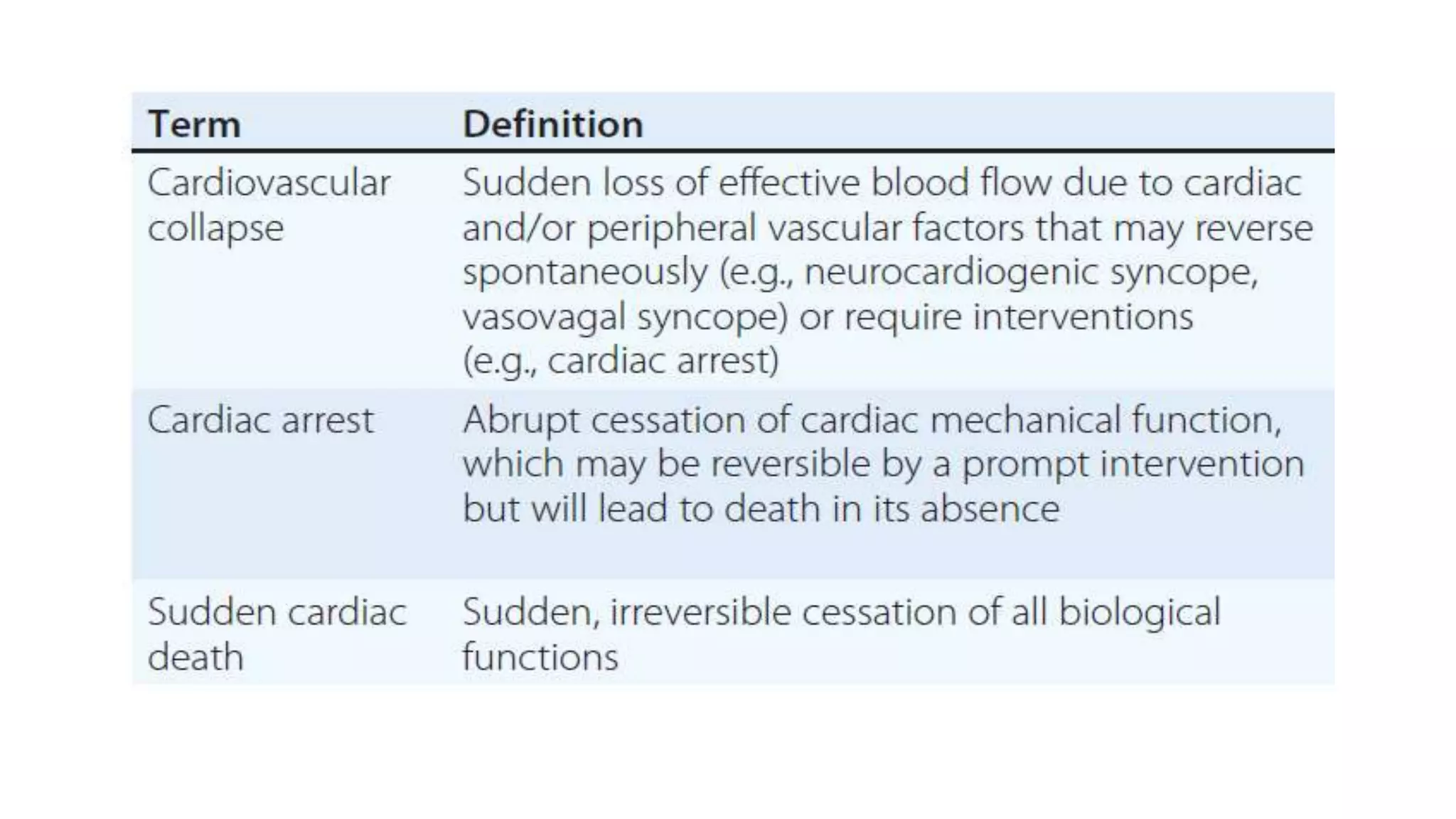
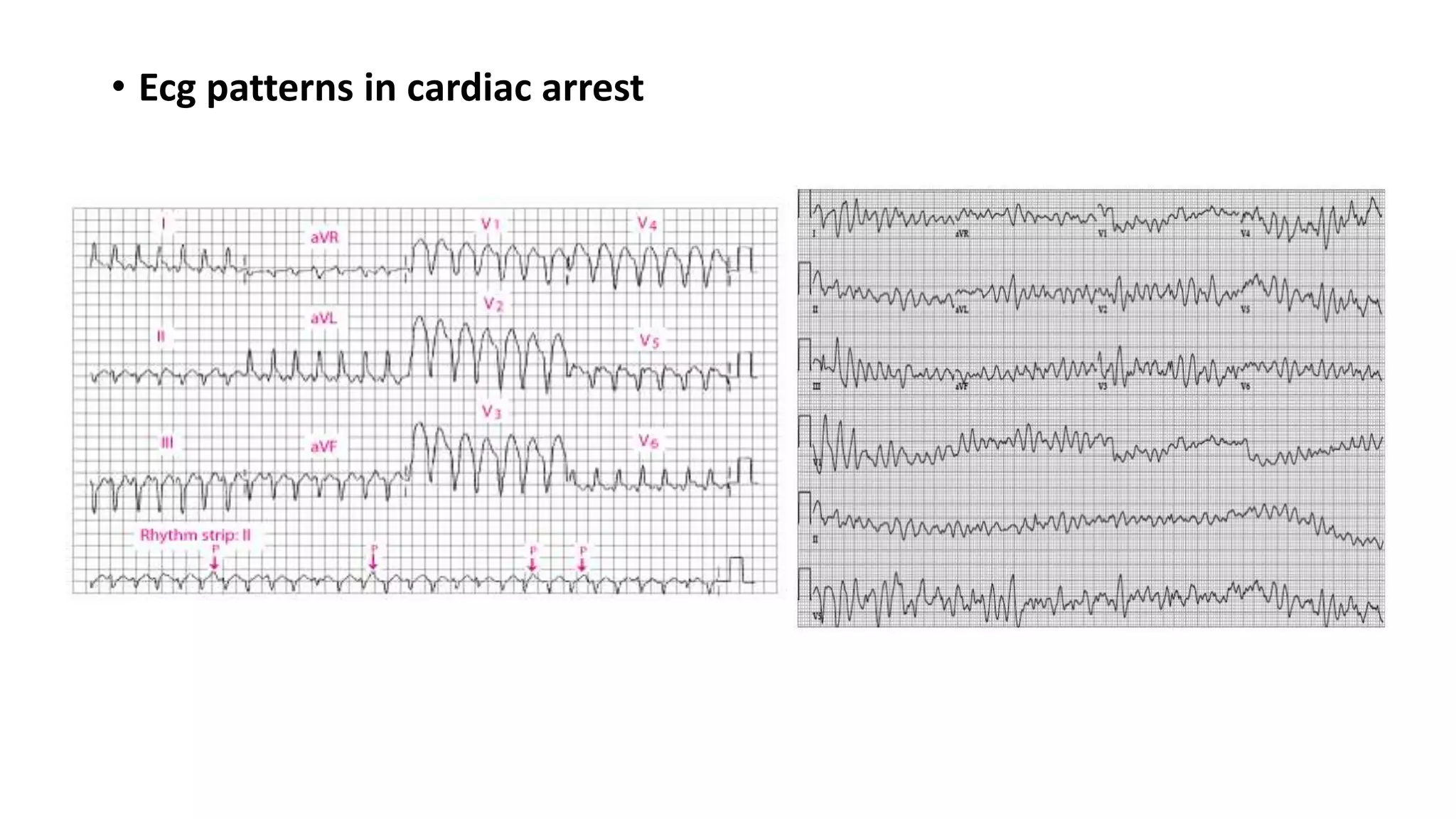
Sudden cardiac death is defined as an abrupt loss of consciousness within one hour of the onset of symptoms due to a cardiac cause. The main risk factors include age, race, sex, hereditary factors, lifestyle like smoking and obesity, left ventricular dysfunction, and ventricular arrhythmias. The most common causes are coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathies, acute heart failure, and electrophysiological abnormalities. Management of cardiac arrest focuses on continuous cardiopulmonary support, early defibrillation if needed, advanced life support including intubation, medications, and post-cardiac arrest care like therapeutic hypothermia. The goal is to restore spontaneous circulation and hemodynamic stability through these interventions.