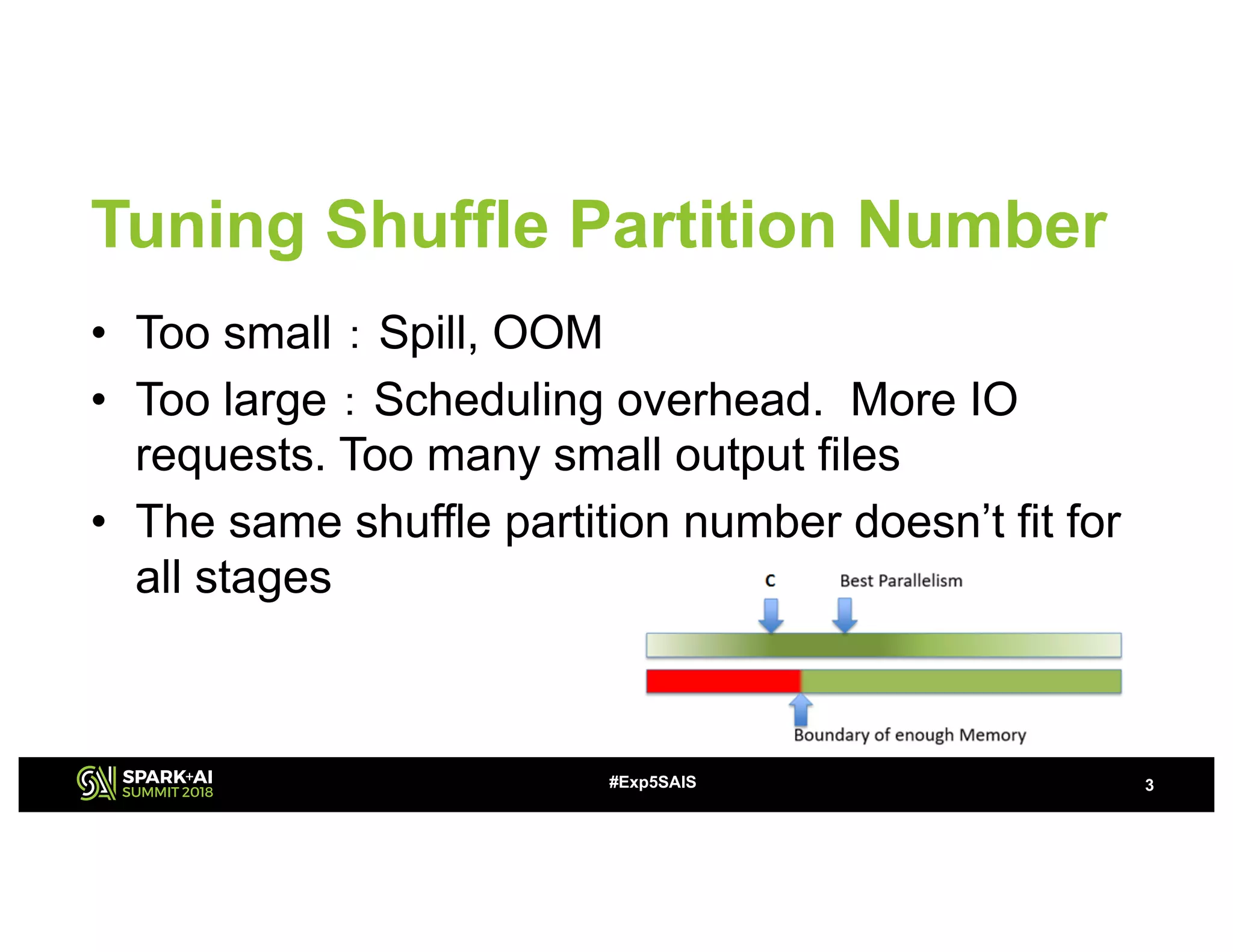
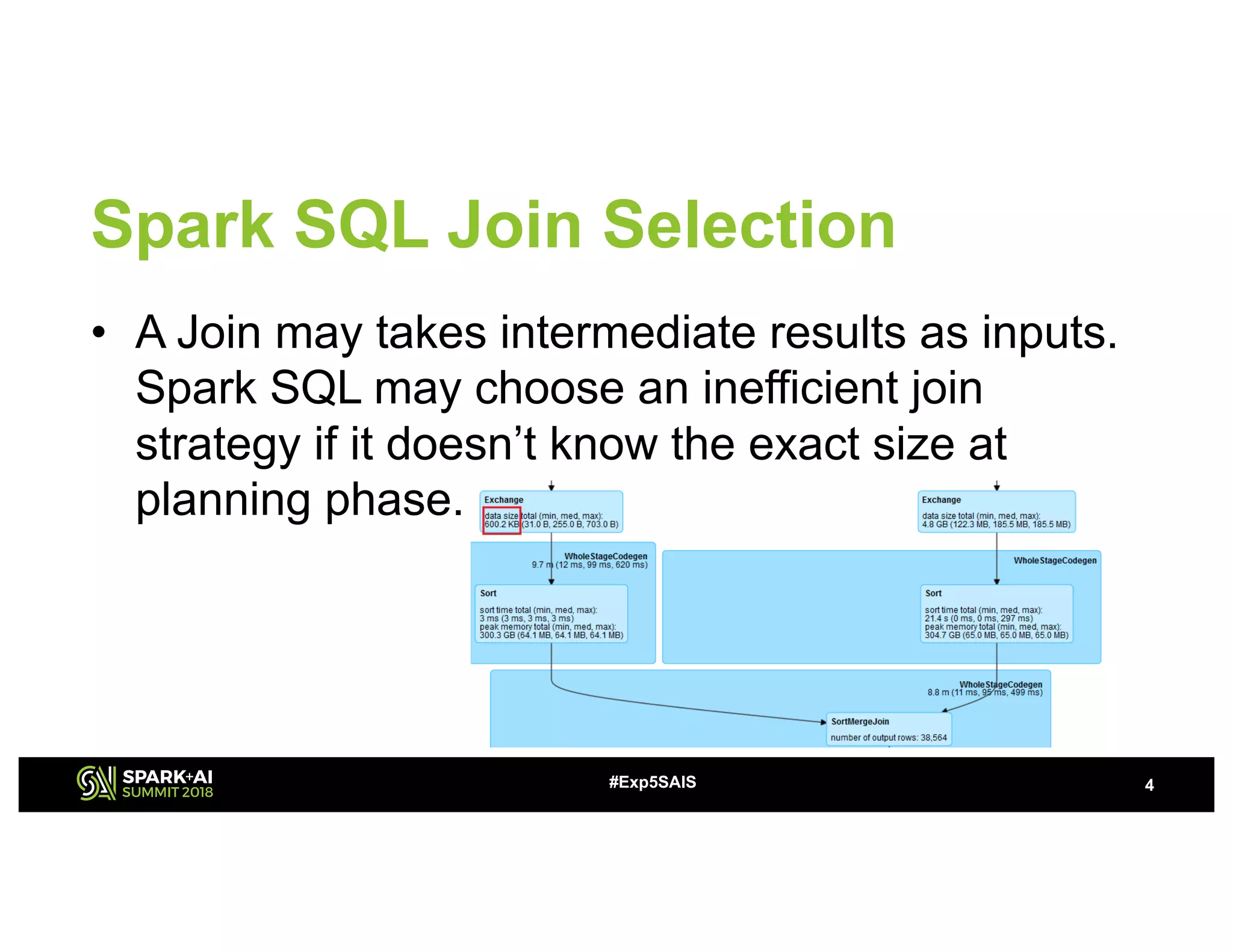
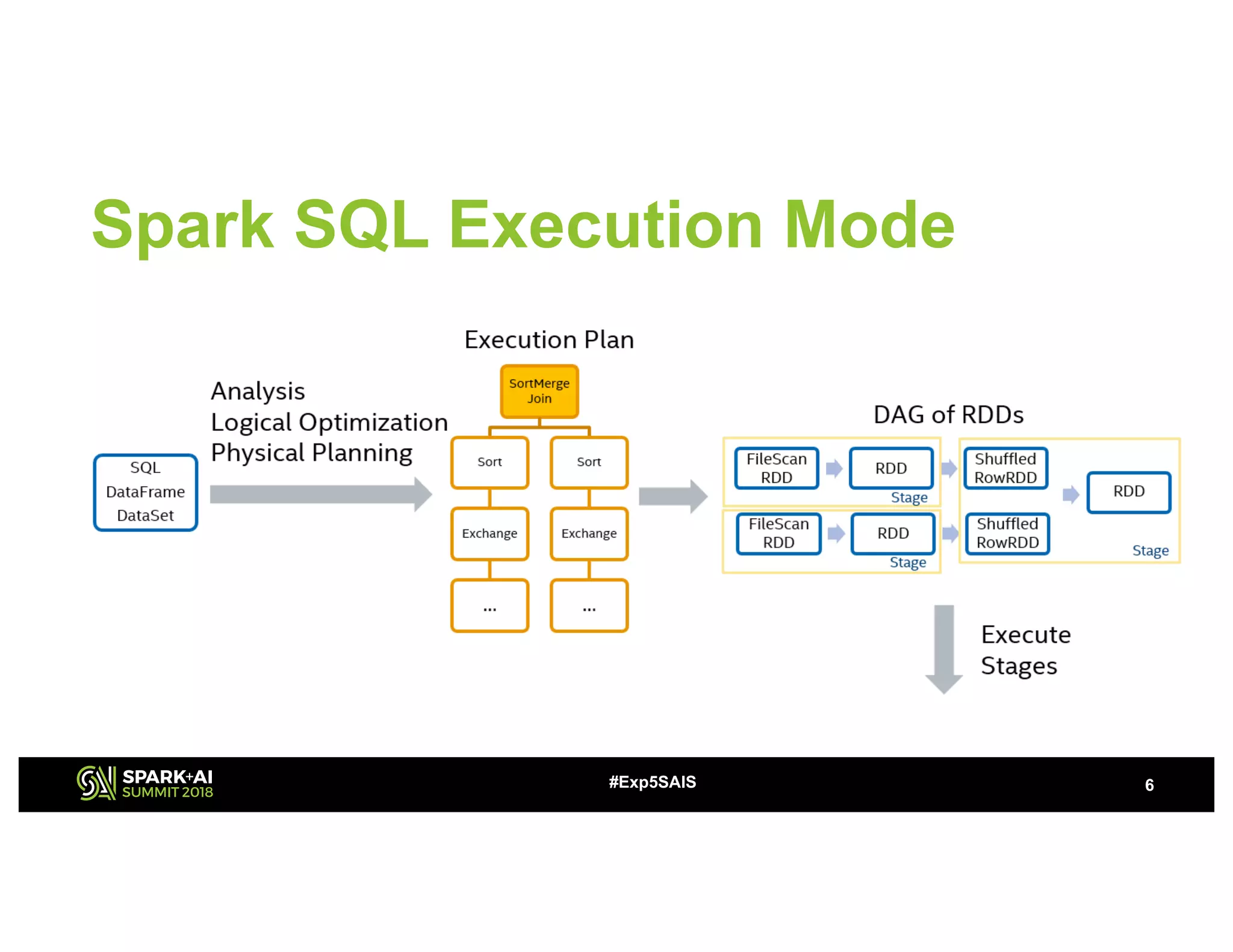
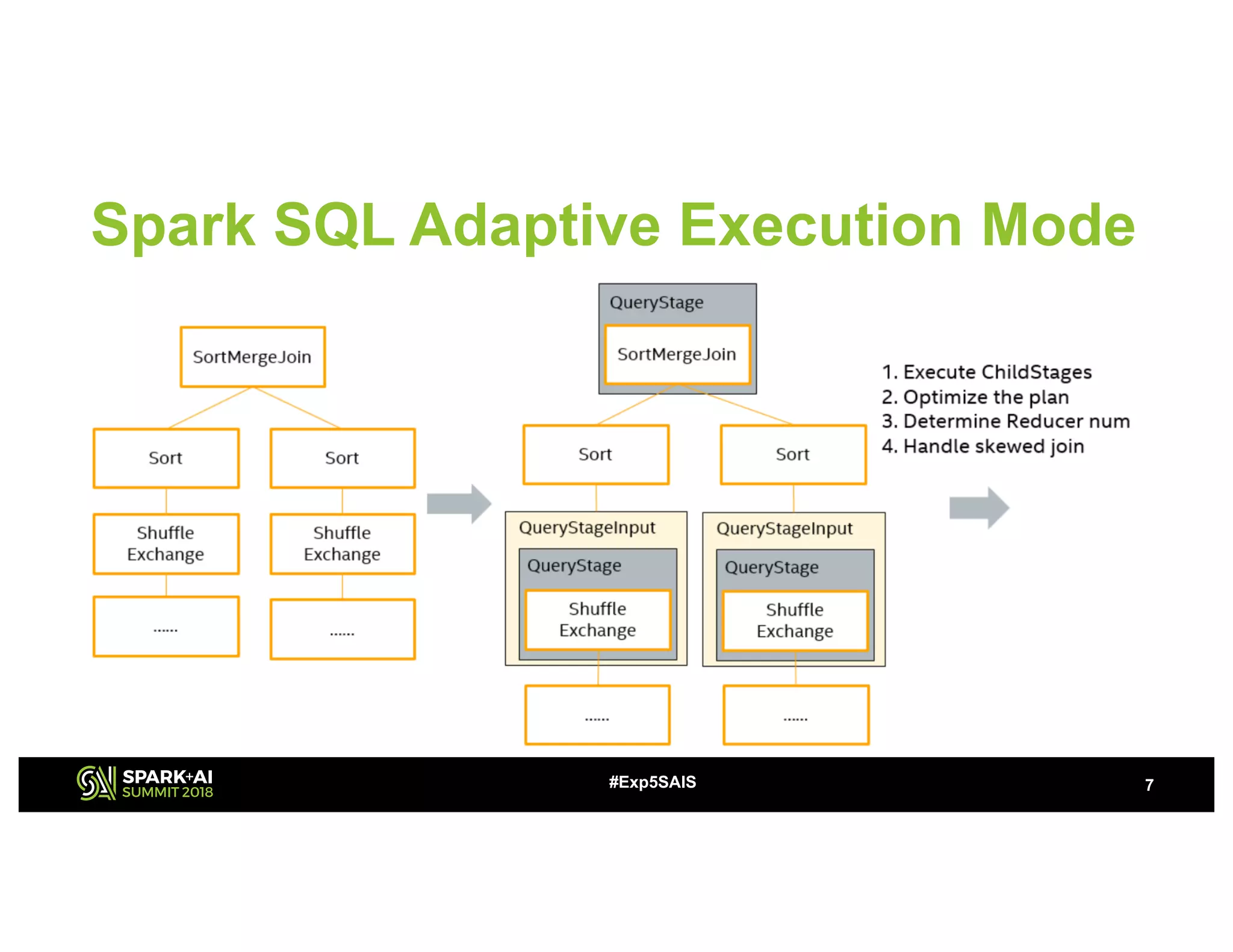
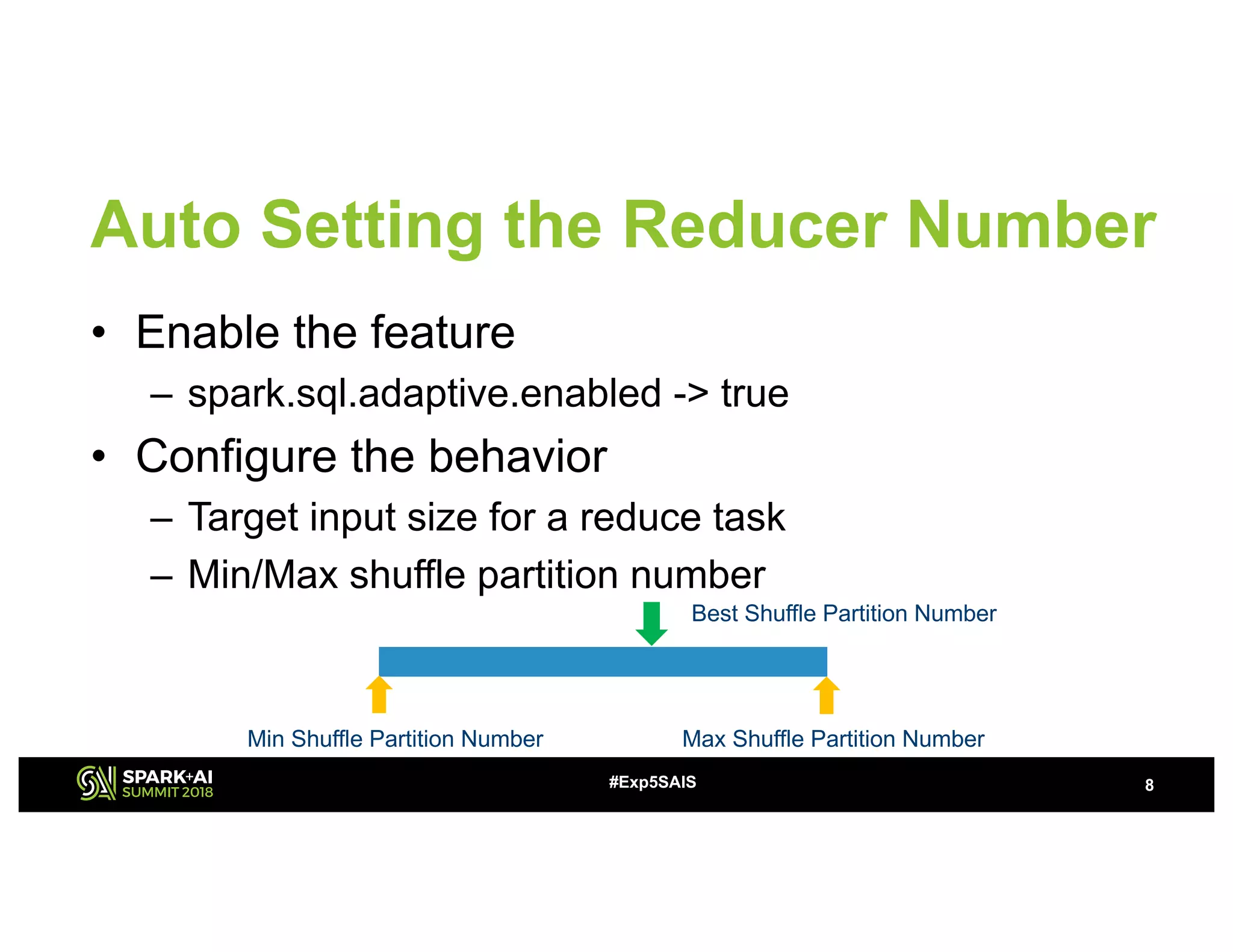
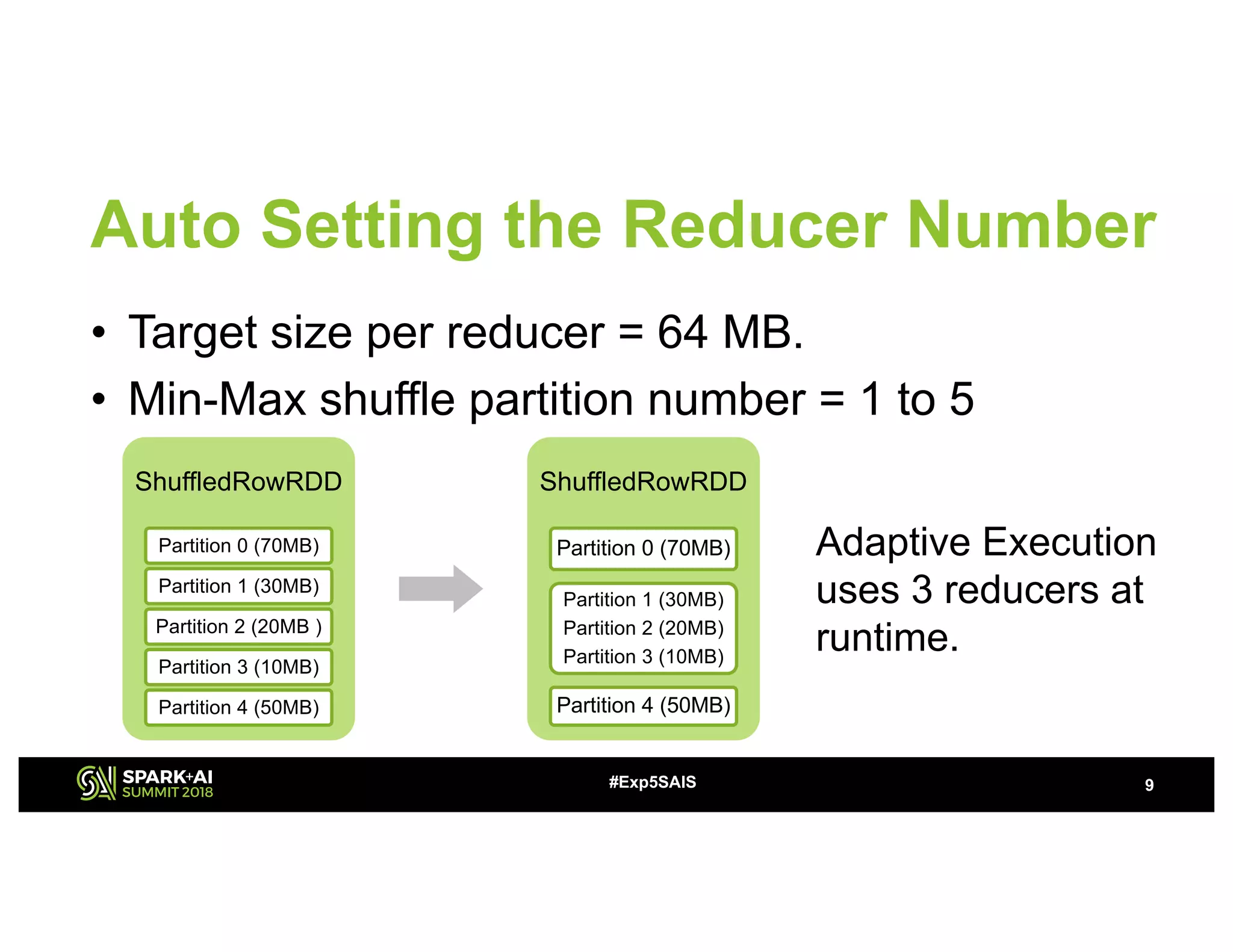
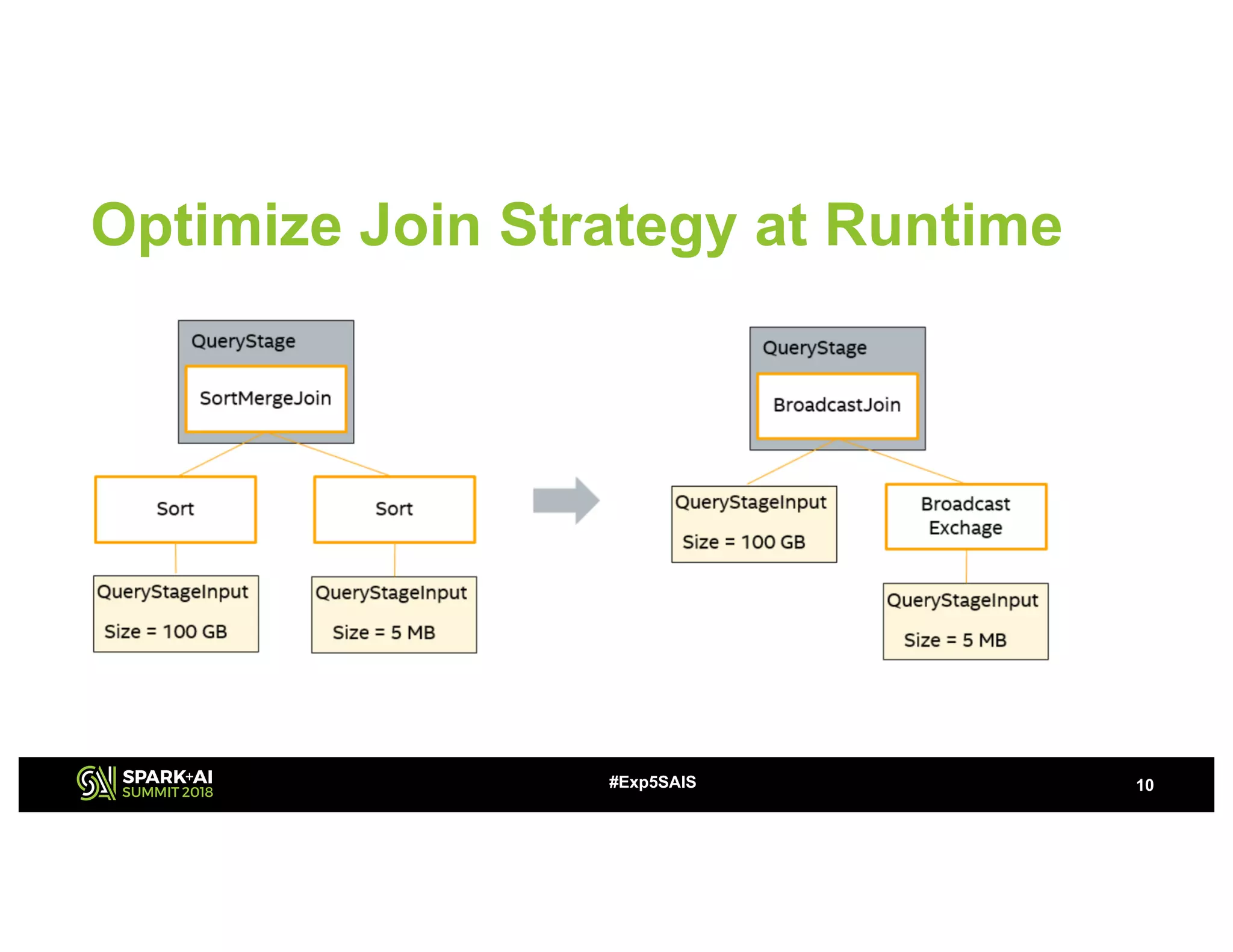
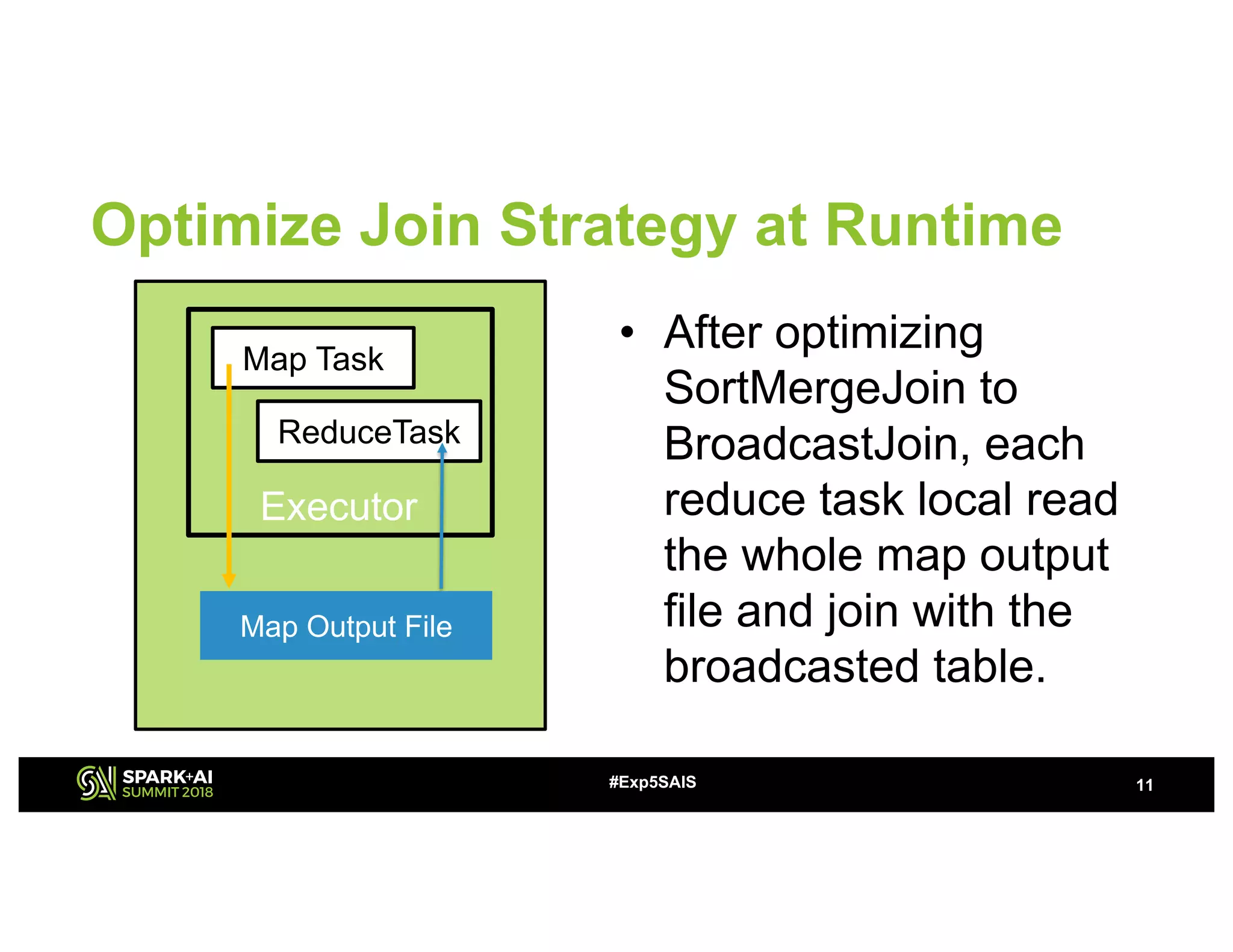
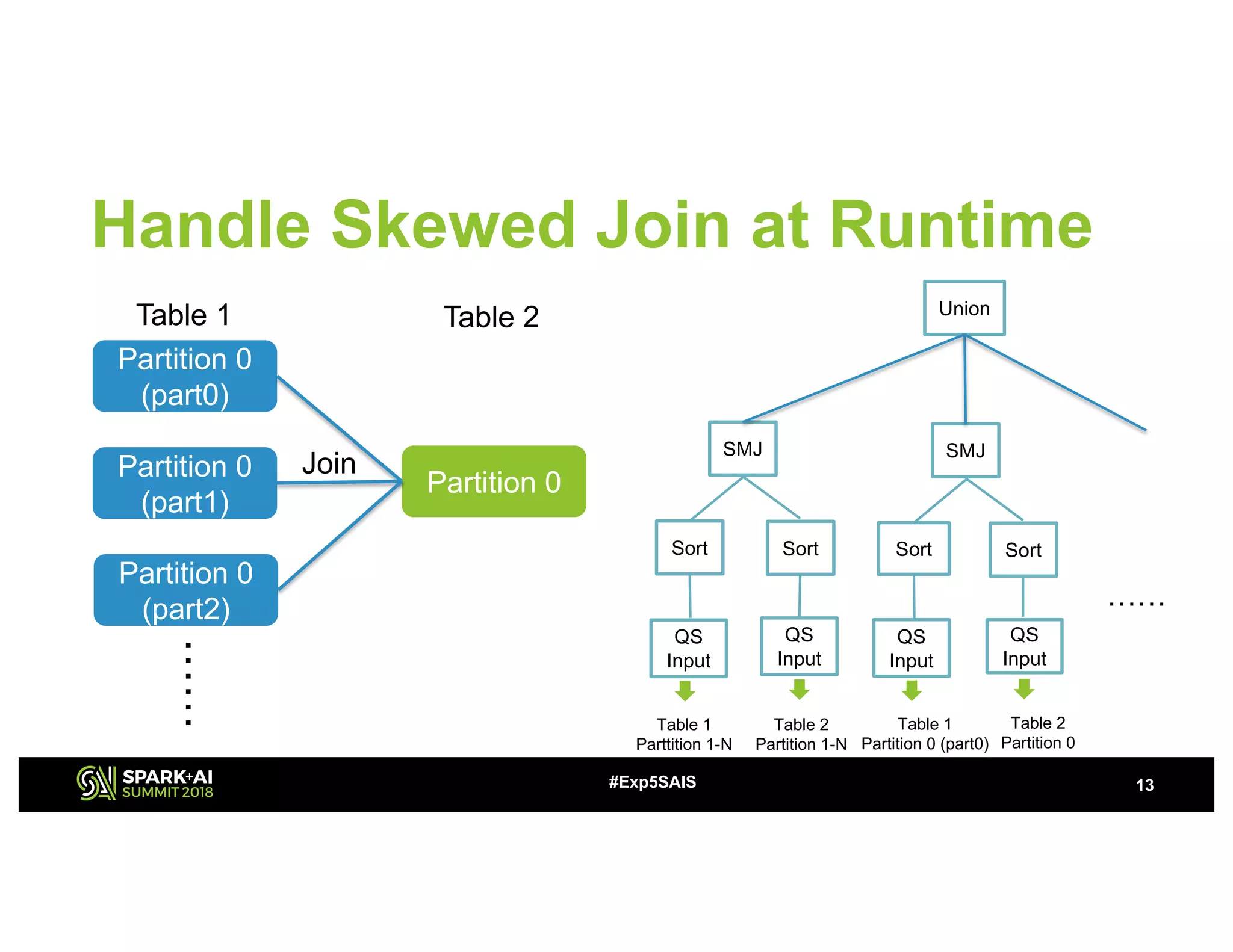
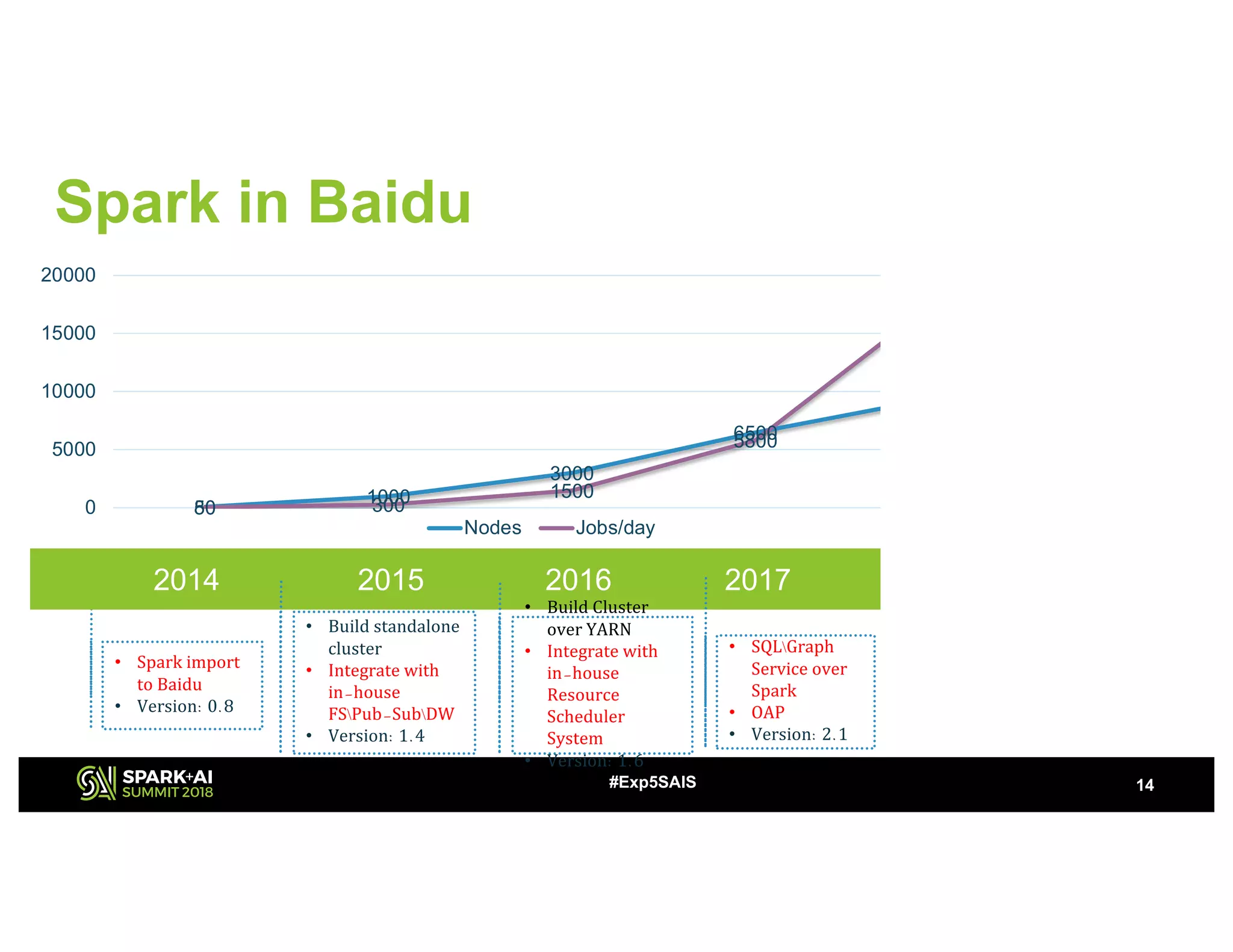
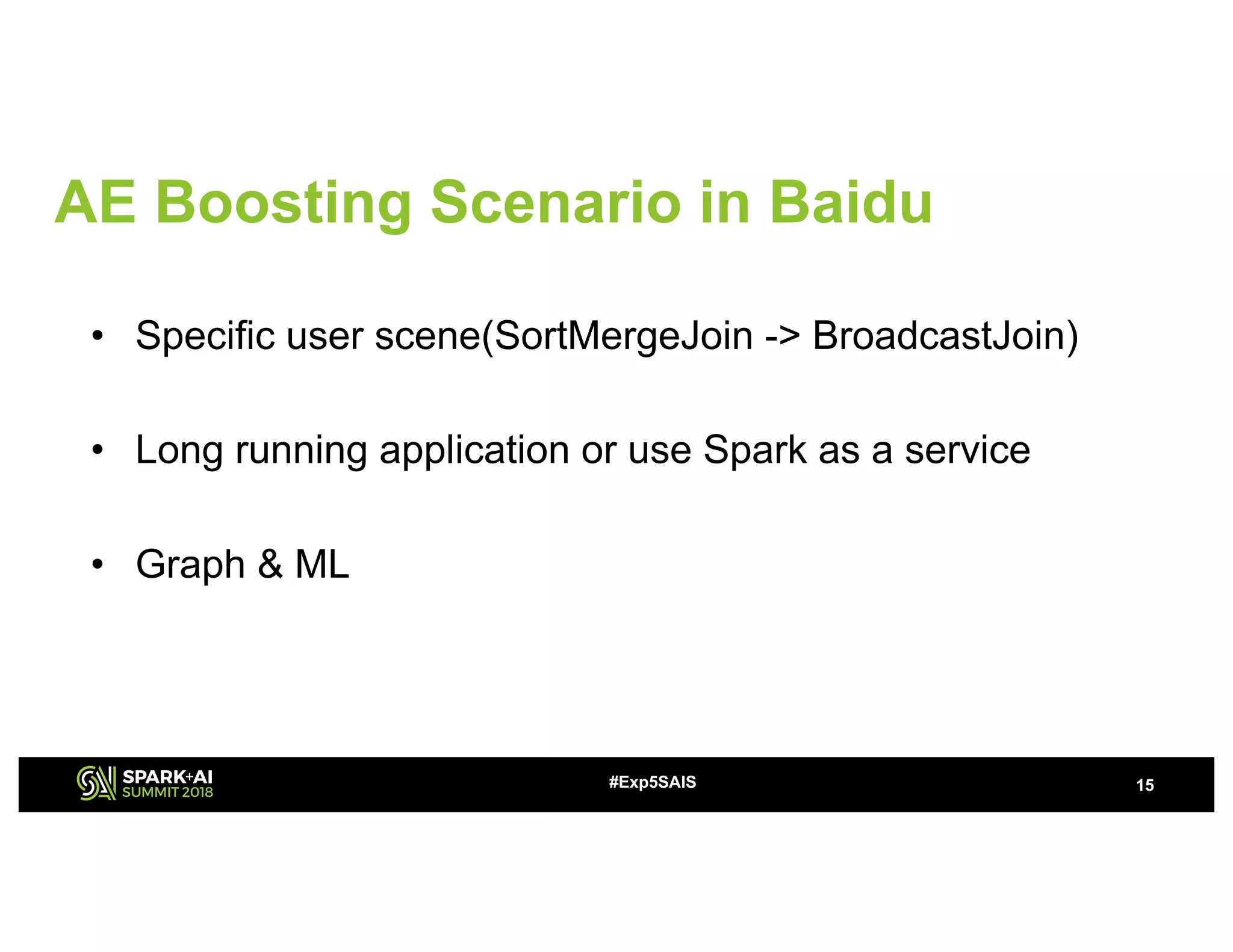
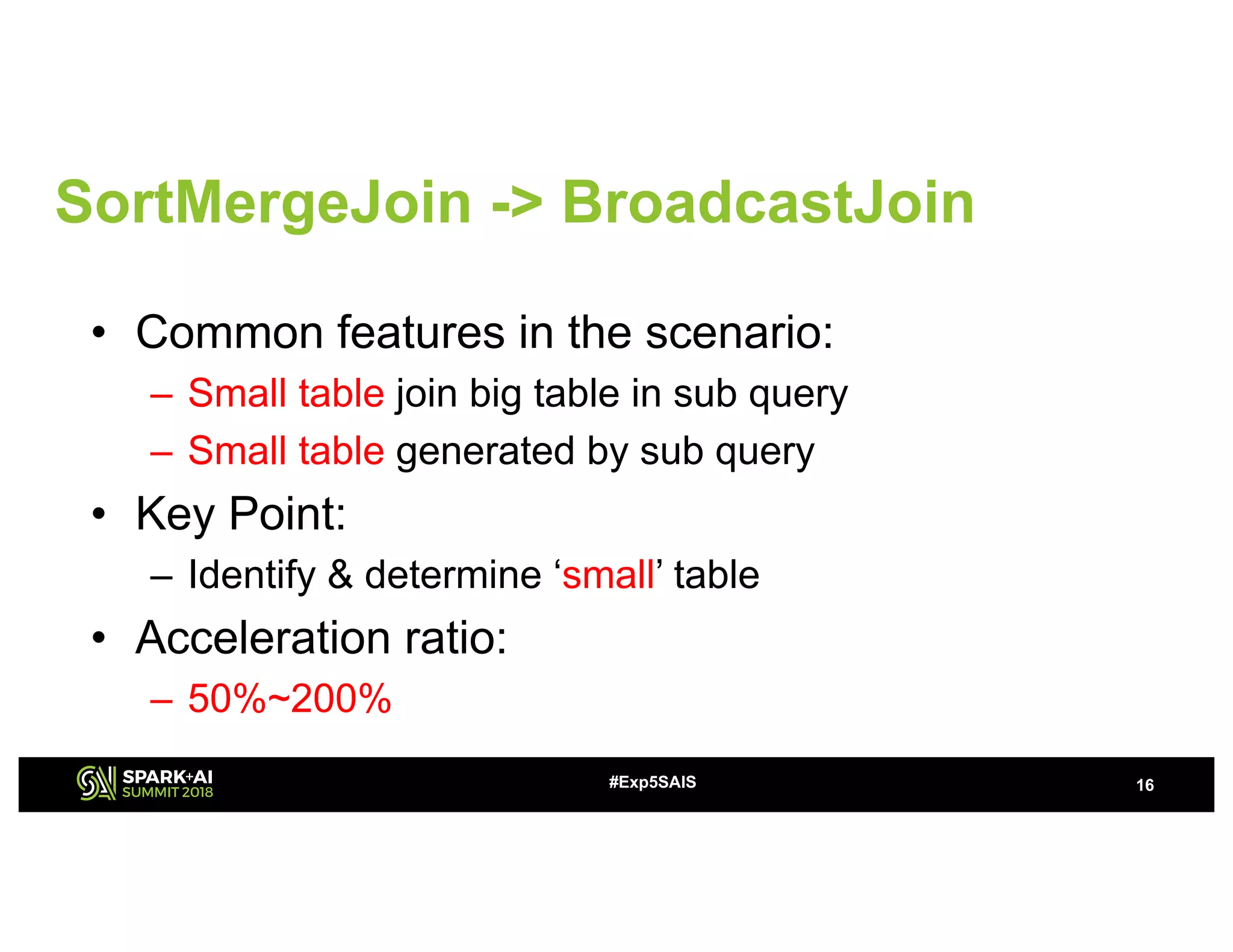
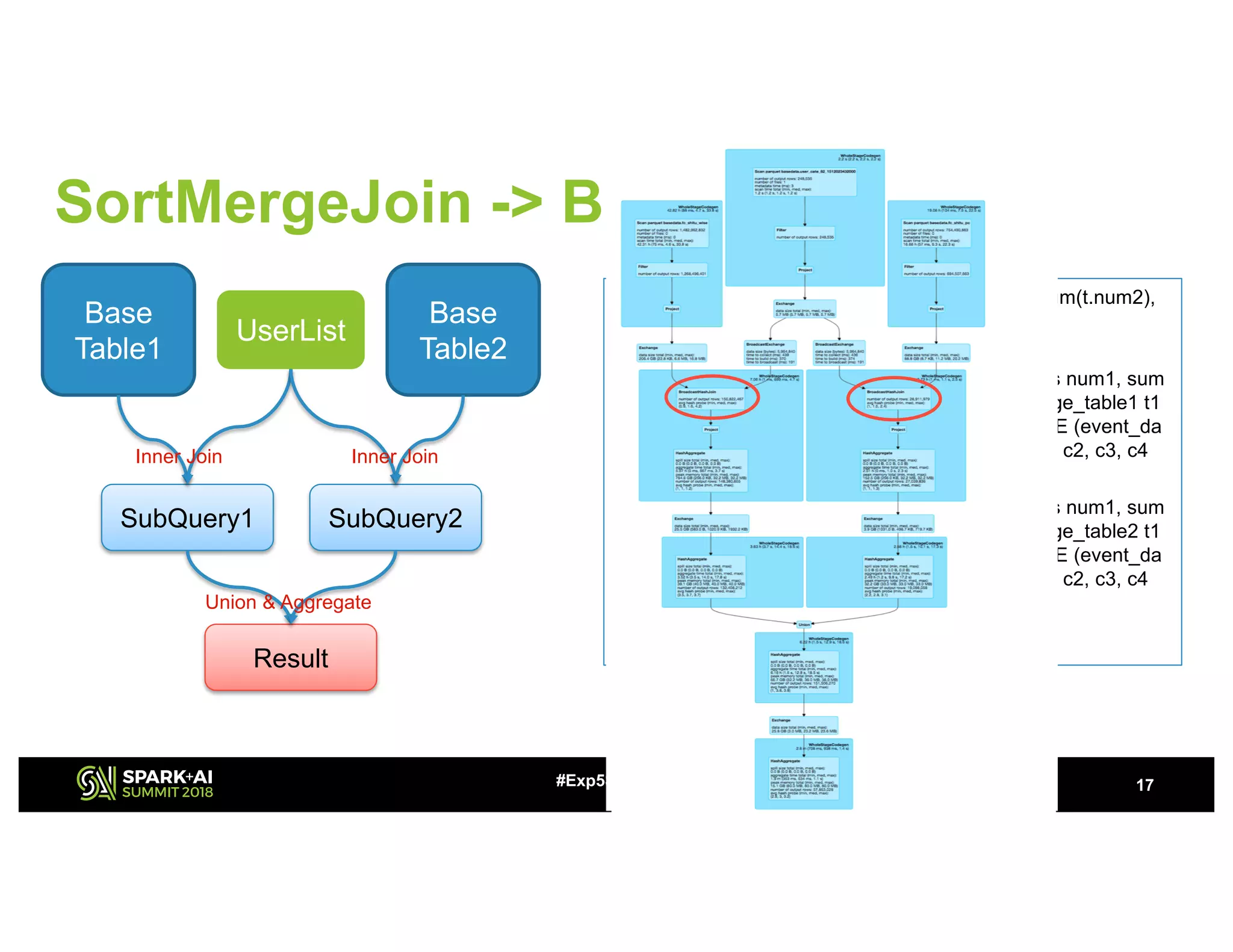
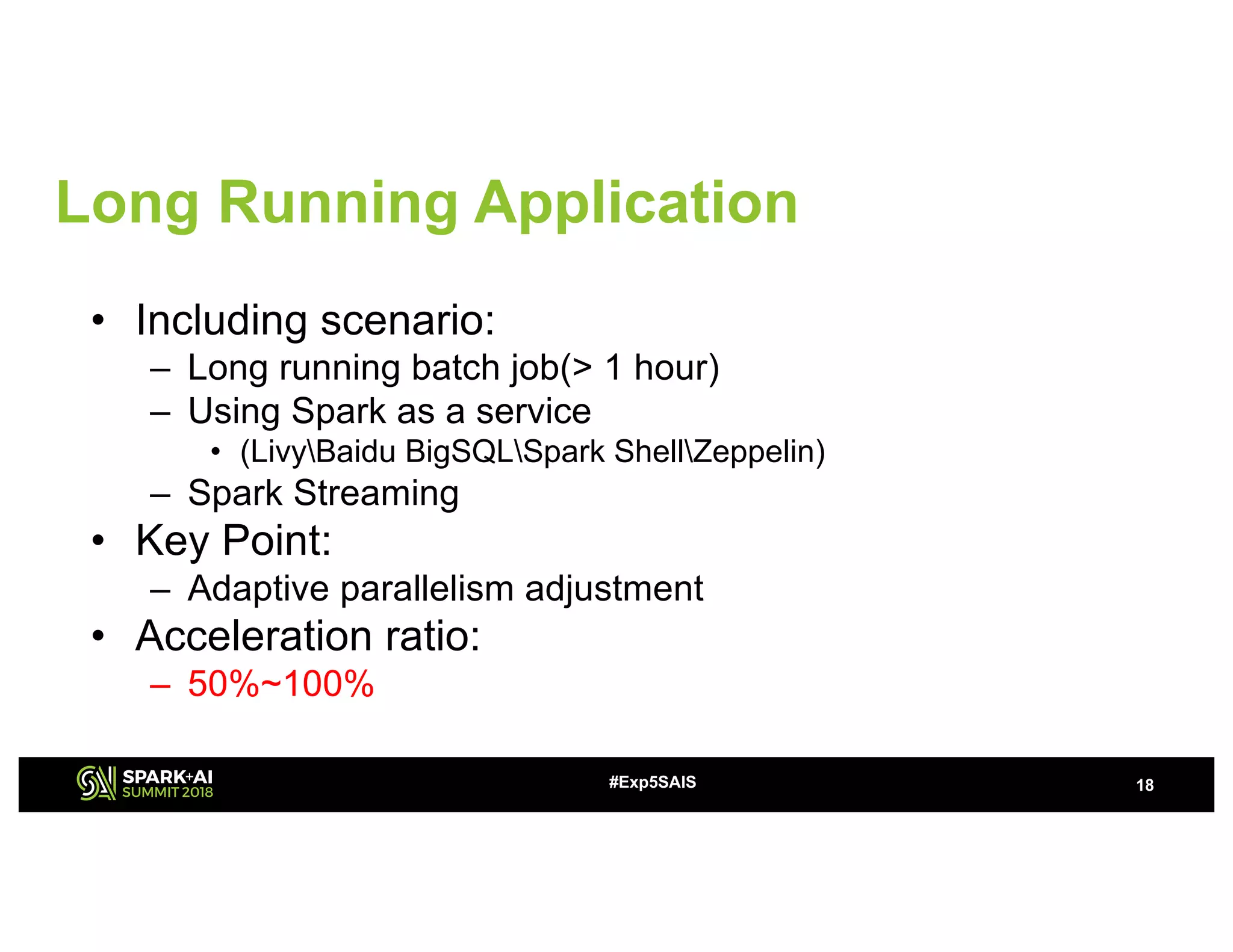
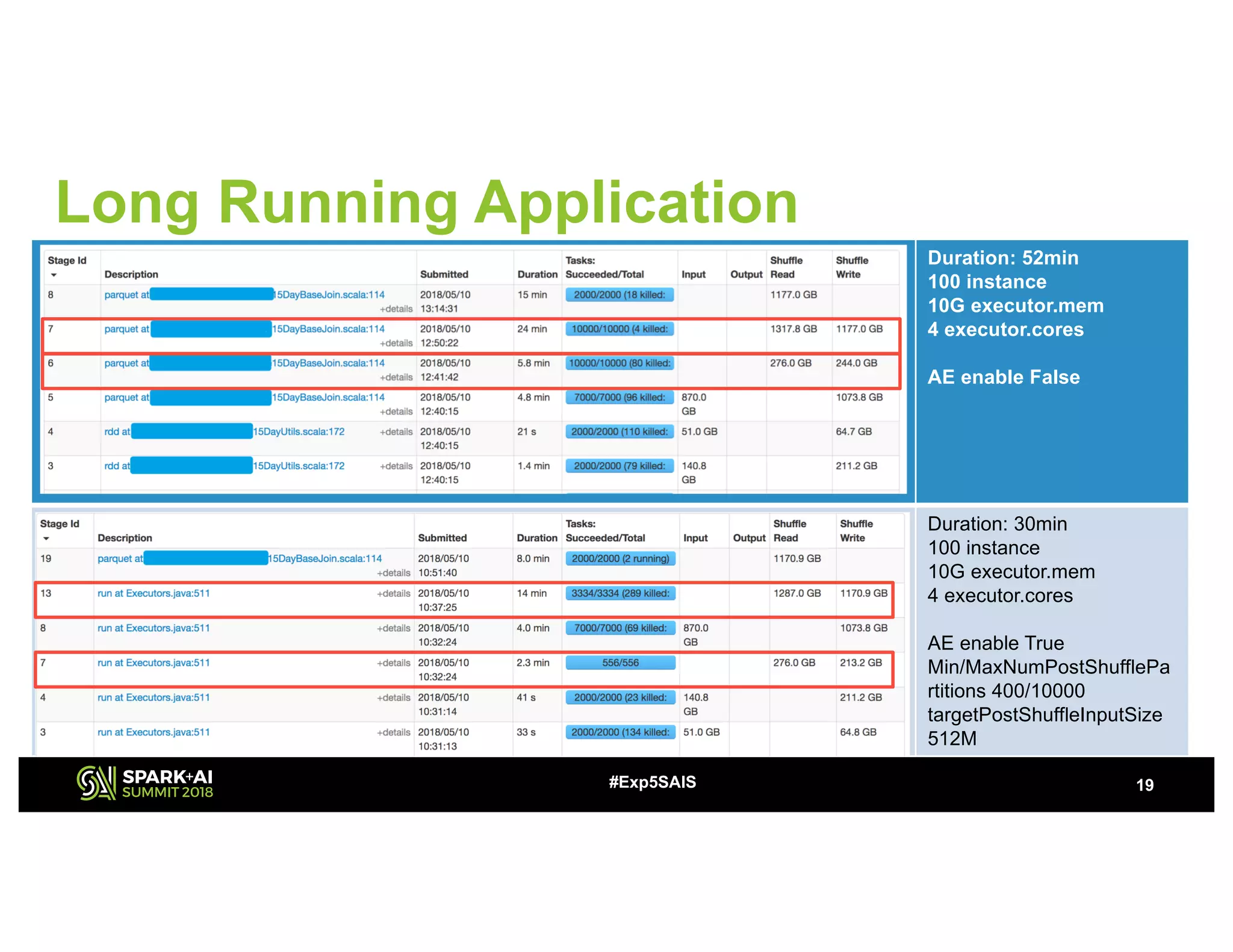
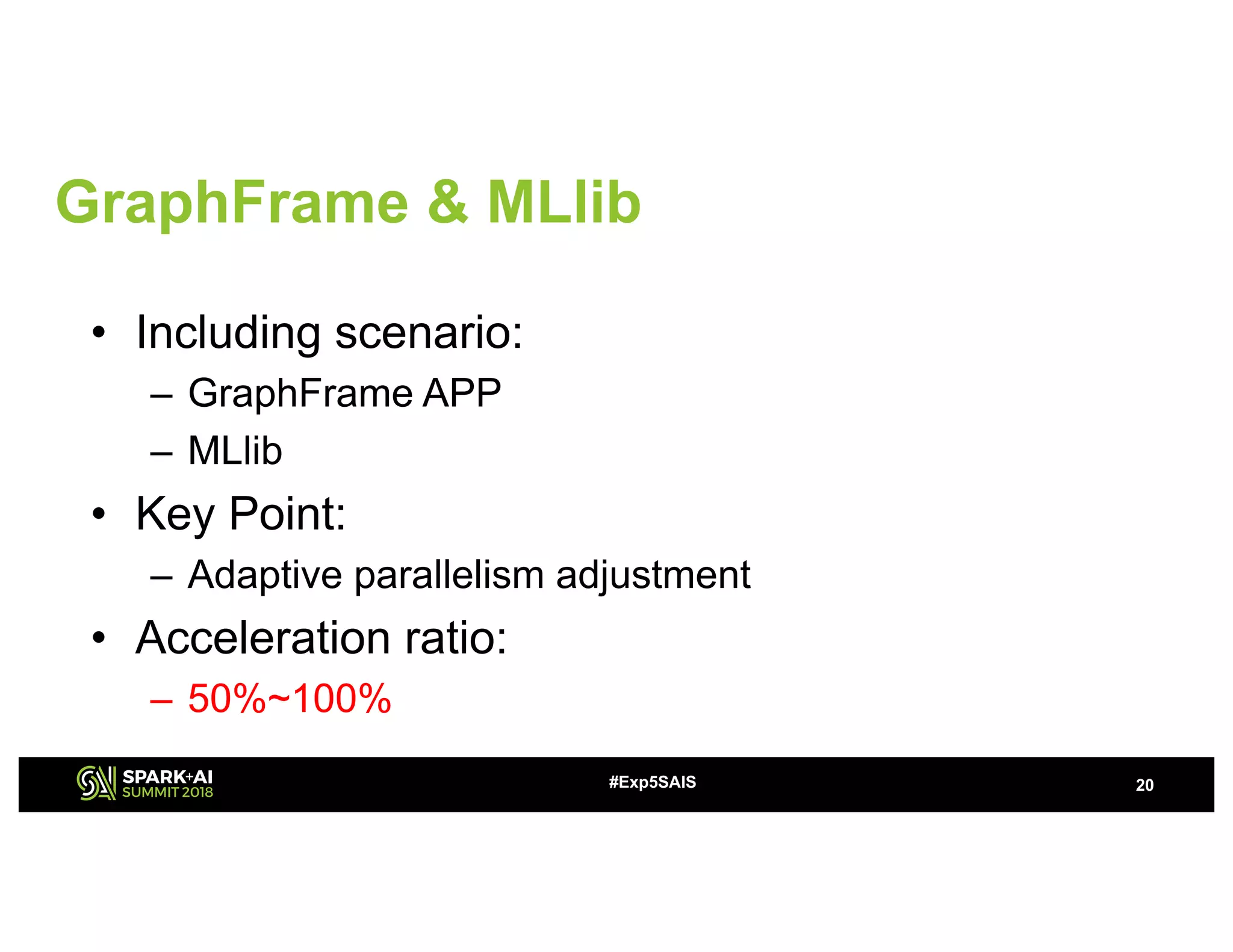
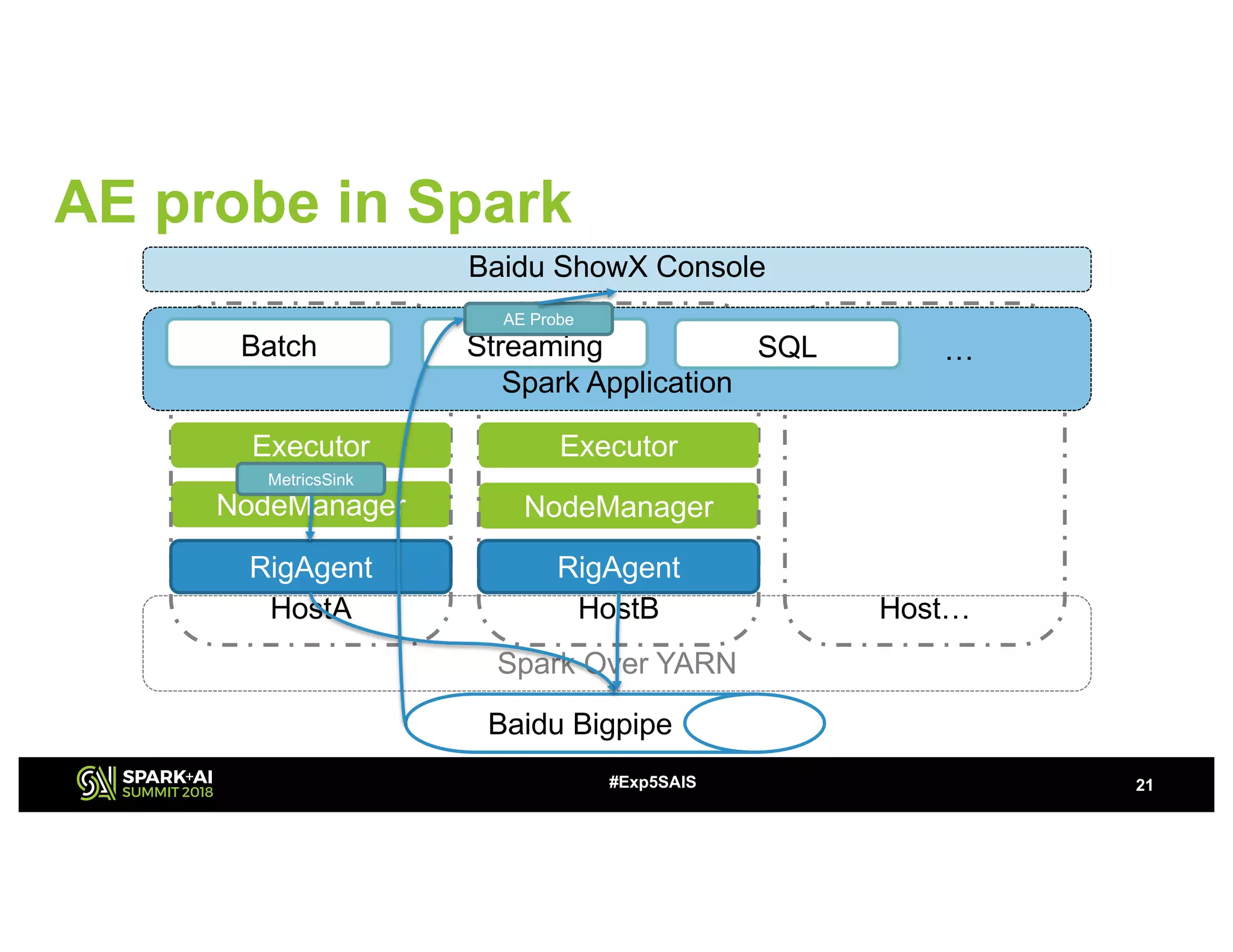
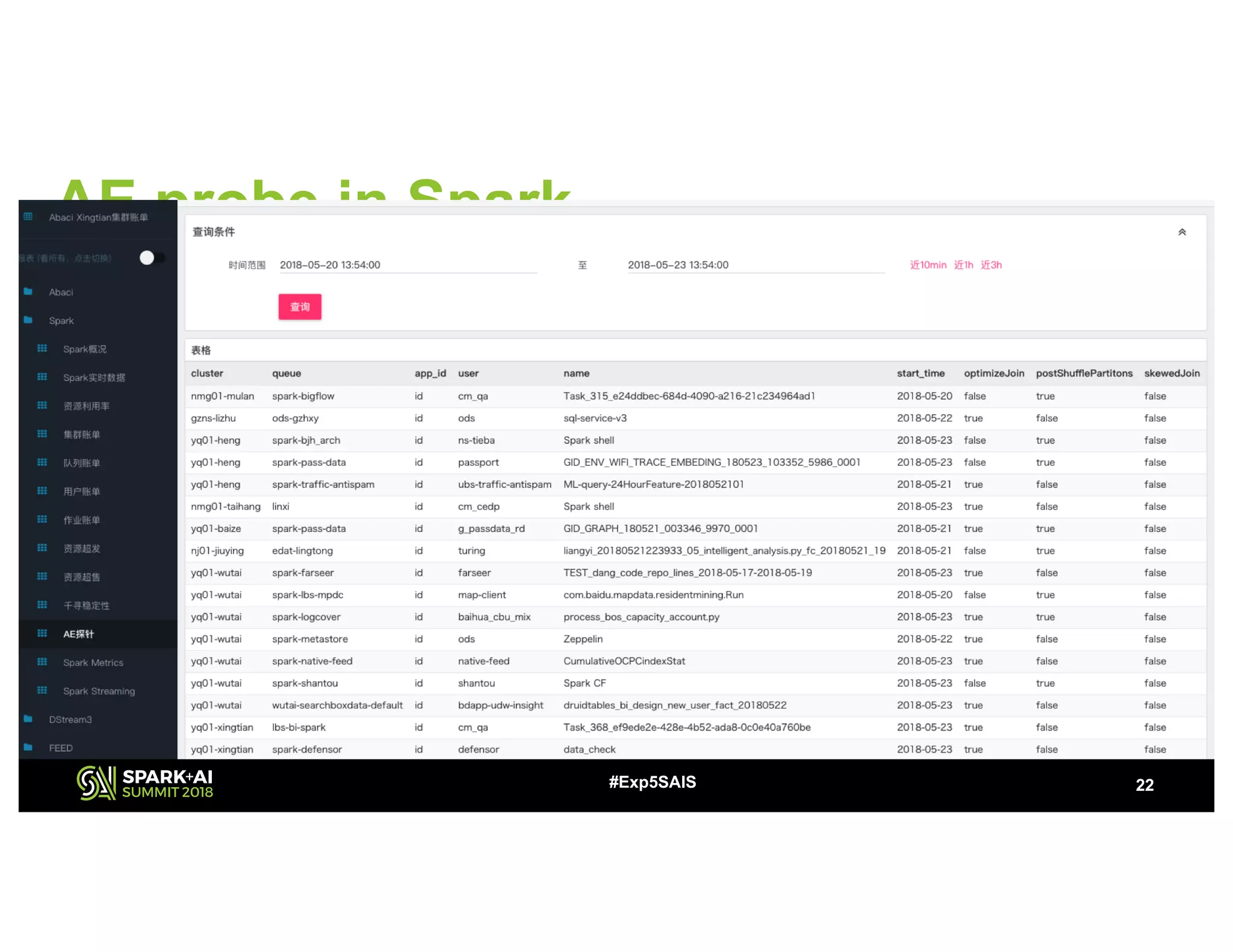
The document discusses challenges and advancements in Spark SQL adaptive execution, including tuning shuffle partition numbers and optimizing join strategies to enhance performance in large-scale environments, particularly at Baidu. Key features are the automation of shuffle partition number adjustments, runtime optimization of join strategies, and management of skewed joins. It outlines the improvements and results of implementing these adaptations across various applications and scenarios.