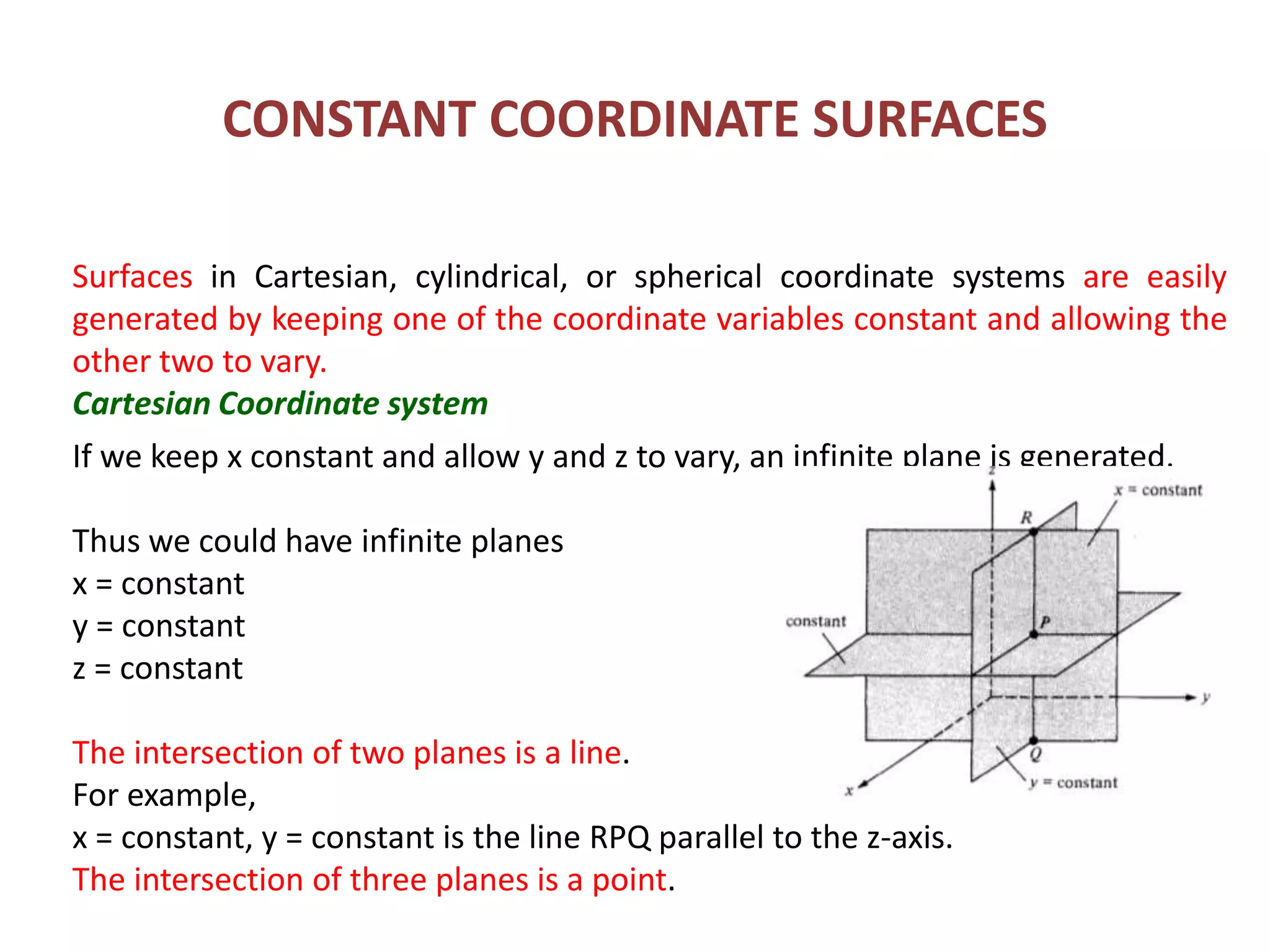
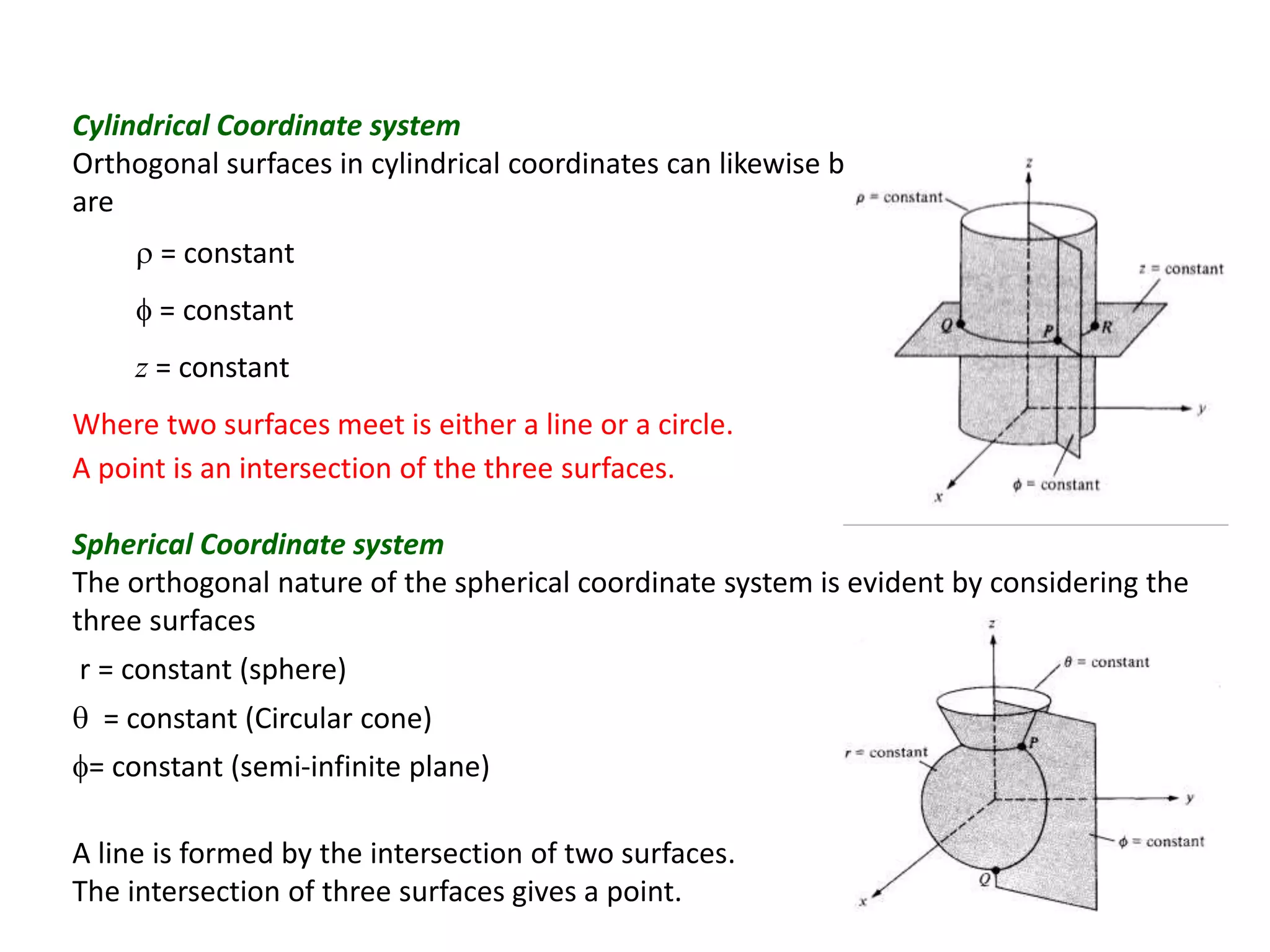
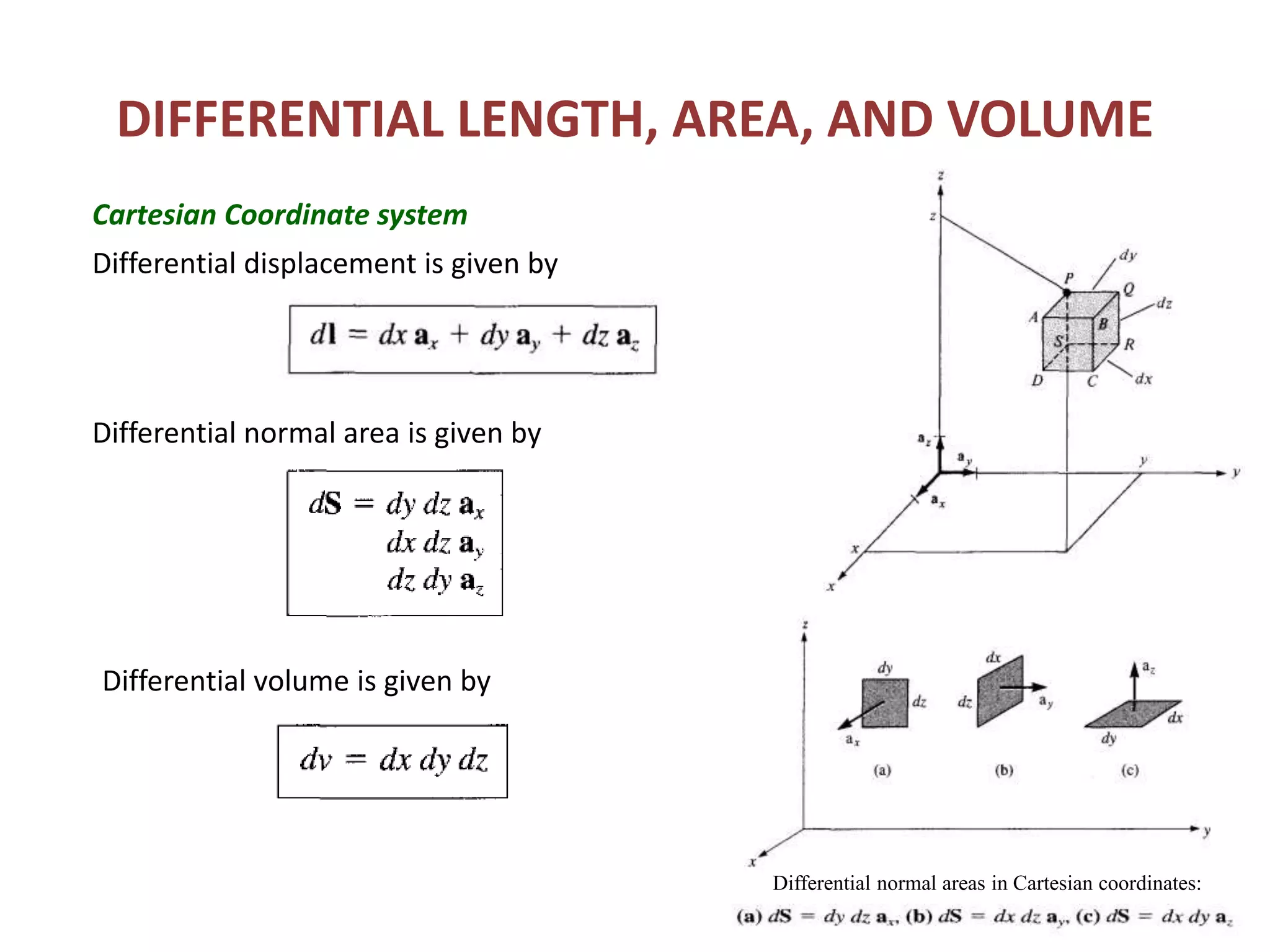
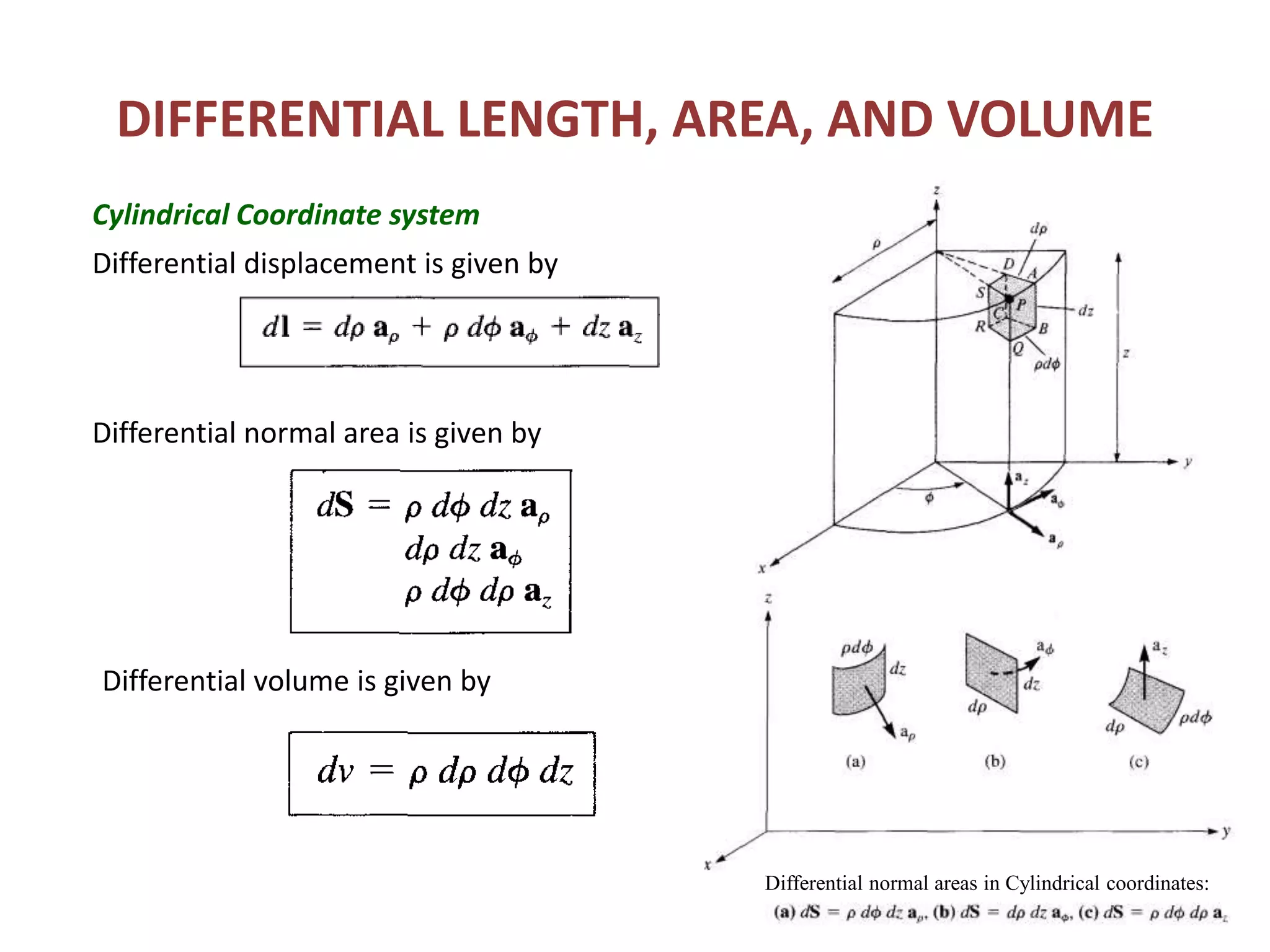
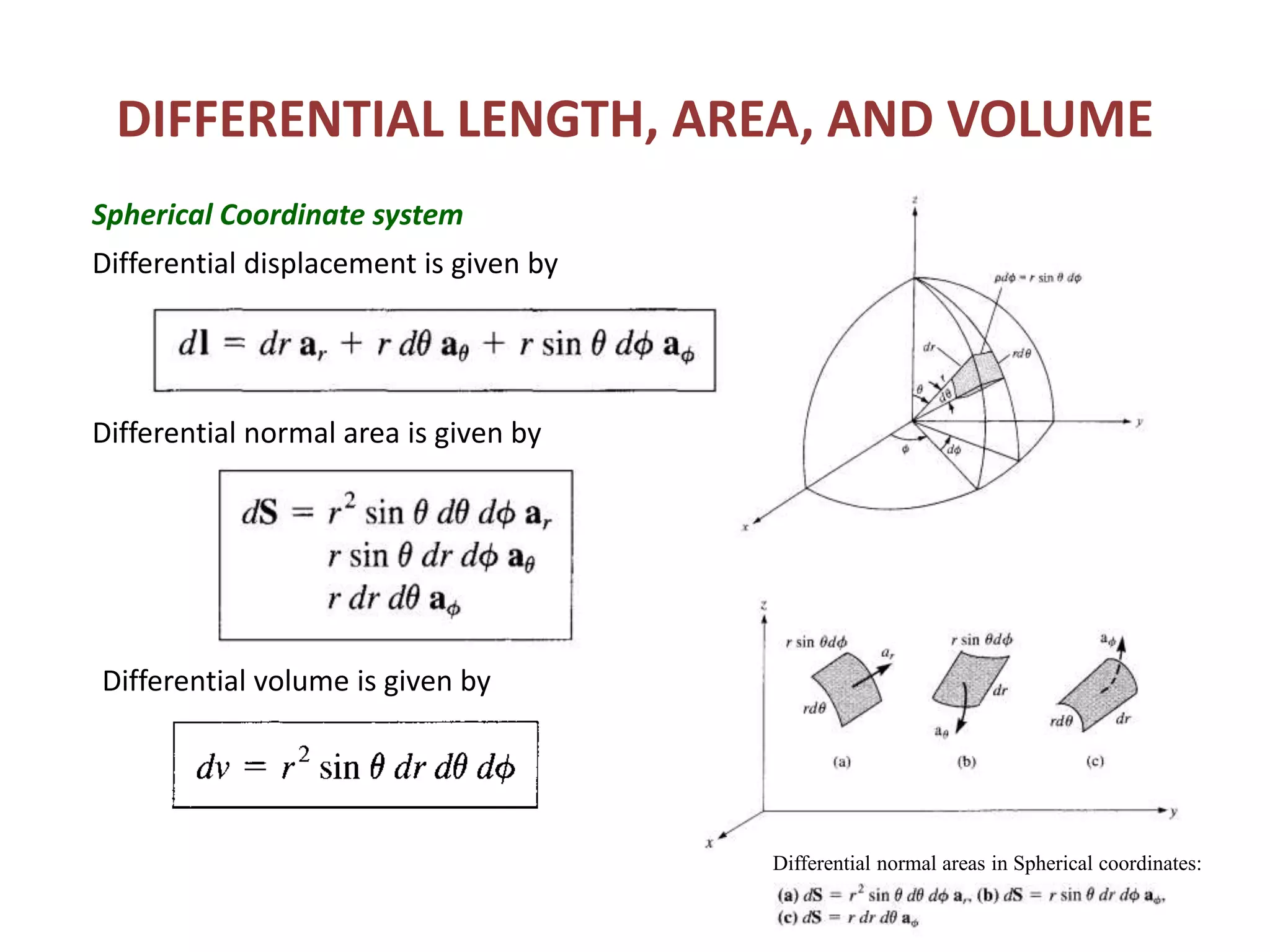
Constant coordinate surfaces can be generated in Cartesian, cylindrical, and spherical coordinate systems by keeping one coordinate constant. In Cartesian coordinates, constant x, y, and z planes intersect to form lines and points. In cylindrical coordinates, constant ρ, φ, and z surfaces intersect to form lines or circles and points. In spherical coordinates, constant r, θ, and φ surfaces intersect to form lines, circular cones, and semi-infinite planes, with points at their intersections. Differential length, area, and volume are also defined differently depending on the coordinate system used.