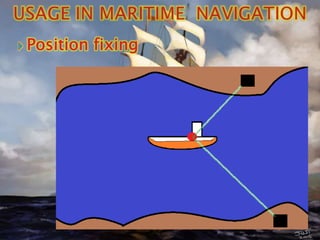
Radio direction finders (RDF) use directional antennas to compare signal strengths from radio sources and determine the direction of the source. They have been used since the early 1900s for navigation by ships, small boats, and aircraft. RDFs work by tuning a receiver to a frequency and rotating a loop antenna to find the strongest signal, indicating the direction of the radio station. Operators would take bearings from multiple stations to locate their position by plotting the intersecting bearings on a map. RDFs were commonly used for maritime navigation and aircraft before modern electronic navigation systems.