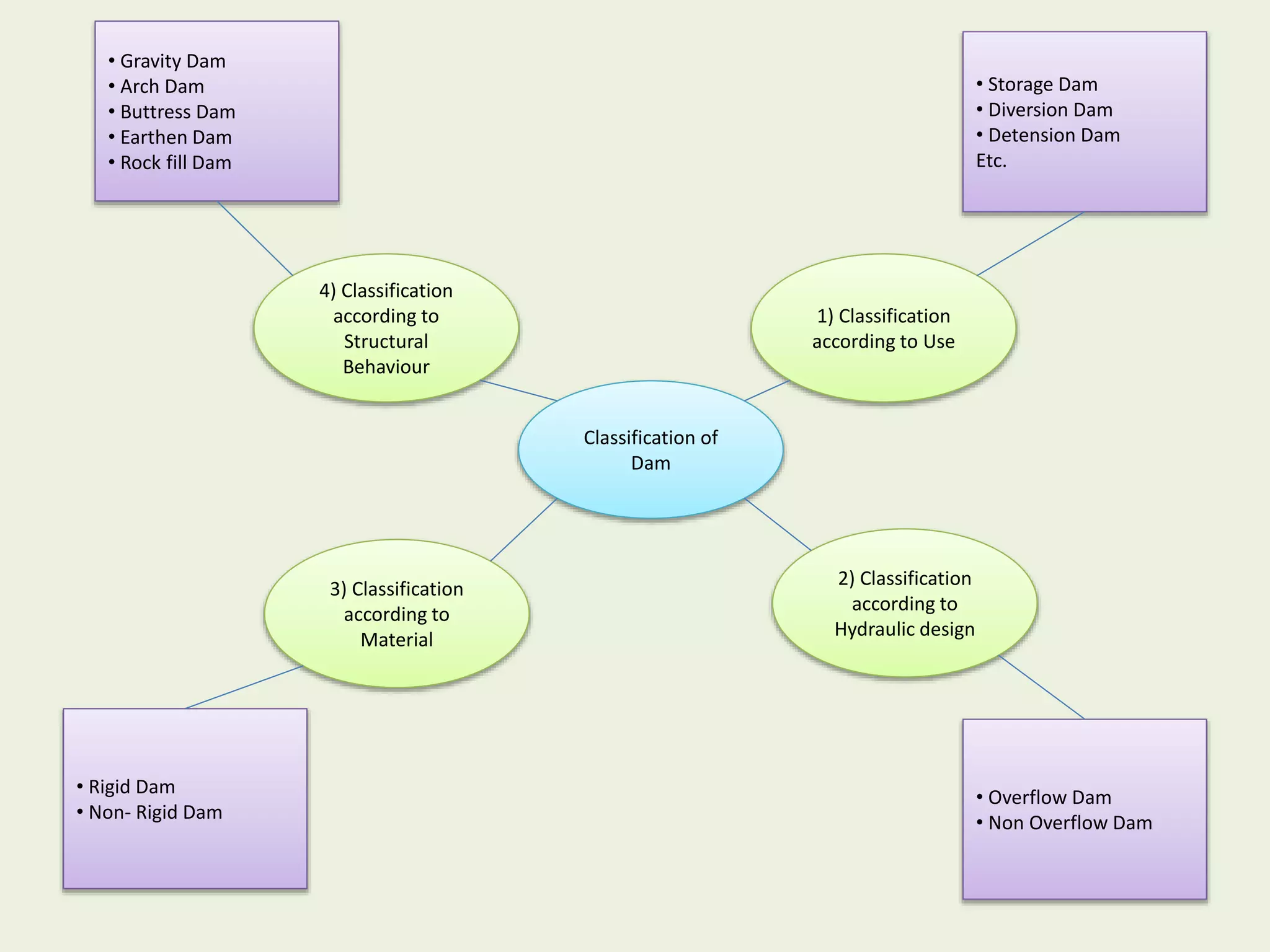
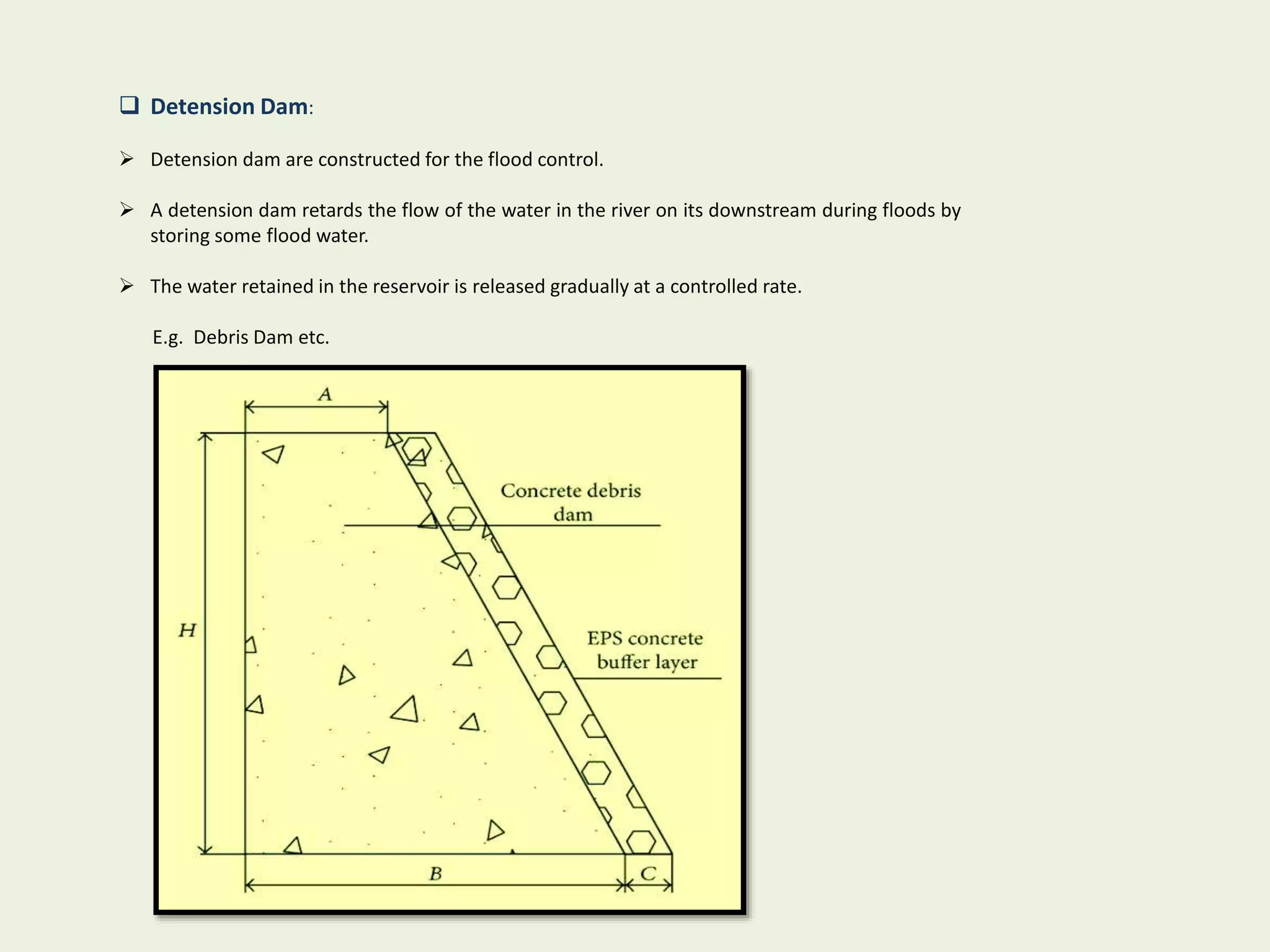
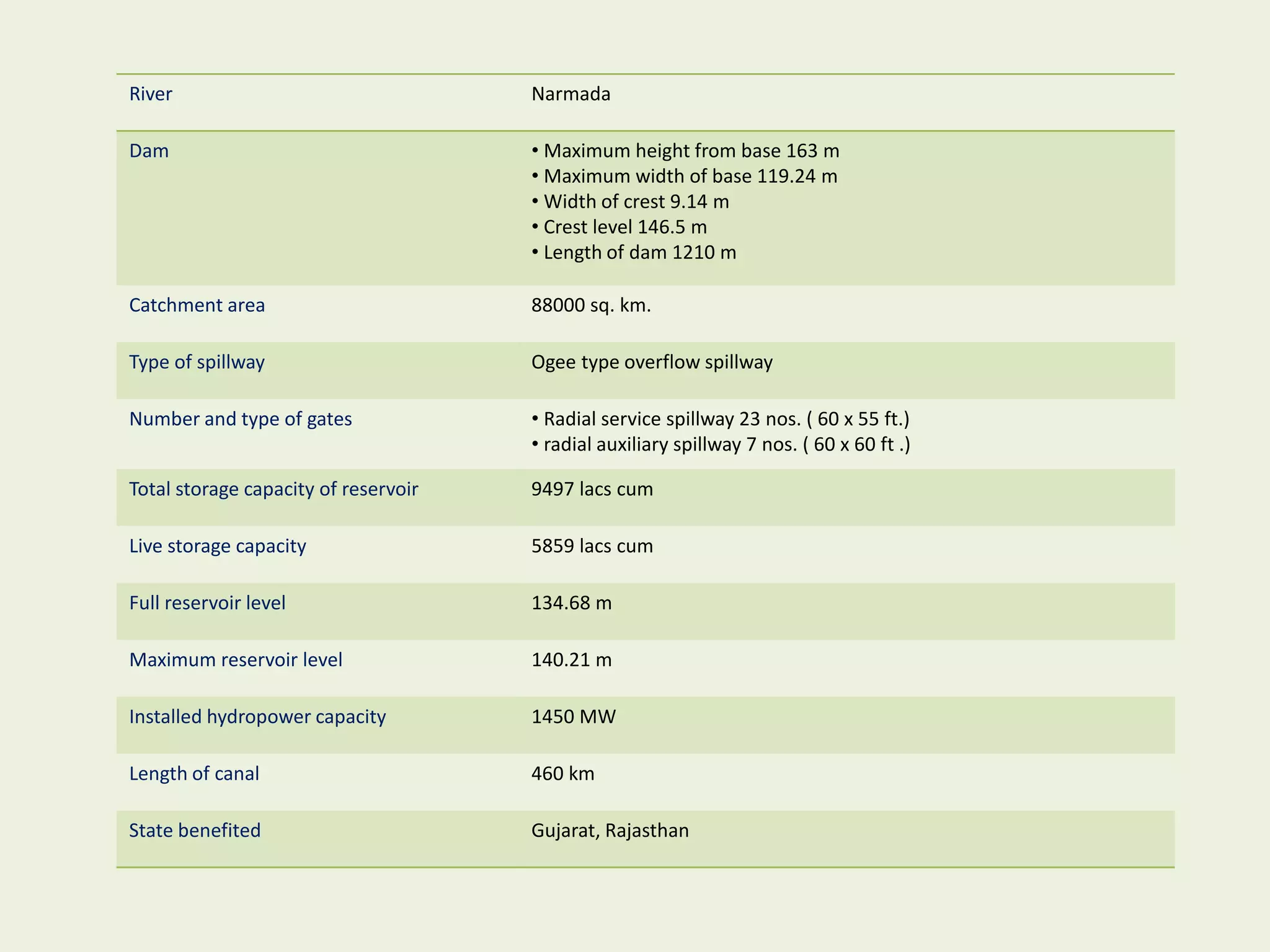
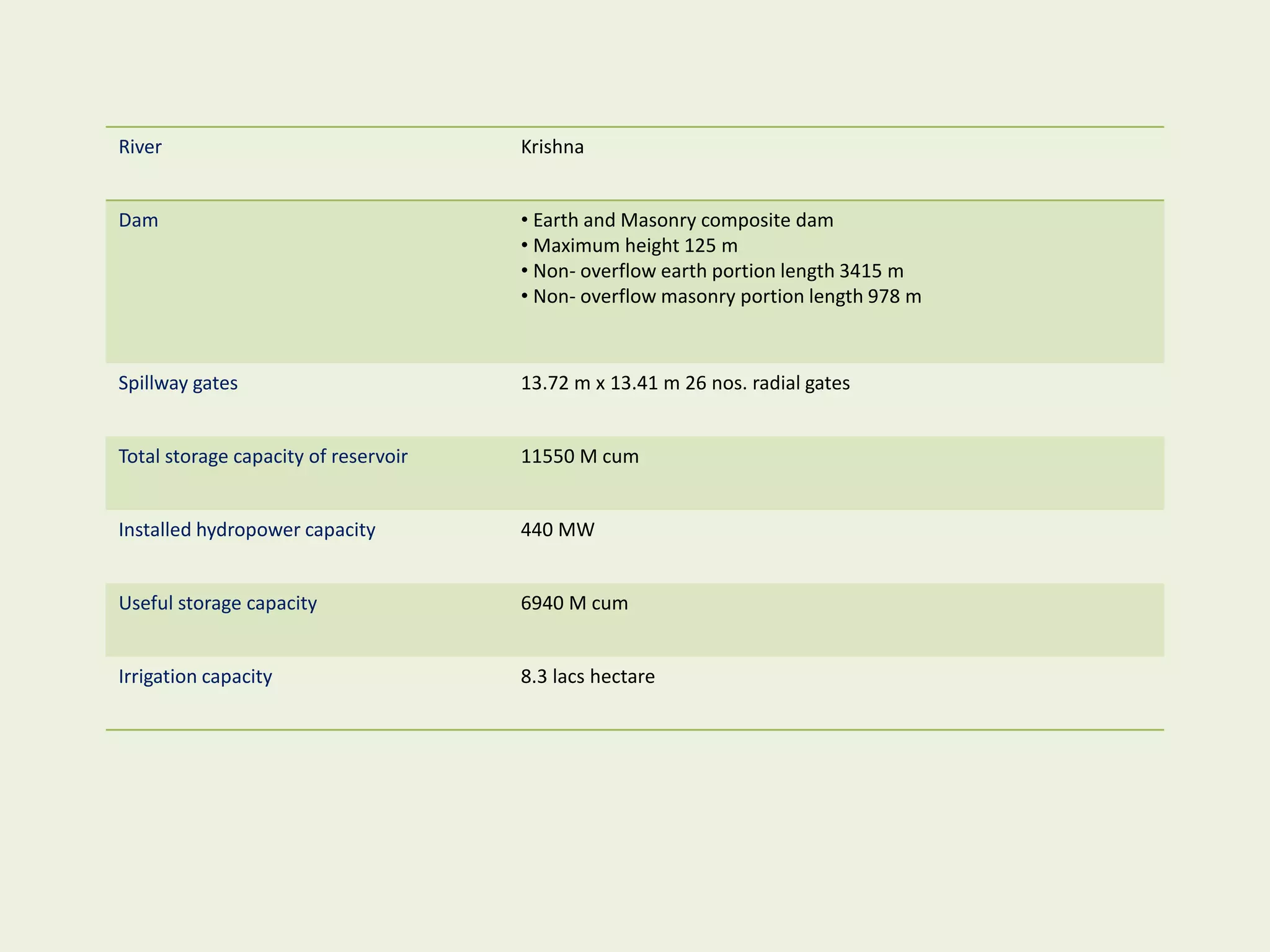
The document provides an overview of dams, including their purpose, classification, and specific types like gravity, arch, buttress, earth, and rock fill dams. It discusses their functions such as water supply, flood control, and electricity generation, along with advantages and disadvantages for each type. Additionally, it highlights salient features of major dams in India, detailing specifications and capacities of several significant projects.