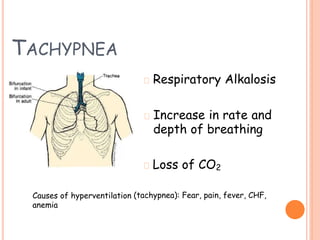
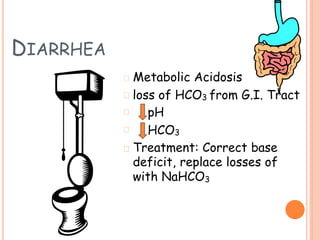
1) Maintenance fluid therapy aims to prevent dehydration, electrolyte disturbances, and protein degradation in sick infants and children whose oral intake is uncertain.
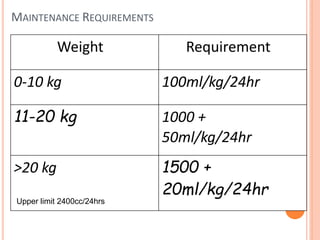
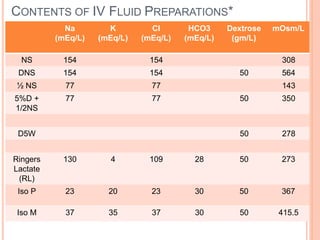
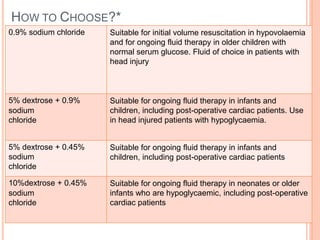
2) Fluid requirements are calculated based on weight and age using the "4-2-1 rule" or Holliday-Segar formula. Common maintenance fluids include 0.45% saline with potassium chloride.
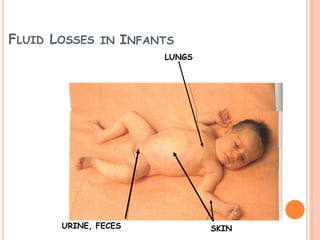
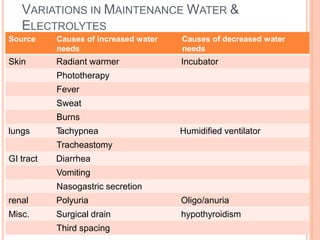
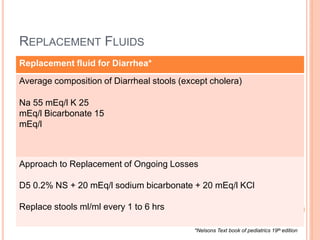
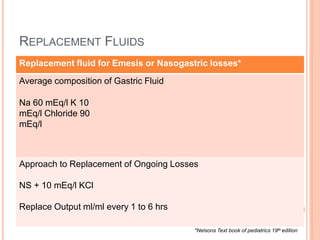
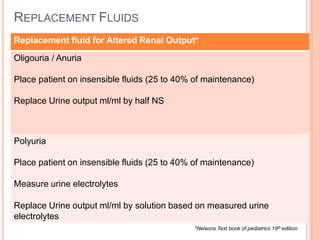
3) Careful monitoring of weight, urine output, and serum sodium is important when administering intravenous fluids to avoid complications like hyponatremia. Replacement fluids should promptly replace ongoing losses from vomiting, diarrhea, or altered renal output.





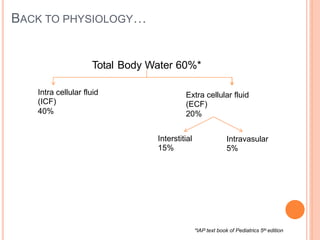
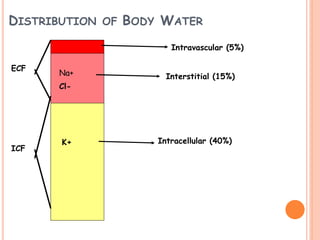
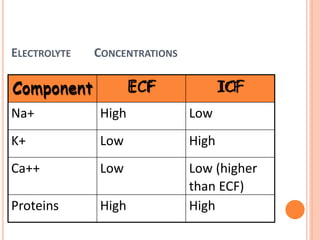
![KEY LEARNING POINT*
Sodium is the Principle electrolyte
[140mEq/L (+/- 5)]
in ECF
Potassium is the Principle electrolyte in ICF
[150mEq/L (+/- 5)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drdeepakseminaronfluid-190309105658/85/Dr-deepak-seminar-on-fluid-11-320.jpg)