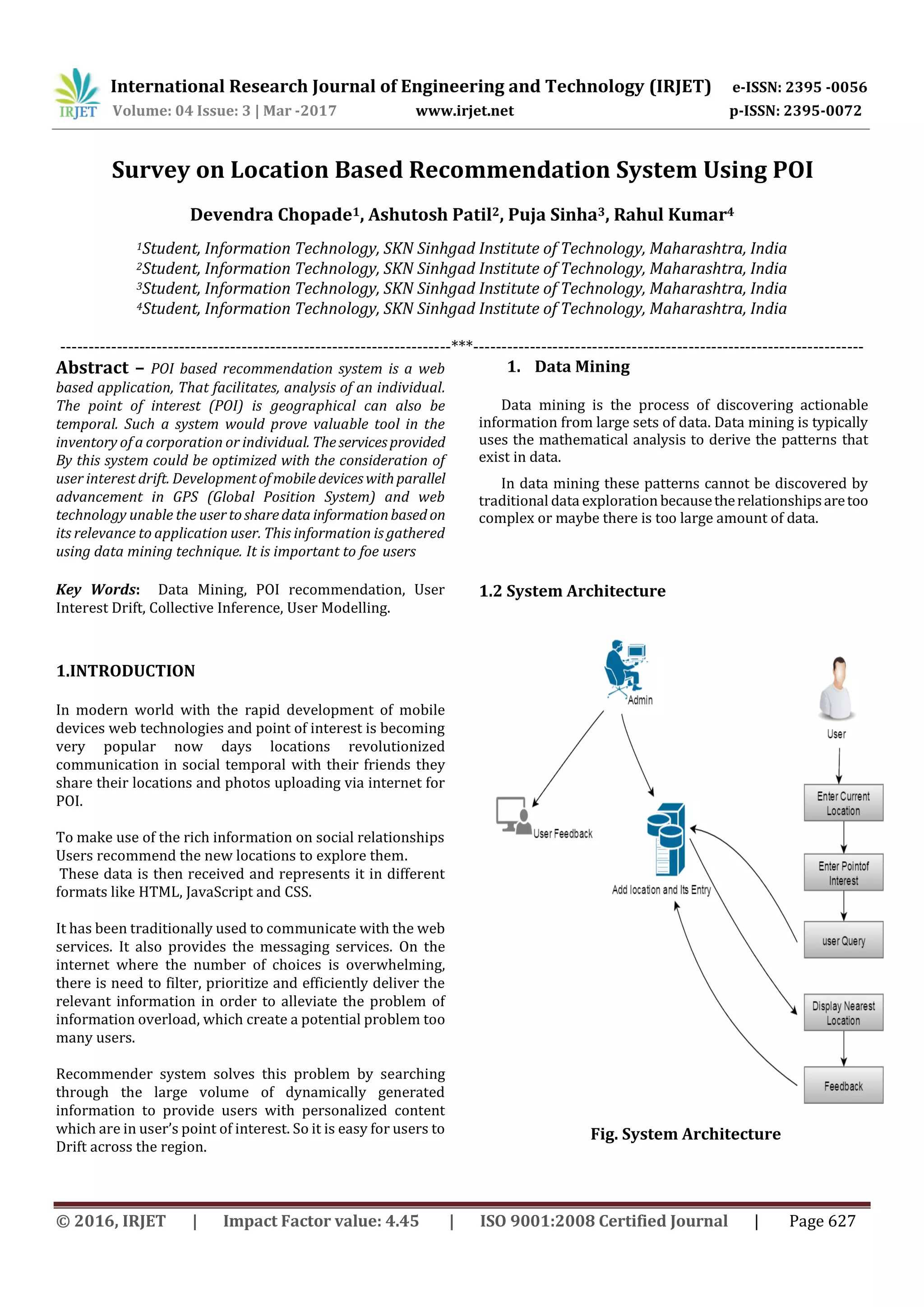
This document summarizes a survey on location-based recommendation systems using points of interest (POIs). It discusses how data mining techniques can be used to analyze user check-in data from location-based social networks to discover patterns and interests in order to provide personalized POI recommendations to users. The system architecture involves collecting check-in data, performing data mining, building user profiles, and generating recommendations. It also reviews several related works on topic modeling, matrix factorization methods, and exploiting sequential check-in data and geographical influences to provide successive POI recommendations. The goal is to develop improved recommendation methods that can recommend new locations for users to explore based on their interests and behaviors.