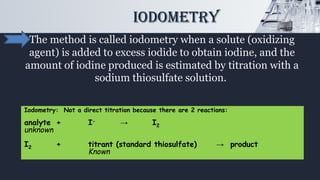
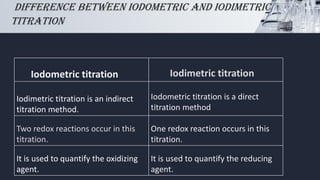
The document discusses iodometric and iodimetric titrations, which are analytical chemistry methods used to determine concentrations of unknown solutions. Iodometry involves indirect titration to estimate oxidizing agents, while iodimetry involves direct titration to quantify reducing agents. The document also highlights various applications of these methods, particularly in determining sulfites, hydrogensulfites, sulfides, and hydrogensulfides.