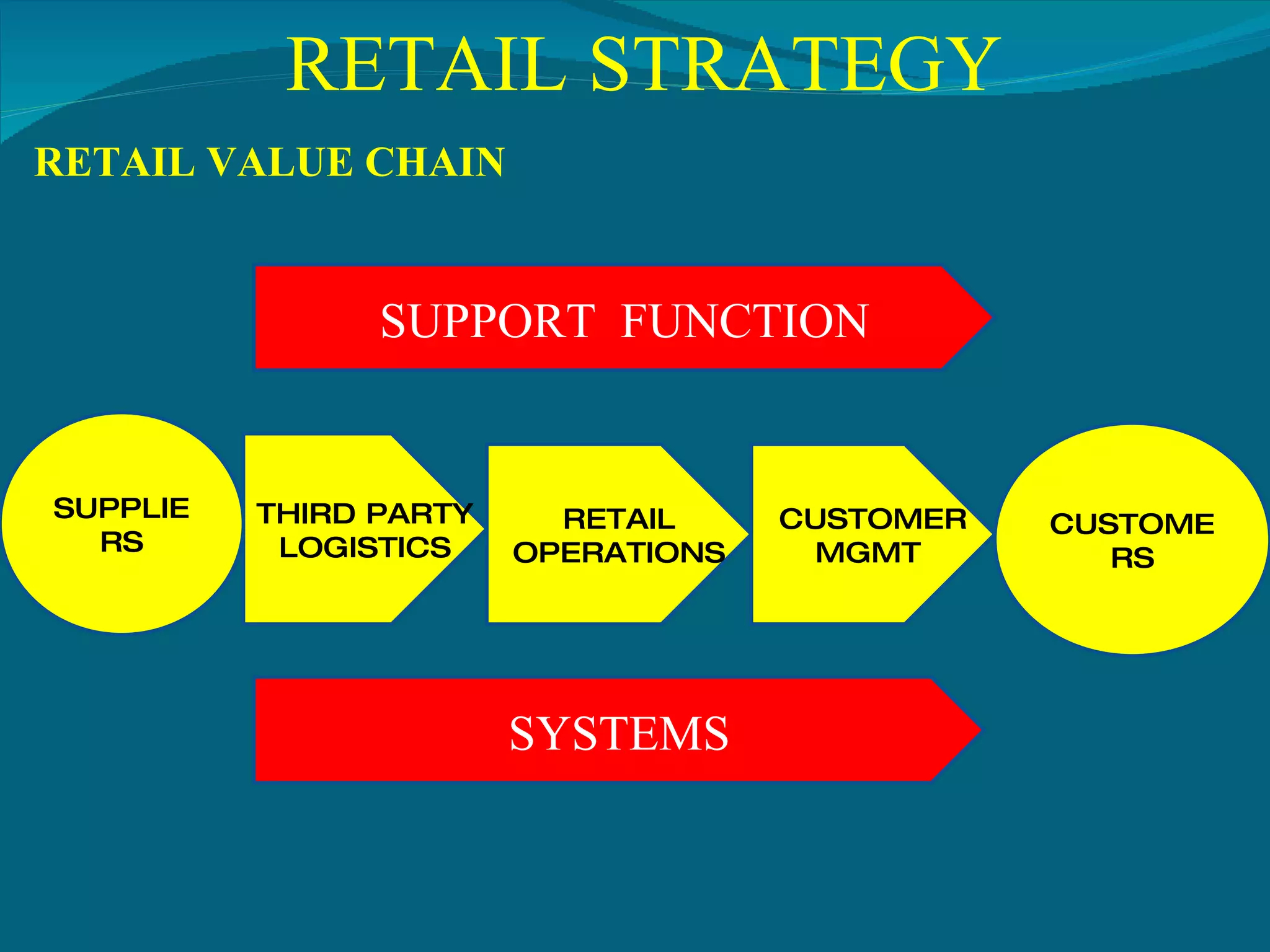
The document discusses retail strategy formulation. It begins with defining the retailer's mission which is the core of its existence. A situation analysis is then conducted to understand strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Various strategic alternatives like market penetration, market development, retail format development and diversification are identified. Objectives are set and resources are obtained to implement the chosen strategy. Progress is then monitored through evaluation and control. International expansion is also discussed as a growth strategy through various methods like exports, franchising, joint ventures, acquisitions and organic growth.