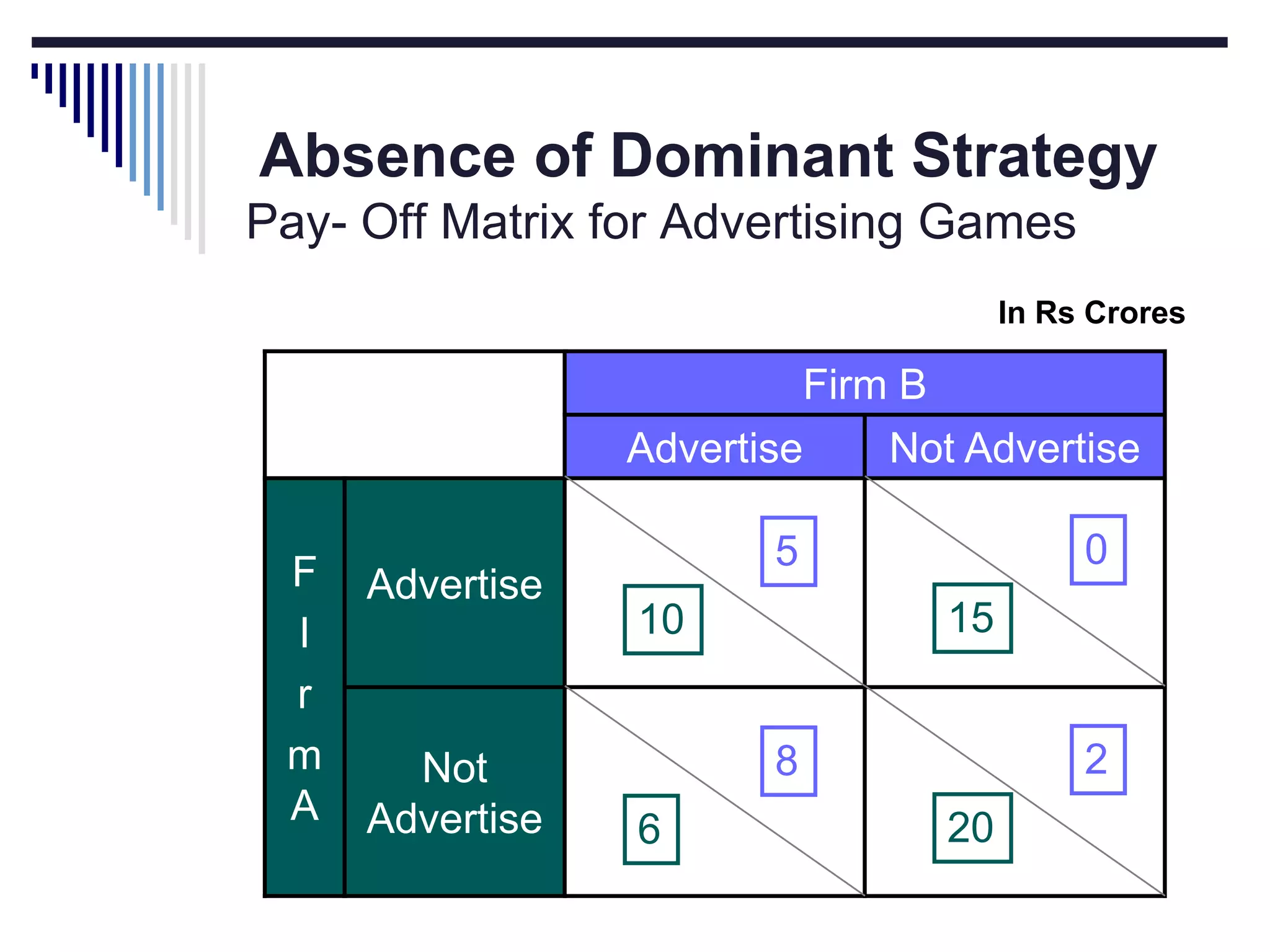
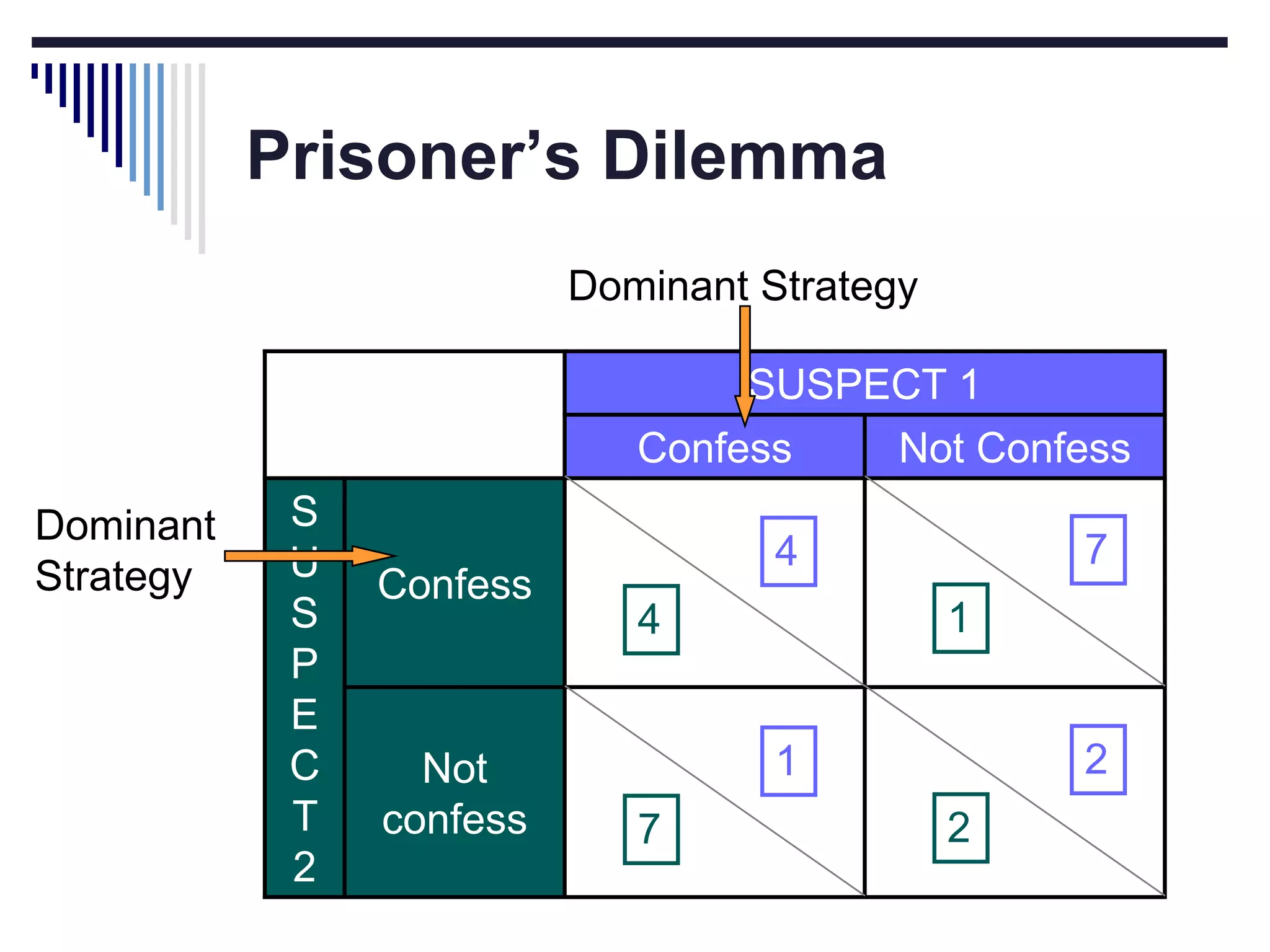
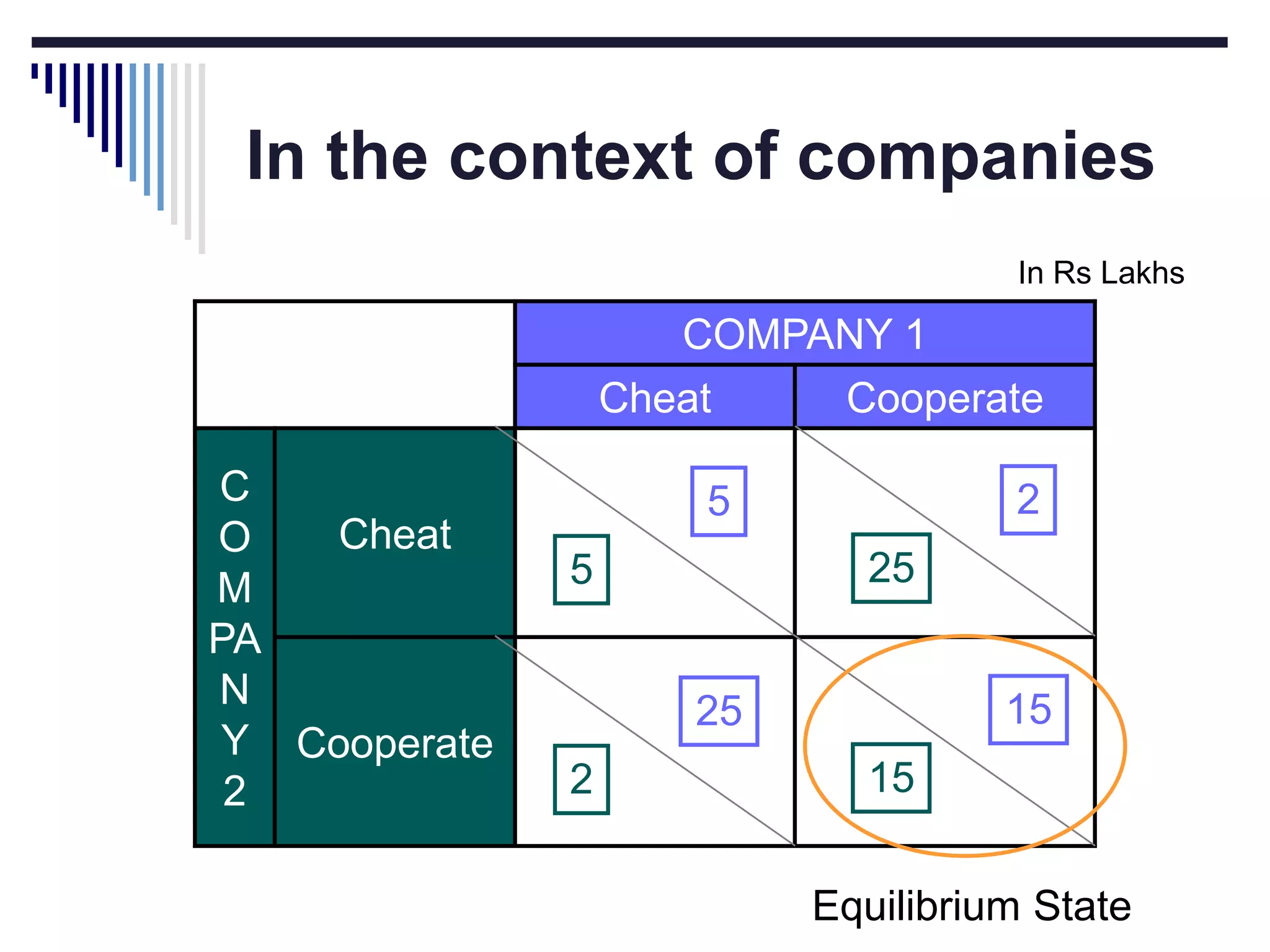
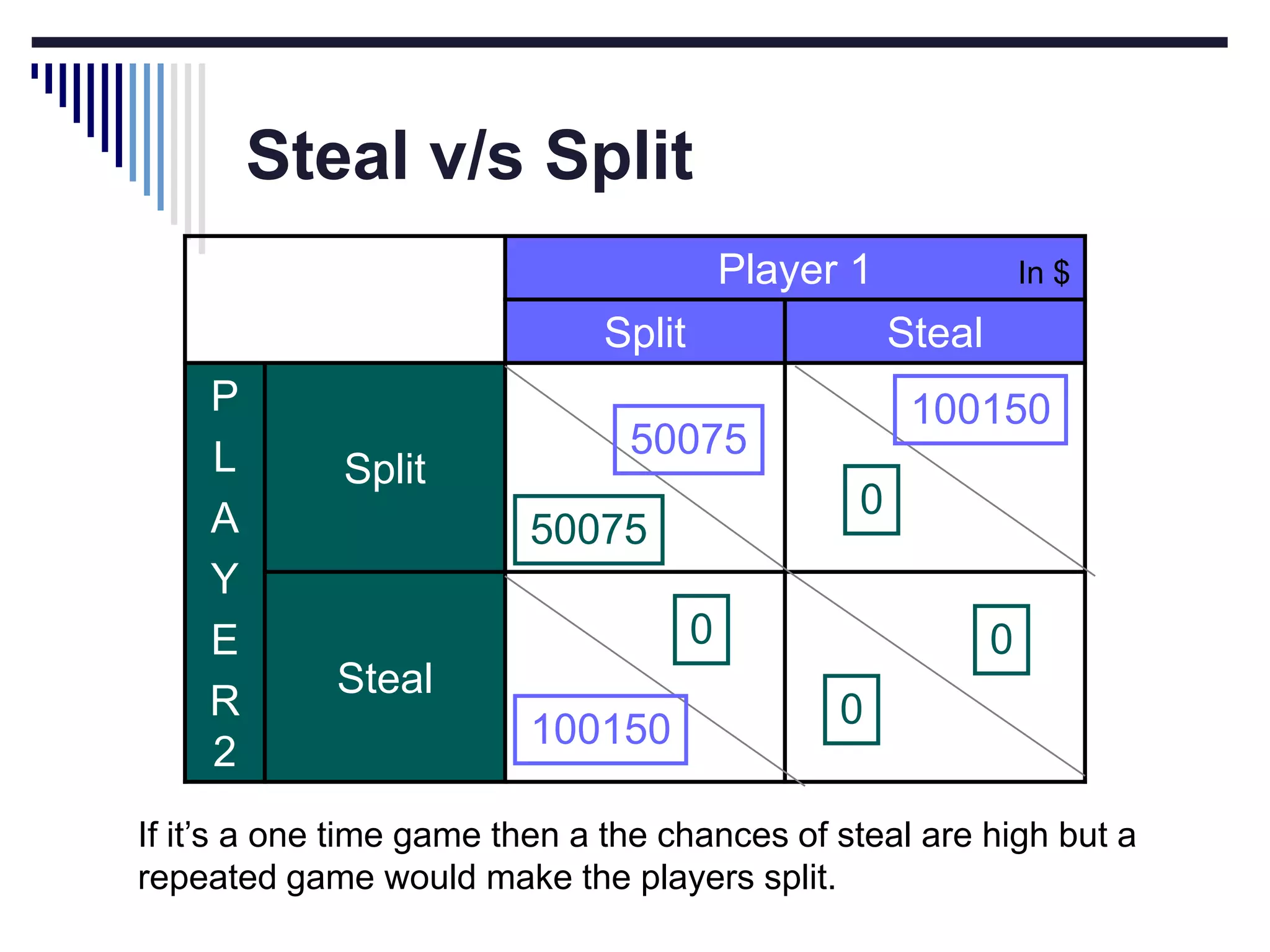
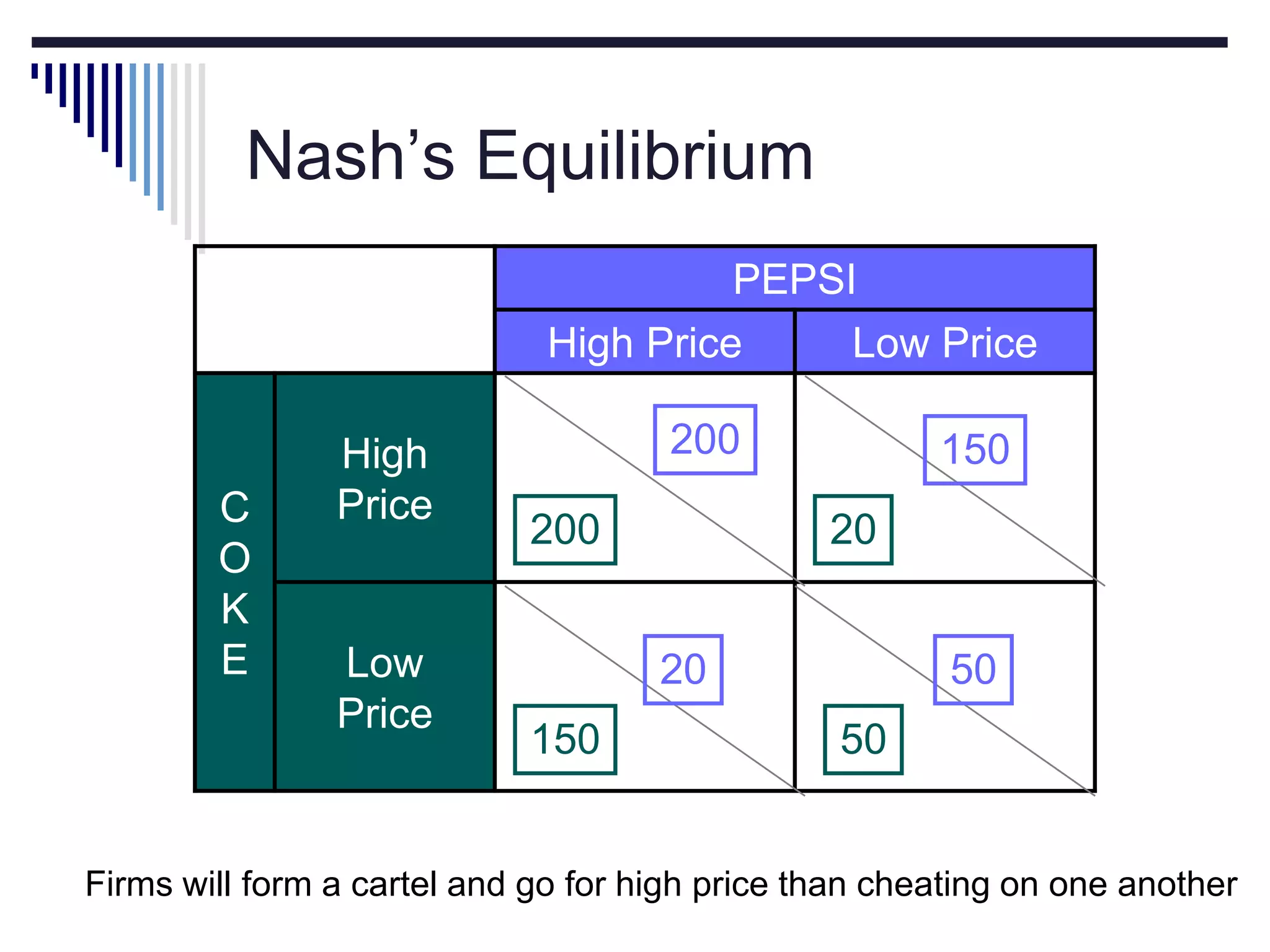
This document discusses game theory concepts including dominant strategies, Nash equilibrium, prisoner's dilemma, and repeated games. It provides examples of how companies could use game theory to determine pricing strategies. In a prisoner's dilemma scenario where two suspects can confess or not confess, confessing dominantly dominates as the strategy. However, in repeated games firms can adopt a cooperative "tit for tat" strategy and set high prices to maximize joint profits in a Nash equilibrium.