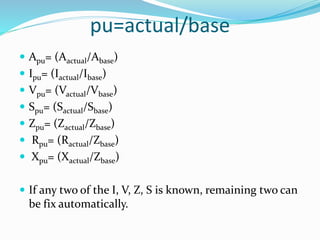
This chapter discusses per unit representation, which expresses values like current, voltage, impedance, and power as a ratio of an actual value to a reference or base value. This makes the quantities unitless and independent of physical size or ratings. The document provides examples of converting actual values to per unit values and explains the advantages, which include representing apparatus values consistently over a wide range, simplifying computations, and specifying machine impedances in per unit values according to manufacturers.