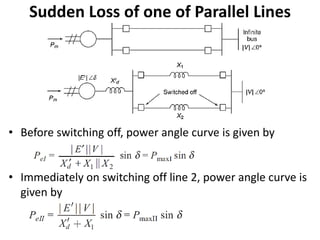
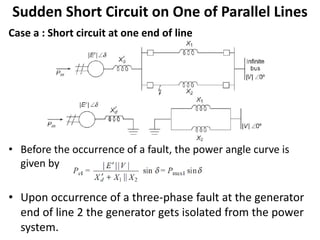
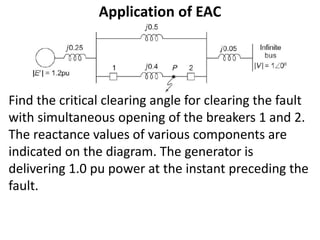
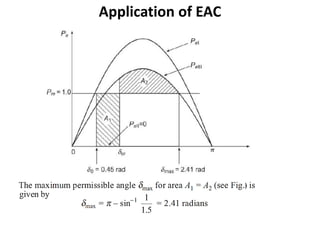
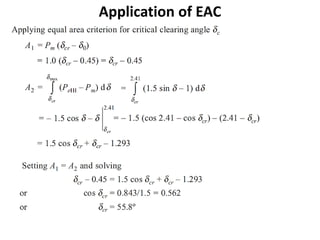
1) The document discusses the application of the Equal Area Criterion (EAC) to analyze power system stability under different fault conditions.
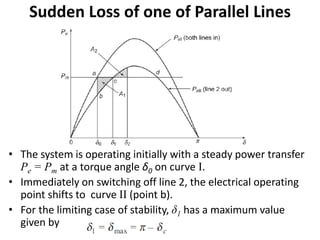
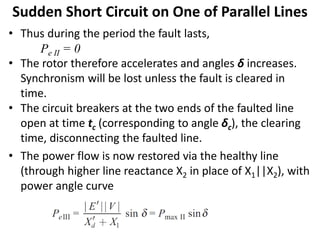
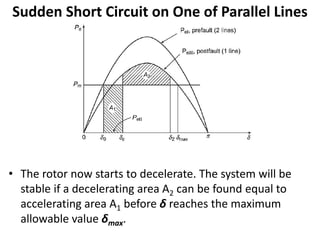
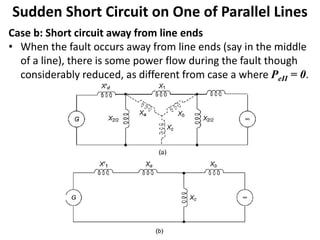
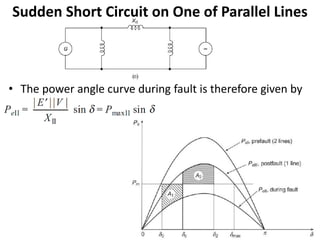
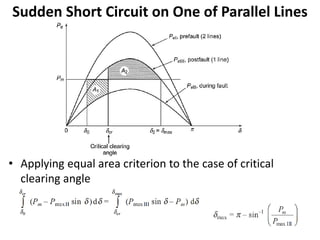
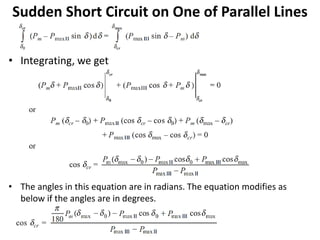
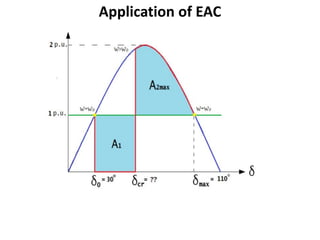
2) It describes how the power angle curve changes when lines are switched off or short circuited, and how the EAC can be used to determine the critical clearing angle for faults.
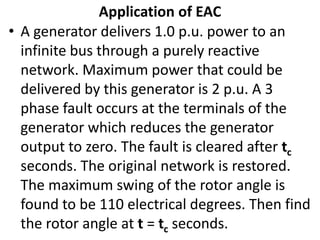
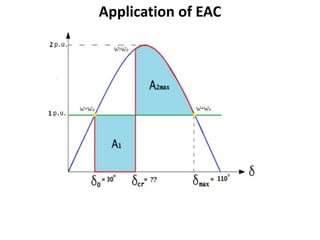
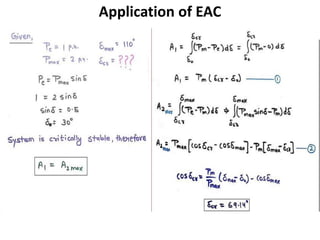
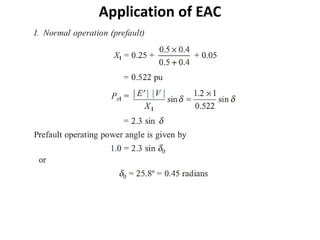
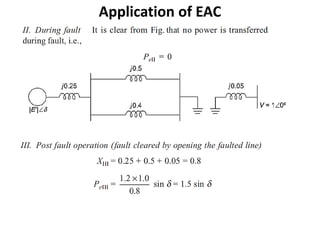
3) Examples are provided to demonstrate how to use the EAC to calculate the rotor angle at fault clearing times and determine the maximum swing of the rotor angle before losing stability.