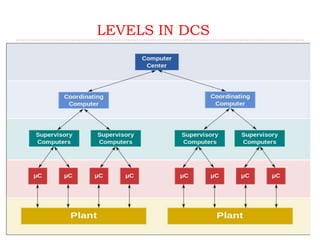
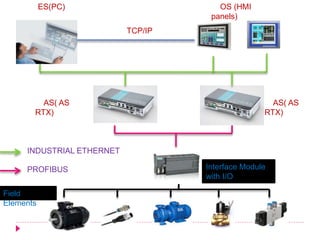
DCS is a distributed control system used to control large, complex industrial plants. It consists of three main stations - the engineering station which configures the system, the operator station which monitors the system, and automation stations which connect to field elements and control processes. DCS systems distribute control elements throughout a plant rather than centralizing them. This allows for greater flexibility and reliability. Common DCS systems include Siemens' Simatic PCS7, which uses programming languages like CFC and SFC and integrates process control capabilities. DCS is primarily used in large industries like chemical plants, oil refineries, and power grids.