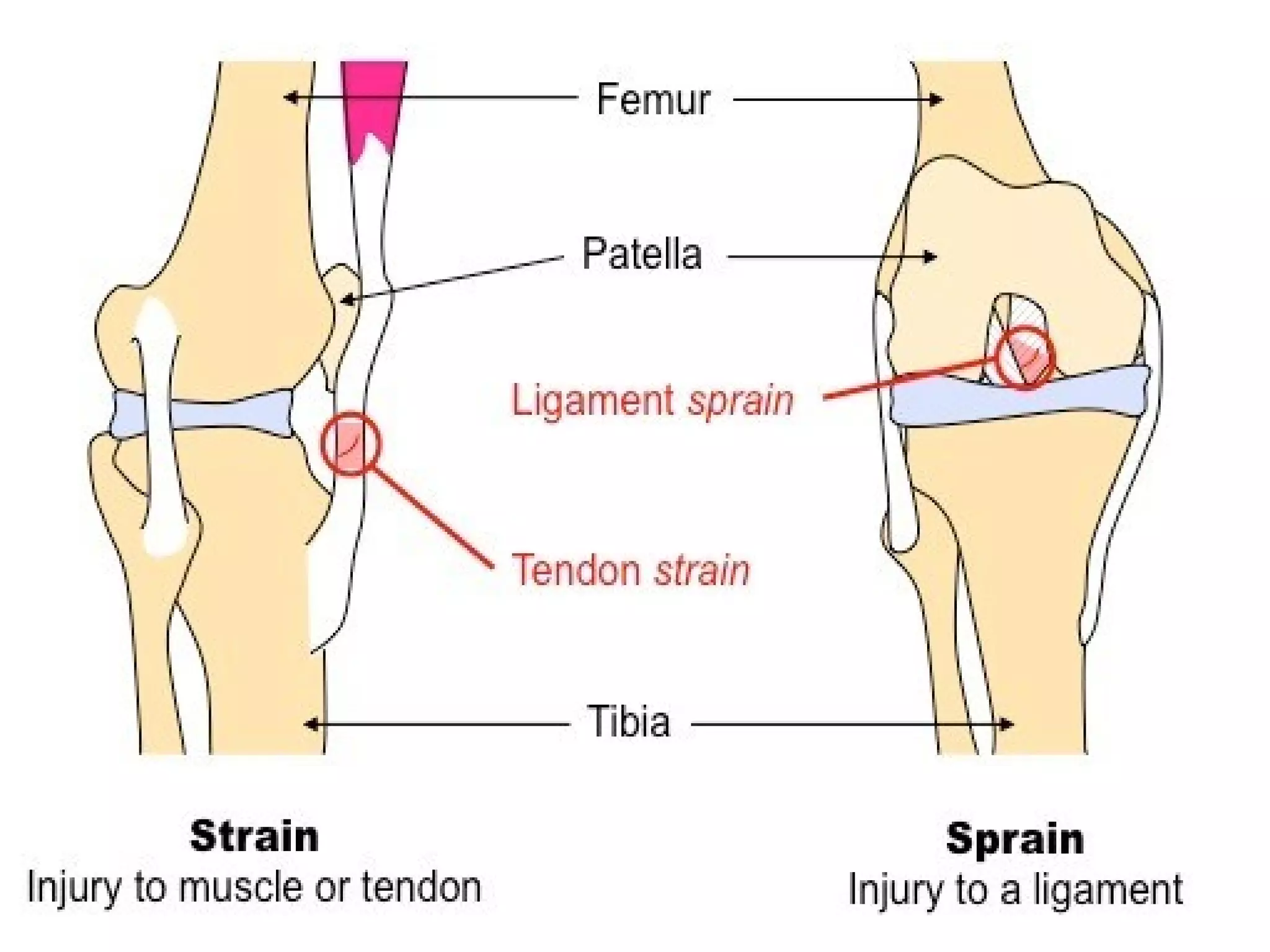
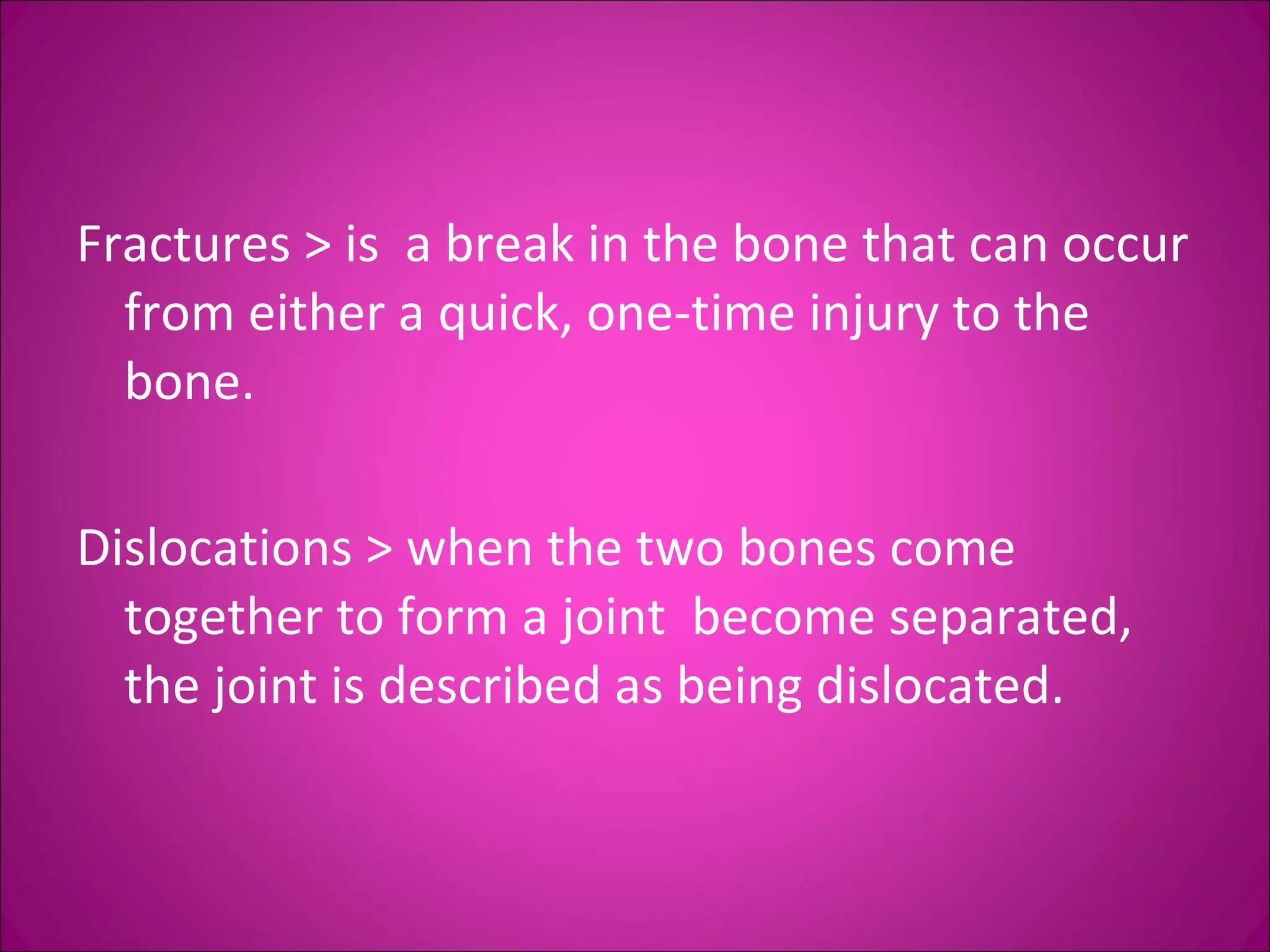
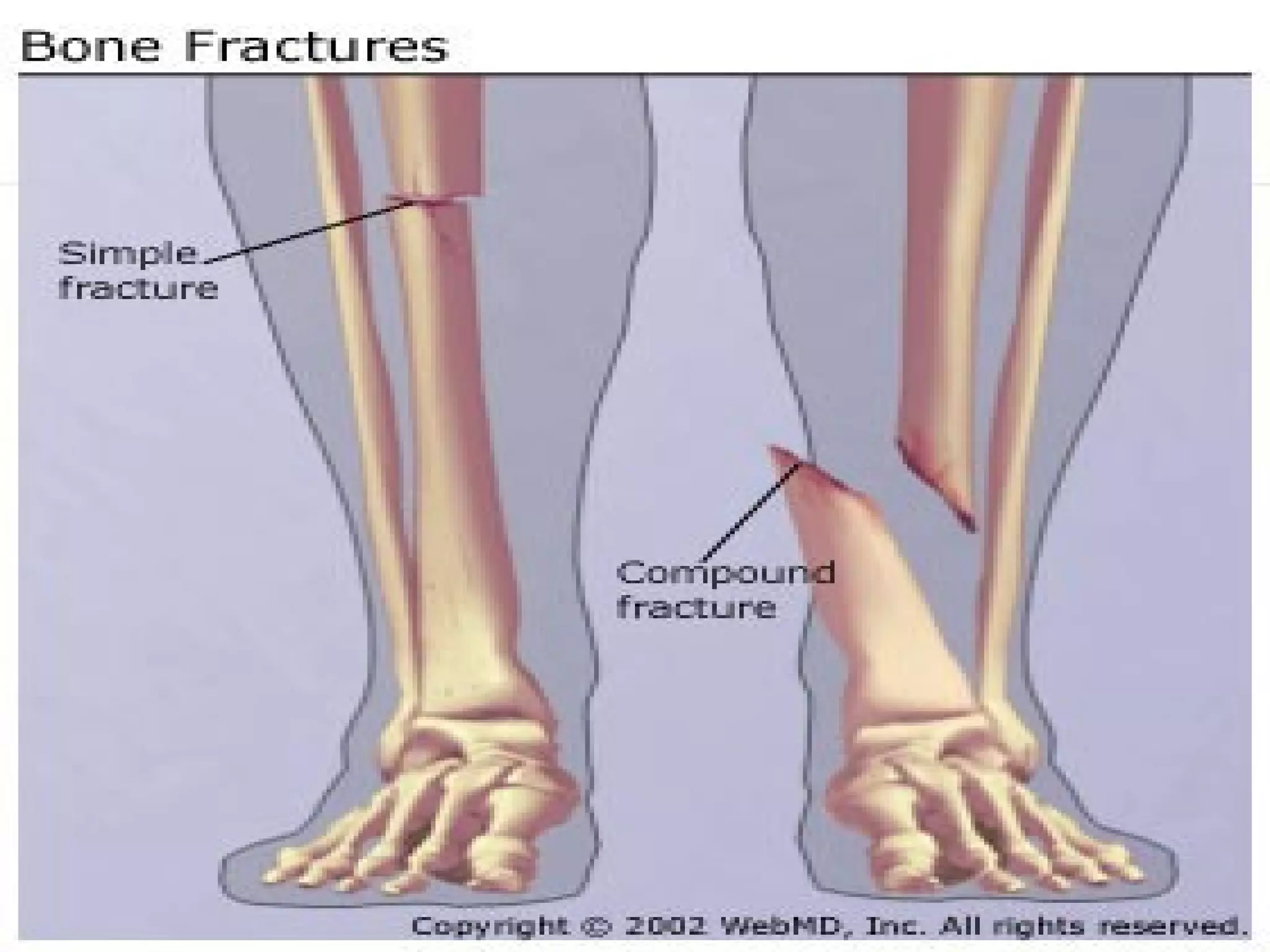
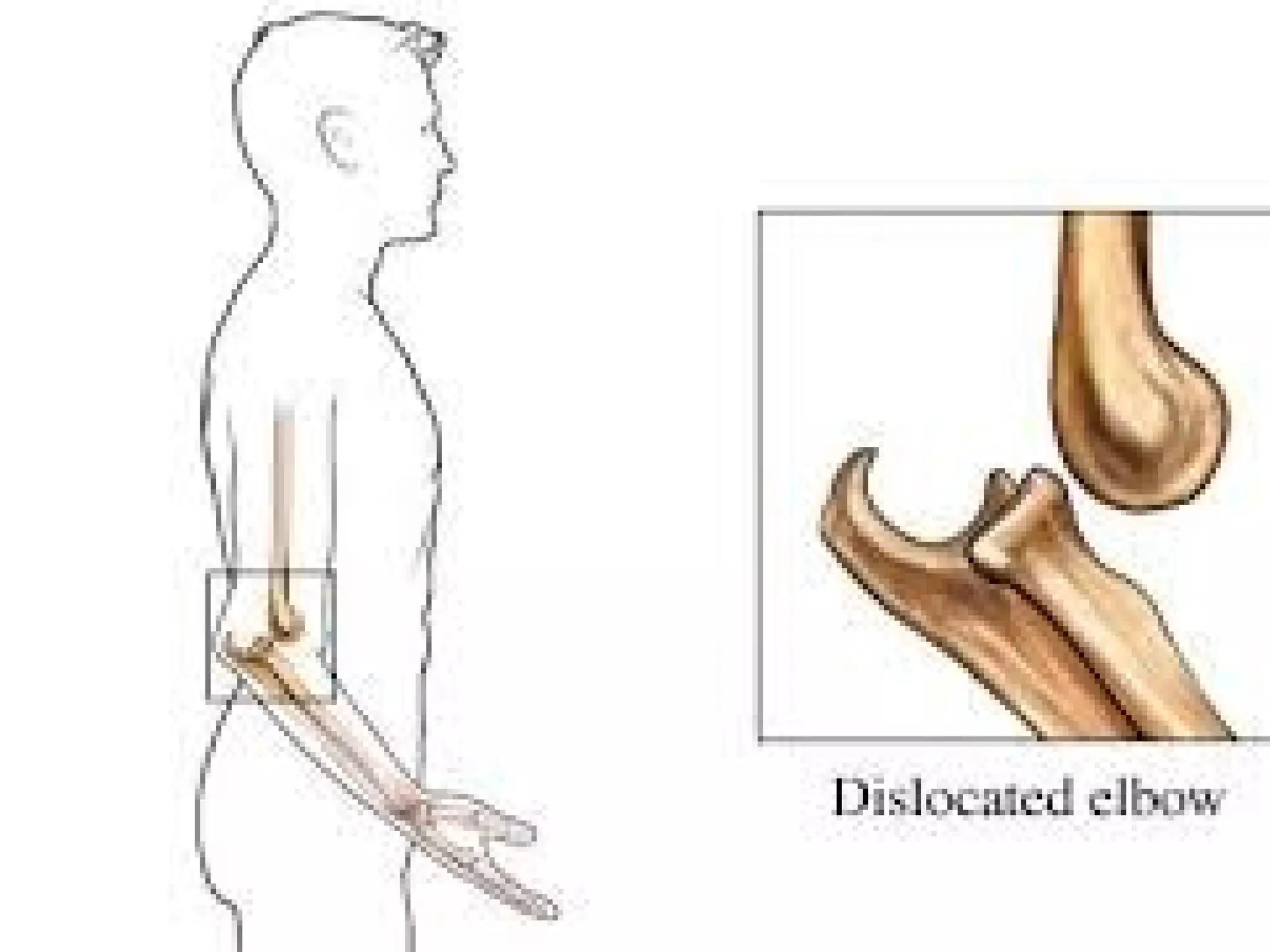
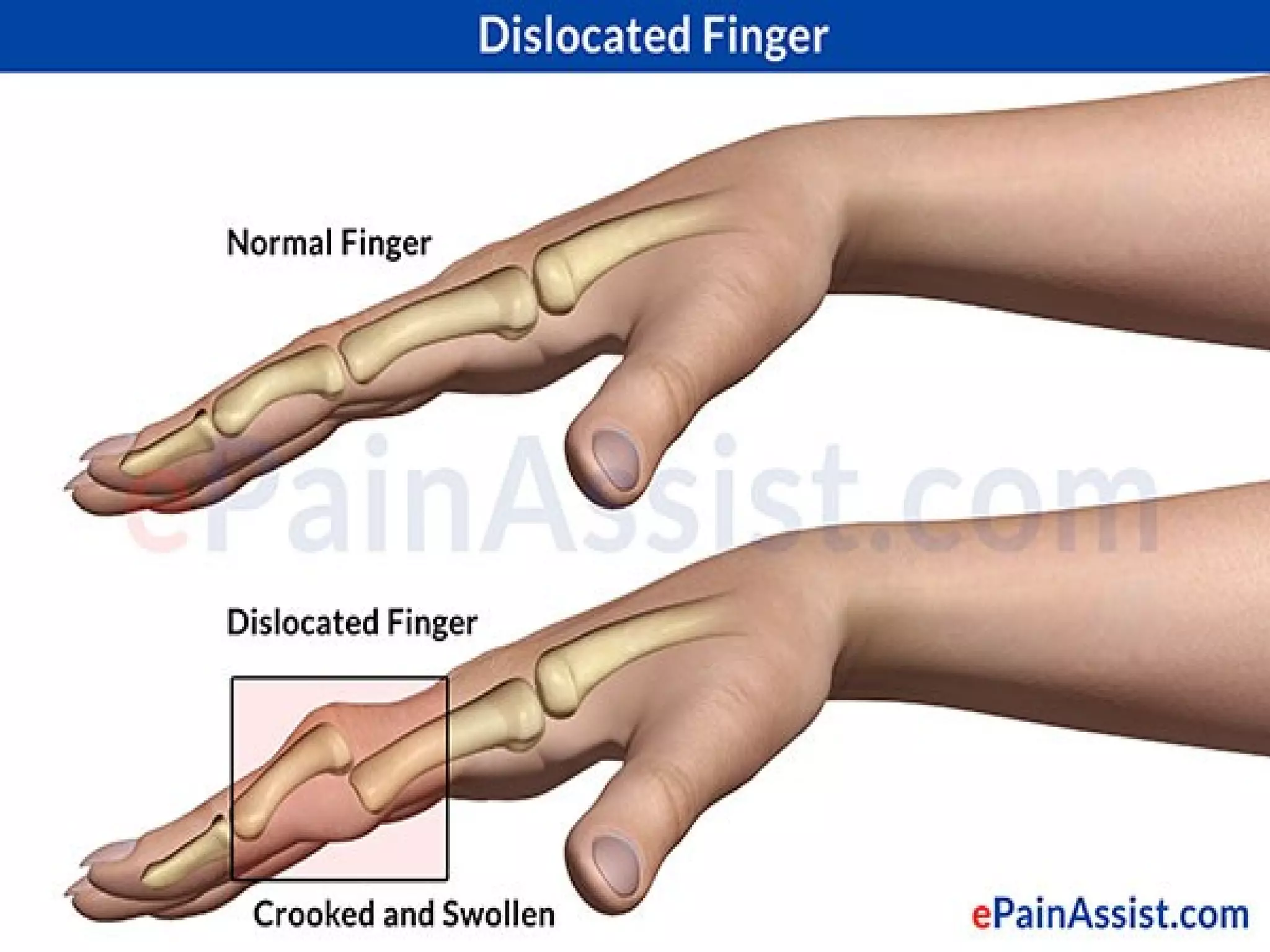
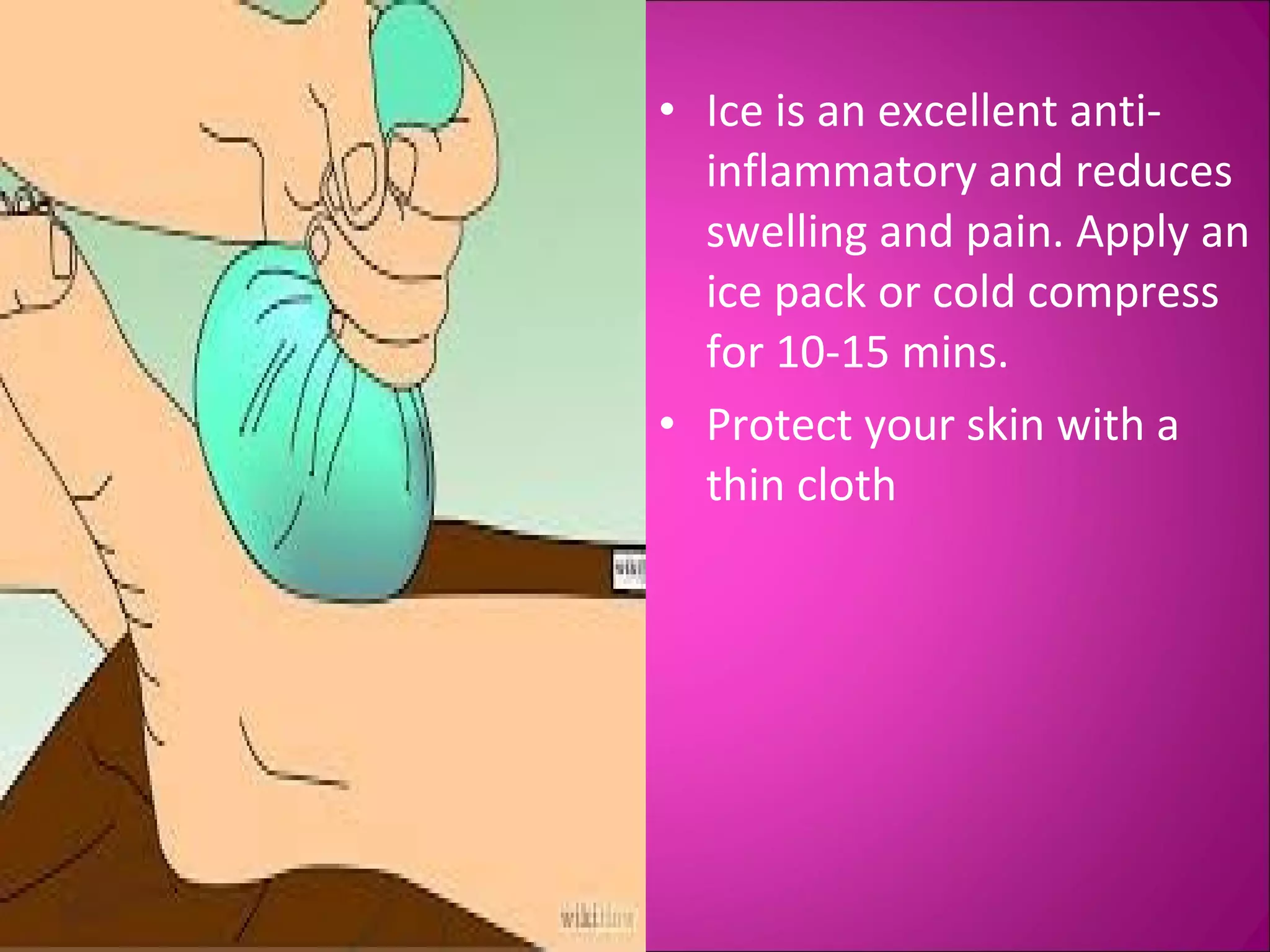
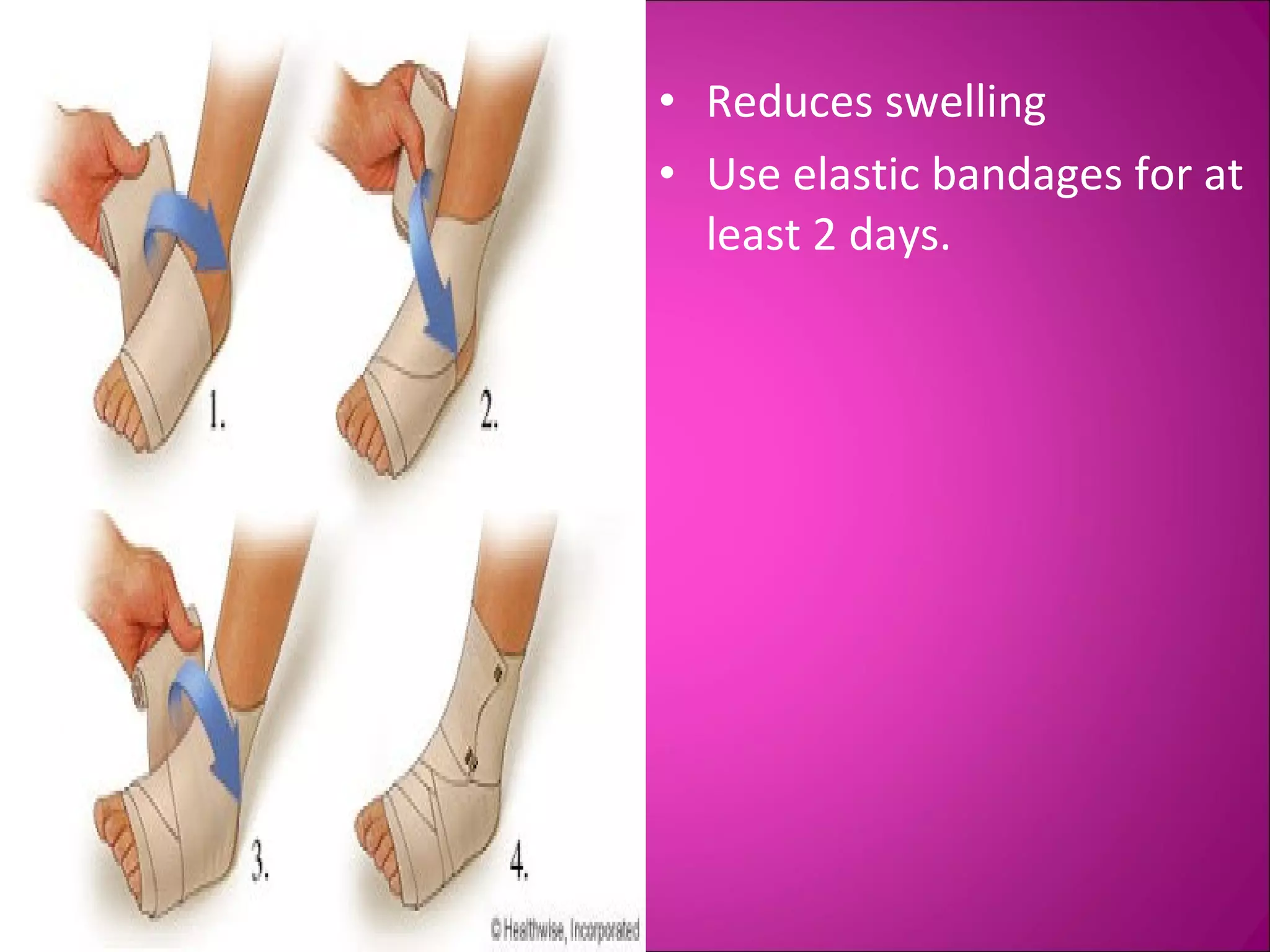
This document provides information on basic first aid, common injuries like sprains, strains, fractures and dislocations. It describes the differences between sprains and strains, signs and symptoms. Treatment recommendations include RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) for sprains, strains and fractures. Home treatments and when to see a doctor are outlined. Prevention tips like proper warm up/cool down and using correct form are also mentioned.