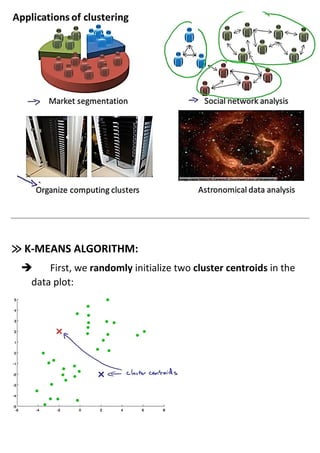
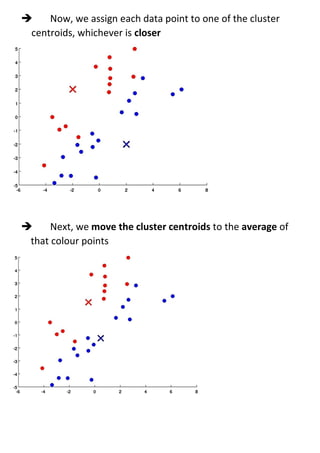
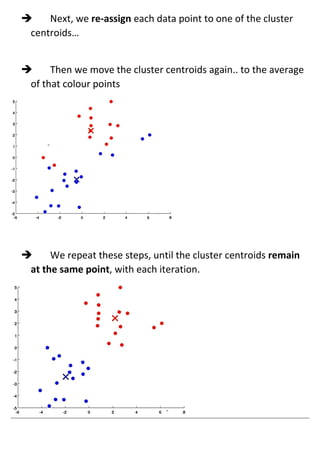
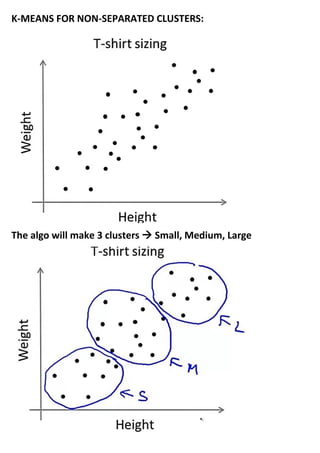
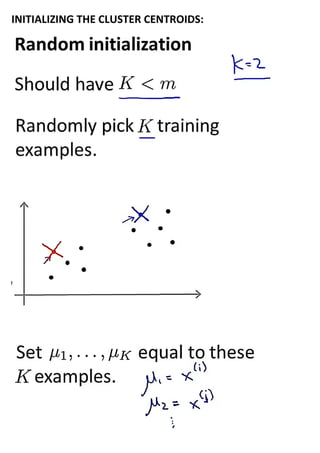
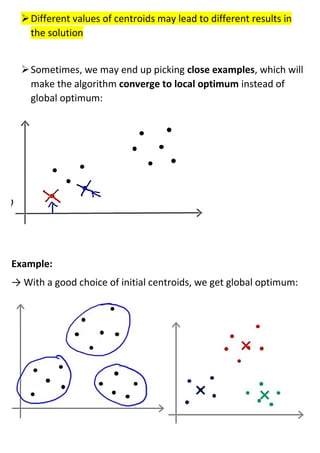
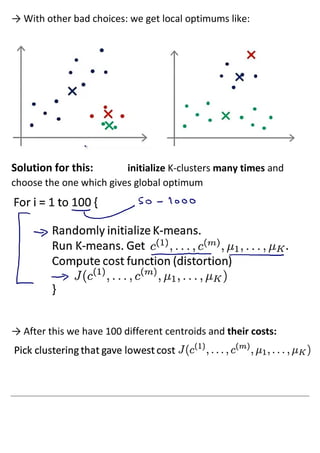
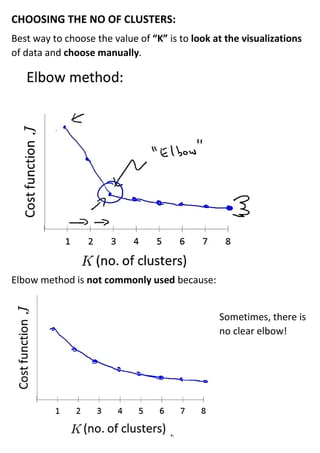
Unsupervised learning uses unlabeled datasets to group inputs into clusters without provided outputs. The k-means clustering algorithm initializes cluster centroids randomly and assigns data points to the closest centroid, iteratively moving centroids to cluster averages until convergence. It aims to minimize the squared distance between points and centroids, optimizing a distortion cost function through alternating cluster assignment and centroid movement steps until local or global optimization is reached. Proper initialization of centroids and choosing the number of clusters k is important for k-means effectiveness.