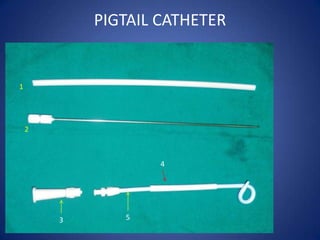
This document discusses the pigtail catheter, which is a drainage catheter used to drain fluids from parts of the body. It has side holes at the tip and a tightly coiled tail. This allows for single-stick placement through a trocar needle and helps hold it in place. It can drain bile, urine, pancreatic fluids, air, and be used for pleural drainage and imaging studies. It has advantages over larger chest tubes as it is smaller and less painful. However, it is more prone to obstruction and kinking. The document then describes the components, placement procedure, and uses of pigtail catheters.