A Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN) is designed for low-power communication and integrates small sensors in or around the human body for monitoring health-related functions. The document outlines its architecture, hardware requirements, applications in healthcare and defense, advantages like emergency services accessibility, and disadvantages such as battery life issues. WBAN technologies offer promising potential for consumer electronics but still face several challenges.


![Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN)
Introduction
Intoduction
DEFINITION BY IEEE: A communication standard
Optimized for low power device for their operation On , in
and around the human body to serve a variety of
applications including medical , consumer electronics or
personal entertainment and other.[4]
Standardization of WBAN : IEEE 802.15.6[7][4]
3 / 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160320132711/85/Wireless-body-area-network-3-320.jpg)
![Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN)
Introduction
Wireless Body Area Network
WBAN is a network around the human body.
It allows the integration of intelligent, miniaturized, low
power sensor node in, on or around a human body to
monitoring body function.[1]
It senses biological, physical, chemical changes of our
body and alarms the person who wears it.[4]
It helps in auto medication in case of emergency
4 / 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160320132711/85/Wireless-body-area-network-4-320.jpg)
![Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN)
Literature Survey
Literature Survey
Wireless Personal Area Network : Interconnect
information devices[4]
Wireless Body Area network : Short range, Low Power,
Low cost [4][7]
Jan 2006 : Working group established for examination of
new topics and direction
May 2008 : Task group compiled all submitted
application into single document
April 2010: First draft of 802.15.6
Feb 2012 : Approved version of 802.15.6
5 / 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160320132711/85/Wireless-body-area-network-5-320.jpg)
![Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN)
Literature Survey
Figure: Evolution of IEEE 802.15 standard[7]
6 / 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160320132711/85/Wireless-body-area-network-6-320.jpg)
![Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN)
Architecture Of WBAN
Architecture Of WBAN
Tier-1: Intra-WBAN communication
Tier-2: Inter-WBAN communication
Tier-3: Beyond-WBAN communication[3][4]
Figure: Communication Tiers in a Wireless Body Area Network 7 / 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160320132711/85/Wireless-body-area-network-7-320.jpg)
![Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN)
Layers of WBANS
Layers of WBANS
Physical Layer : The PHY layer of IEEE 802.15.6 is
responsible for the following tasks[4][3];
1 Activation and deactivation of the radio transceiver
2 Clear channel assessment (CCA) within the current
channel
3 Data transmission and reception.
MAC Layer : The IEEE 802.15.6 working group defines to
control channel access[4][3].
The hub (or coordinator) divides the entire channel (or
time axis) into a chain of superframes for time
referenced resource allocations. The hub also chooses
beacon periods of equal length to bound the
superframes.
8 / 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160320132711/85/Wireless-body-area-network-8-320.jpg)
![Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN)
Hardware required for WBAN
Hardware required for WBAN
There are two types of hardware devices required of BAN[4].
Wearable devices are used on the body surface of human.
Medical Implanted devices are inserted inside human
body.
9 / 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160320132711/85/Wireless-body-area-network-9-320.jpg)
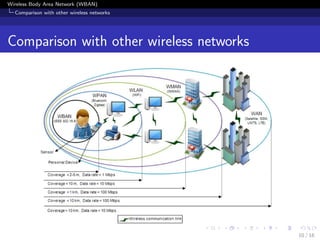



![Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN)
References
References I
[1] Gabriel E. Arrobo and Richard D. Gitlin, “ New approaches to
reliable wireless body area networks”, IEEE International
Conference on , vol., no., pp.1-6, 7-9 Nov. 2011.
[2] Jocelyne Elias and Ahmed Mehaoua,“ Energy-aware topology
design for wireless body area networks”, IEEE International
Conference on , vol., no., pp.3409-3410, 10-15 June 2012.
[3] Riccardo Cavallari,Flavia Martelli, Ramona Rosini, Chiara
Buratti and Roberto Verdone “ A Survey on Wireless Body
Area Networks: Technologies and Design Challenges”,IEEE
Communications Surveys and Tutorials , vol.16, no.3,
pp.1635-1657, Third Quarter 2014.
14 / 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160320132711/85/Wireless-body-area-network-14-320.jpg)
![Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN)
References
References II
[4] Samaneh Movassaghi, Mehran Abolhasan,Justin Lipman,
David Smith and Abbas Jamalipour,“Wireless Body Area
Networks: A Survey”, IEEE Communications Surveys and
Tutorials , vol.16, no.3, pp.1658-1686, Third Quarter 2014.
[5] Peter Van Daele, Ingrid Moerman, and Piet
Demeester“Wireless body area networks: Status and
opportunities”, IEEE General Assembly and Scientific
Symposium (URSI GASS), vol., no., pp.1-4, 16-23 Aug. 2014.
15 / 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160320132711/85/Wireless-body-area-network-15-320.jpg)
![Wireless Body Area Network (WBAN)
References
References III
[6] Sang-Hun Han and Sang Kyu Park“Performance Analysis of
Wireless Body Area Network in Indoor Off-body
Communication”,IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics,
Vol. 57, No. 2, May 2011.
[7] “IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks -
Part 15.6: Wireless Body Area Networks”,in IEEE Std
802.15.6-2012 , vol., no., pp.1-271, Feb. 29 2012
[8] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.15.6
16 / 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-160320132711/85/Wireless-body-area-network-16-320.jpg)