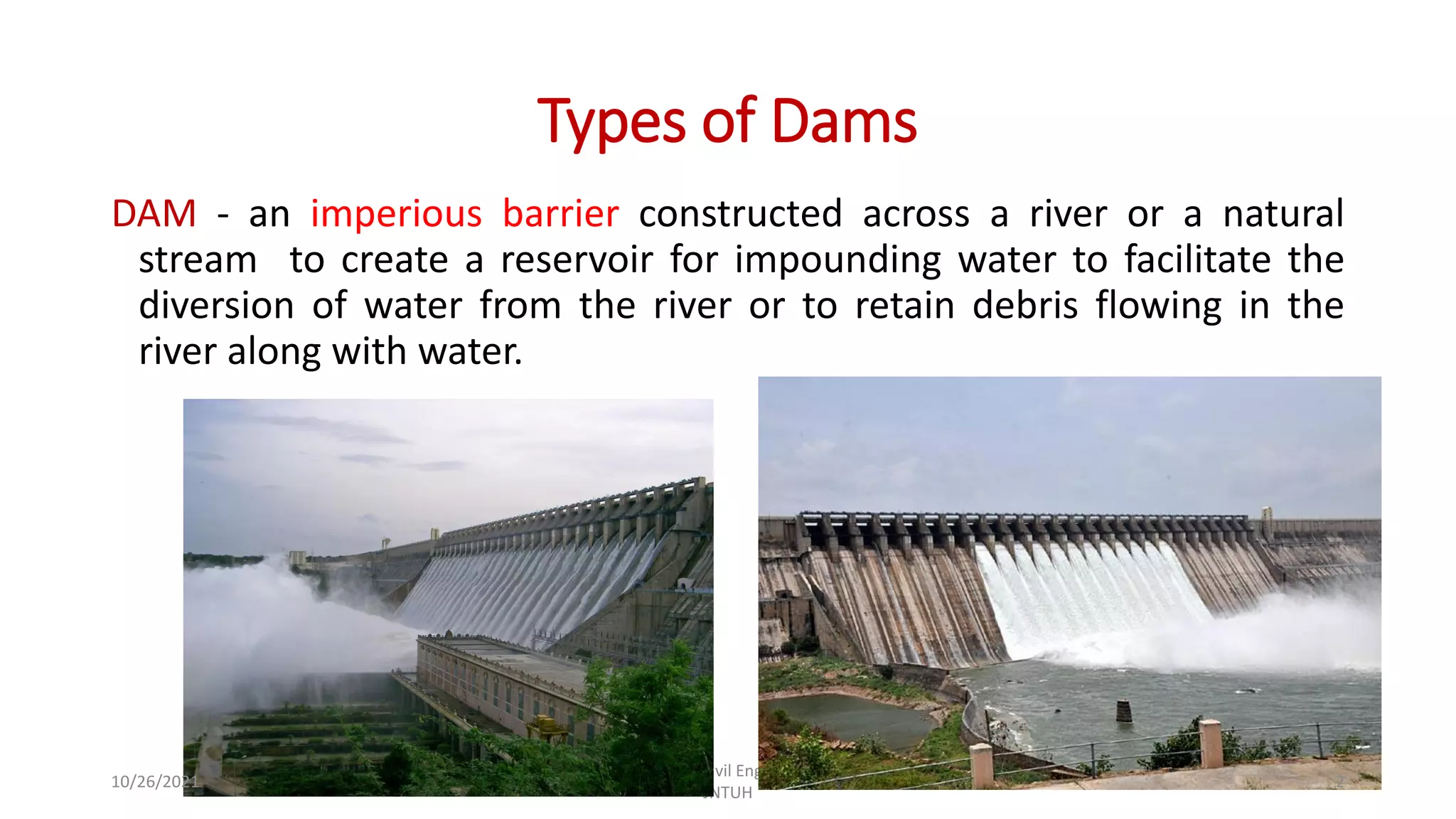
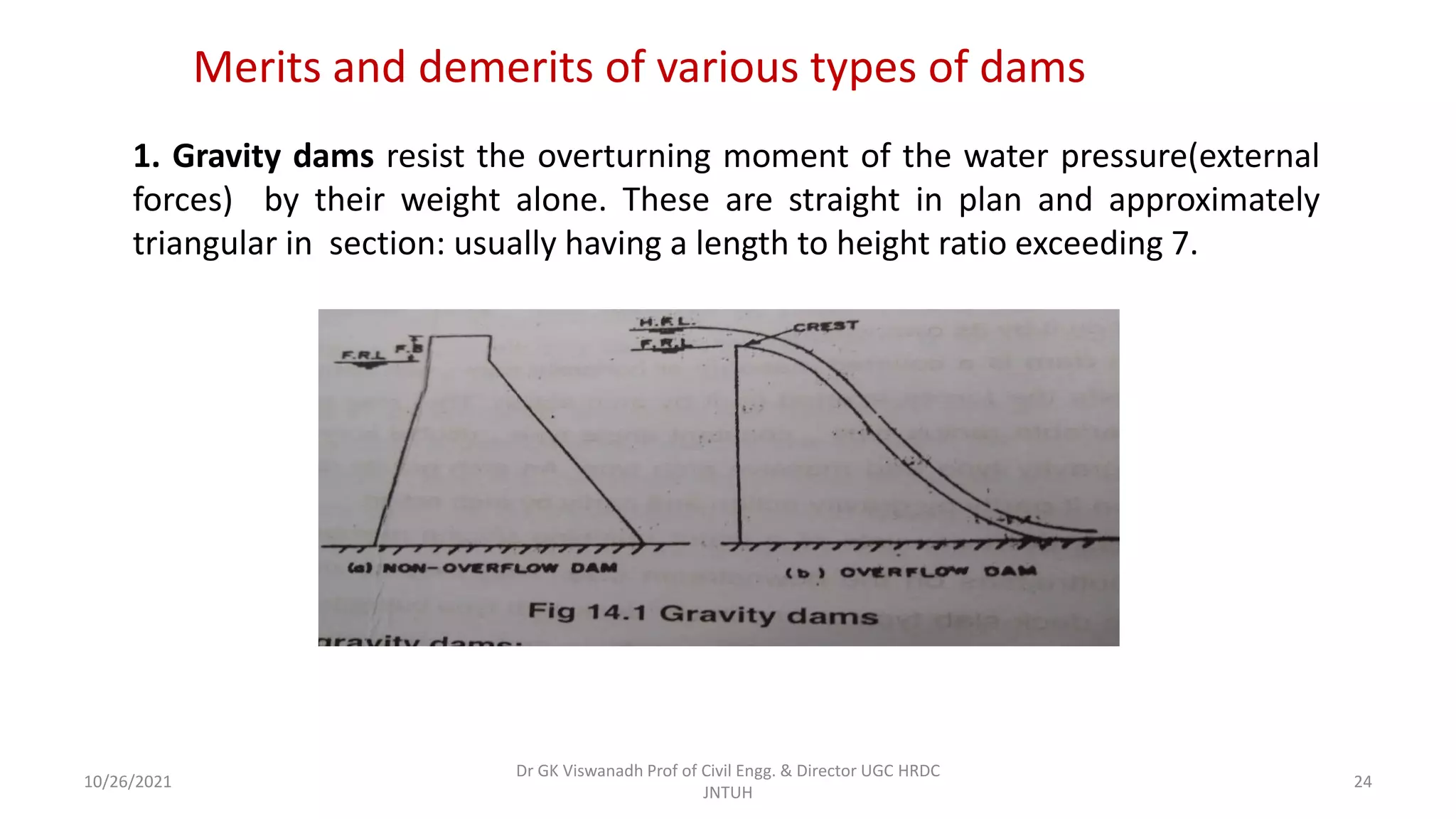
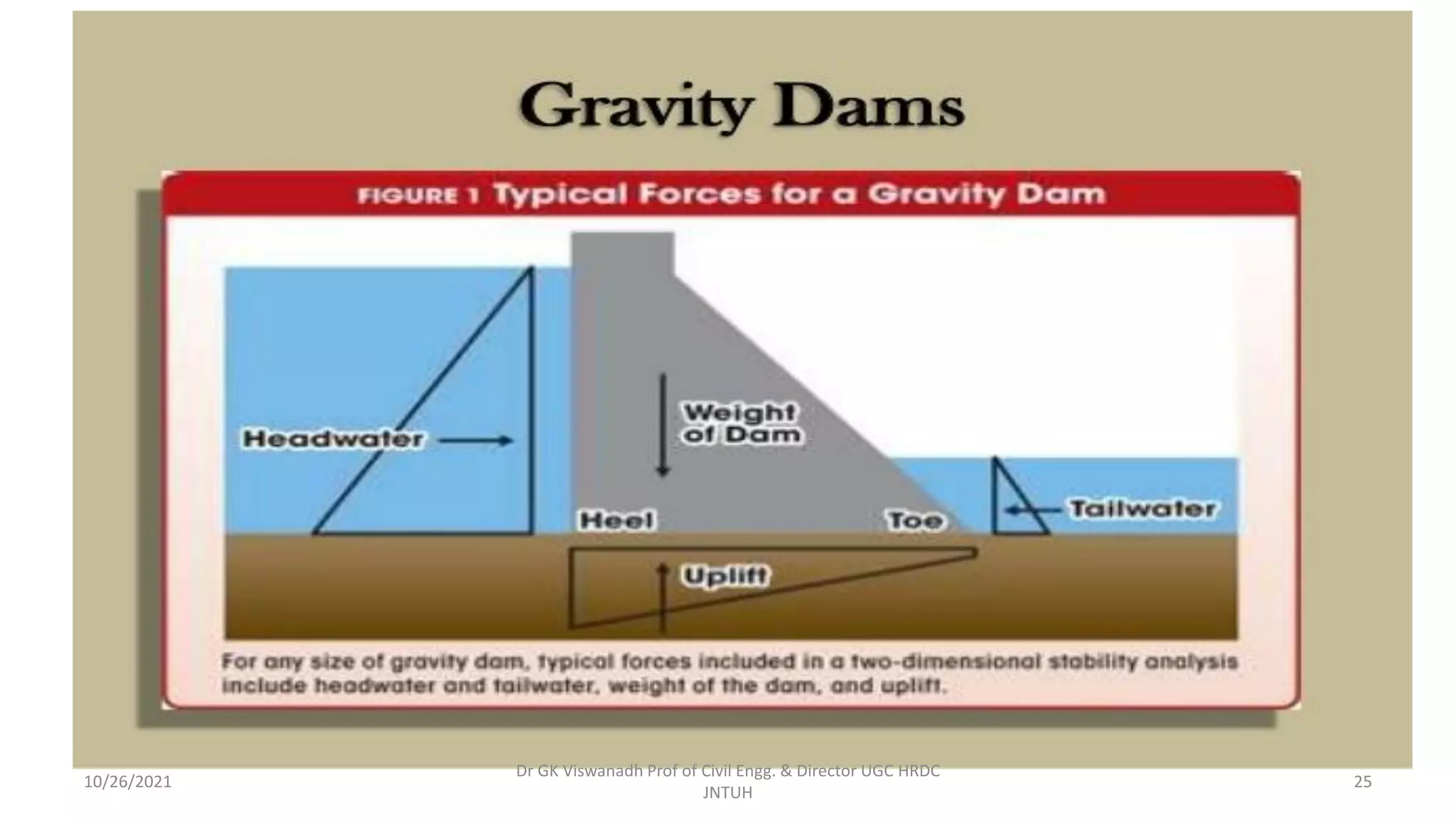
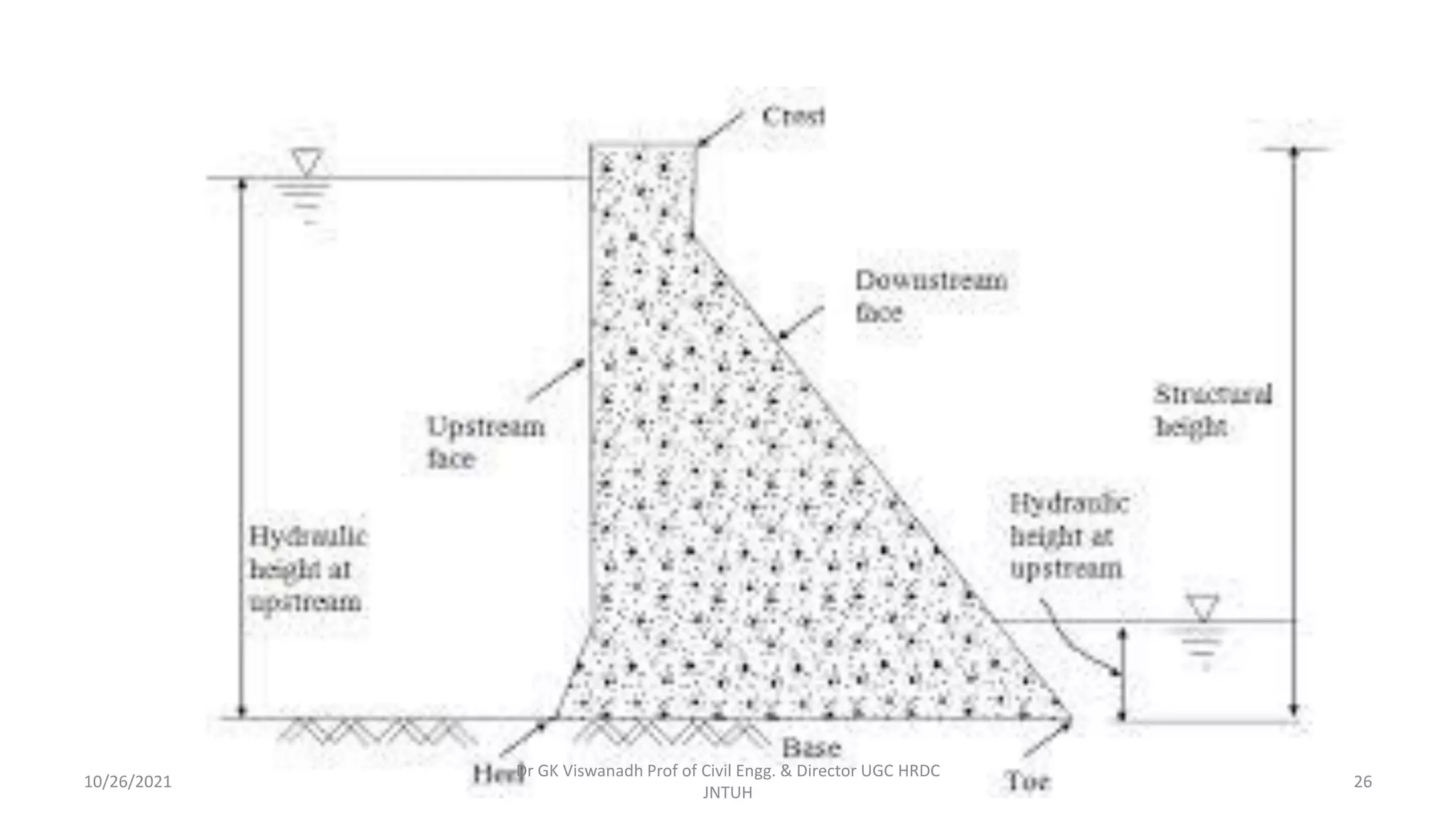
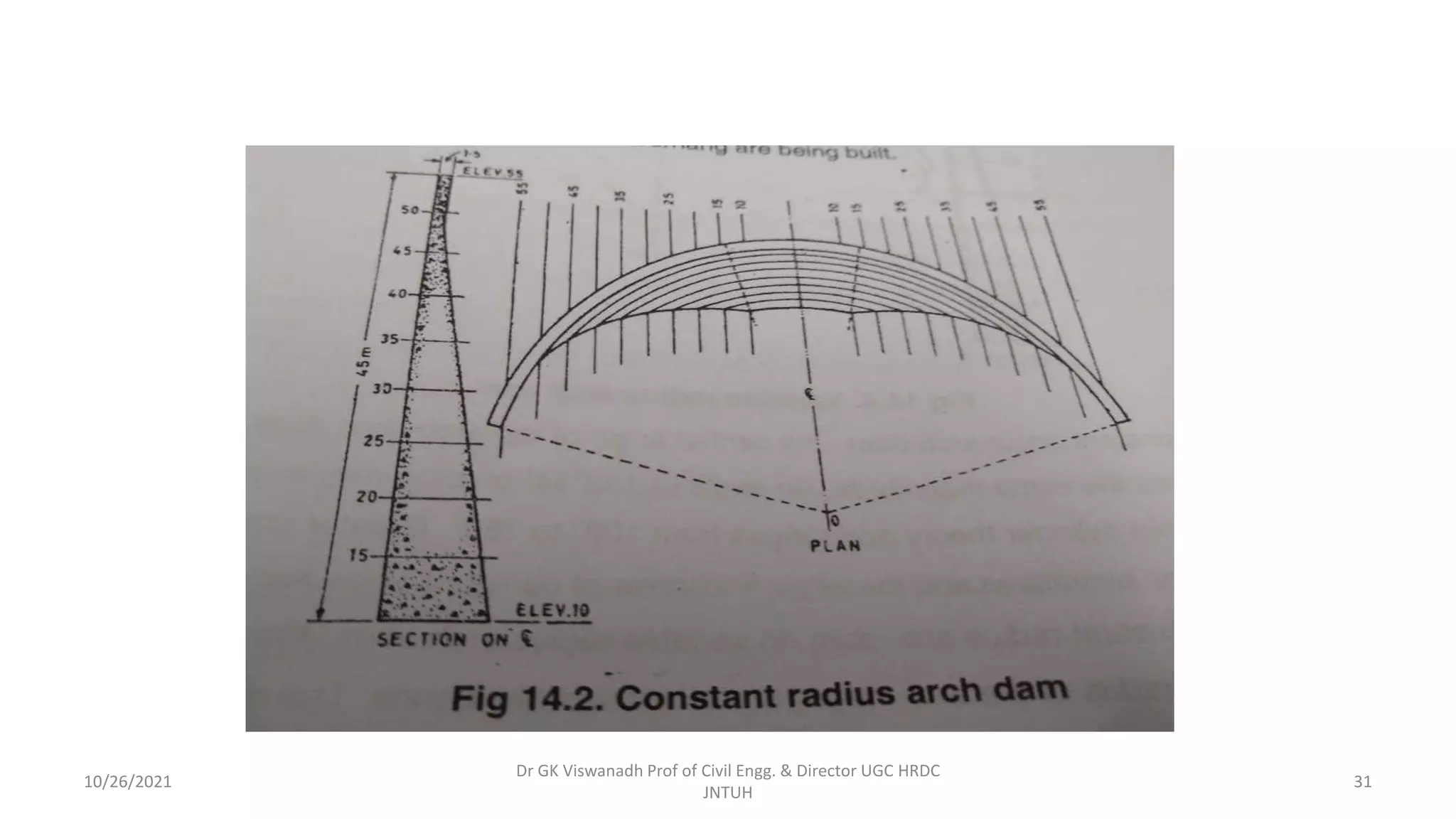
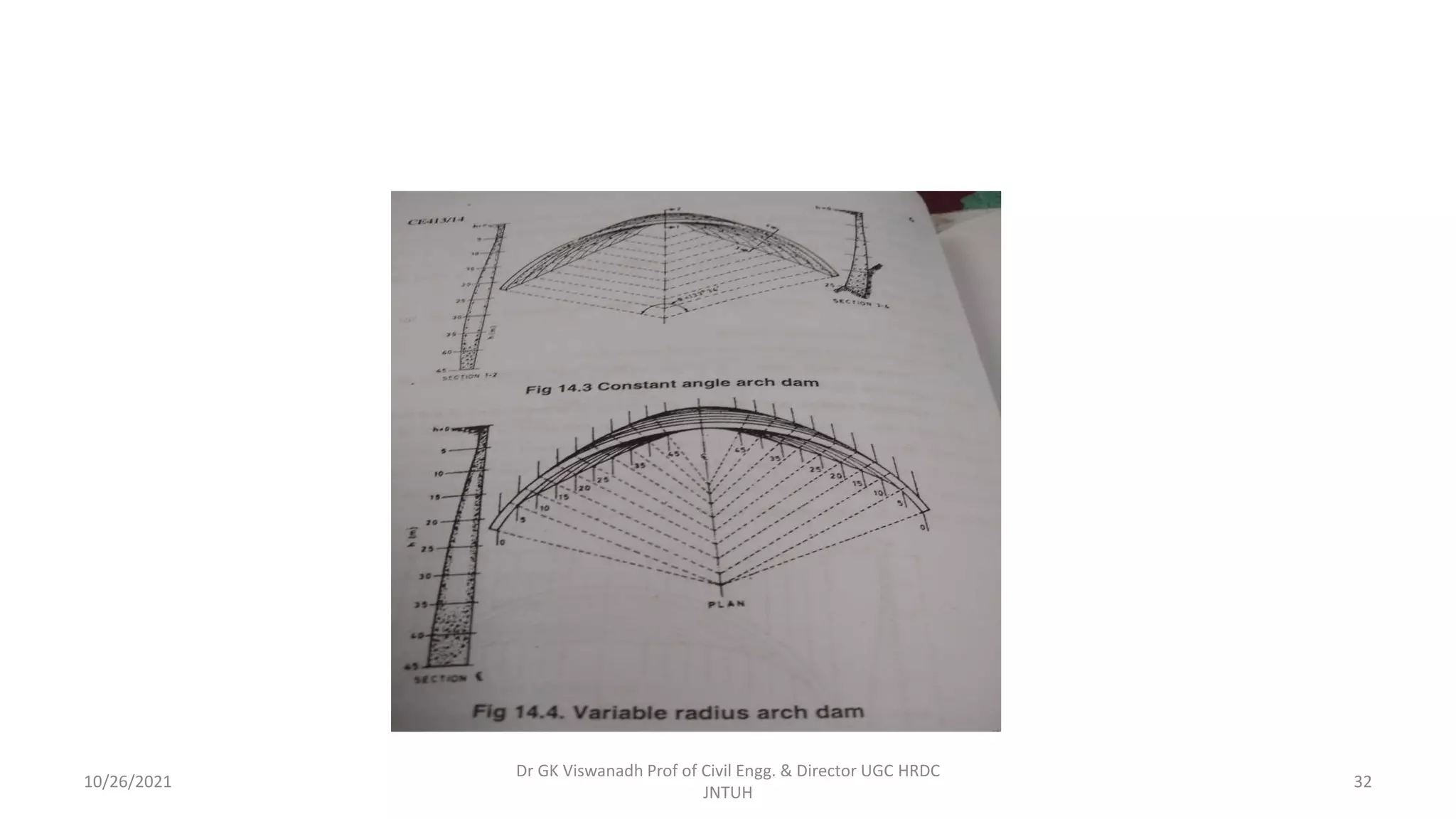
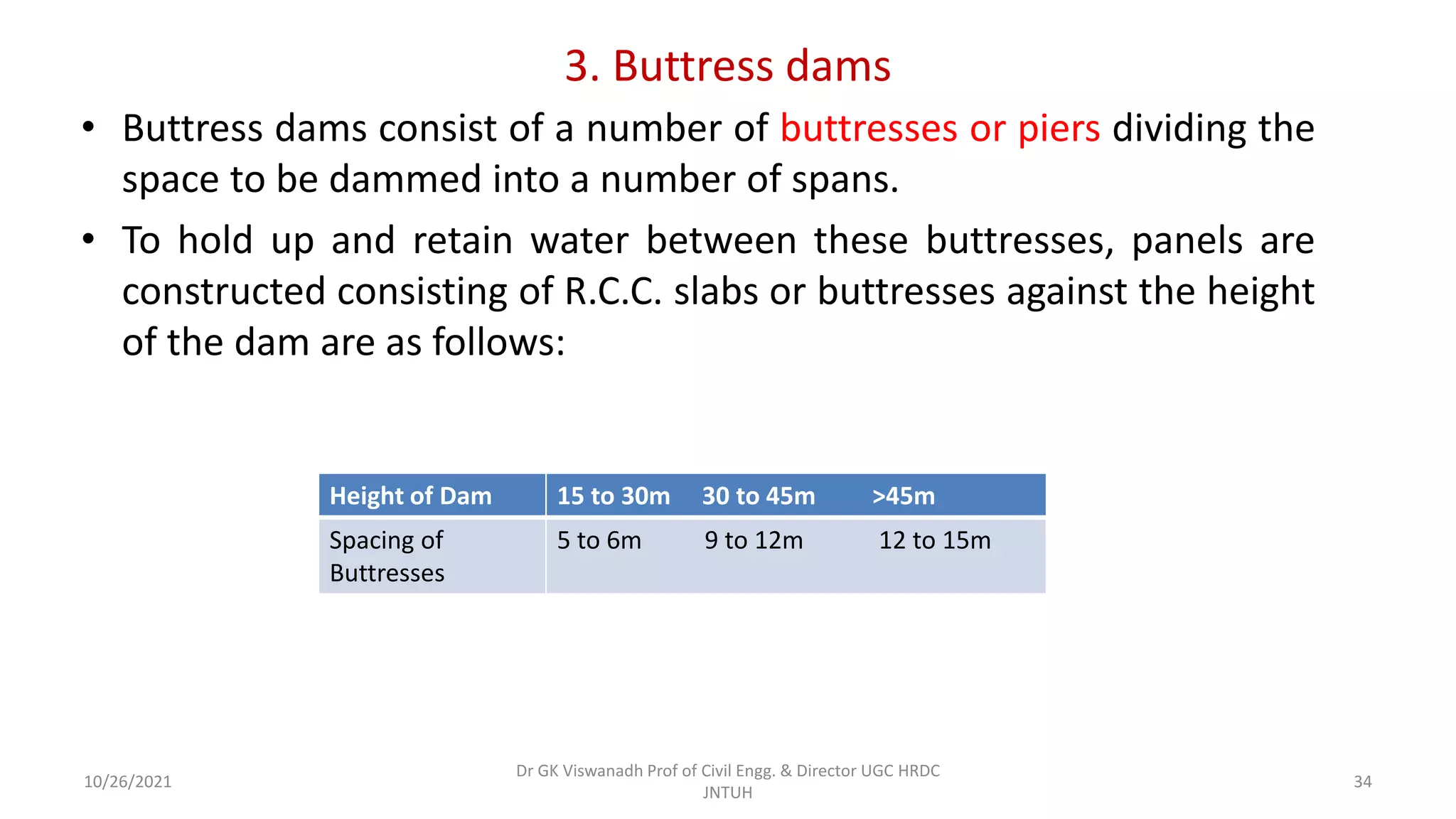
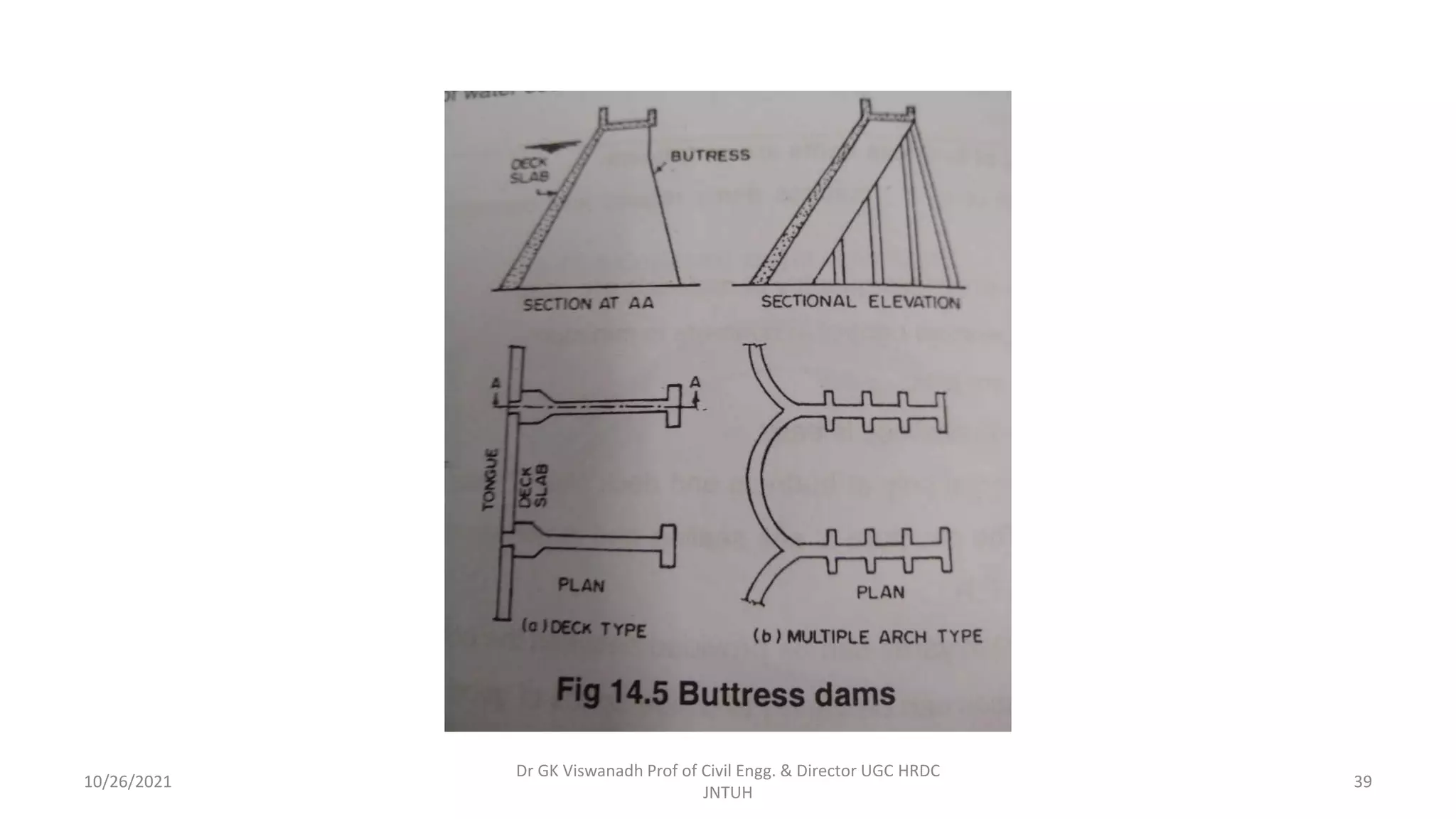
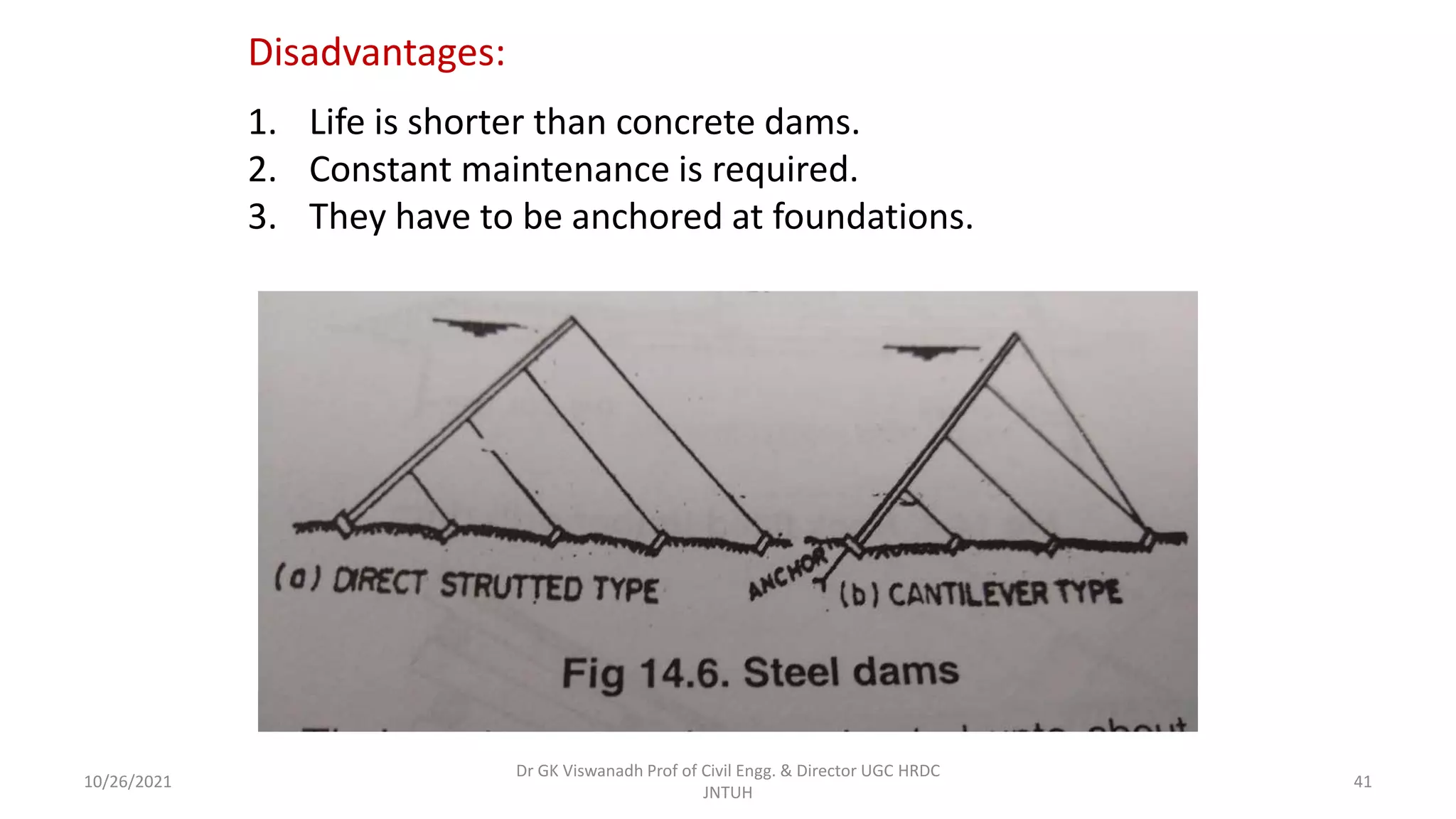
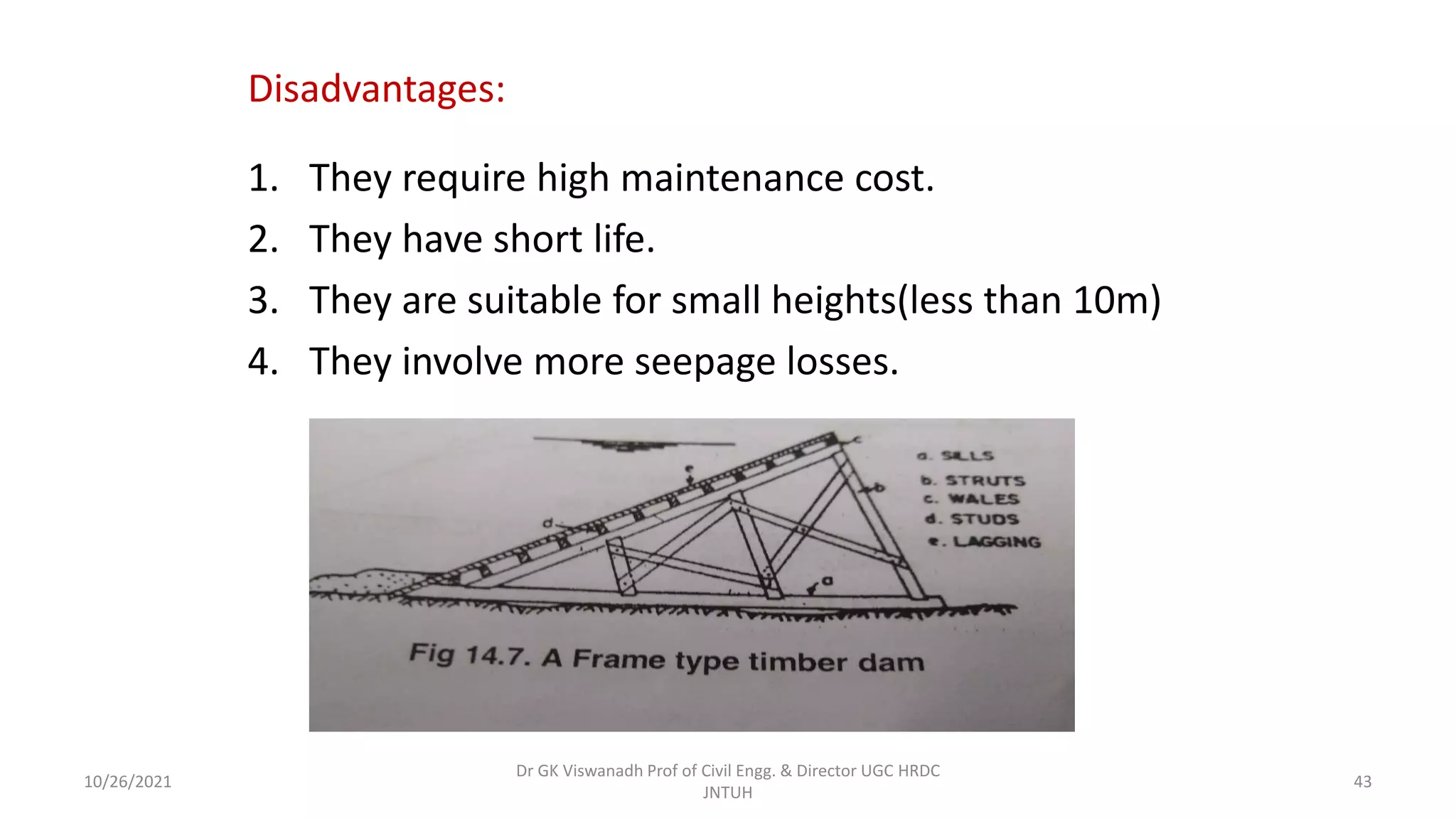
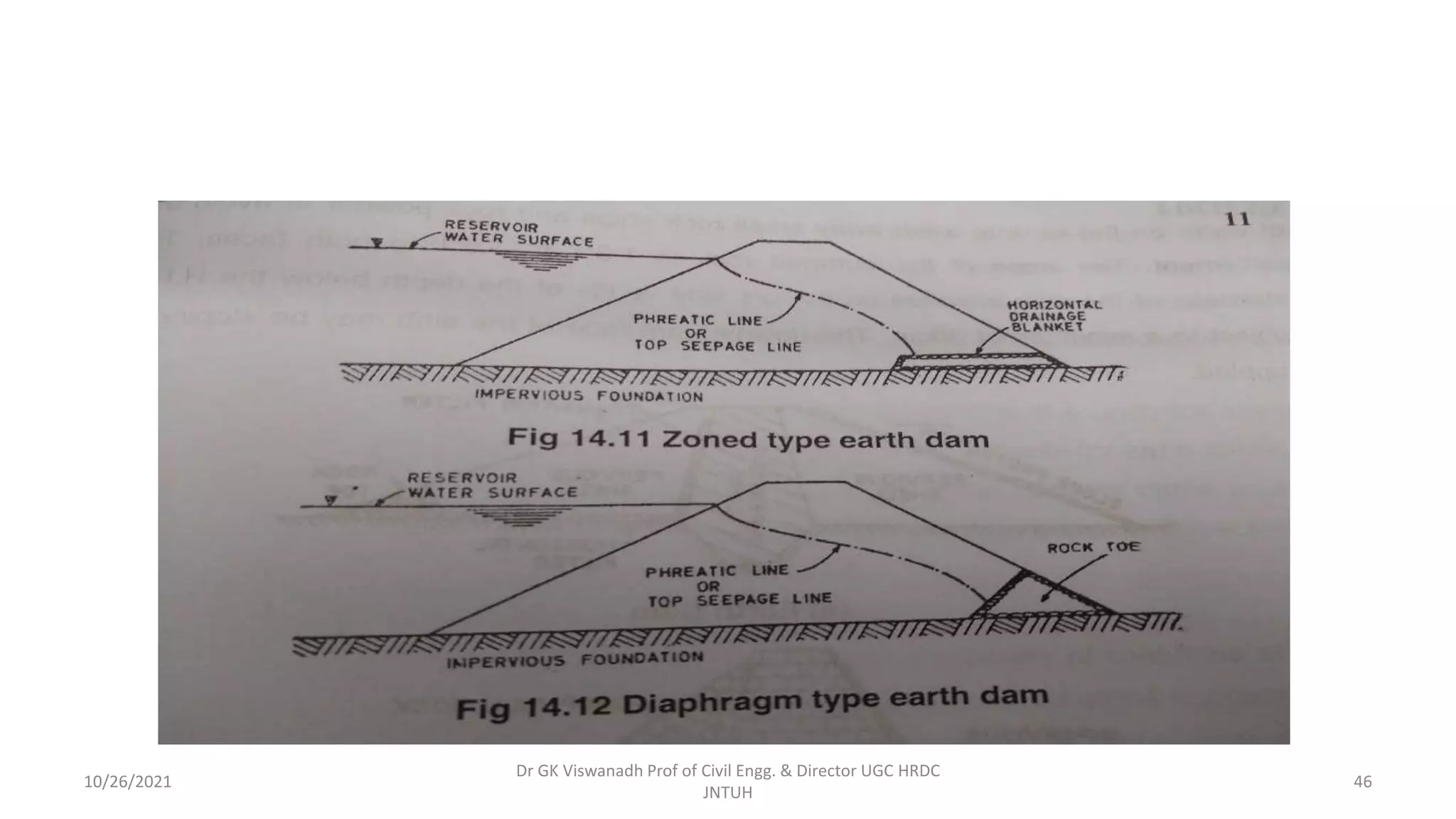
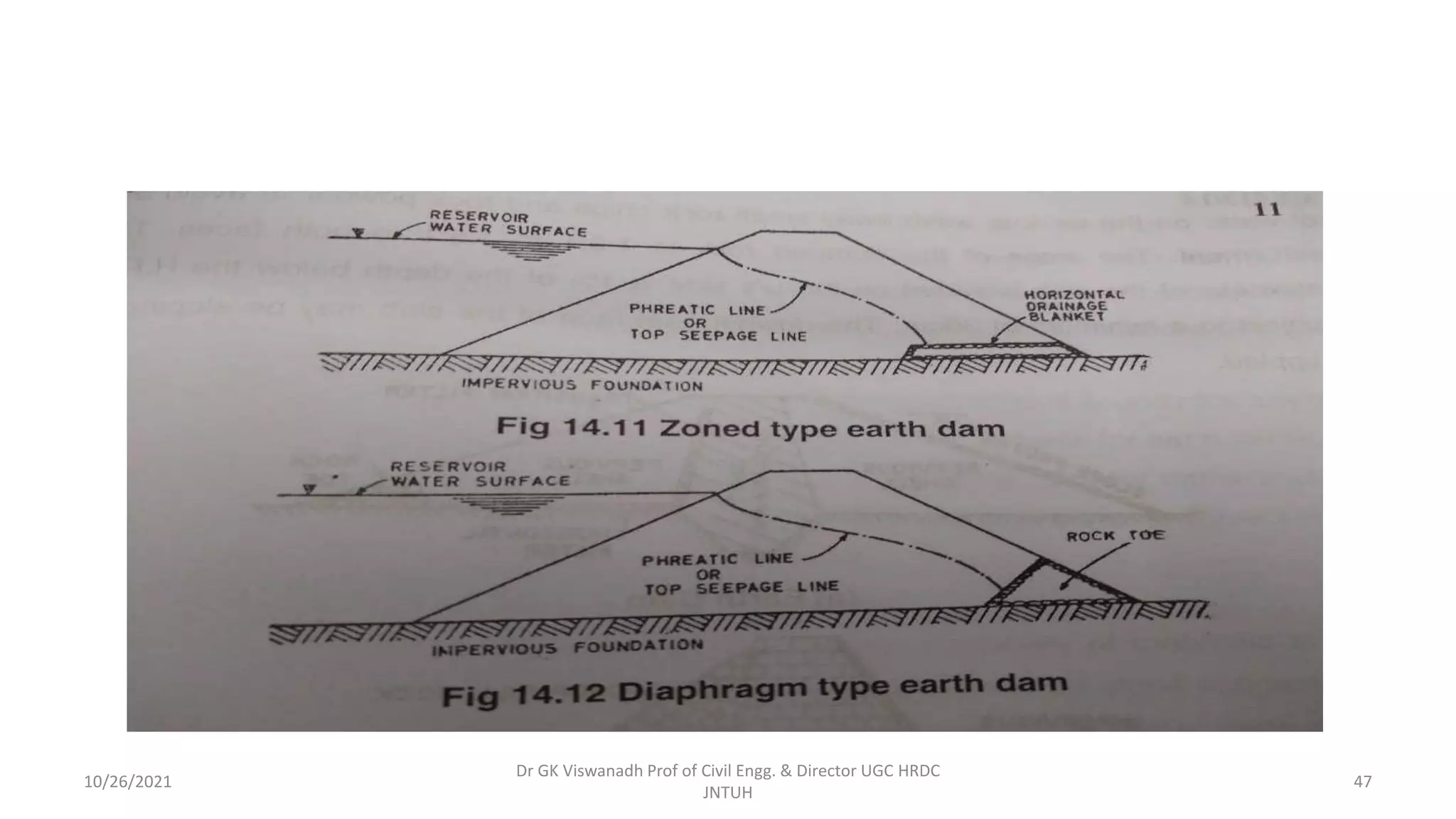
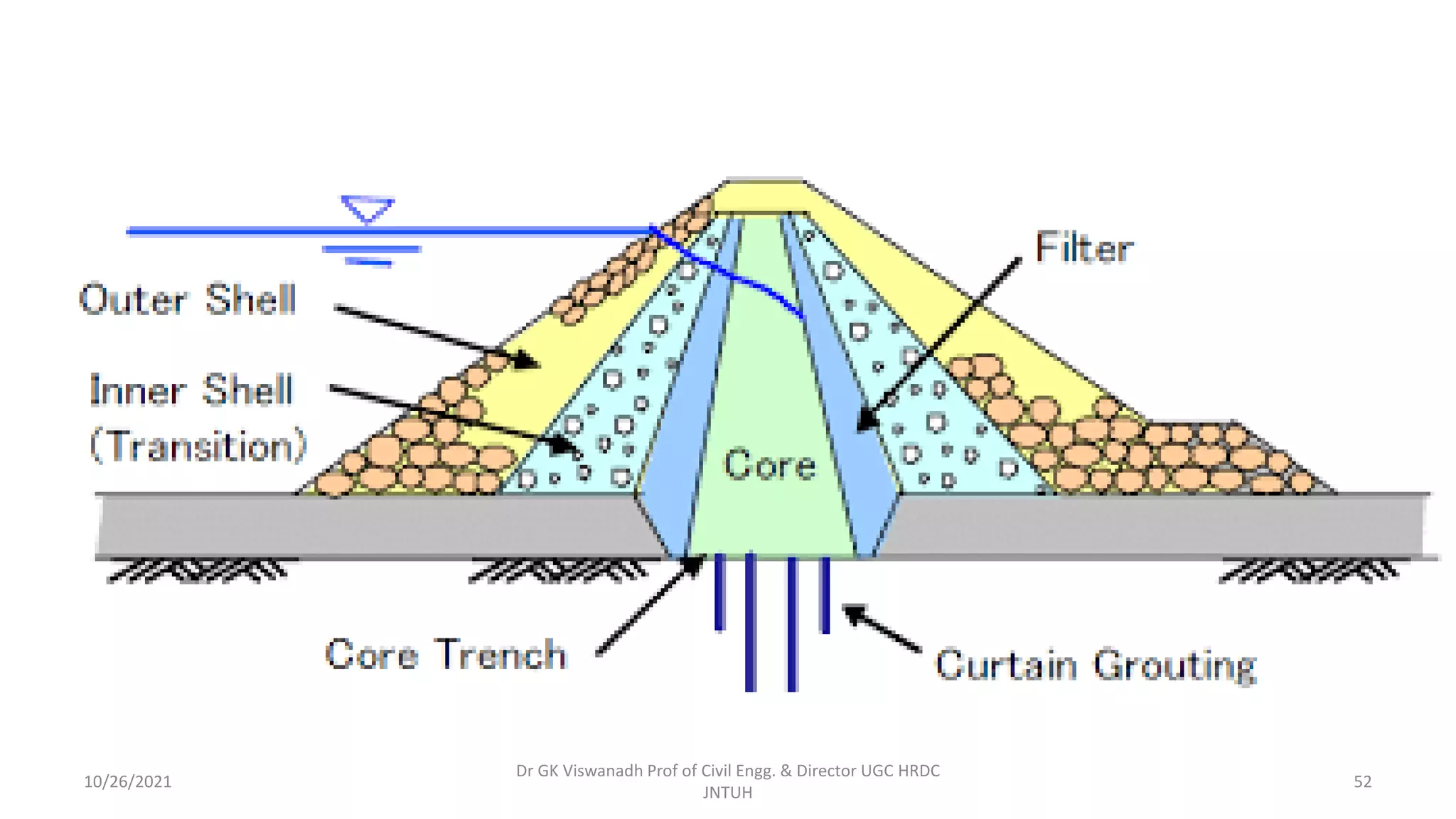
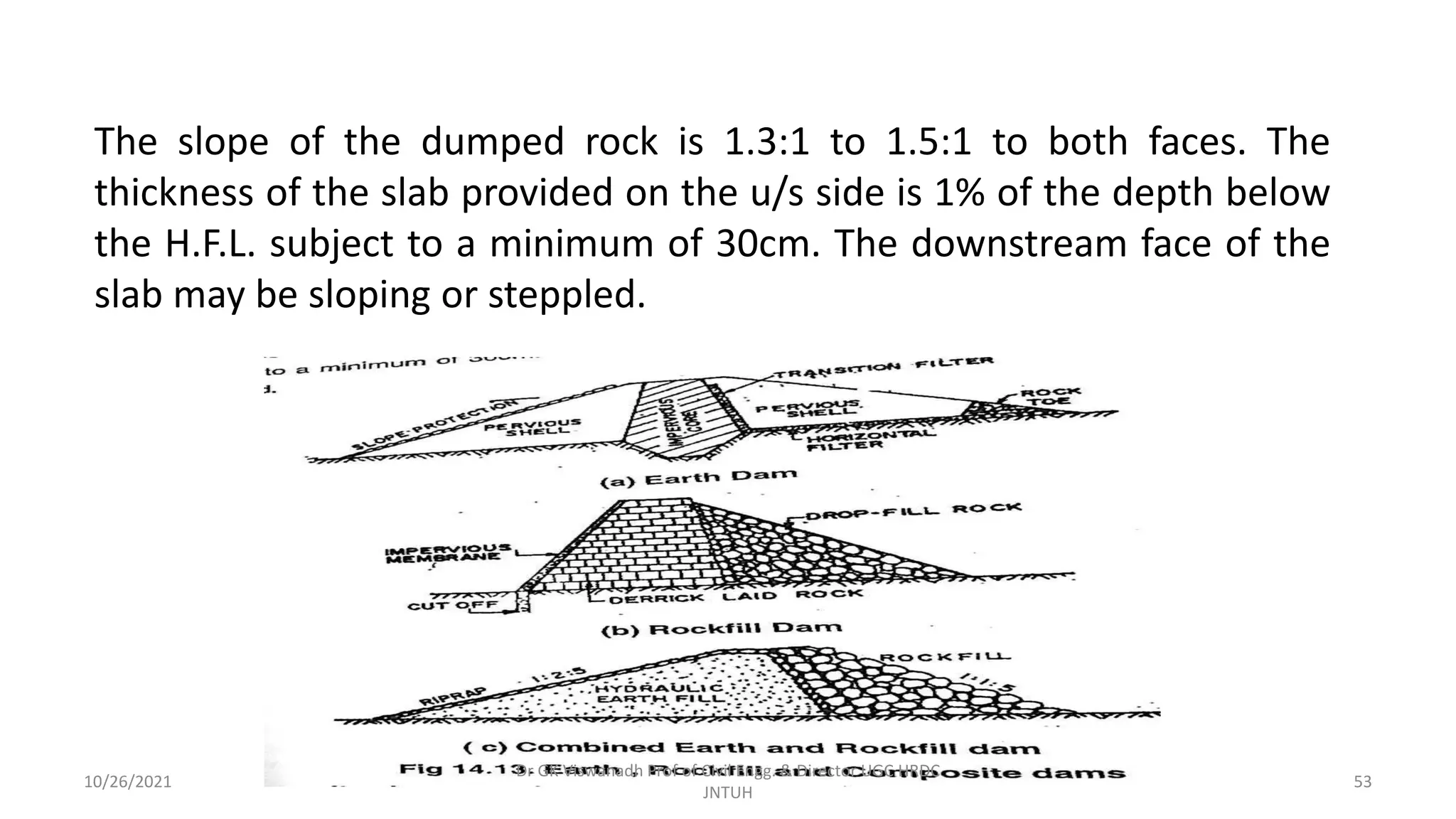
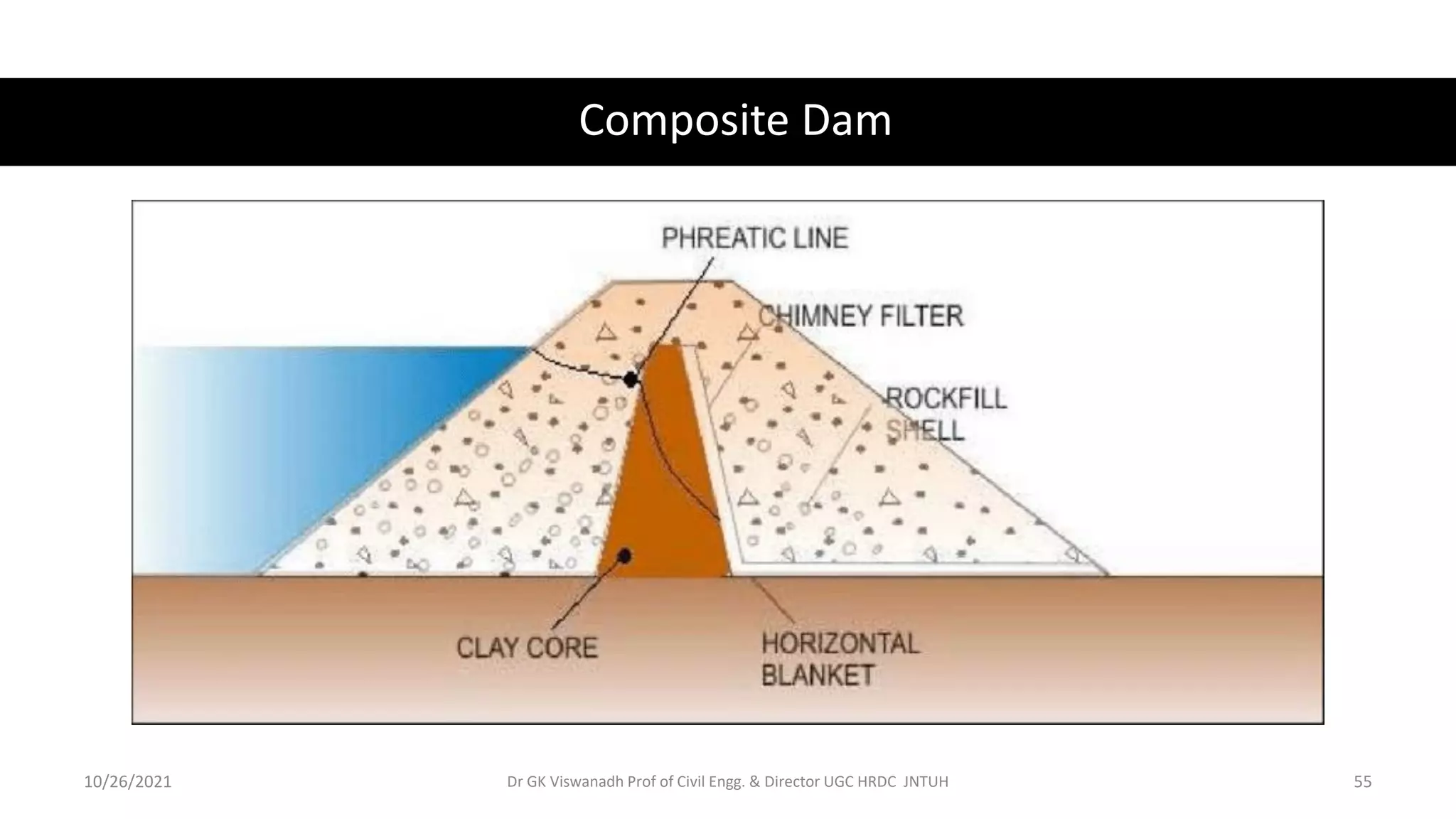
The document discusses different types of dams and reservoirs. It describes dams classified based on their function (e.g. storage, diversion), hydraulic design (e.g. overflow, non-overflow), structural design (e.g. gravity, arch, buttress), and materials used (e.g. masonry, earth). Key factors in selecting a dam type include the site conditions and intended purpose of water storage or diversion. Reservoir selection depends on factors like site, storage zones, and capacity estimation methods.