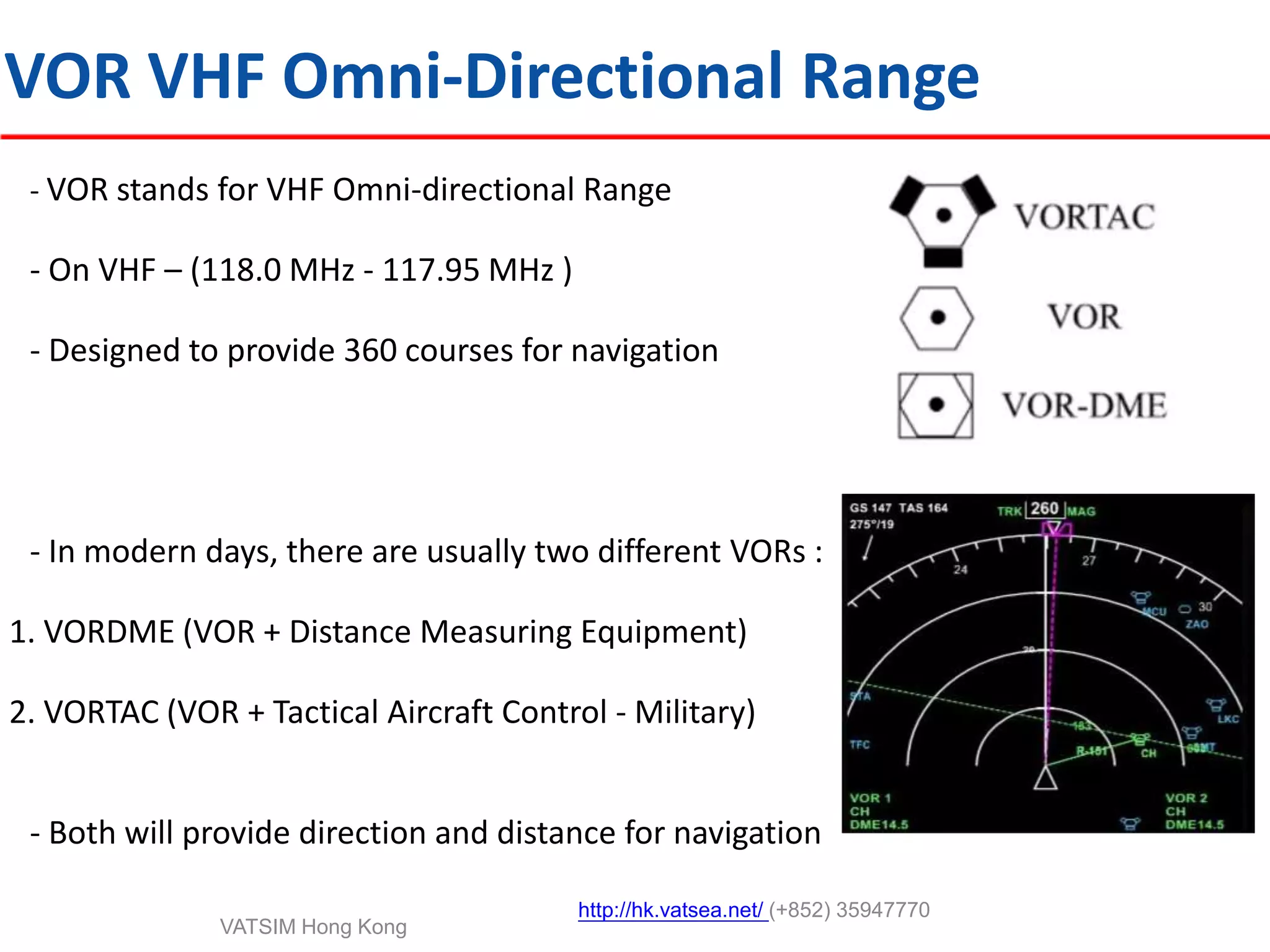
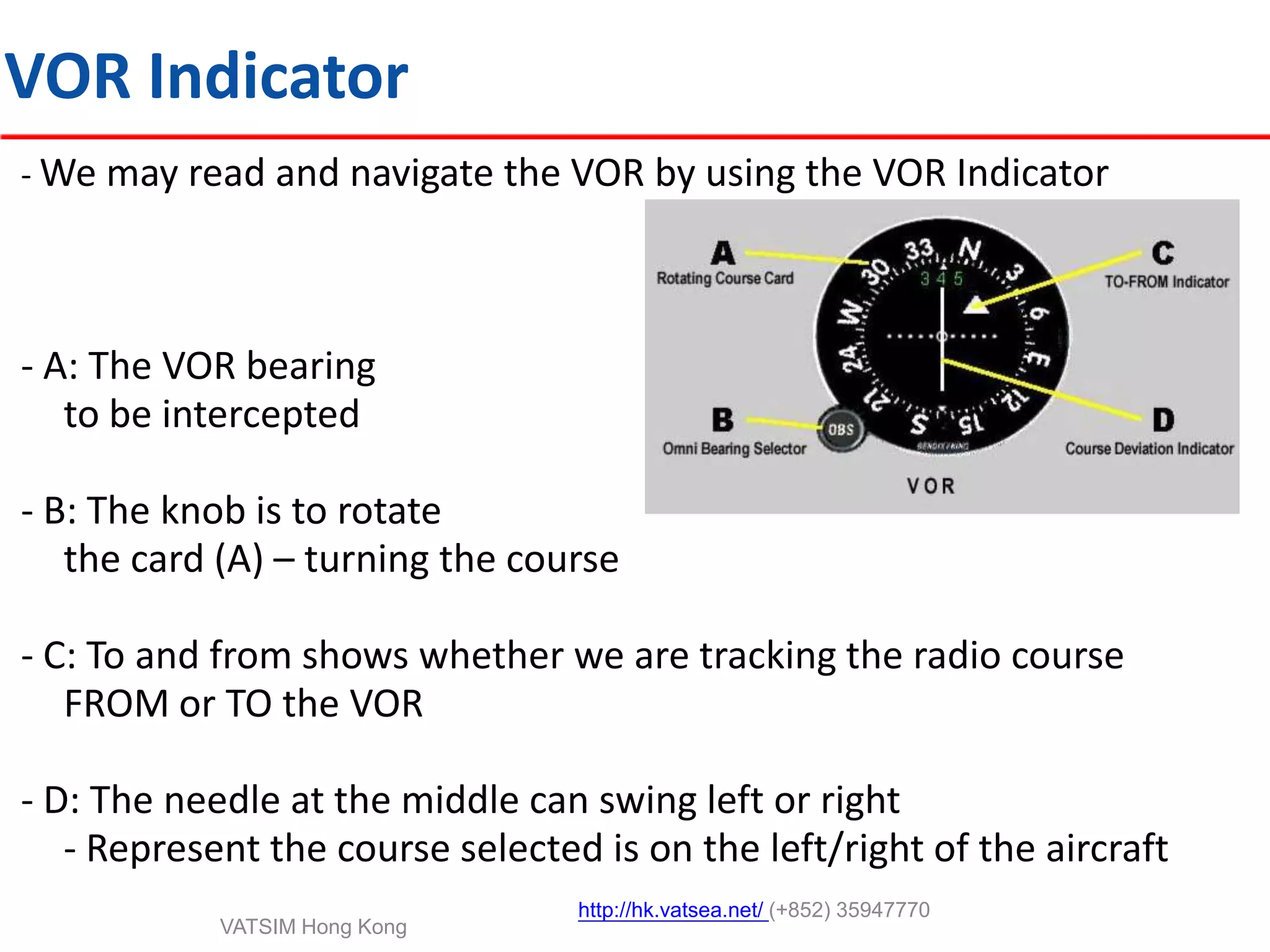
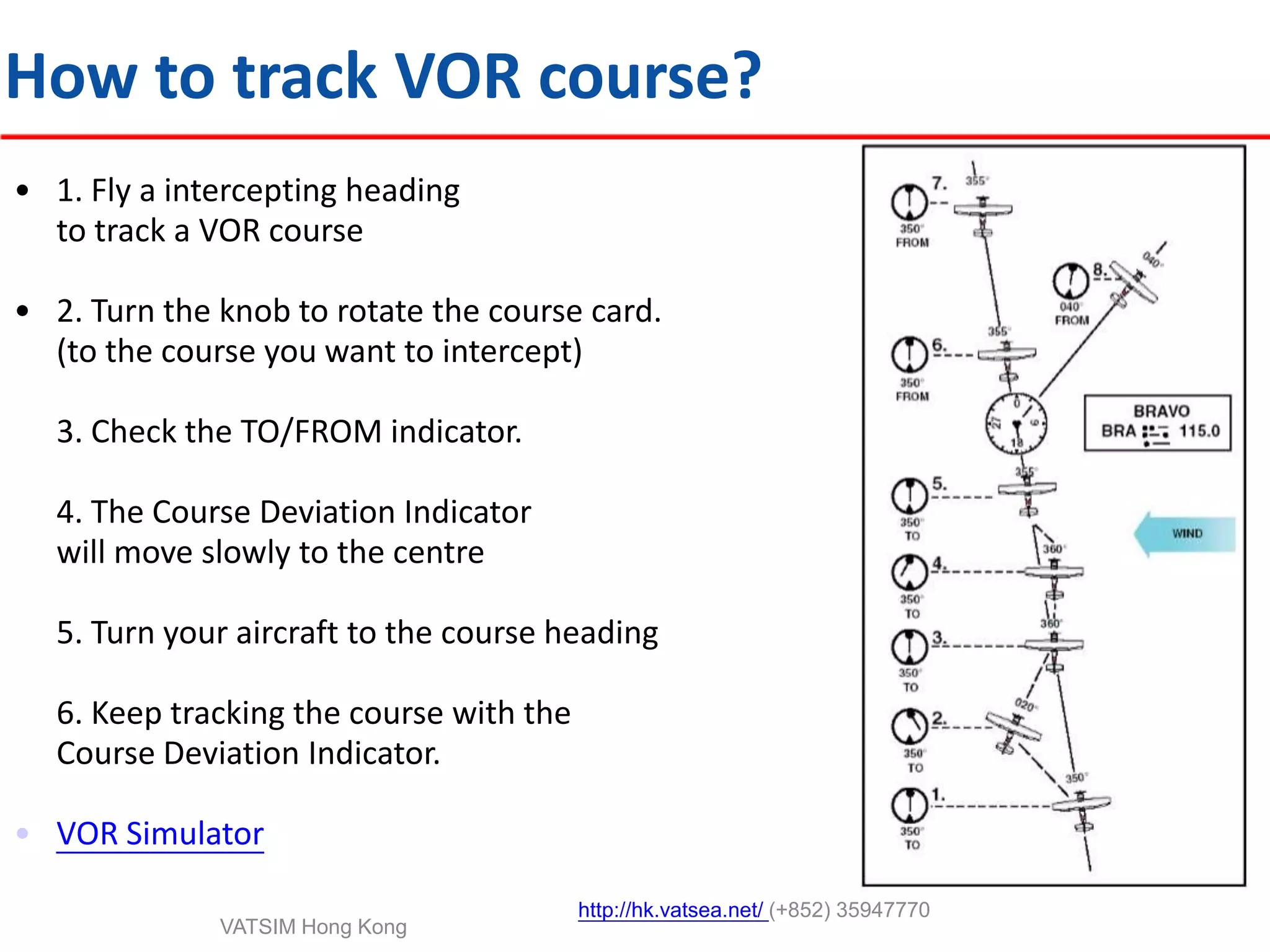
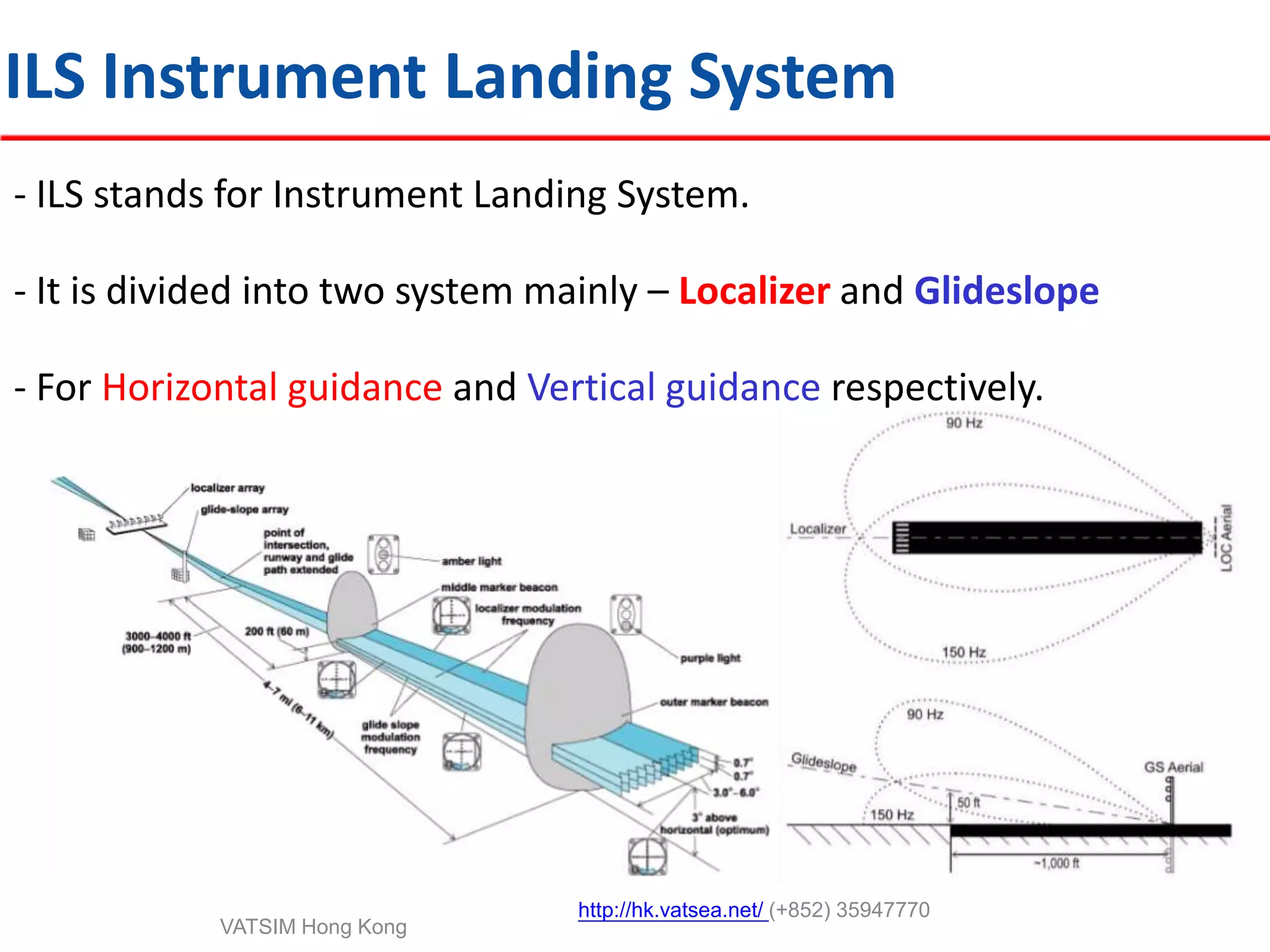
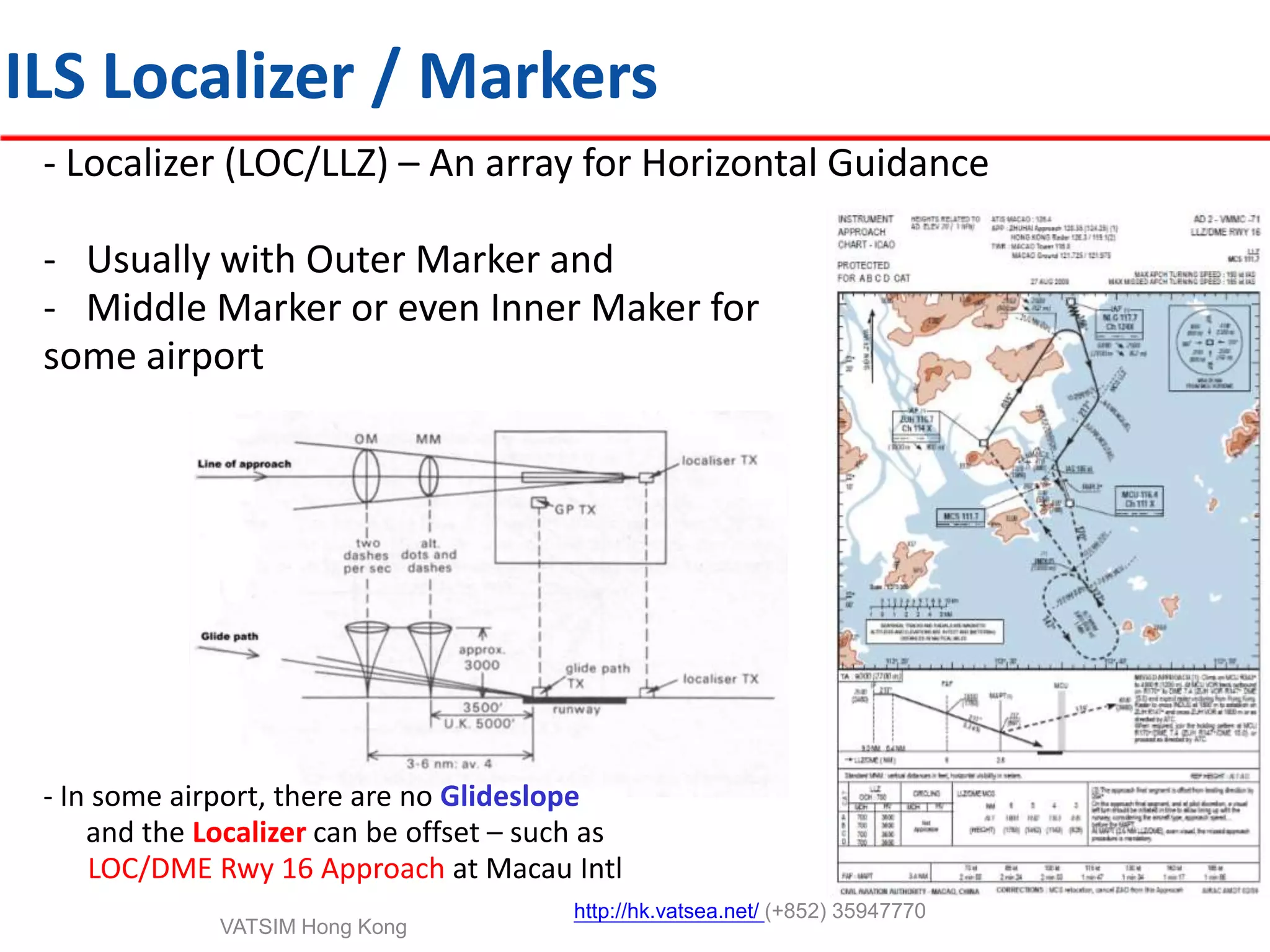
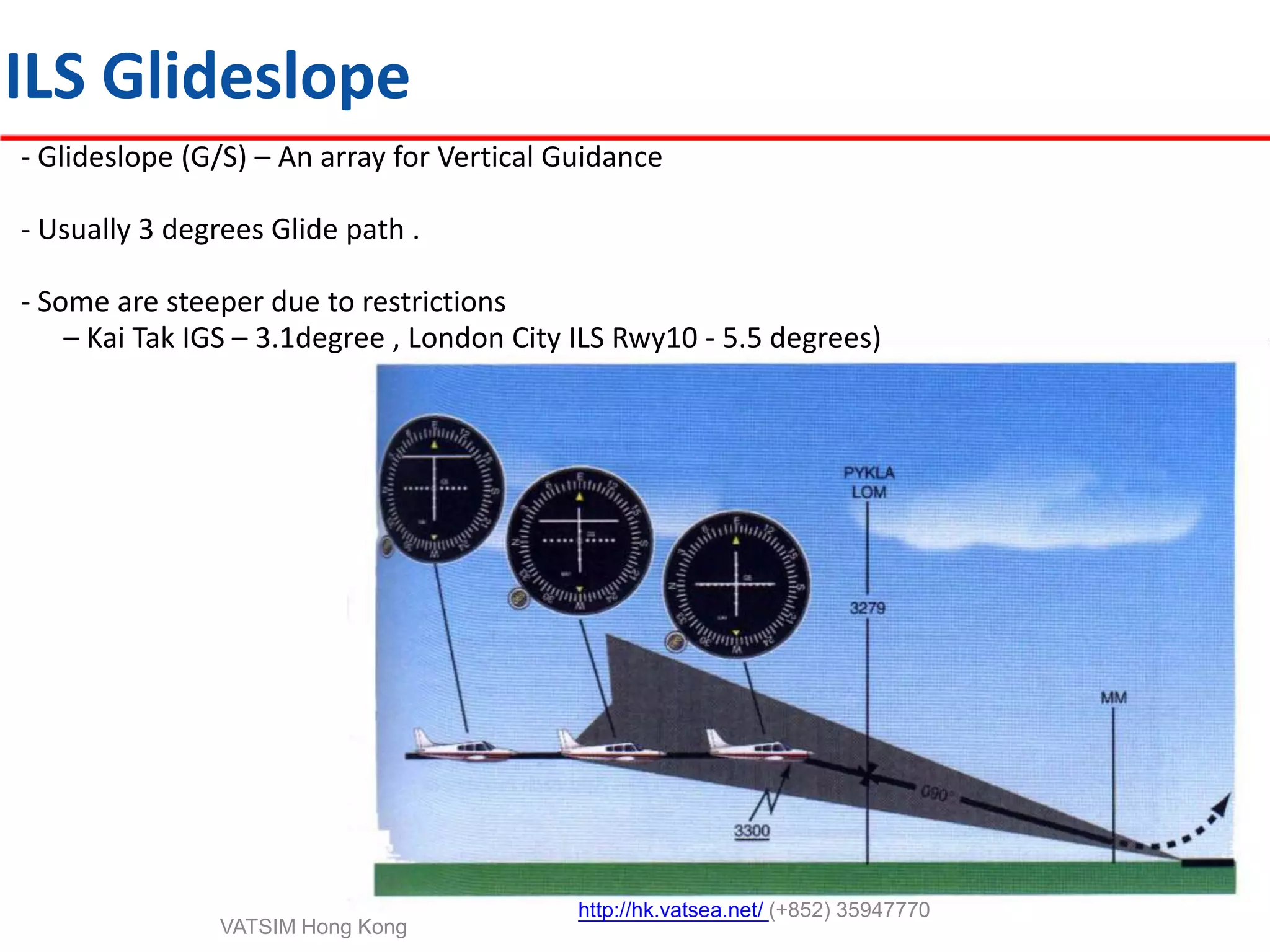
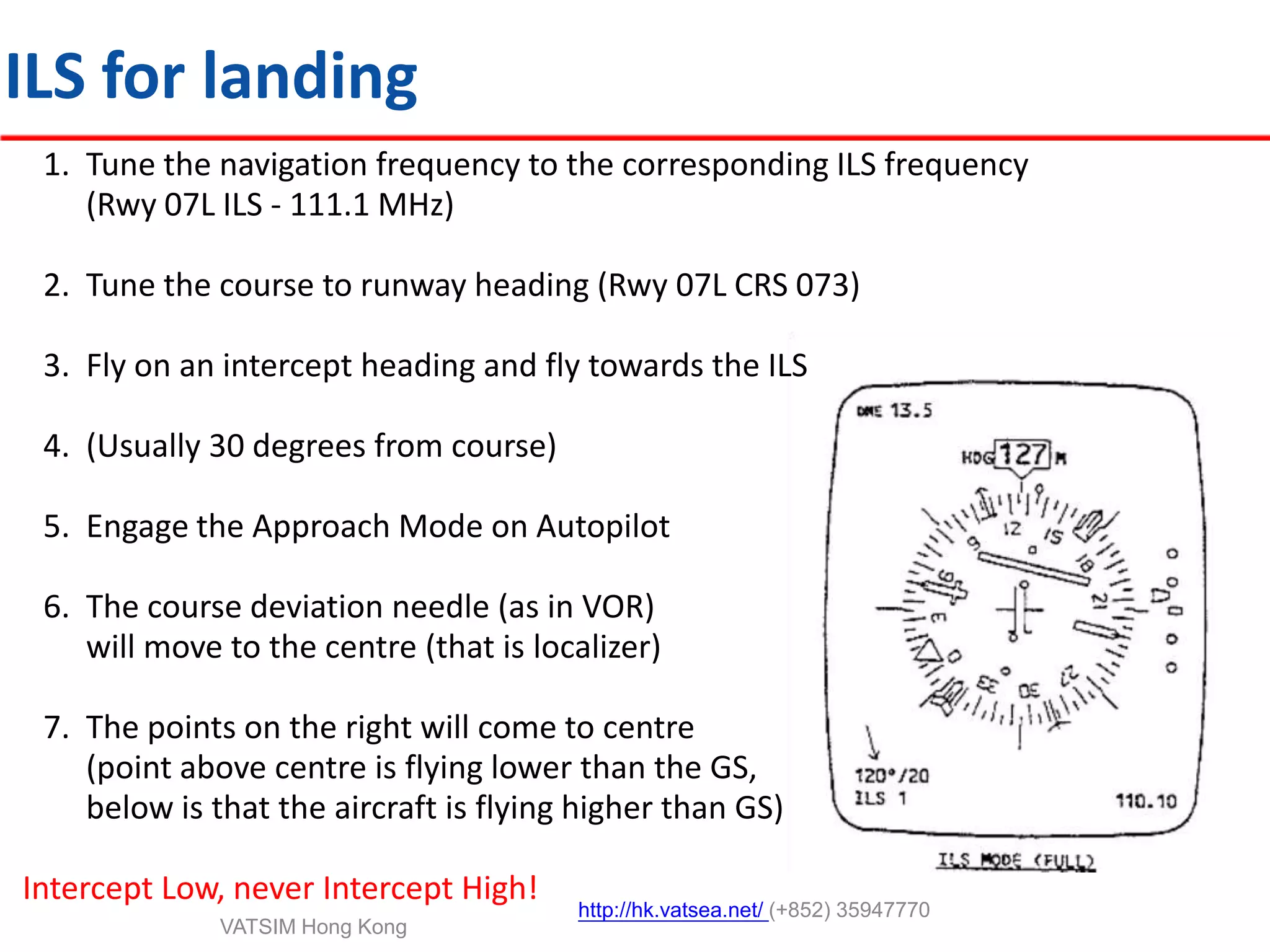
This document provides an introduction to navigation methods for aircraft, including visual flight rules (VFR), instrument flight rules (IFR), and various types of radio navigation equipment. It focuses on radio navigation methods like non-directional beacons (NDB), VHF omnidirectional range (VOR), distance measuring equipment (DME), and instrument landing system (ILS). Key aspects like tracking VOR courses, ILS localizers and glideslopes, and ILS categories are explained. The goal is to prepare pilots flying Boeing 737-800 aircraft to use radio and area navigation methods.