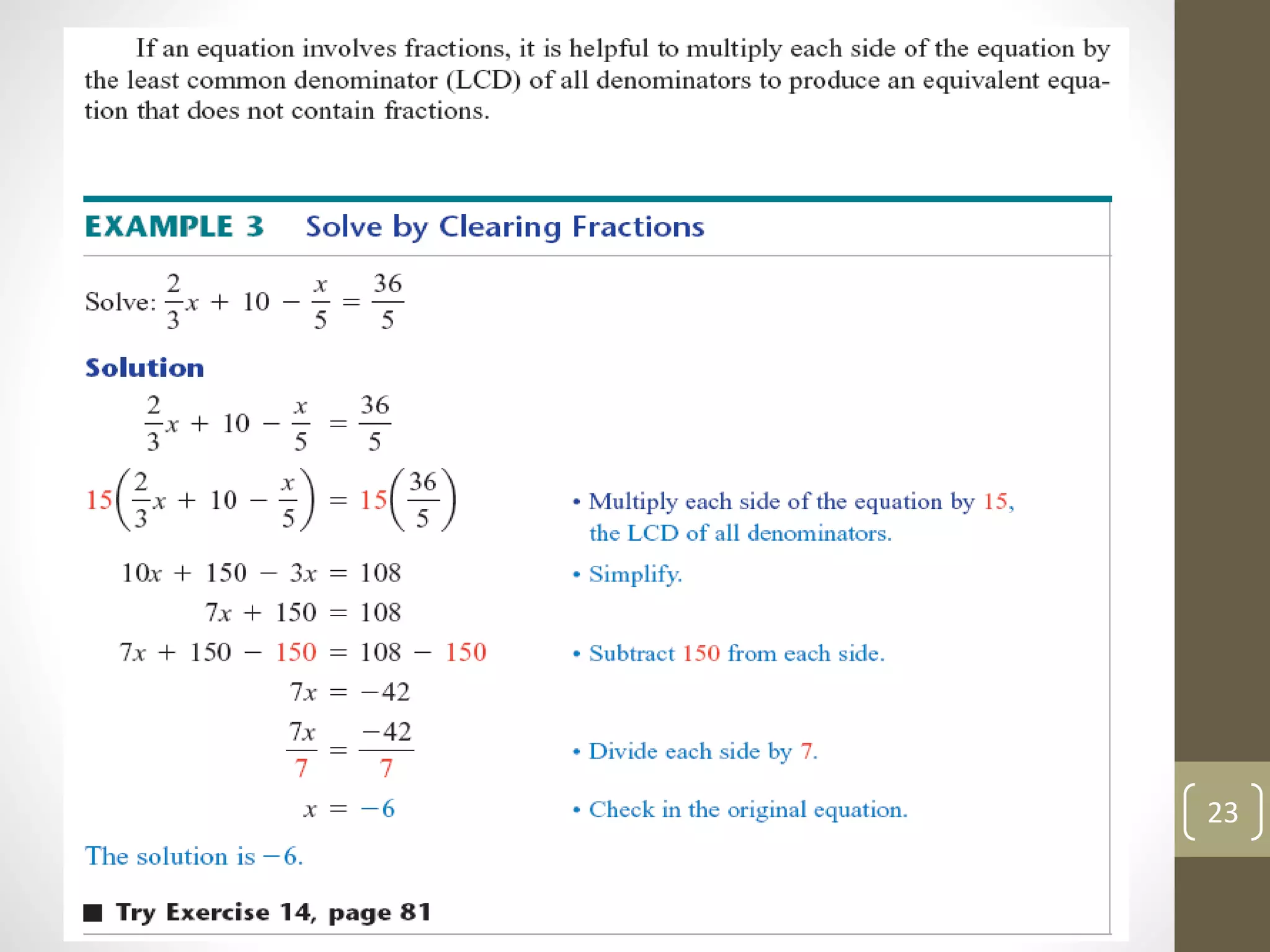
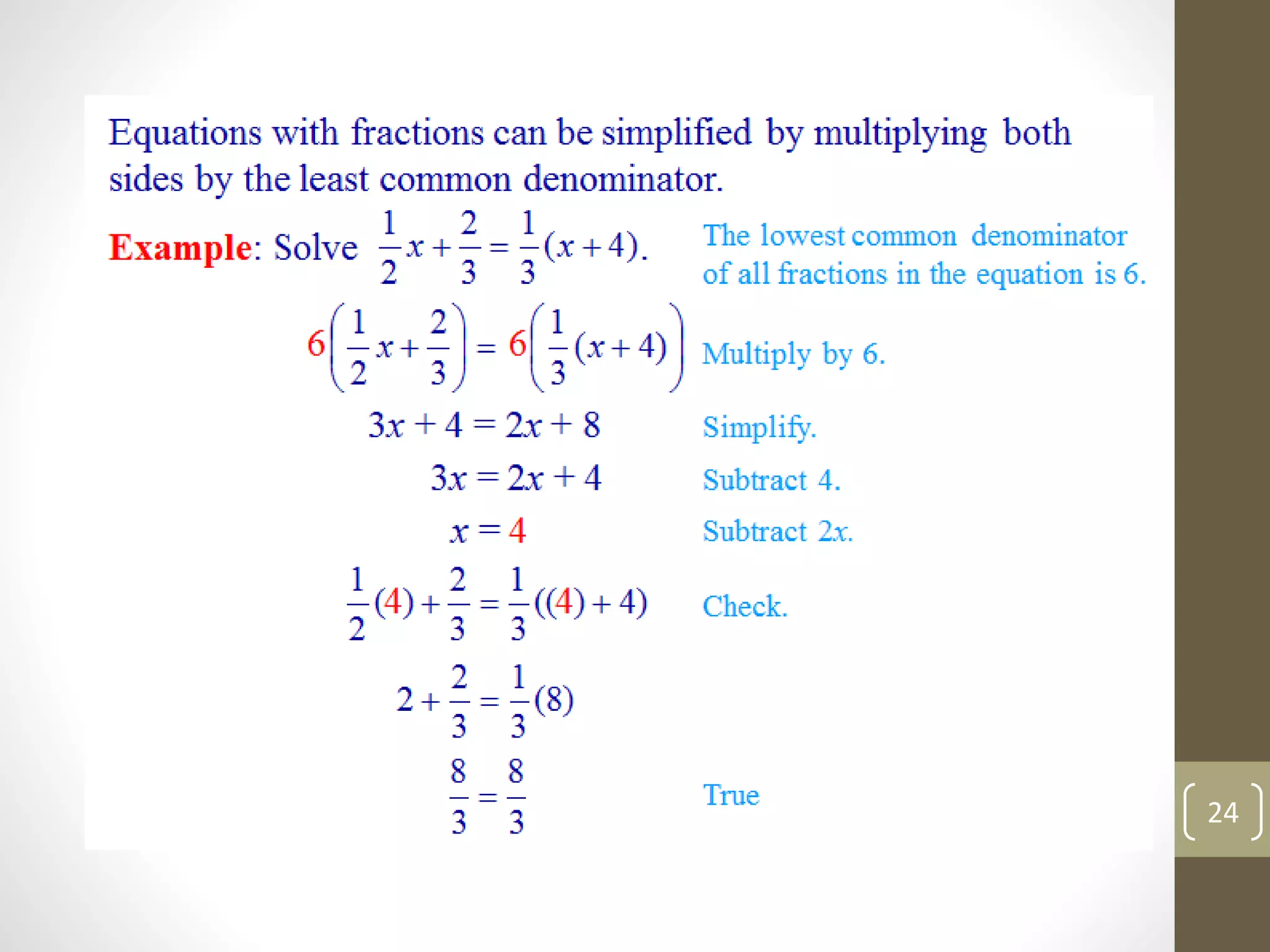
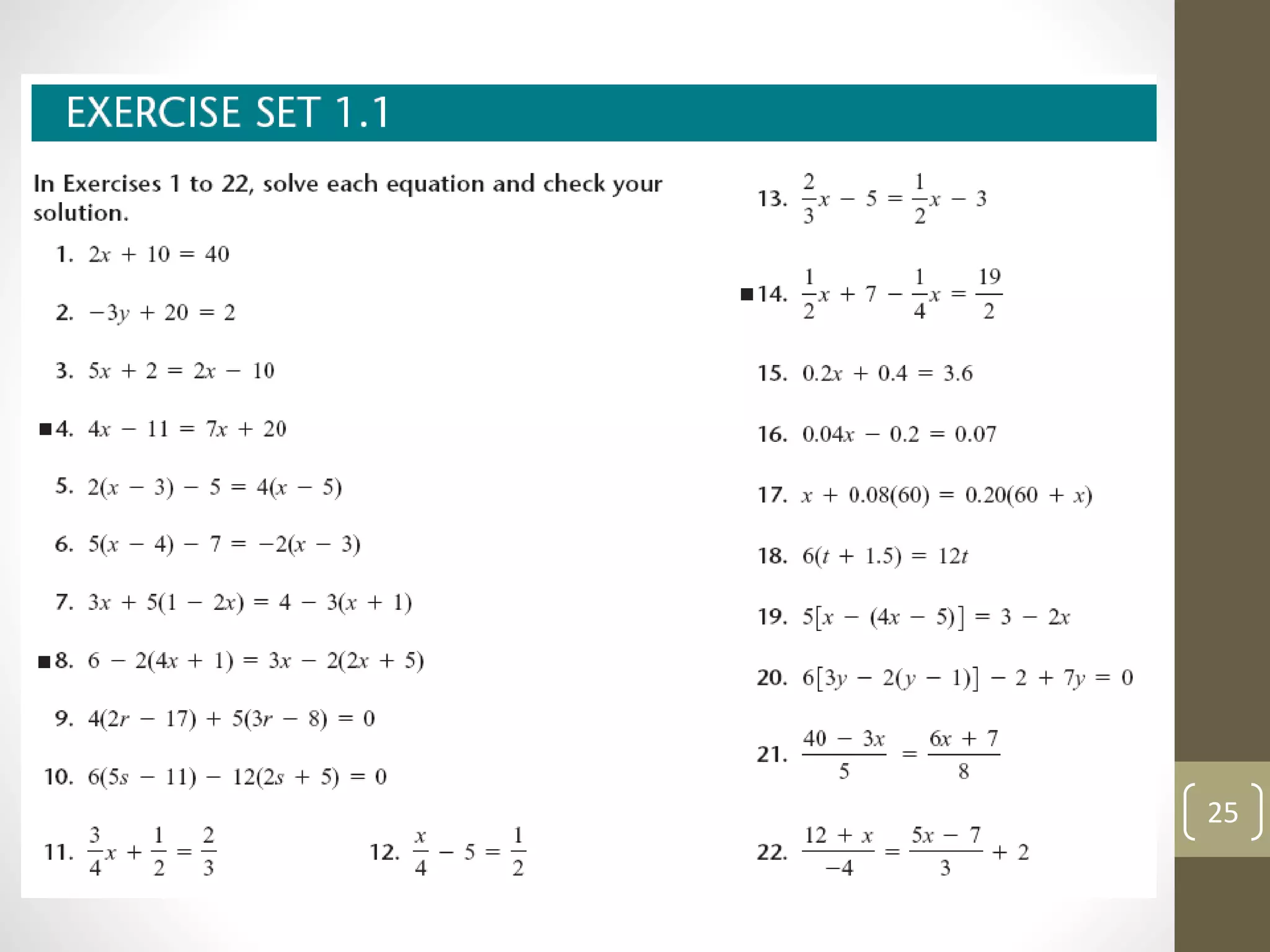
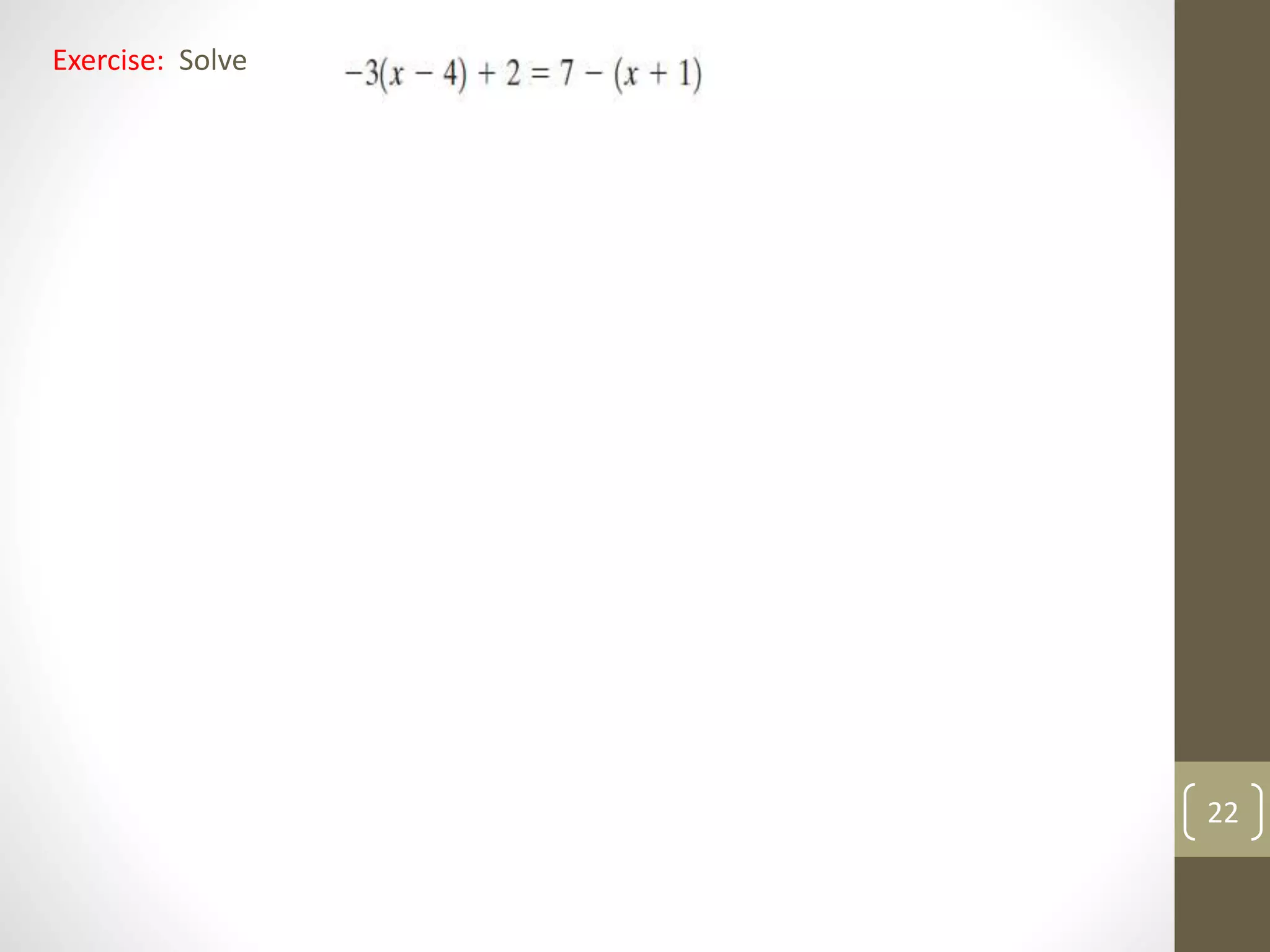This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 3 of a math textbook, including:
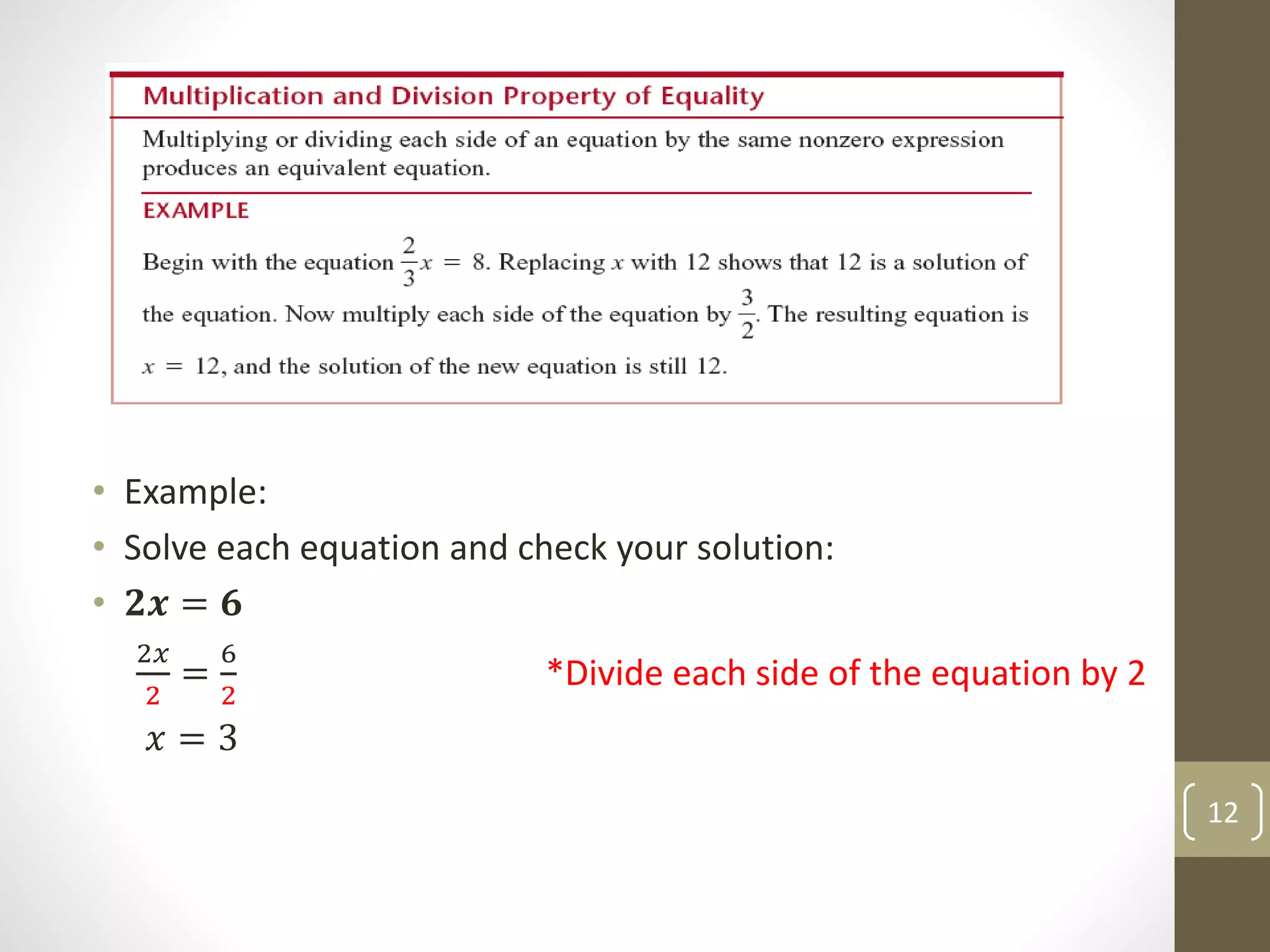
- How to solve linear equations in one variable using properties of equality like combining like terms and adding/subtracting the same quantity from both sides.
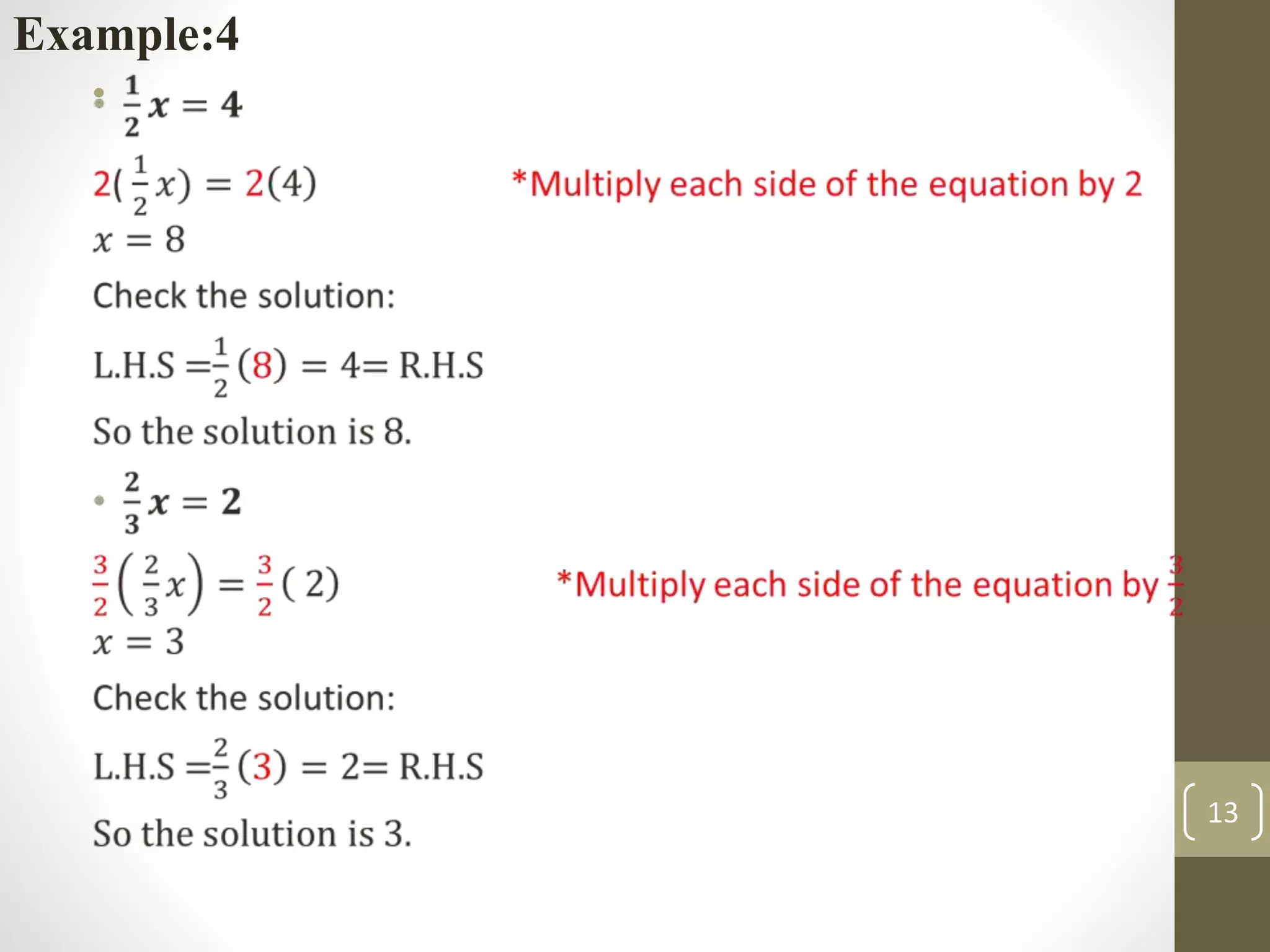
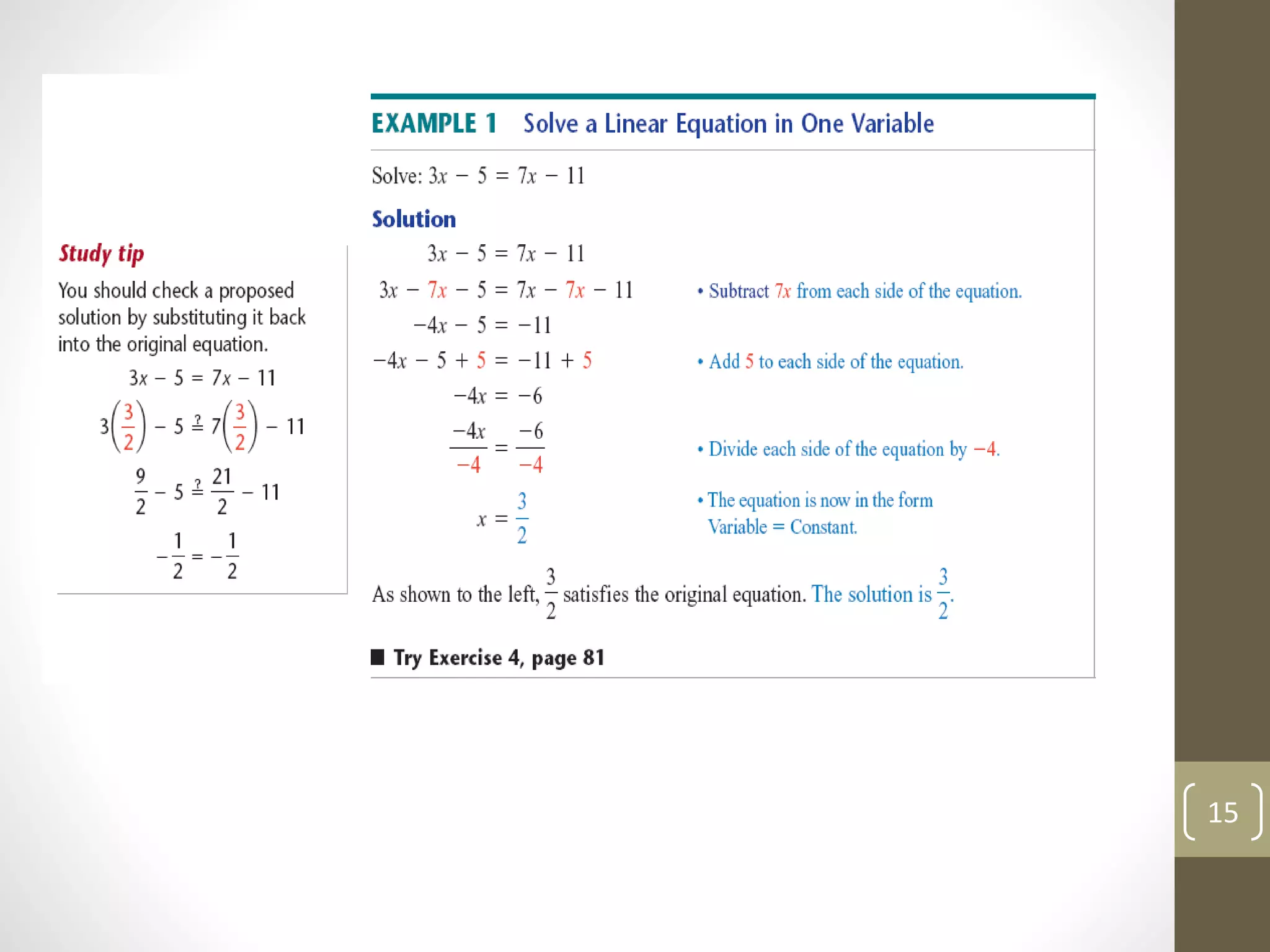
- Examples of solving linear equations by performing inverse operations like subtraction and division.
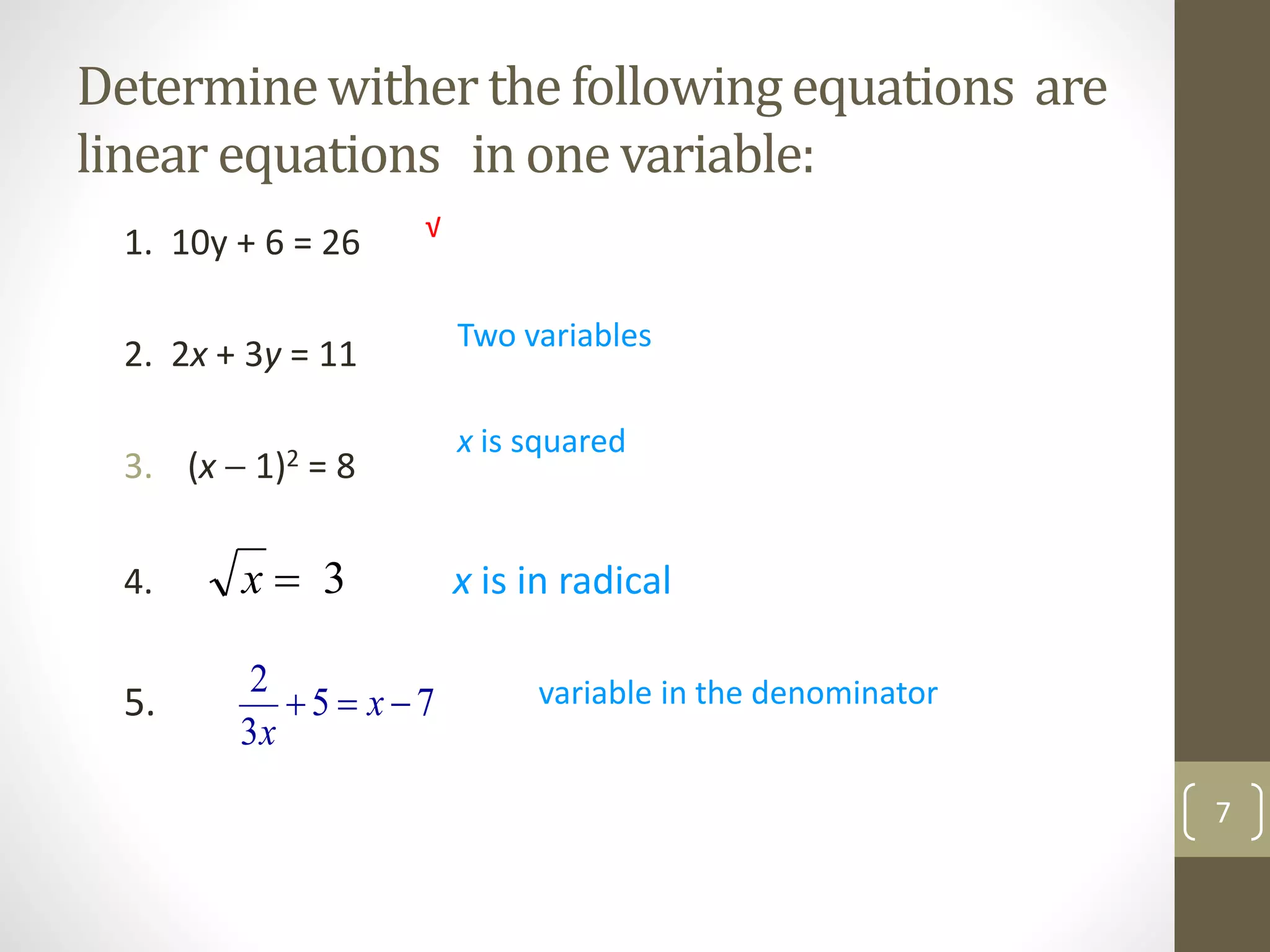
- Determining whether equations are linear based on the highest power of the variable, and providing examples of nonlinear equations.
- Checking solutions by showing that both sides of the original equation are equal when the solution is substituted.