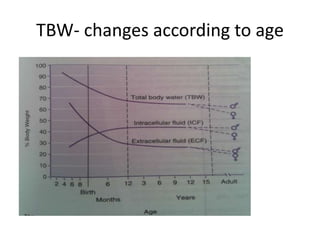
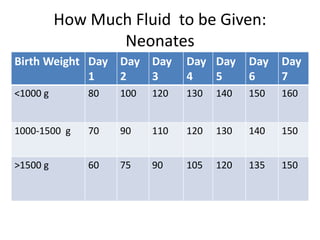
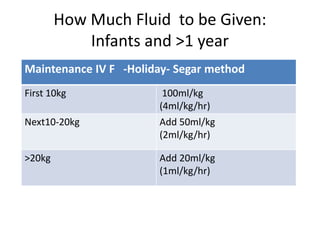
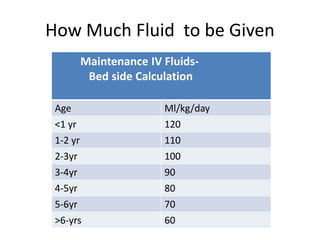
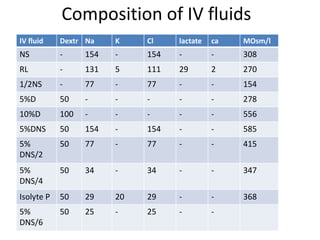
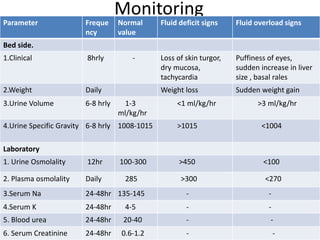
This document discusses intravenous fluid management in newborns. It notes that total body water is highest at birth, around 75% for term infants and 80% for preterm infants. During the first week, excess fluid is lost primarily through urine as extracellular fluid decreases. Preterm infants lose more, around 10-15% of body weight. Intravenous fluids are given to sick newborns or those under 30 weeks gestation. The type and amount of fluids given depends on factors like weight and postnatal age. Fluid needs increase in situations like fever or phototherapy and decrease in conditions causing fluid retention. Monitoring includes weight, urine output, and laboratory tests to avoid dehydration or fluid overload.