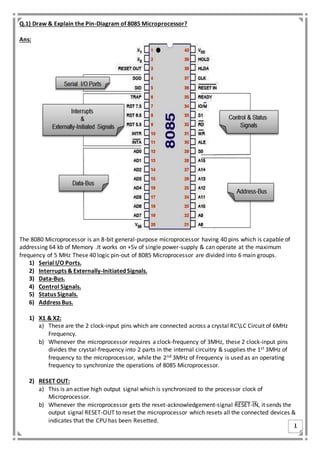
The 8085 microprocessor is an 8-bit device with 40 pins that can address 64KB of memory and operates at a frequency of up to 5 MHz. Its pin functions are categorized into six groups including serial I/O ports, interrupts, data, control, status signals, and address buses, with specific pins assigned for various tasks such as input/output communication and interrupt management. Key pins include clock inputs for frequency management, reset signals for CPU initialization, and read/write control signals for memory and I/O operations.