This document provides information about an upcoming science class including assignments, tests, and review questions. It includes:
1) An announcement of Binder Check #2 due next Thursday and a test on atomic structure on Thursday and Friday of the following week. Students are instructed to make 1/2 page of notes to support themselves on the test.
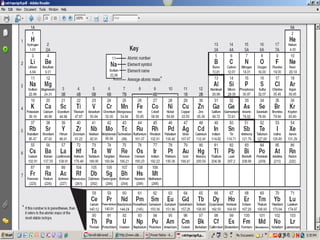
2) A list of review questions about atomic structure, isotopes, ions, and the periodic table.
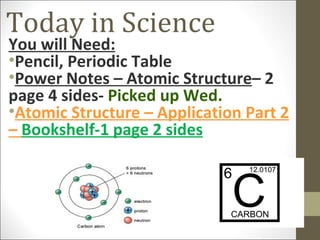
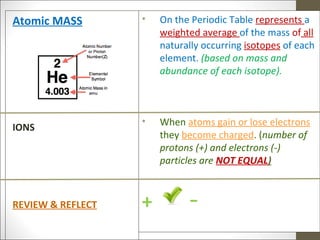
3) Explanations that the atomic number represents the number of protons, isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but different neutrons, and ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons.
4) An activity where students will color code