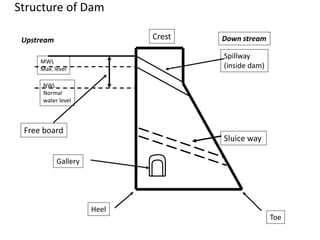
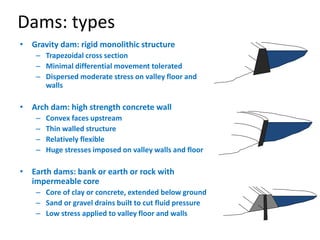
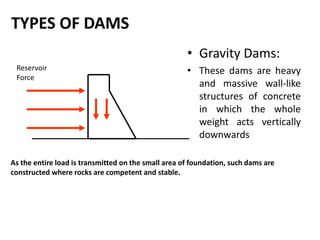
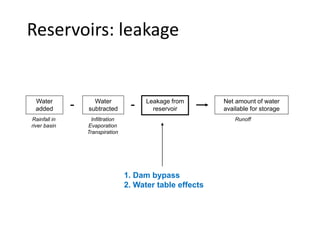
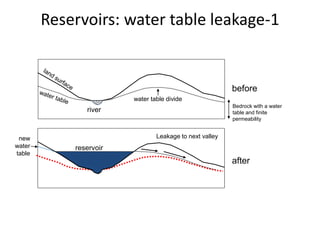
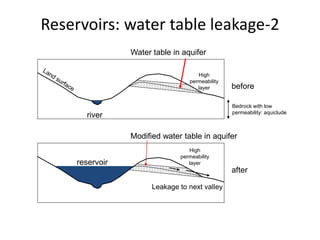
The document provides an overview of dams, including their structures, types, functions, and design considerations. It describes various dam types such as gravity, arch, buttress, earth, and composite dams, along with the purposes of reservoirs, including water storage, flood control, and hydropower generation. Key engineering and geological factors relevant to dam site selection and construction are also discussed.