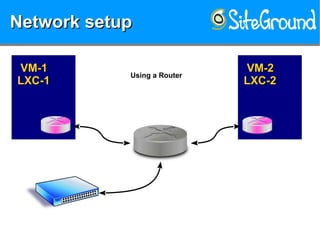
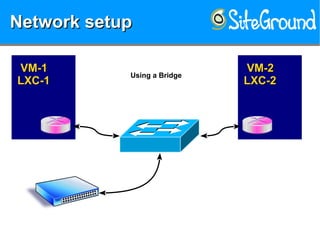
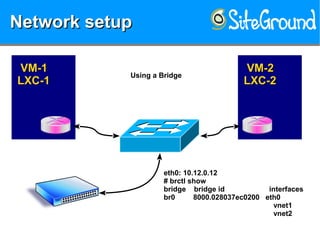
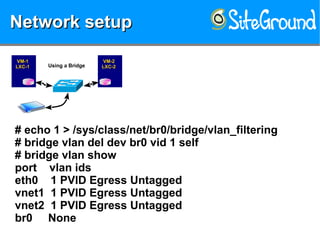
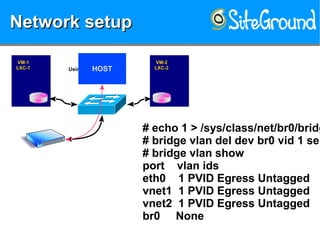
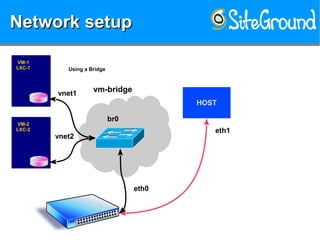
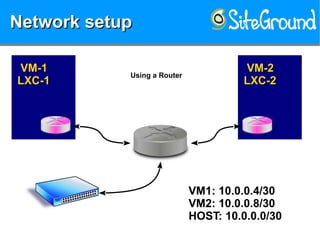
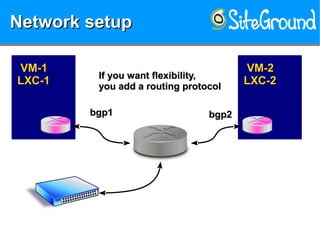
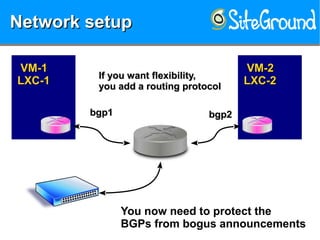
The document discusses securing KVM and container networks, emphasizing the need to understand infrastructure for effective protection against threats like ARP and IP spoofing. It outlines various networking options available for KVM and container configurations, alongside strategies for enhancing security through VLANs, iptables, and arptables. The document concludes with practical examples of network setups and security measures to prevent common network attacks.