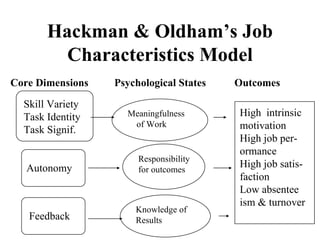
Hackman & Oldham's Job Characteristics Model examines how skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback in a job lead to positive psychological states and outcomes. The document then discusses moderating variables, implementing concepts to improve jobs, designing jobs for teams, using goals to motivate, and using incentives and rewards to motivate individuals and groups. It concludes by summarizing how the job characteristics model can be used and transitioning to a discussion of groups in organizations.