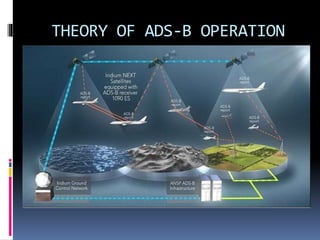
A transponder is an electronic device that produces a response when it receives a radio-frequency interrogation from air traffic control or collision avoidance systems. Transponders assist in identifying aircraft on radar by transmitting a four-digit code called a squawk code that is assigned by air traffic controllers. There are also three emergency codes that notify air traffic control of emergency situations. Secondary surveillance radar uses an aircraft's transponder to transmit additional information like altitude in response to interrogation signals to aid air traffic control. Modern ADS-B transponders automatically broadcast an aircraft's position from satellite navigation to air traffic control and other aircraft to allow self separation without secondary radar.