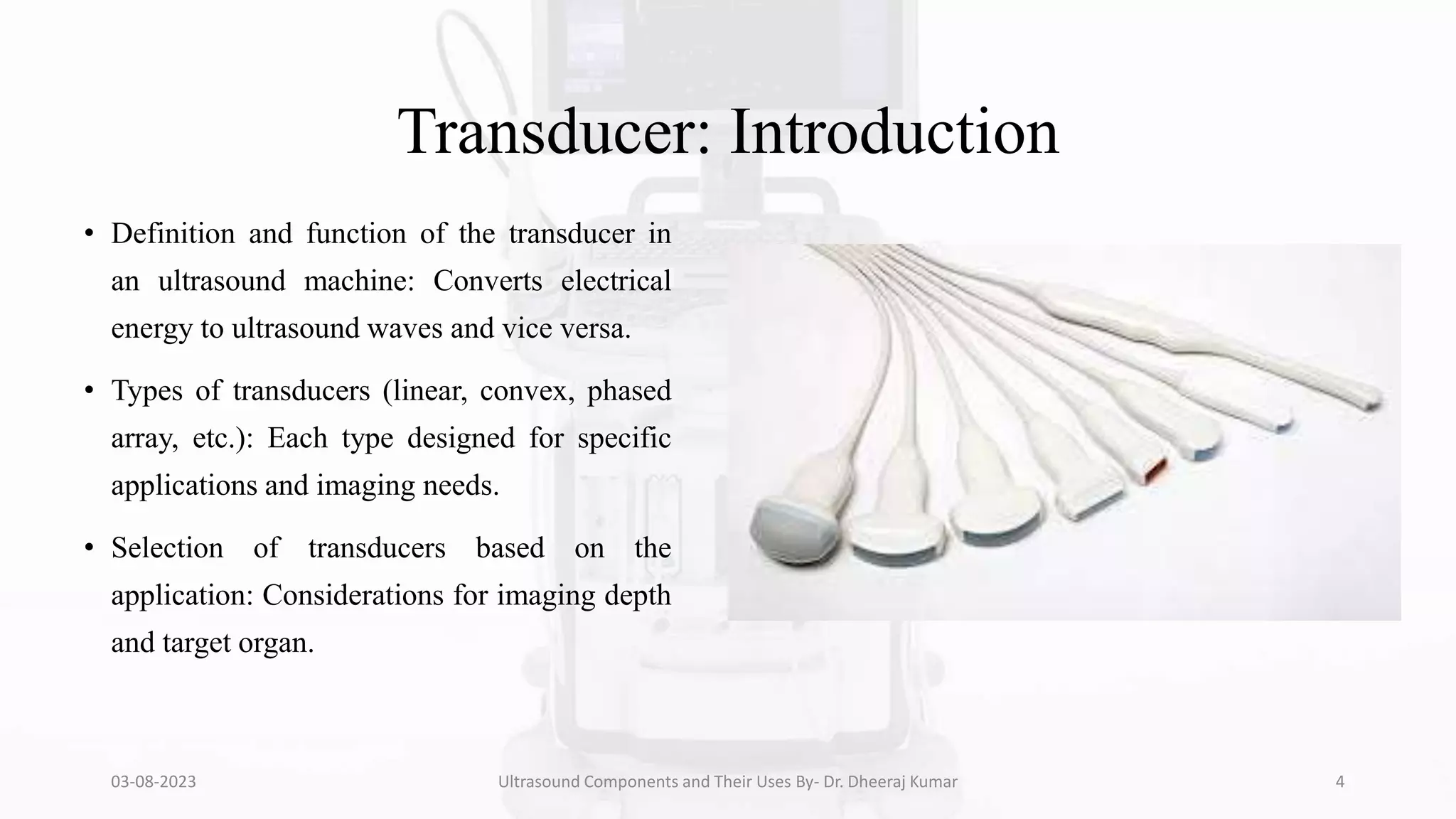
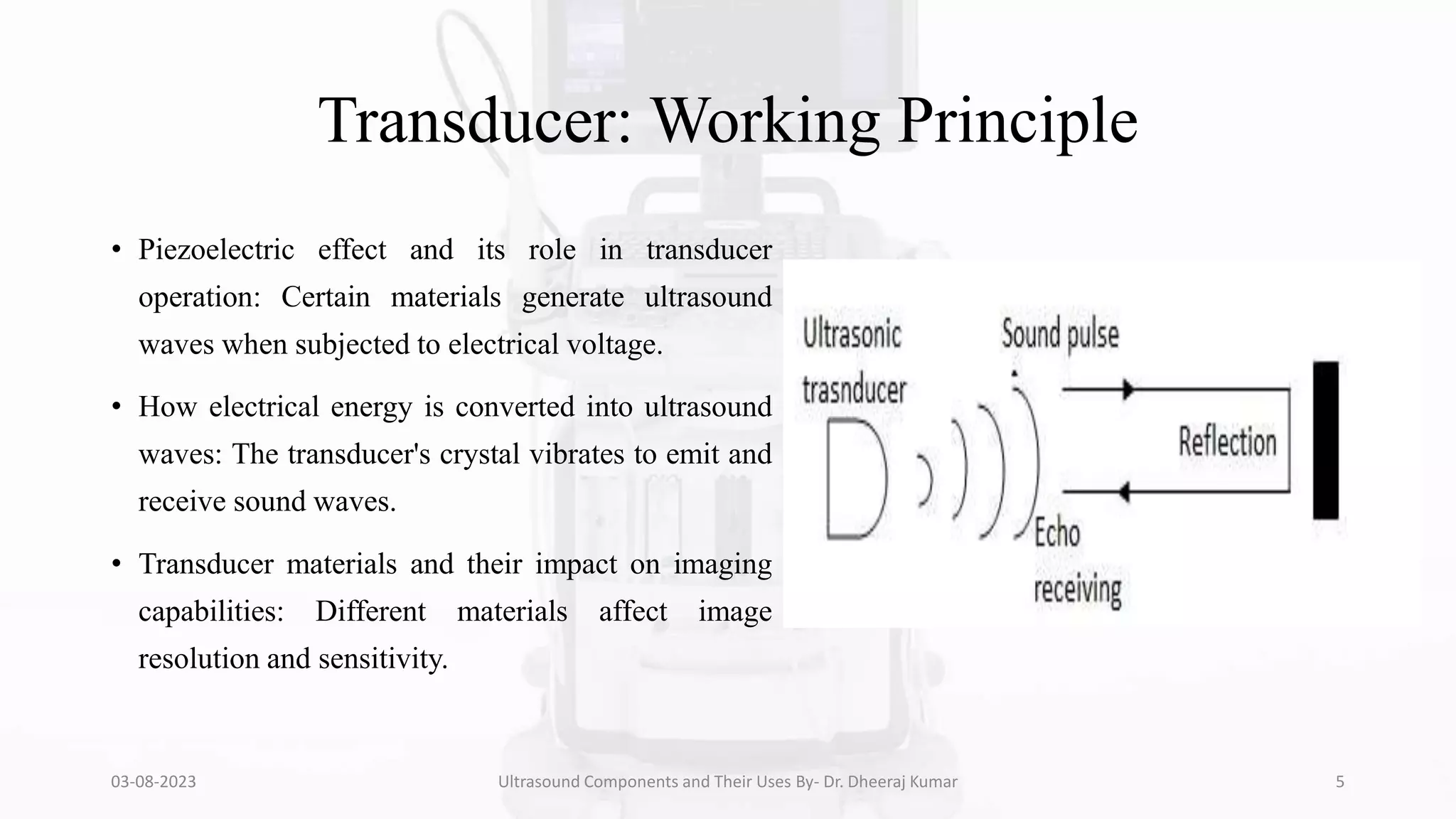
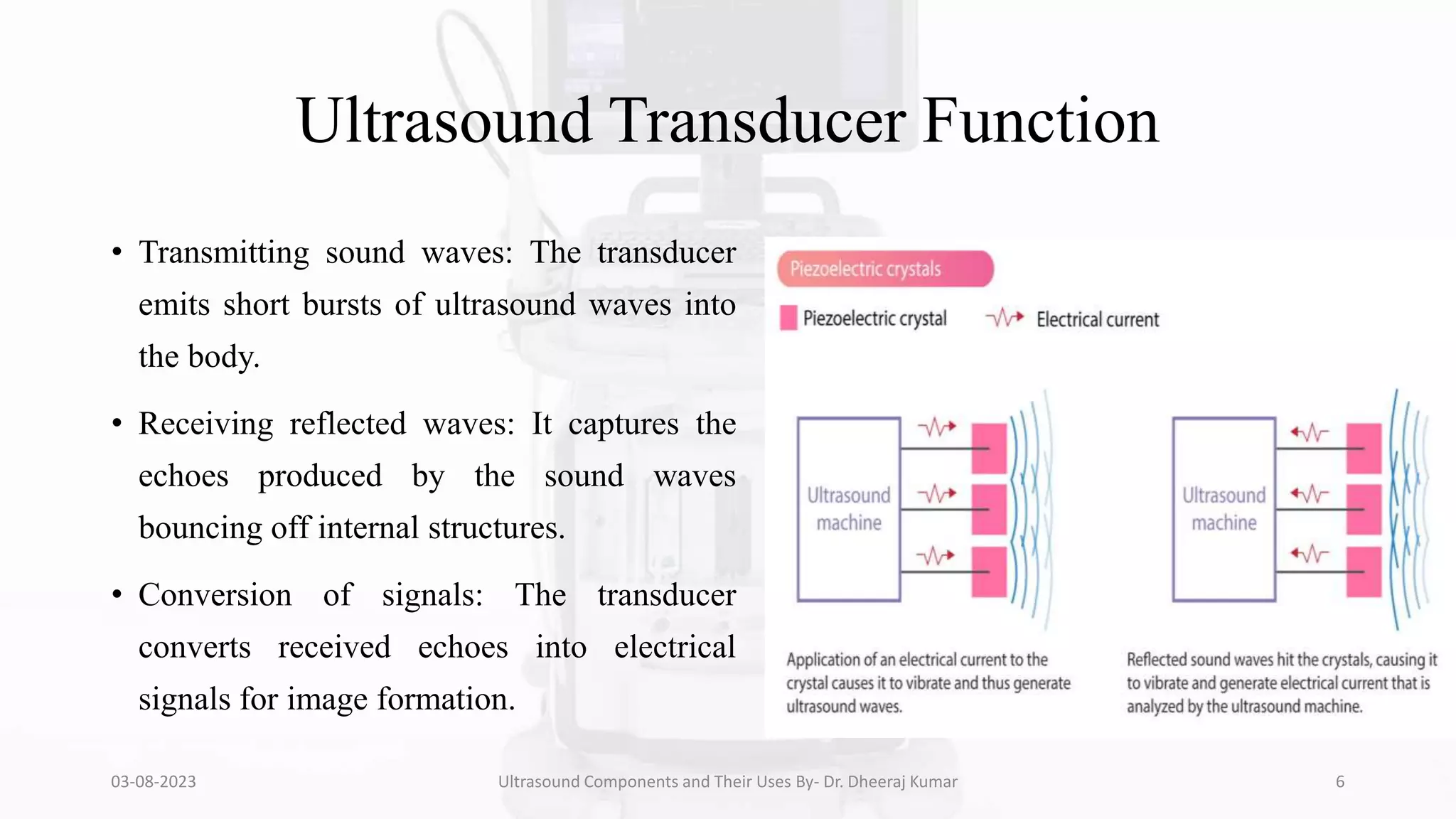
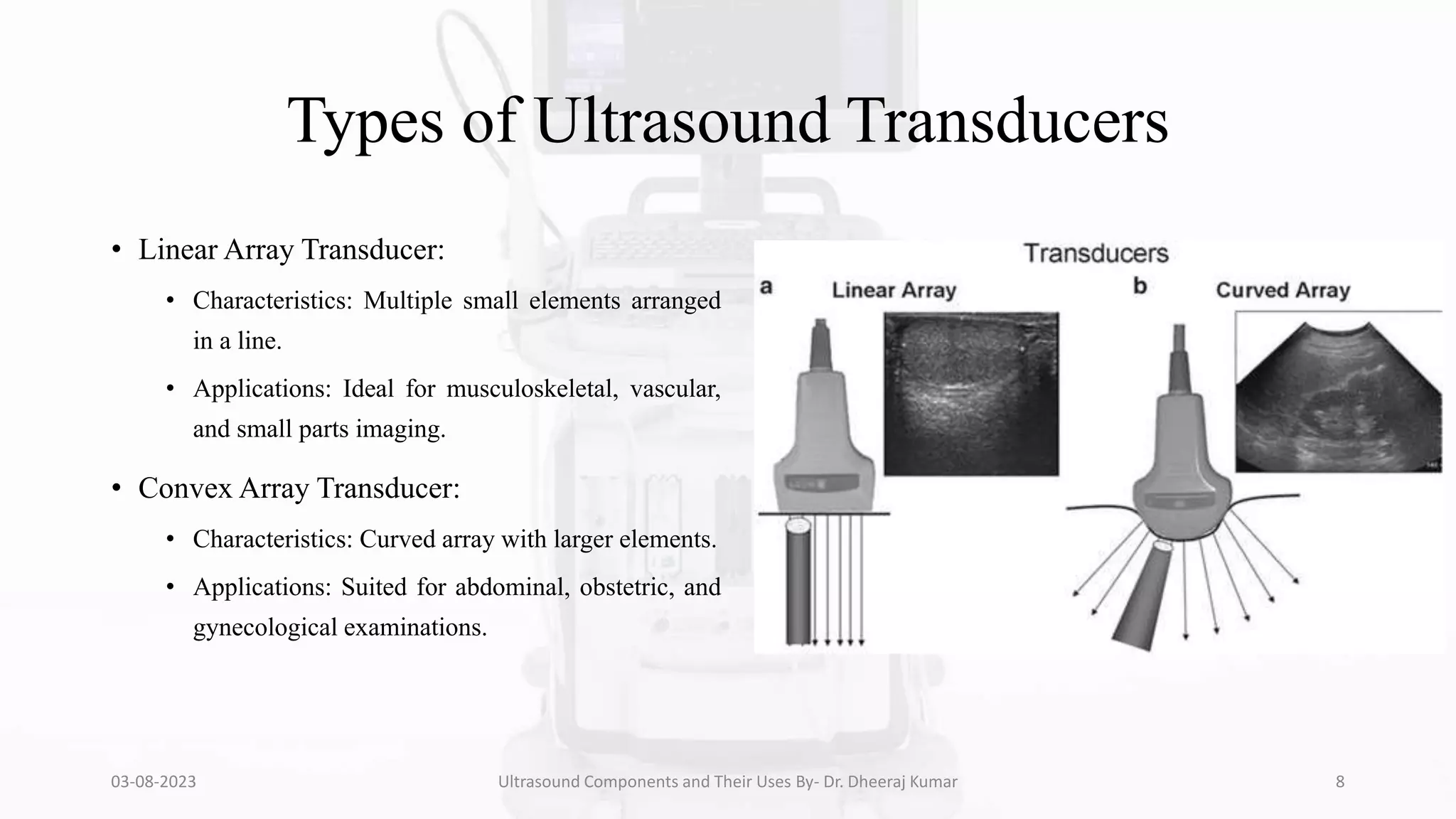
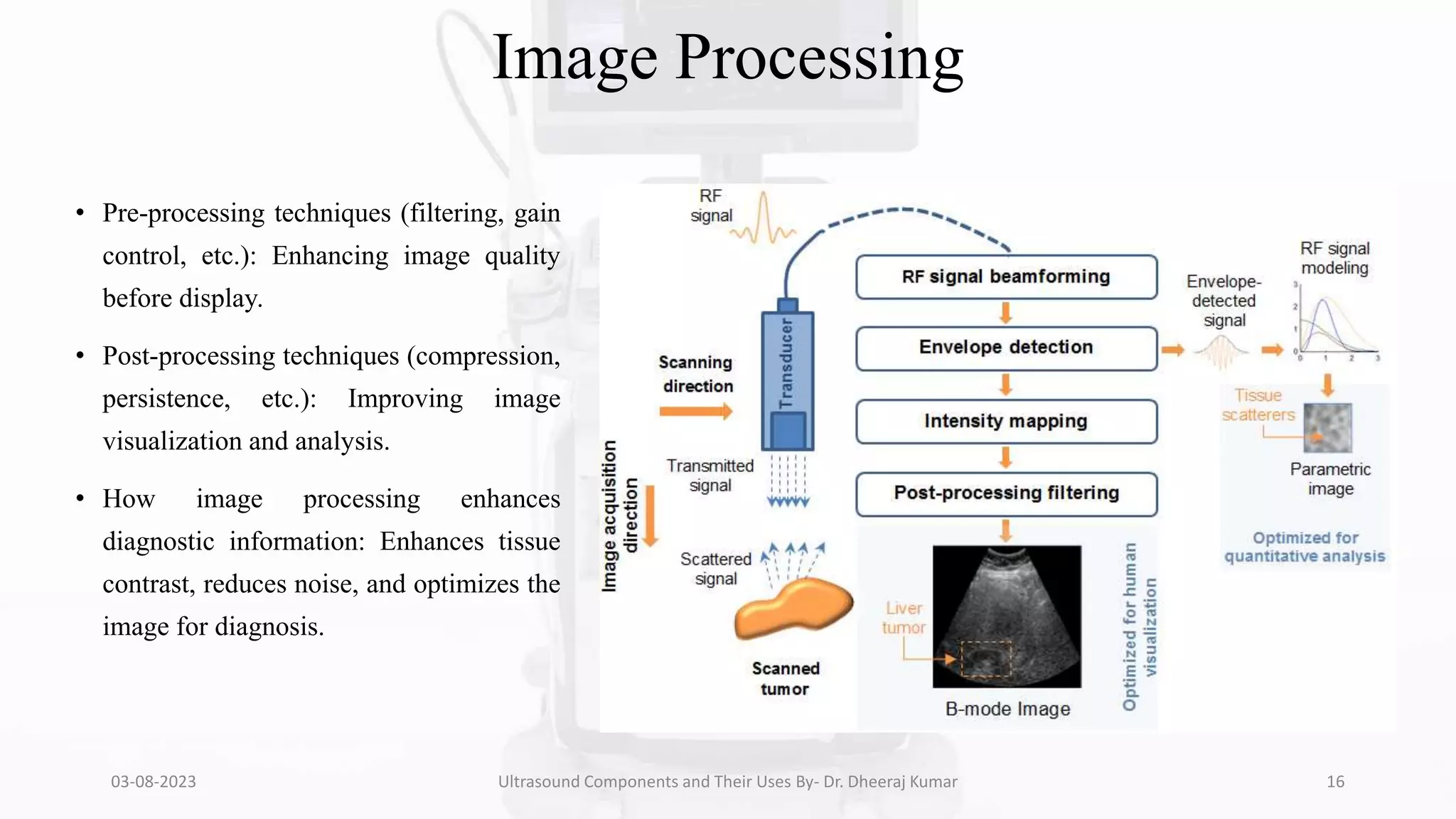
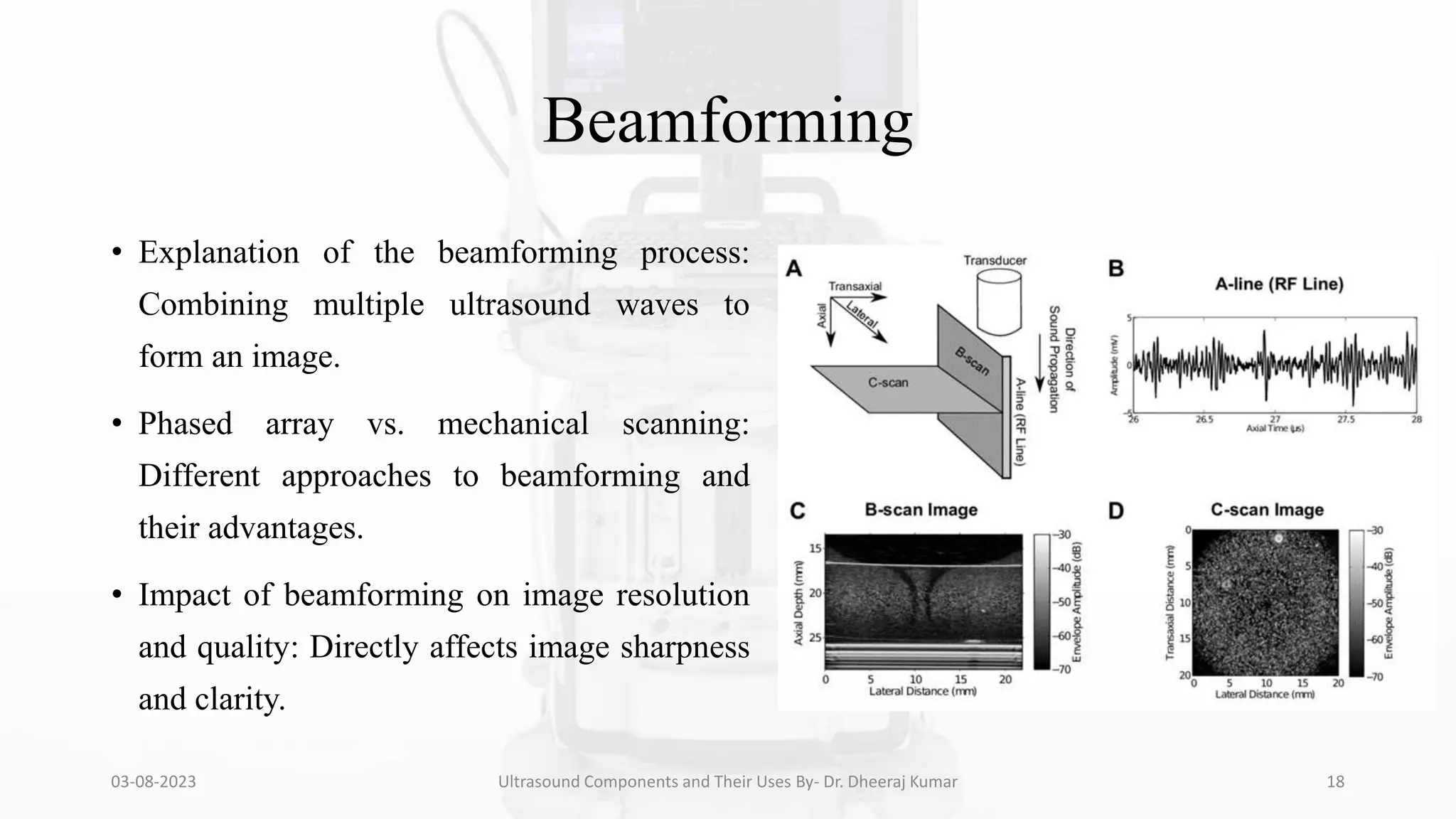
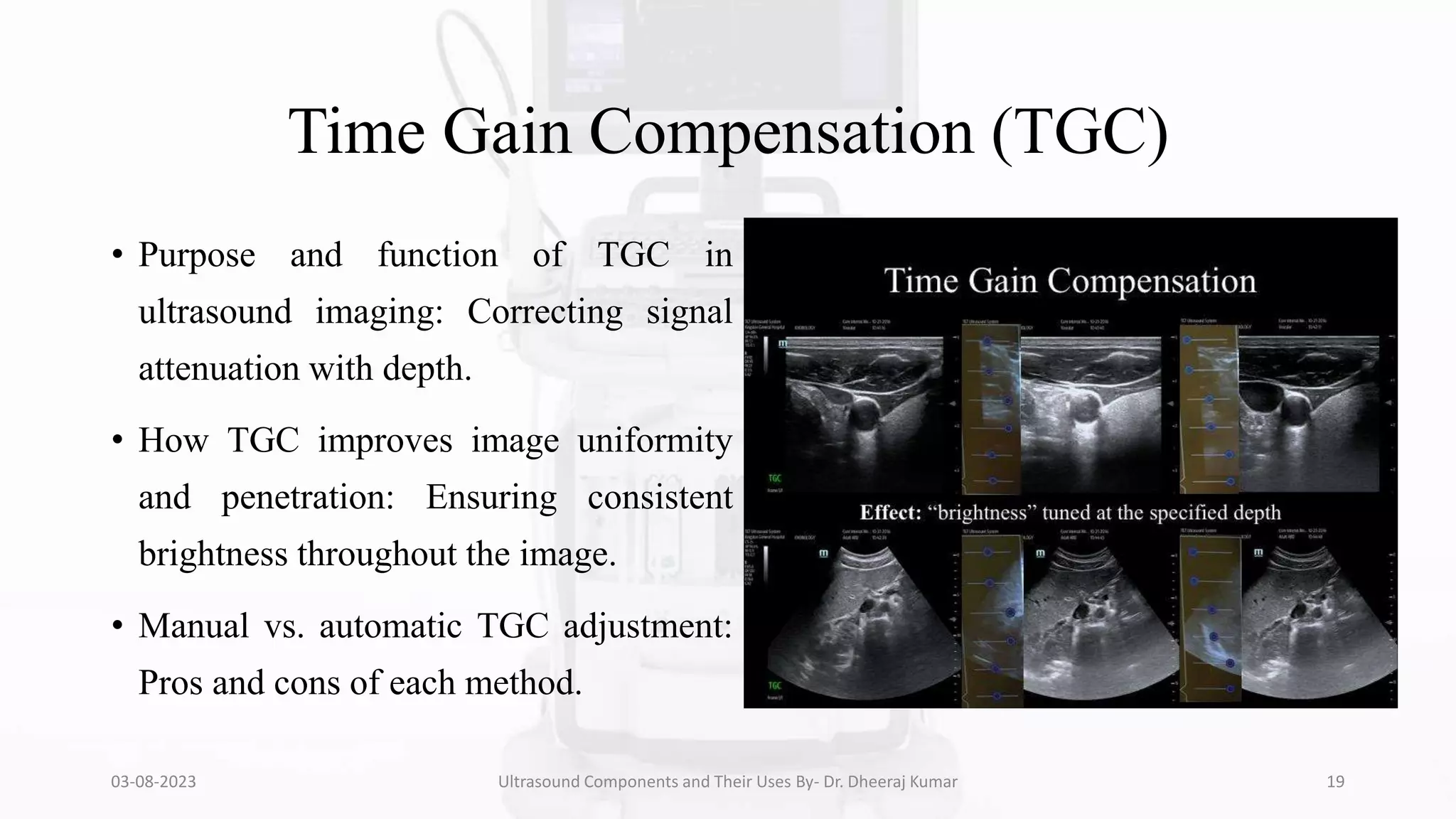
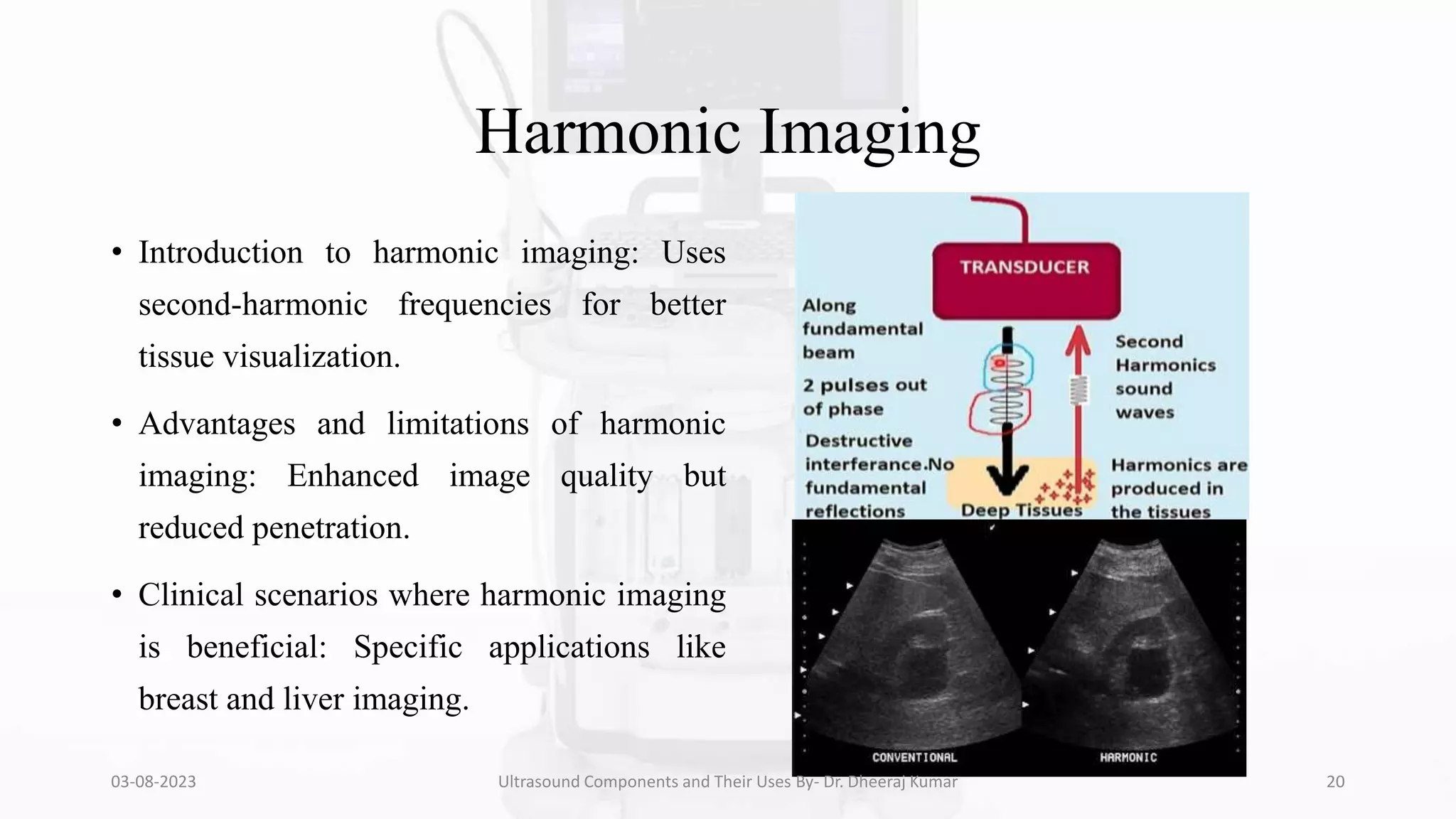
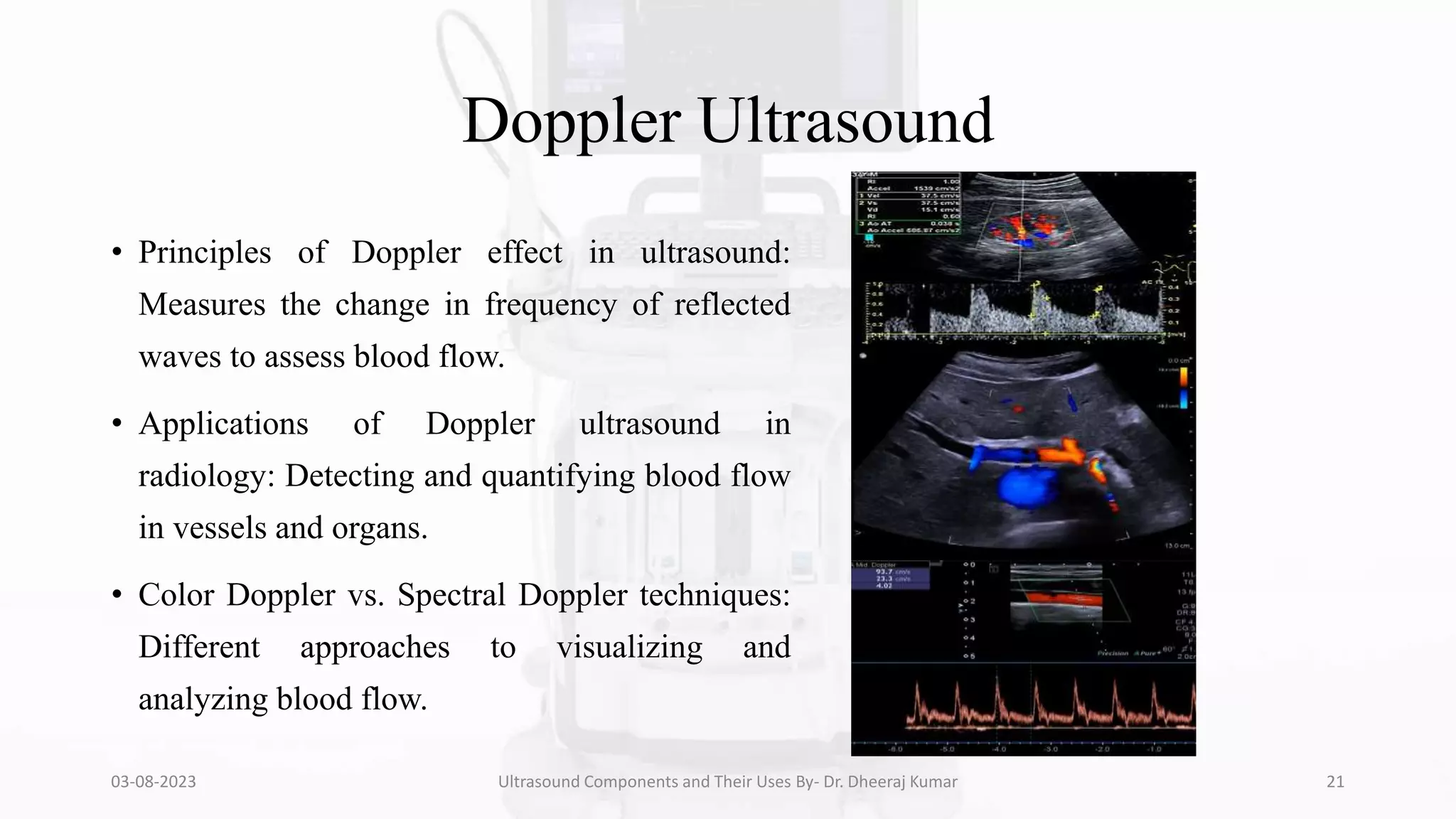
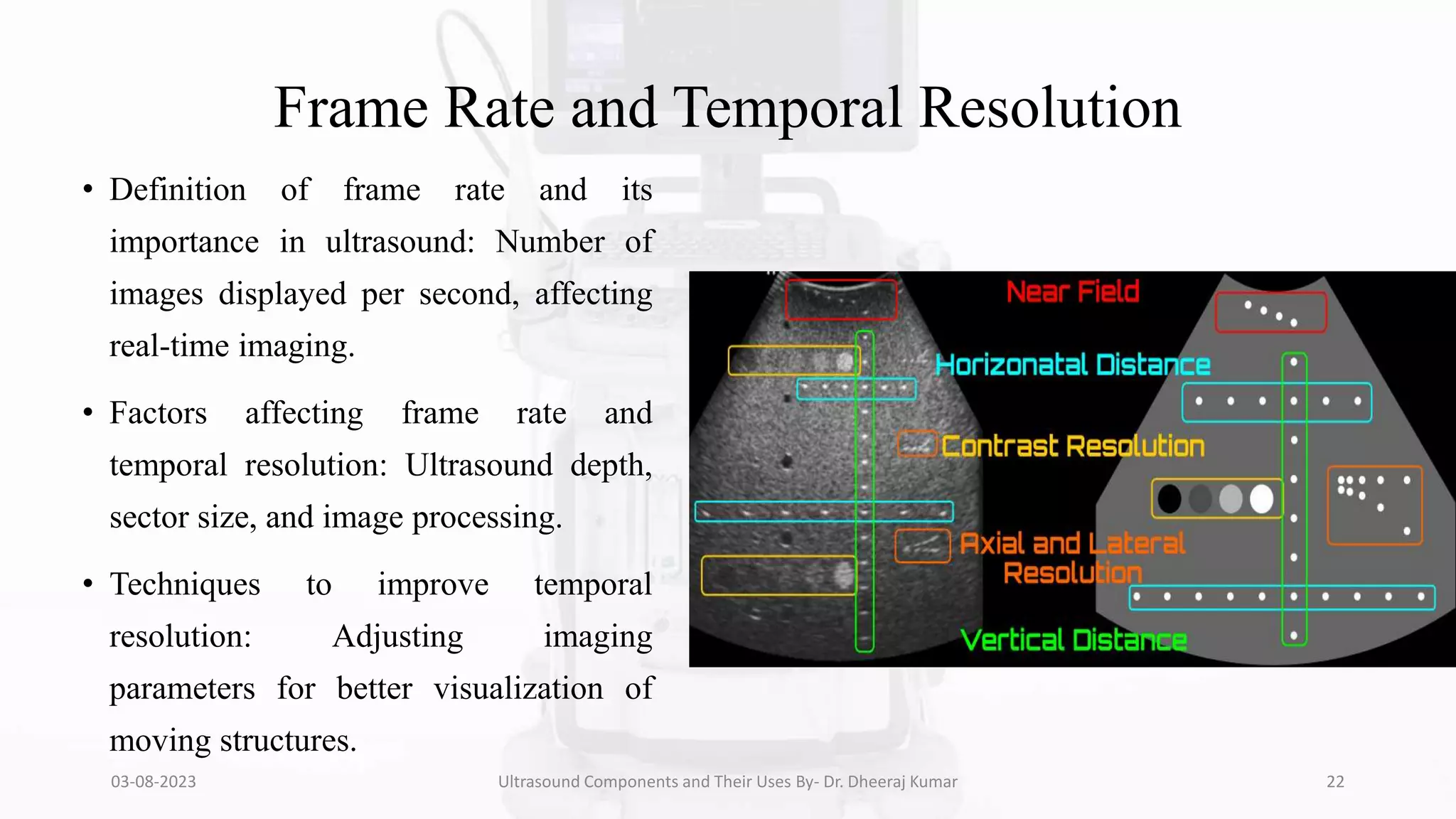
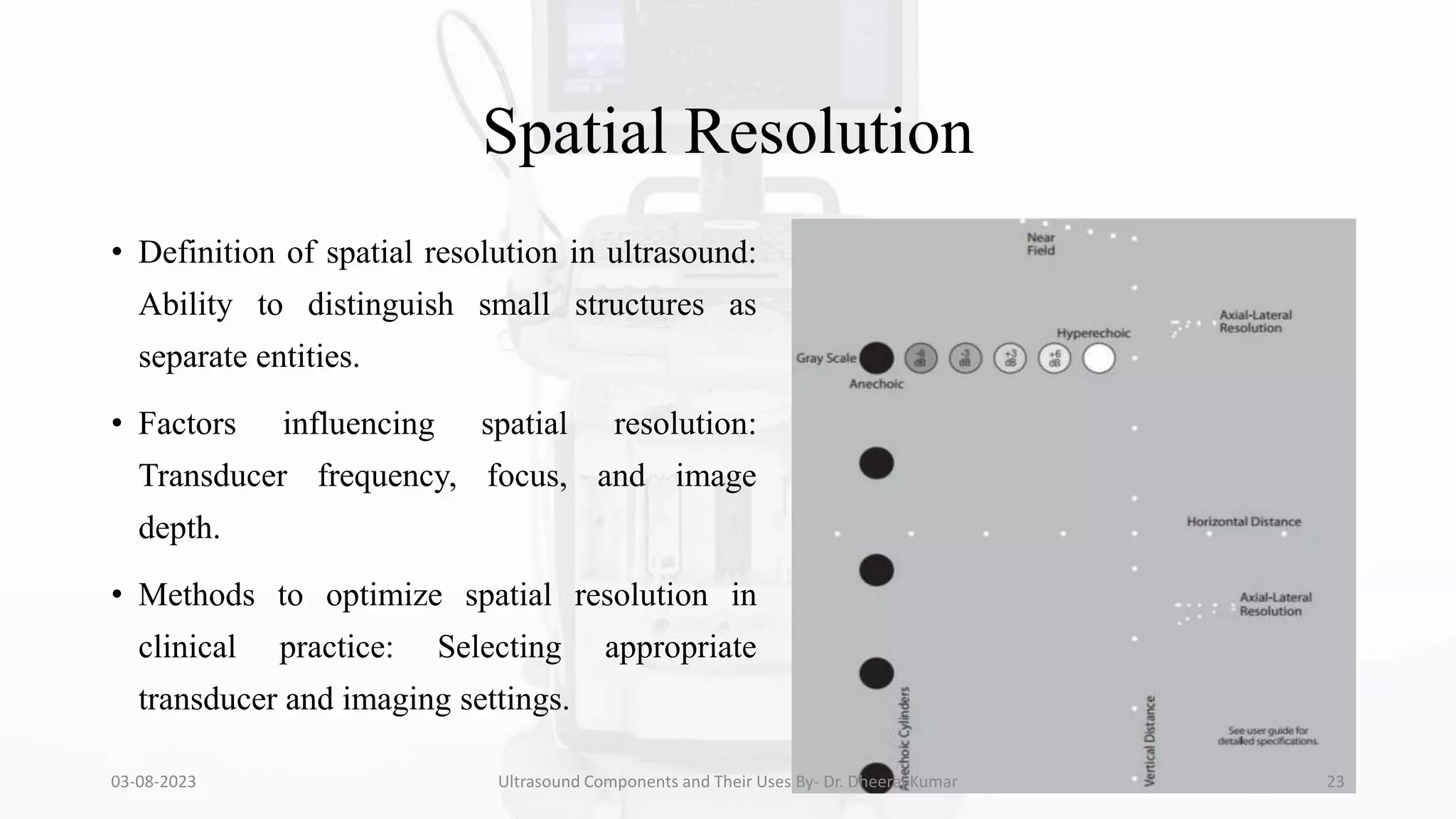
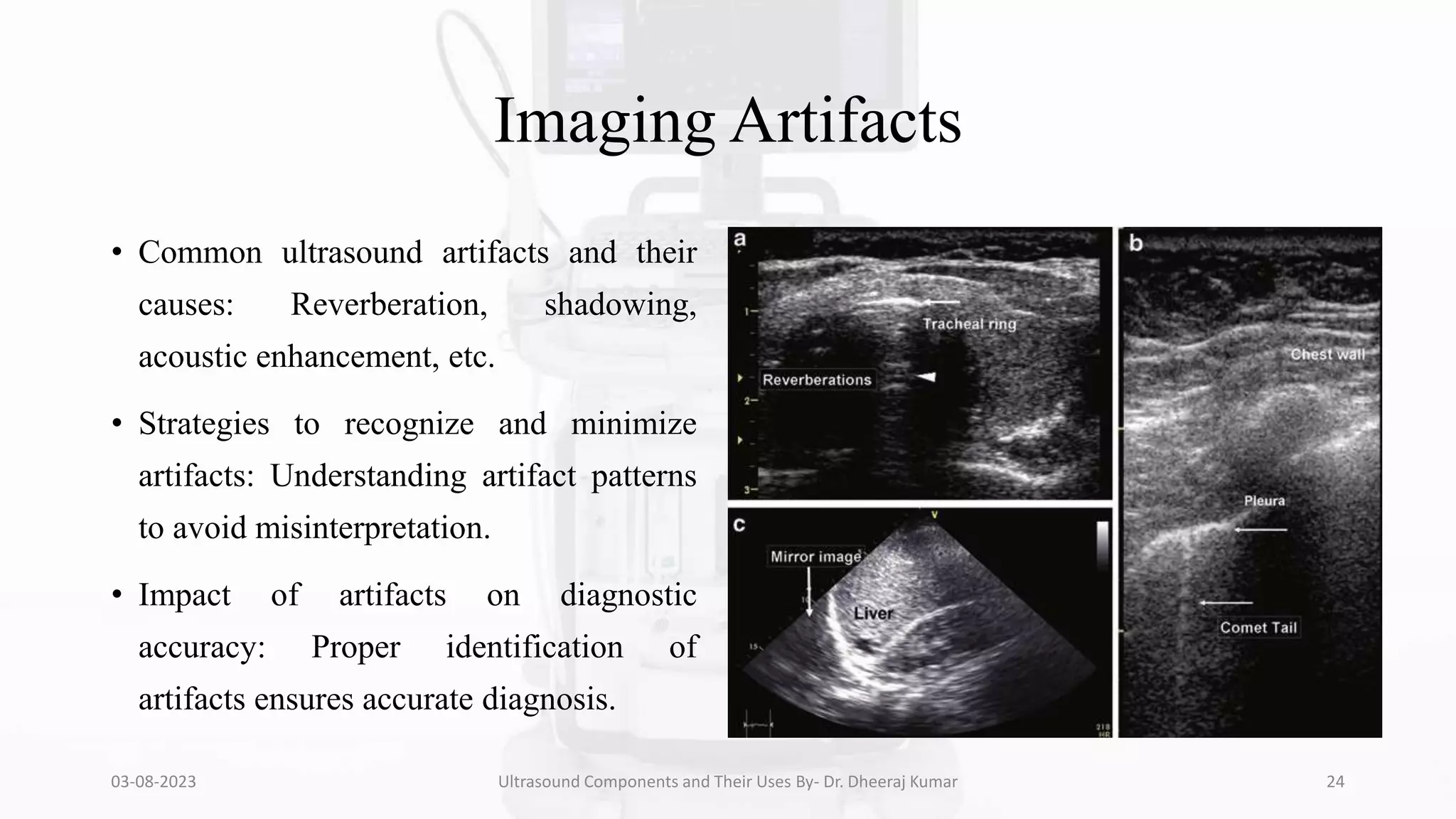
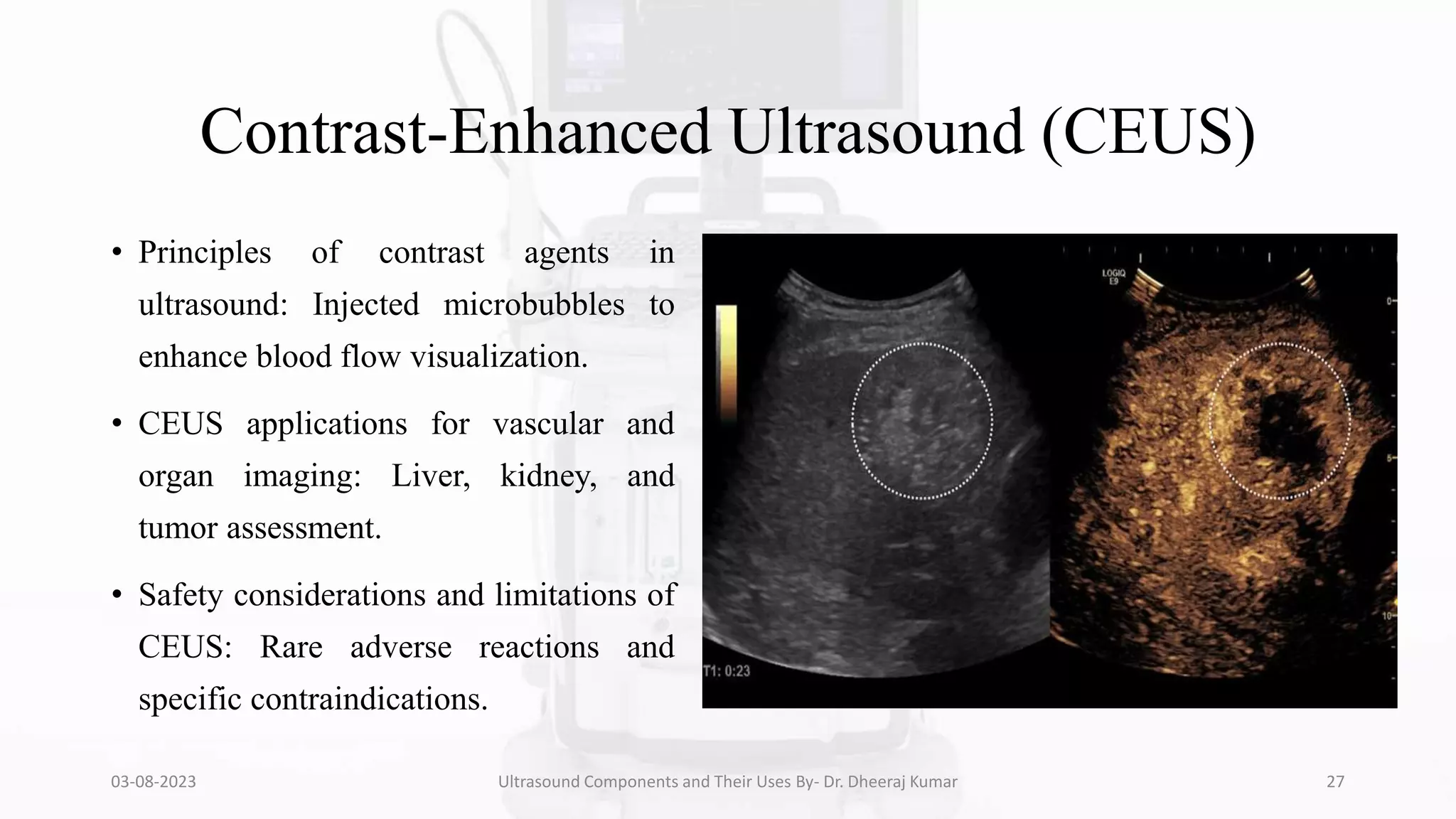
The document is a comprehensive presentation on ultrasound components and their applications in medical imaging, delivered by Dr. Dheeraj Kumar Mrit. It covers the definition of ultrasound, its importance in diagnosis, various types of transducers, and technological advancements, along with details on image processing techniques, safety considerations, and quality assurance. The presentation emphasizes the critical role of ultrasound technology in modern radiology and encourages further exploration and utilization in clinical practice.