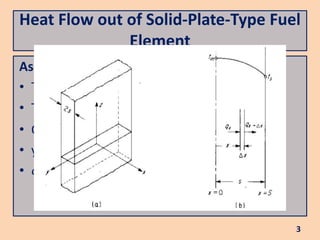
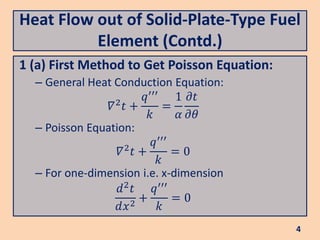
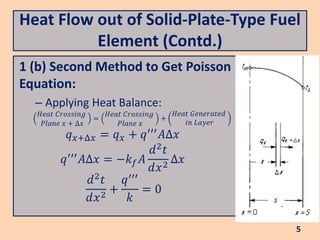
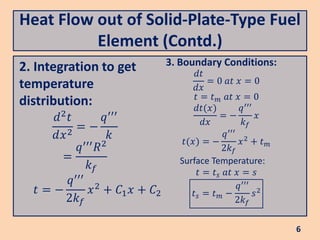
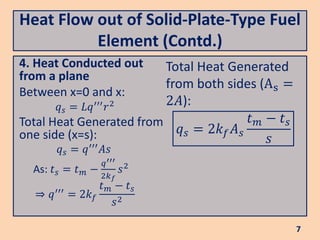
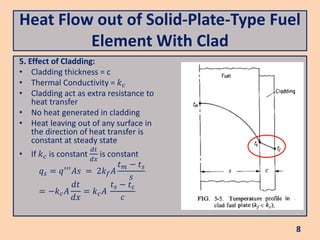
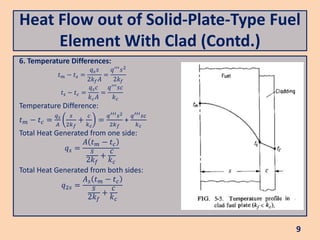
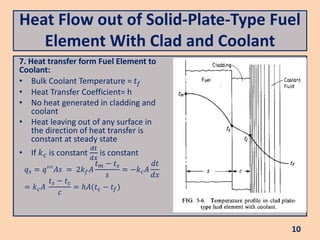
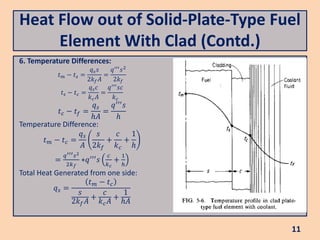
The document discusses heat flow in a solid-plate-type fuel element, detailing the methods to derive the Poisson equation for heat conduction and temperature distribution. It explains the effects of thermal conductivity, boundary conditions, and the impact of cladding on heat transfer. Additionally, it covers the heat transfer from the fuel element to coolant and the resulting temperature differences.