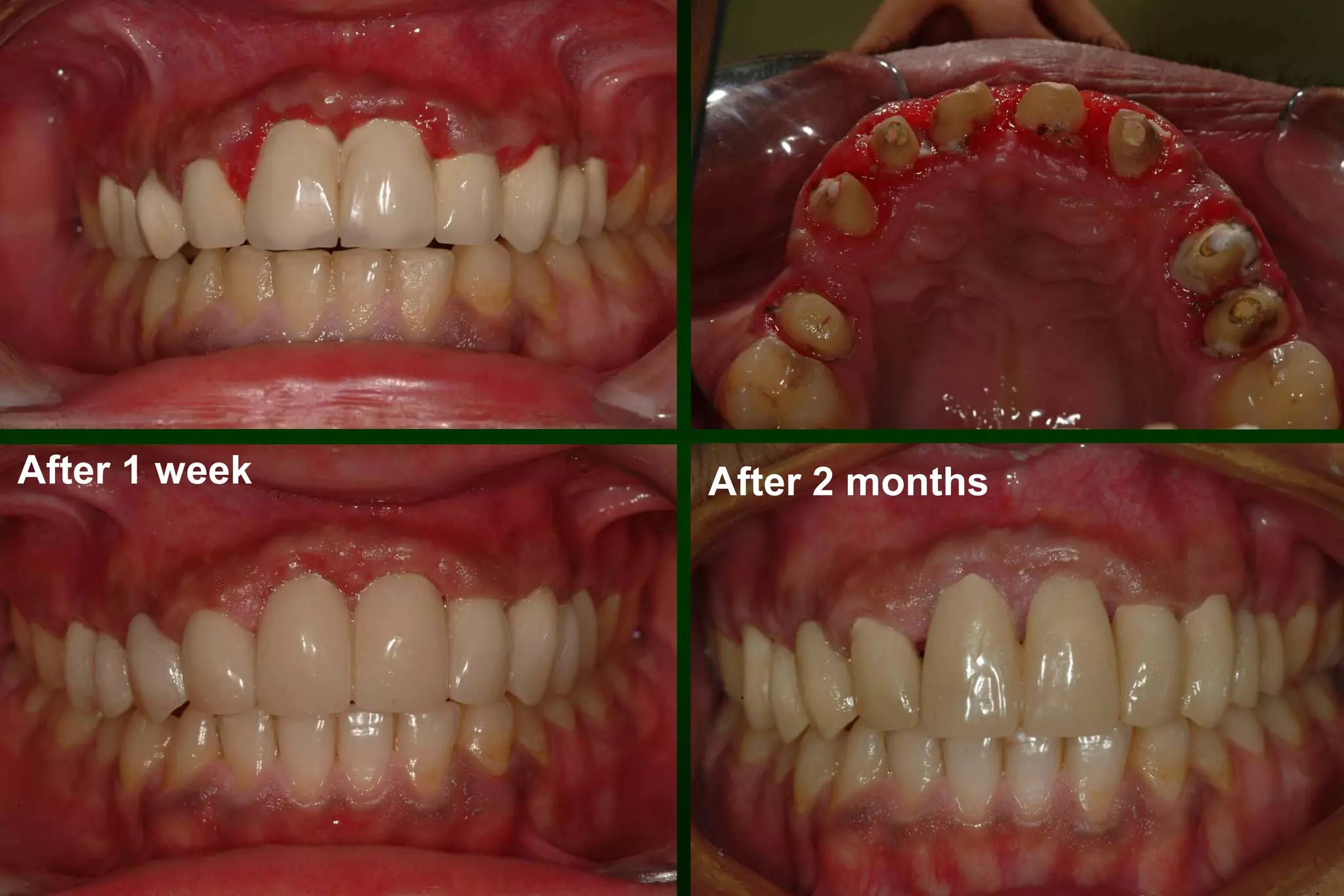
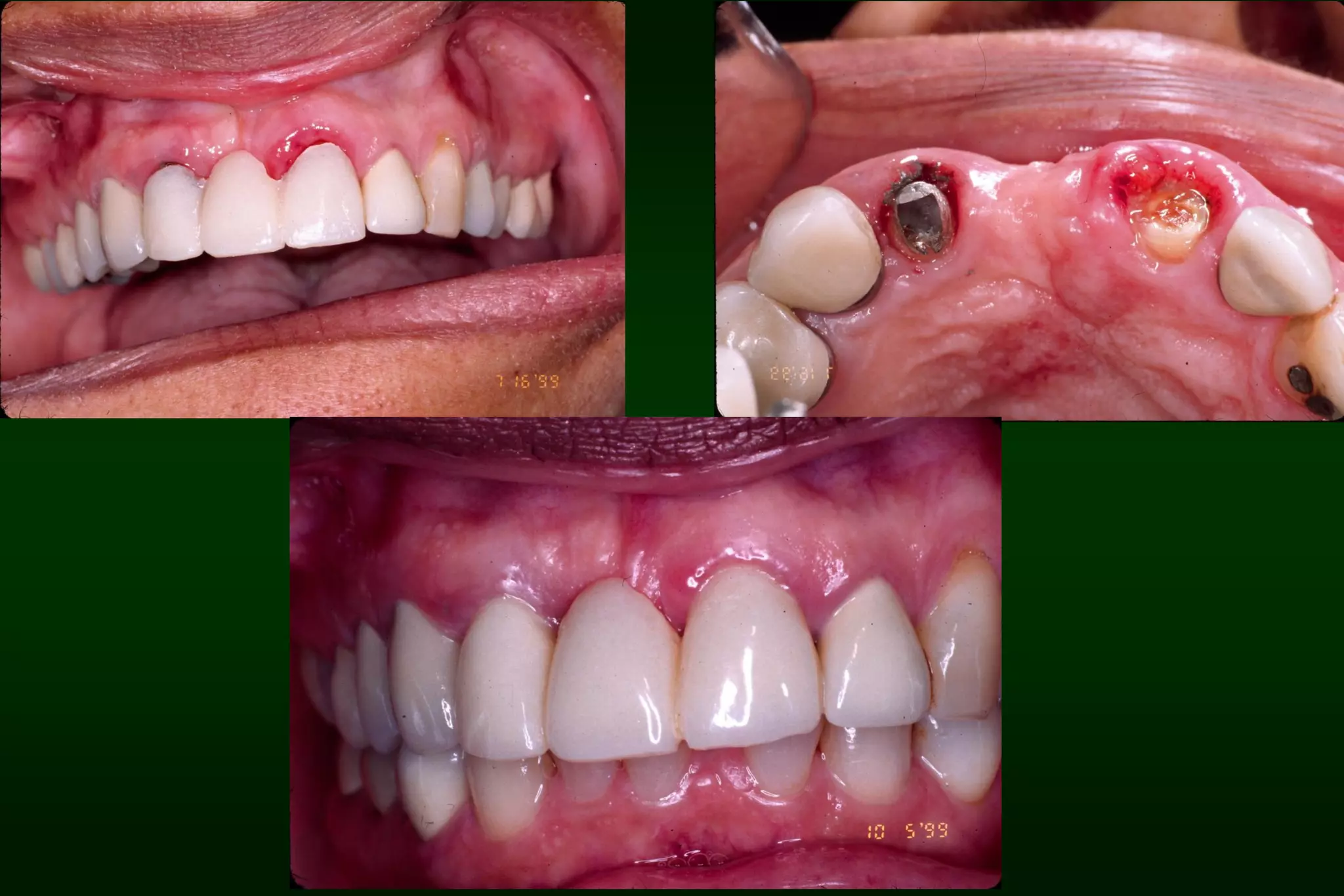
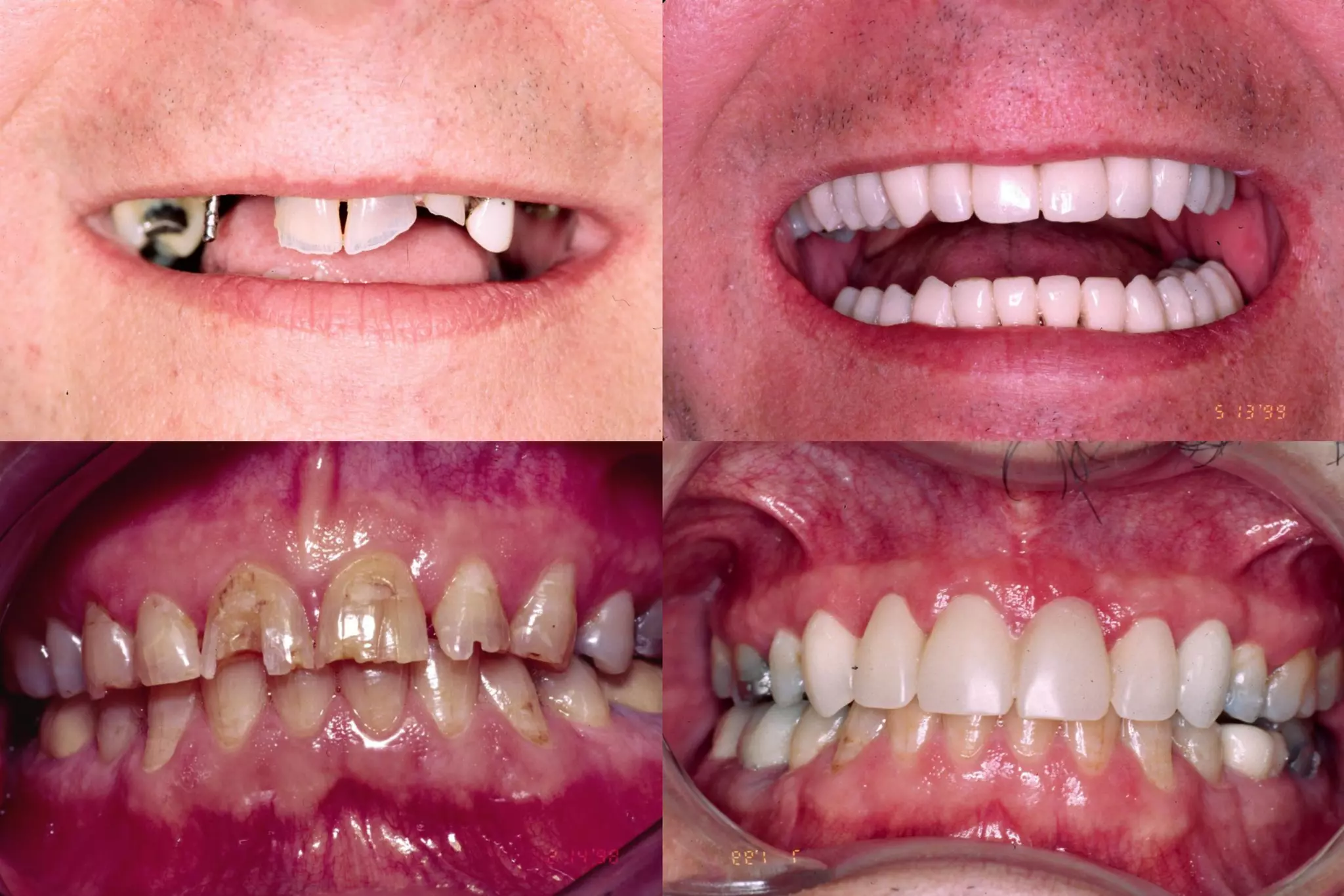
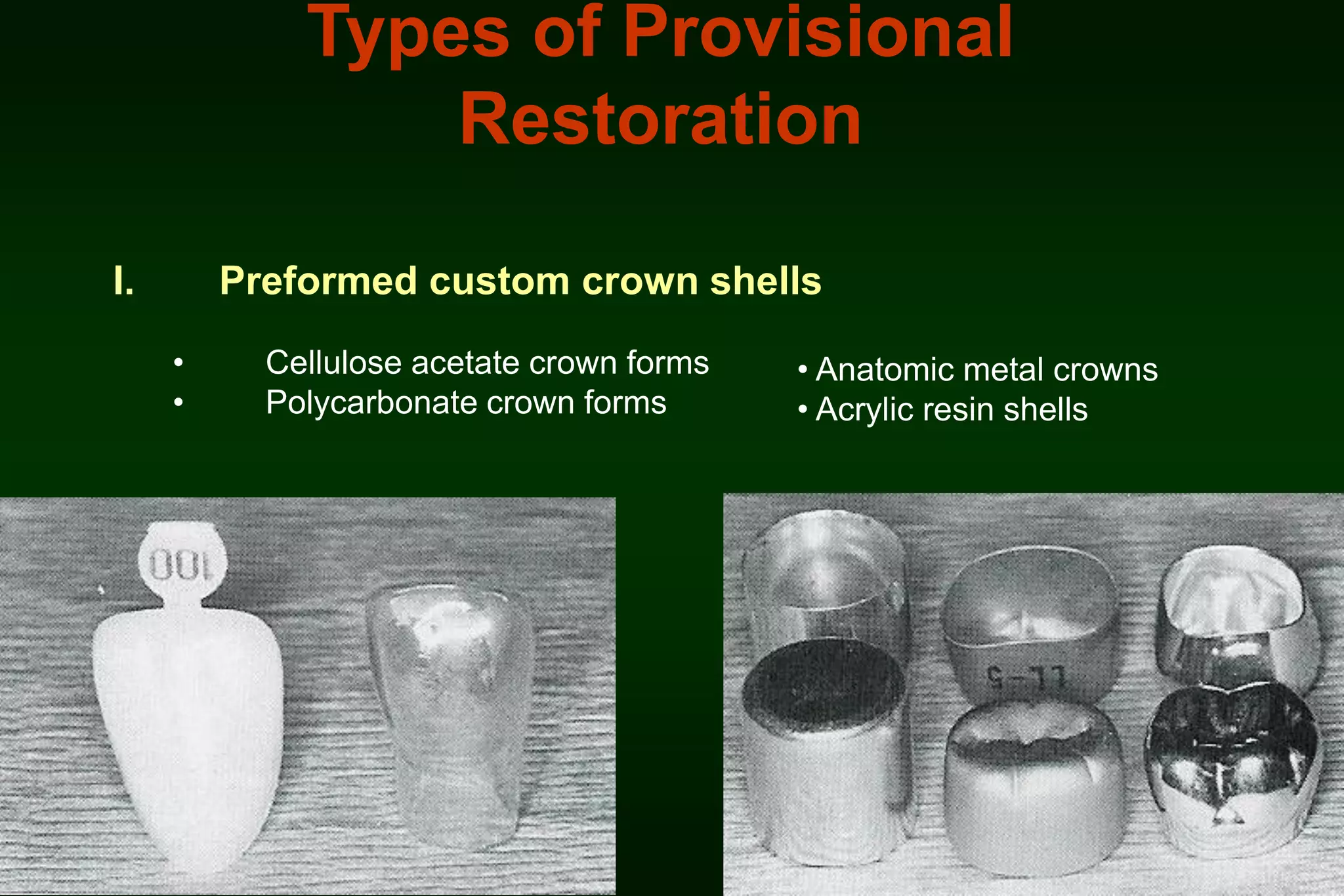
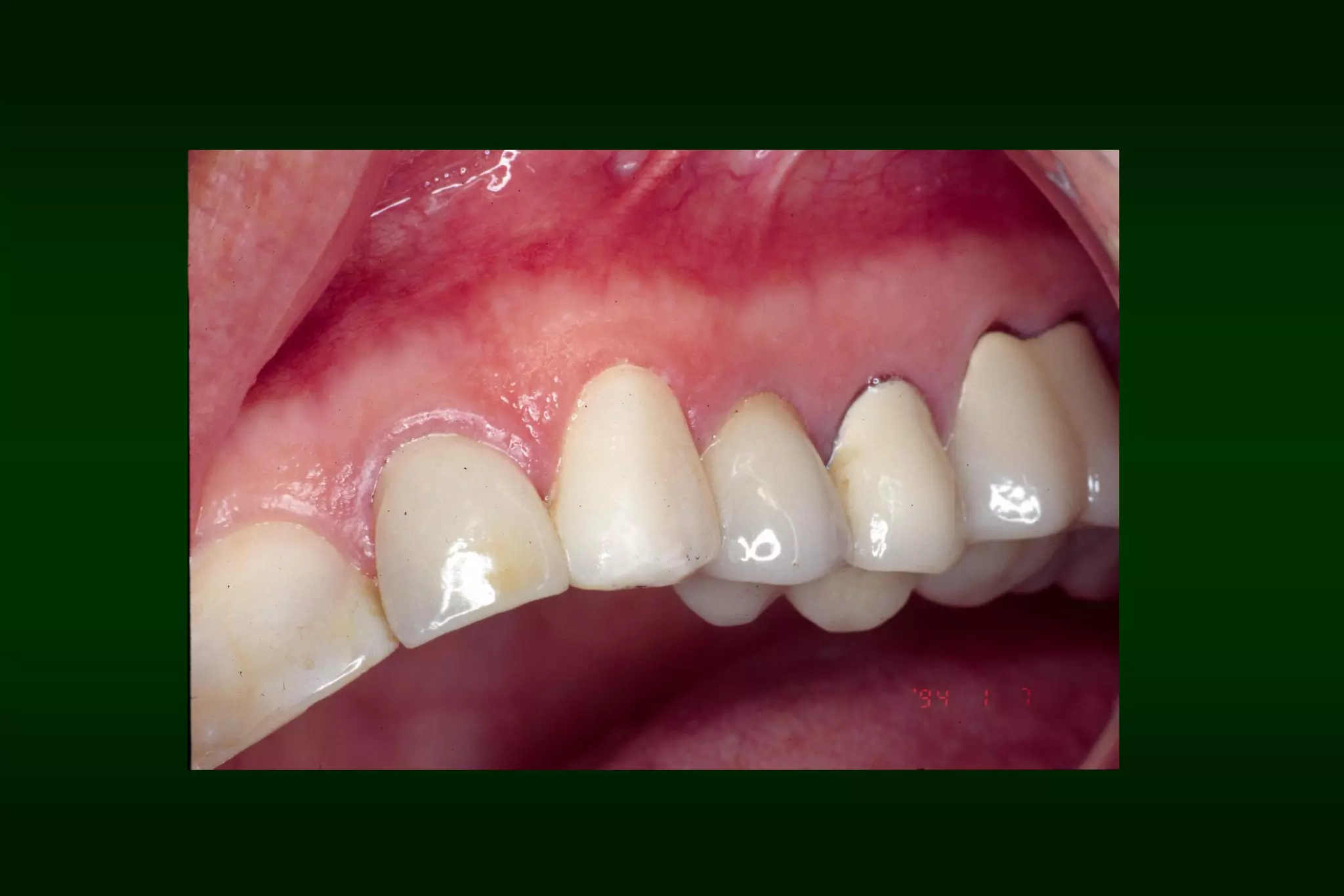
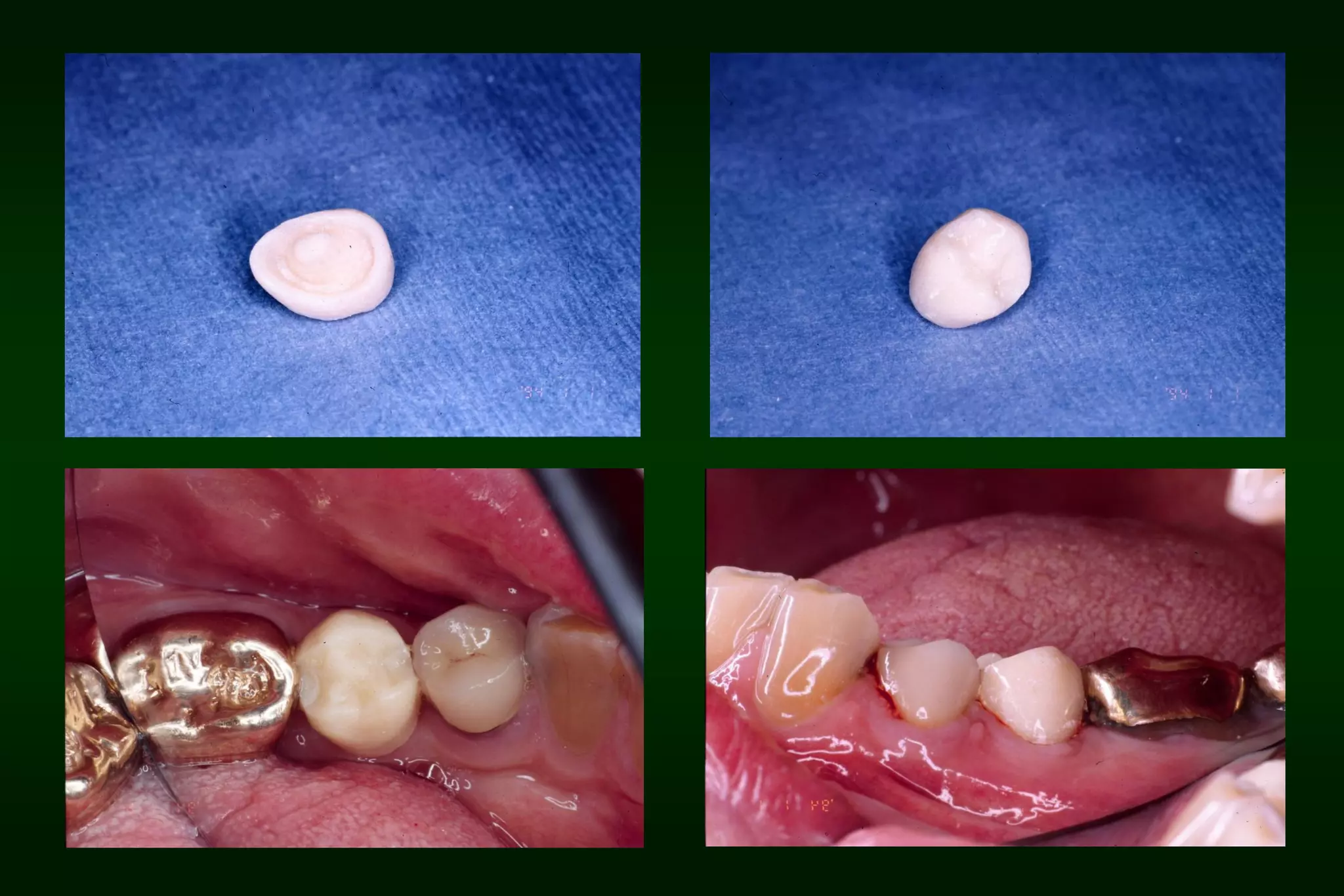
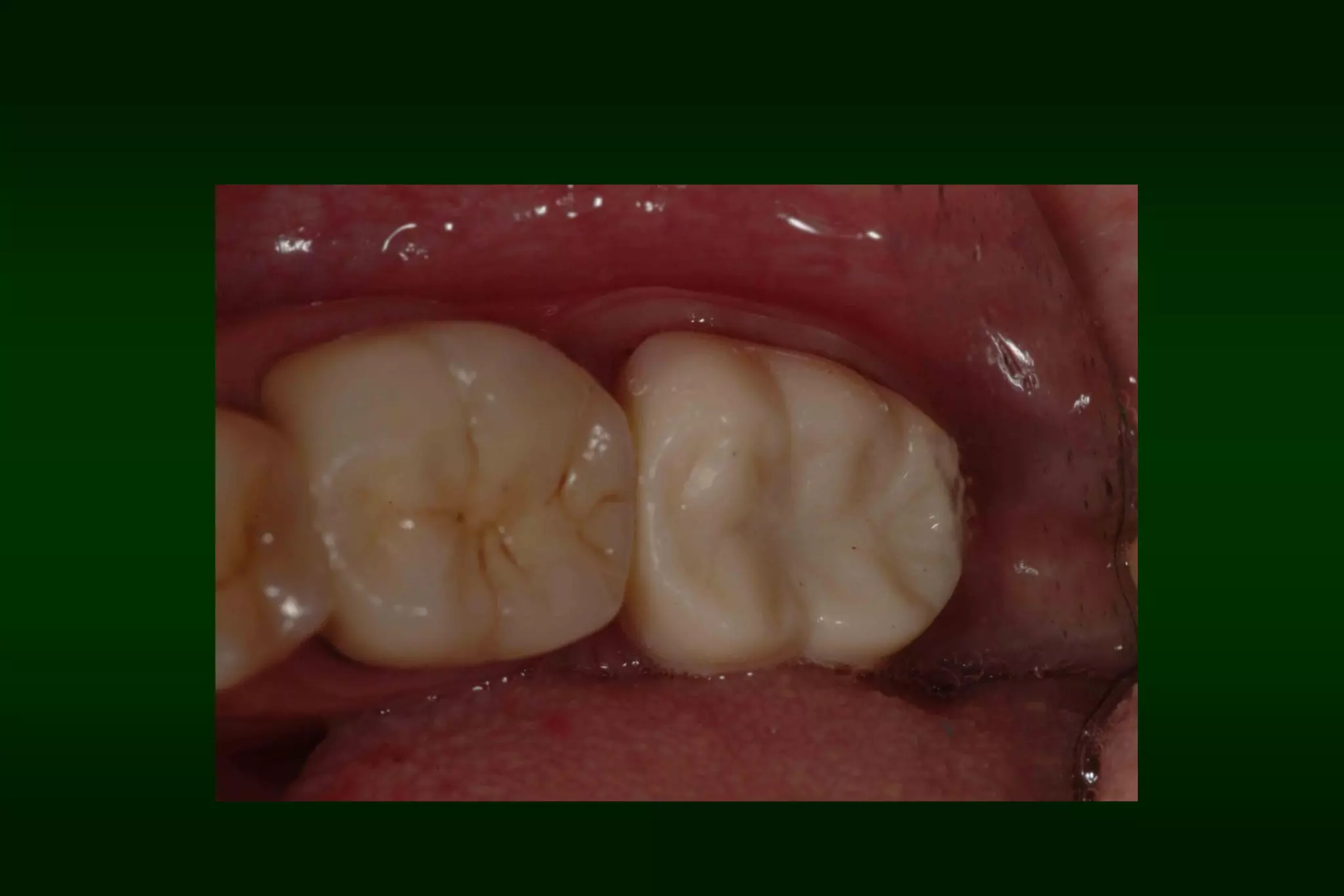
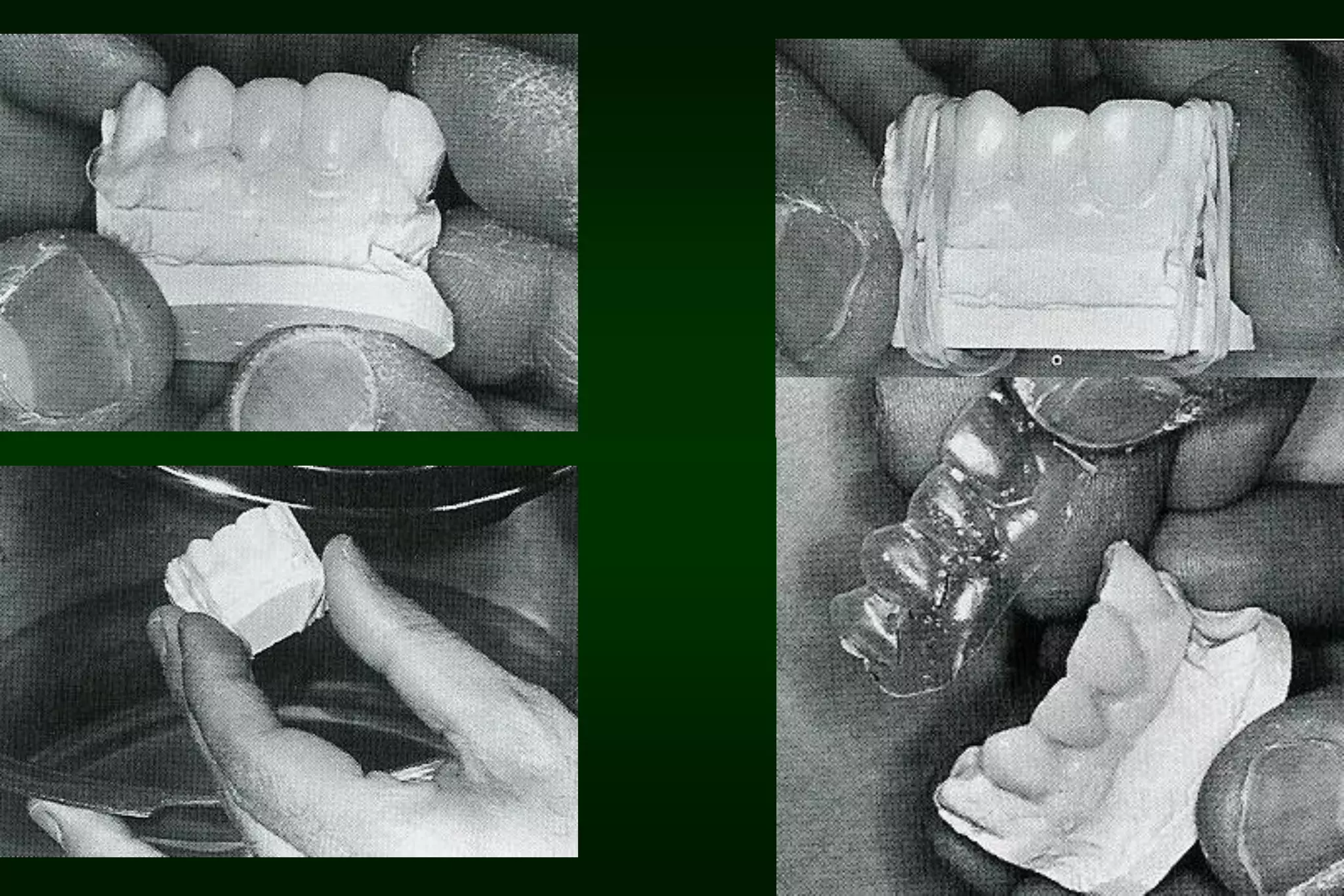
A provisional restoration is a temporary prosthesis used to enhance esthetics, stabilization, and function for a limited time period until being replaced by a definitive prosthesis, and must meet biologic, mechanical, and esthetic requirements to protect pulp, maintain periodontal health, provide functional occlusion, and resemble natural teeth. Provisional restorations can be preformed custom crown shells or customized resin restorations made using direct, indirect, or combination techniques with various acrylic resin materials that must be biocompatible, dimensionally stable, easy to contour and repair, and compatible with luting agents.