Embed presentation
Downloaded 154 times

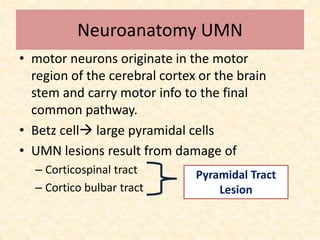
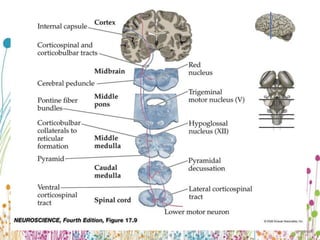


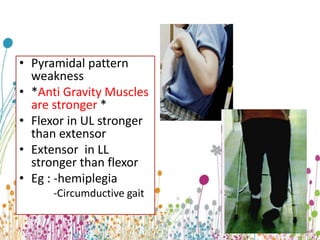
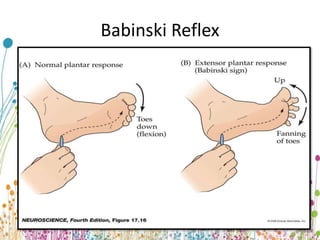


Upper Motor Neuron Lesion Upper motor neurons originate in the brain and brainstem, carrying motor signals through tracts like the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts. Damage to these tracts above the pyramidal decussation causes contralateral weakness, while damage below causes ipsilateral weakness. Symptoms include spasticity, increased tone and reflexes, clonus, and an extensor plantar response. Weakness follows a pyramidal pattern with anti-gravity muscles stronger and flexors dominating over extensors, leading to issues like hemiplegia and circumductive gait.







