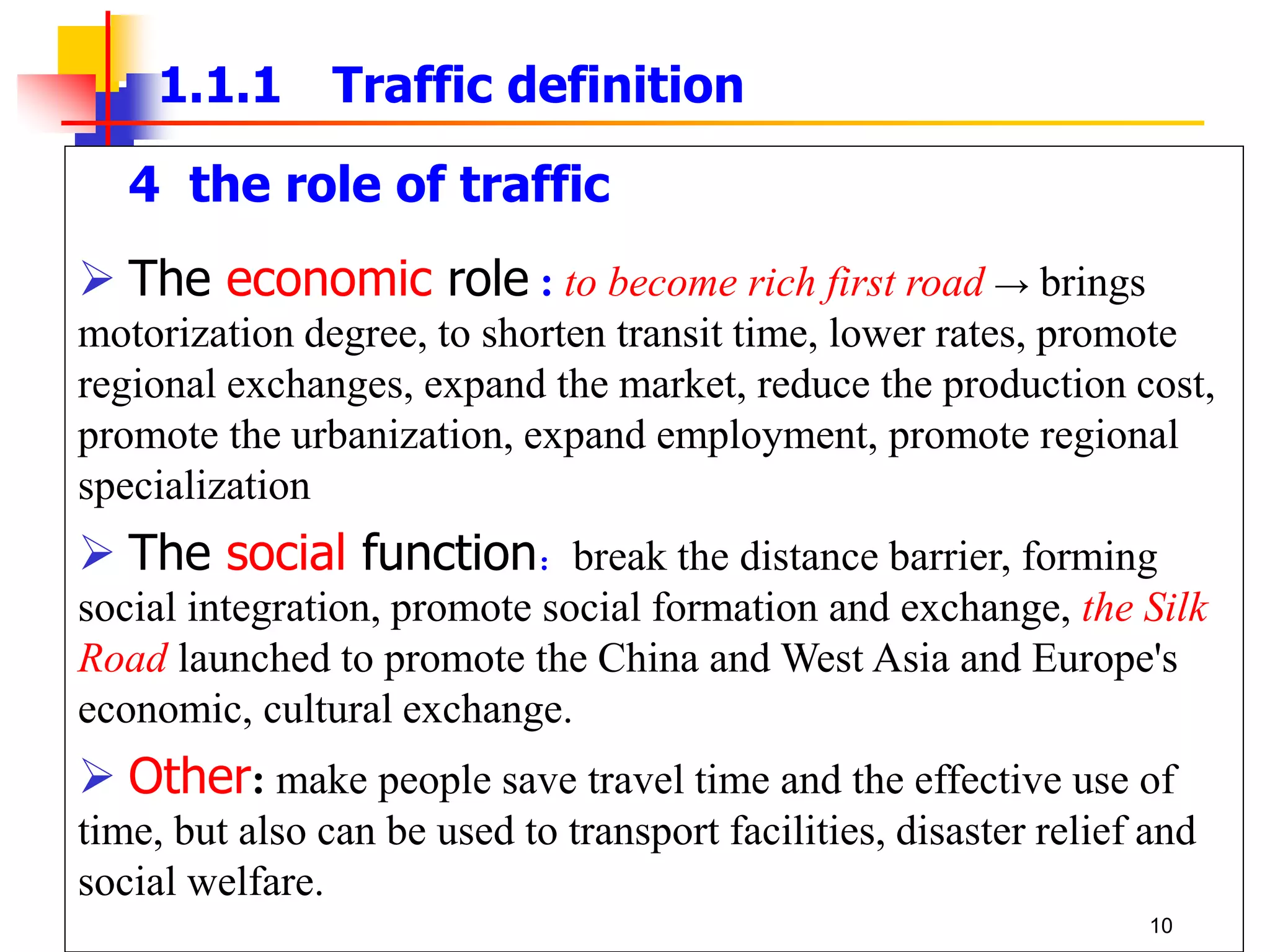
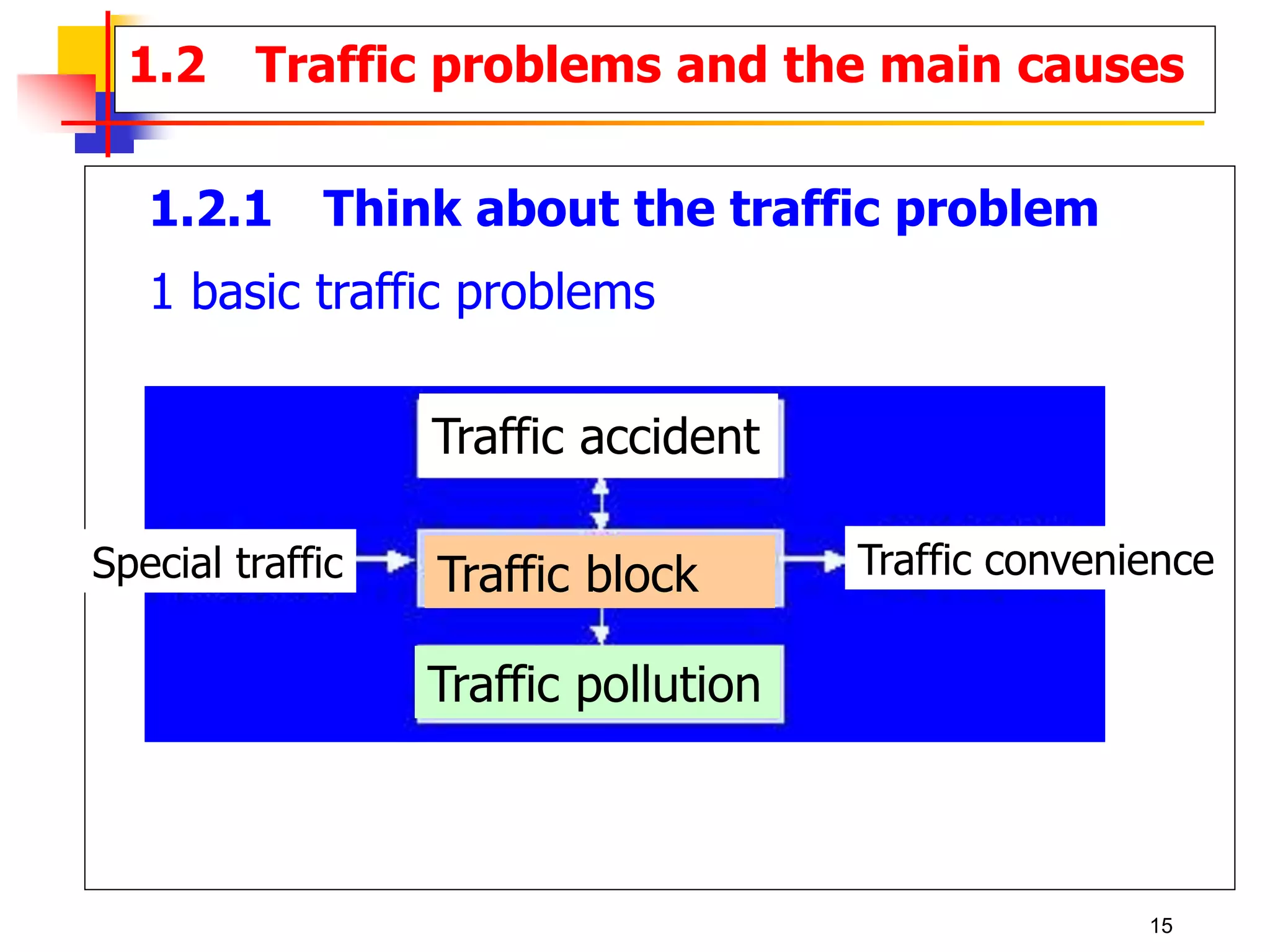
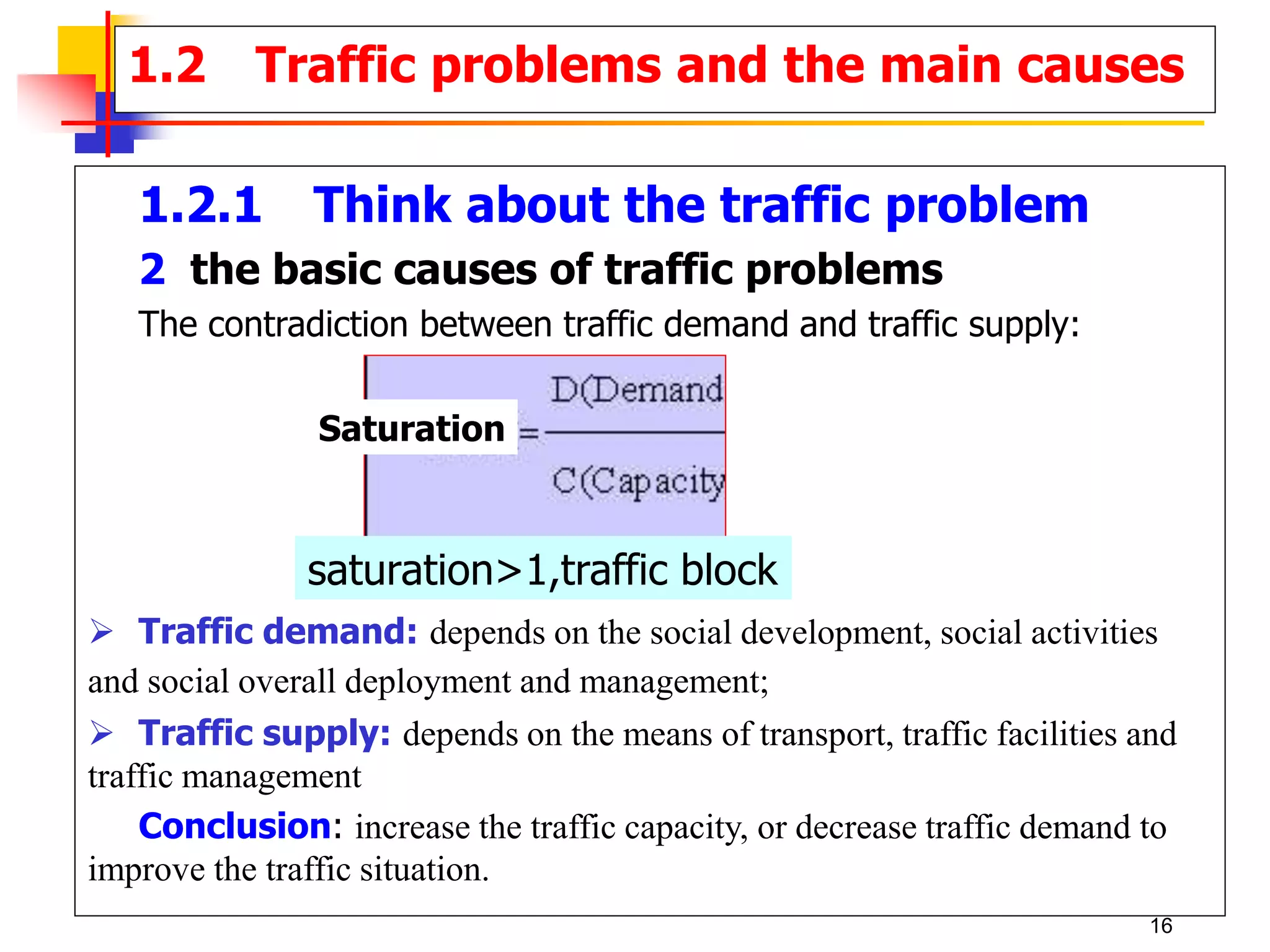
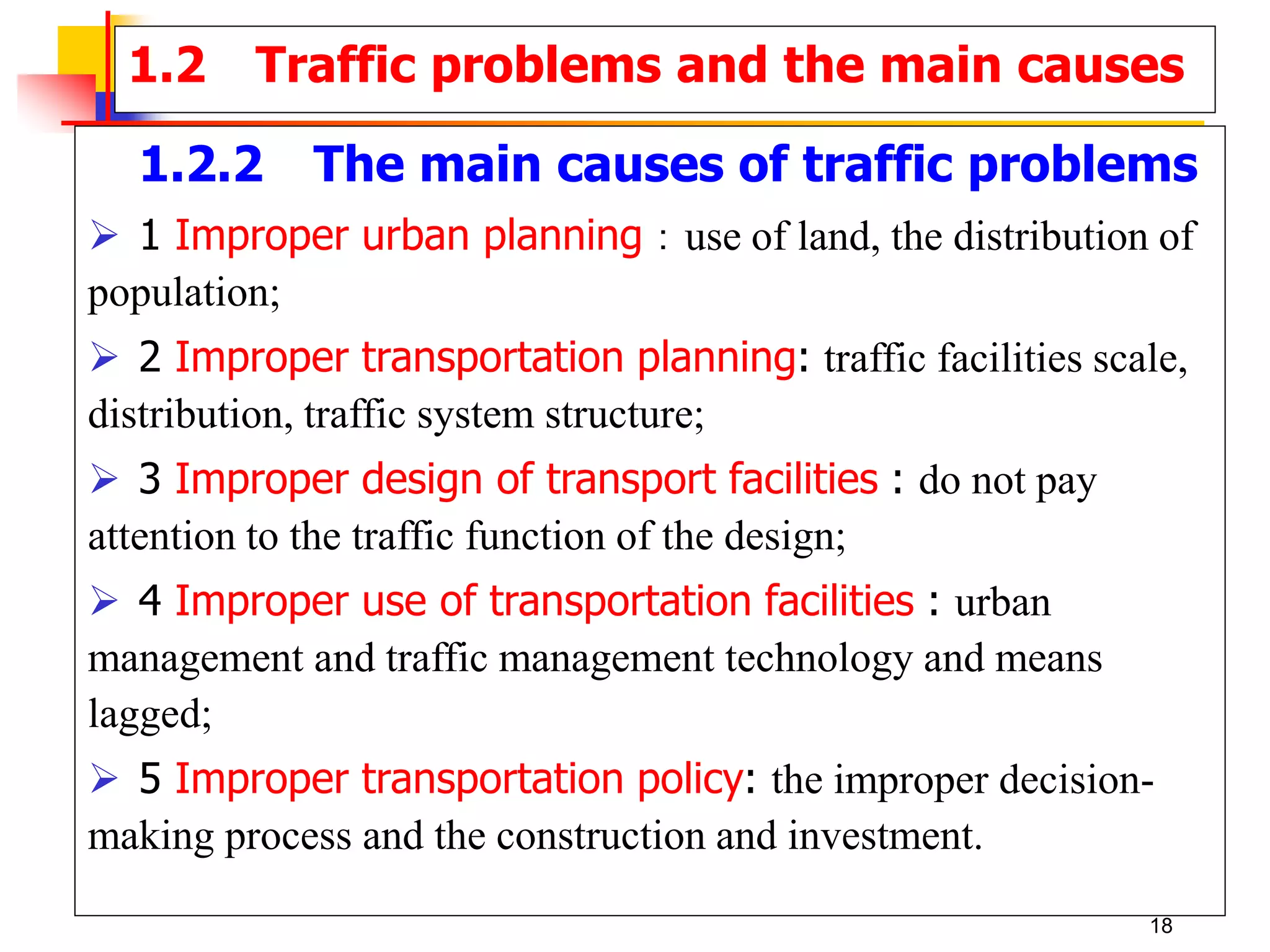
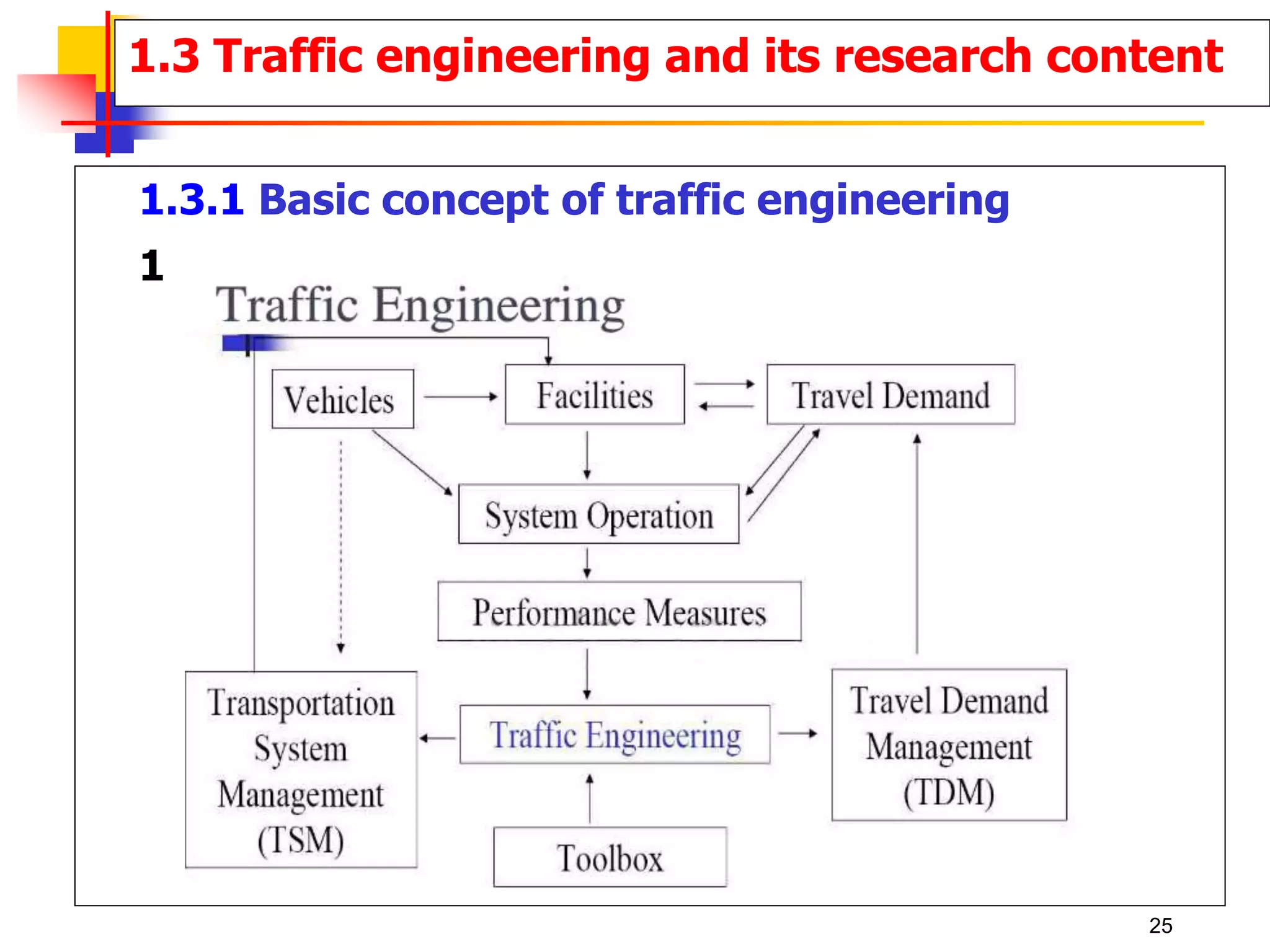
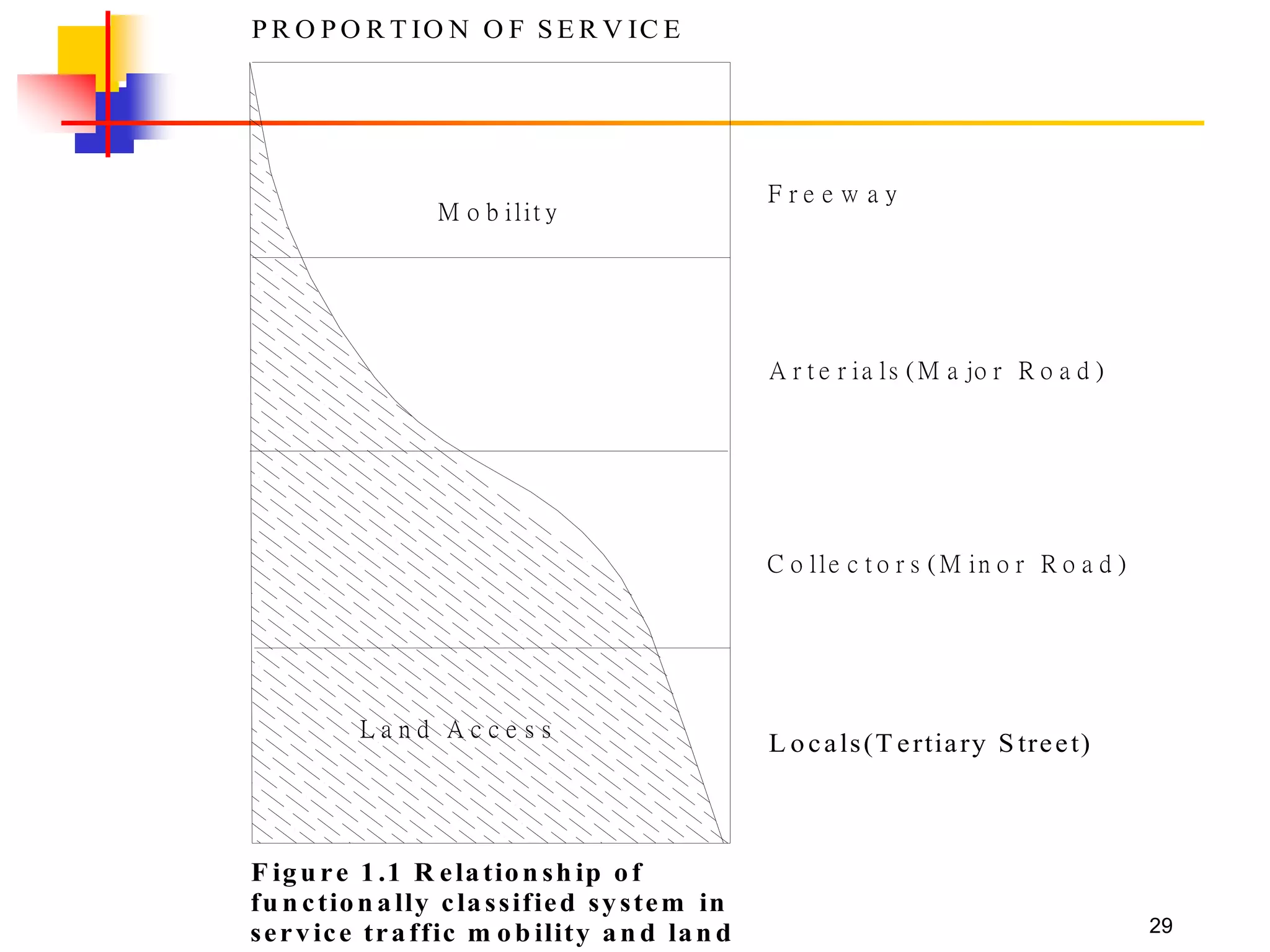
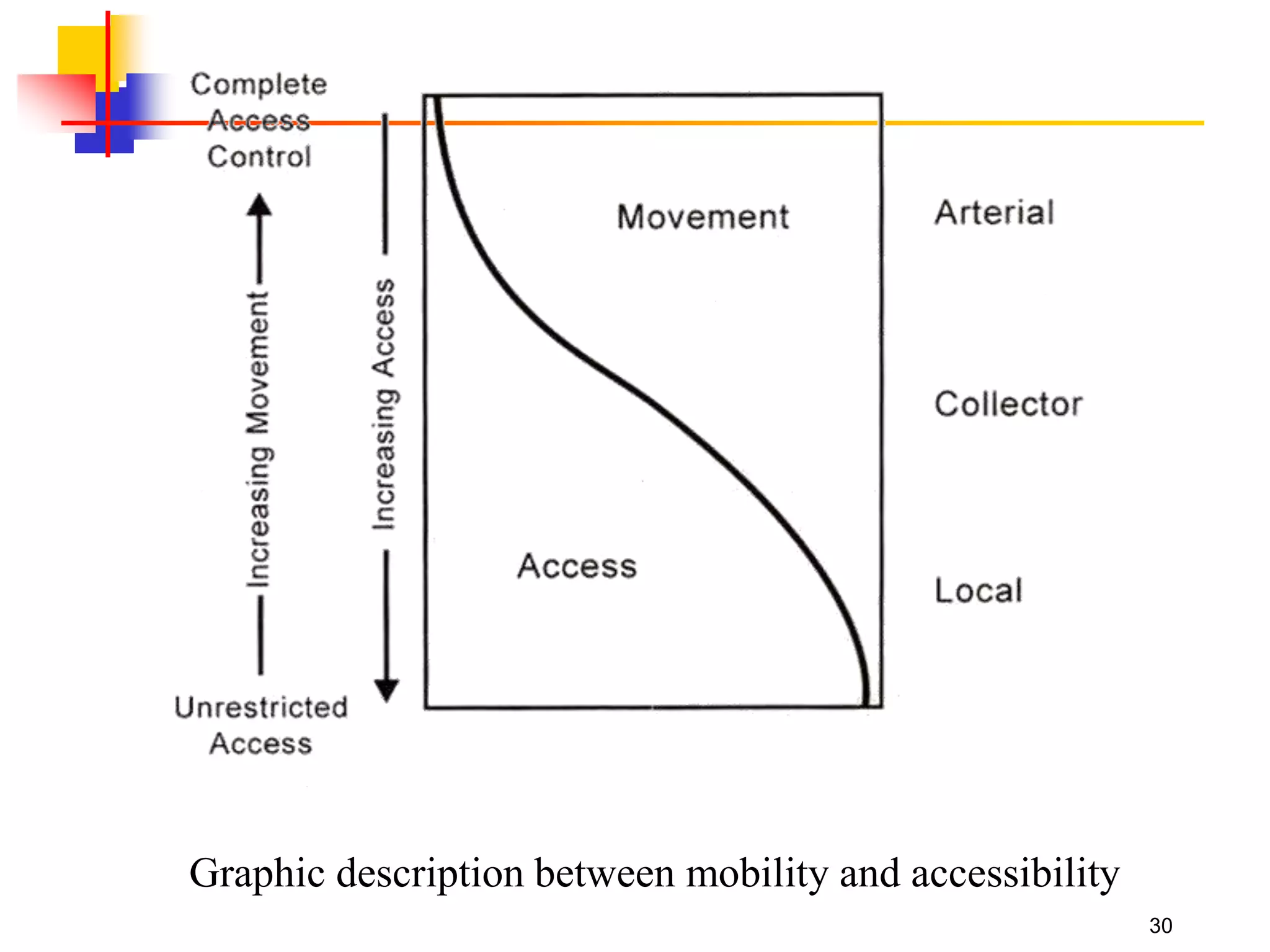
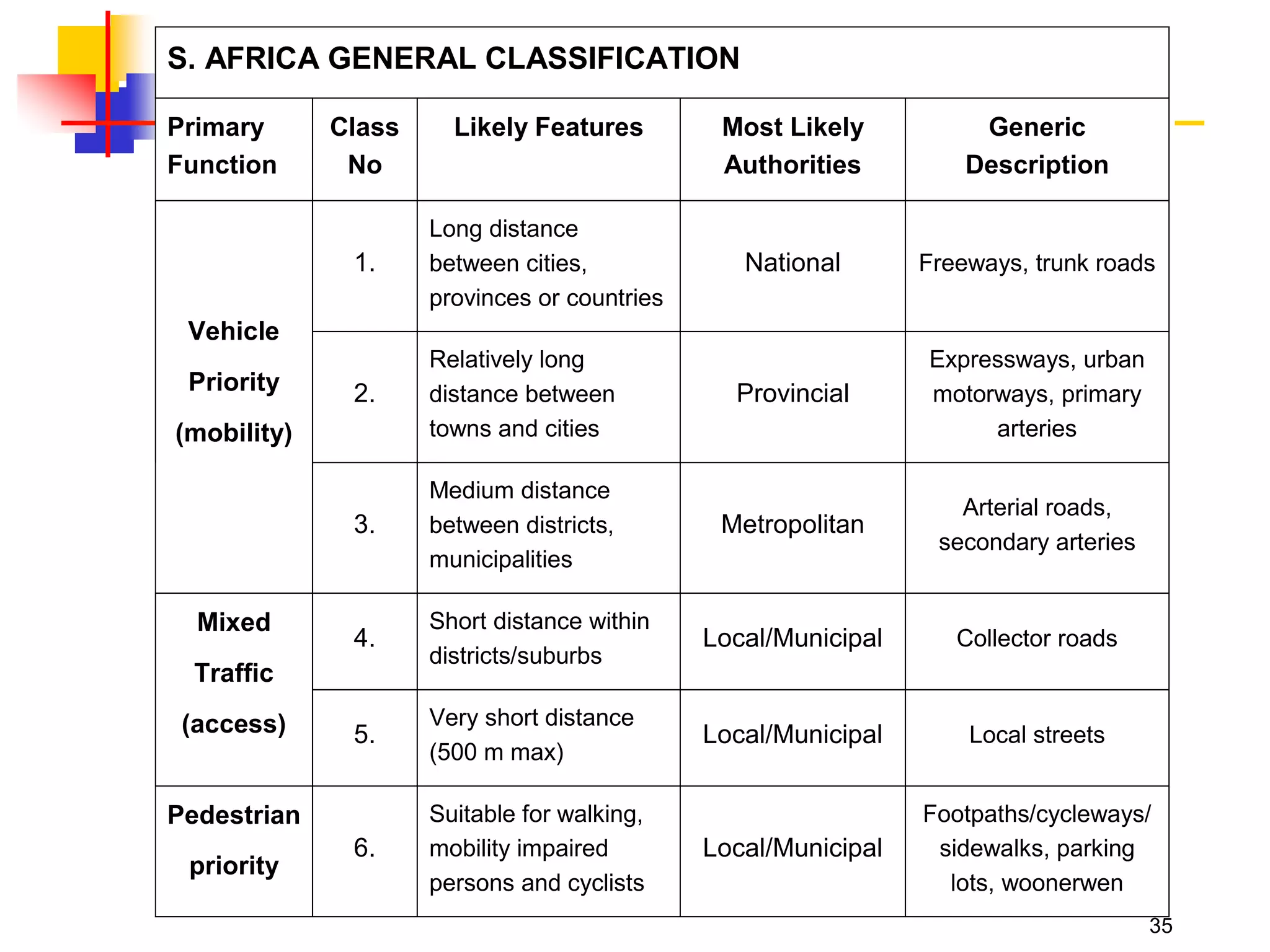
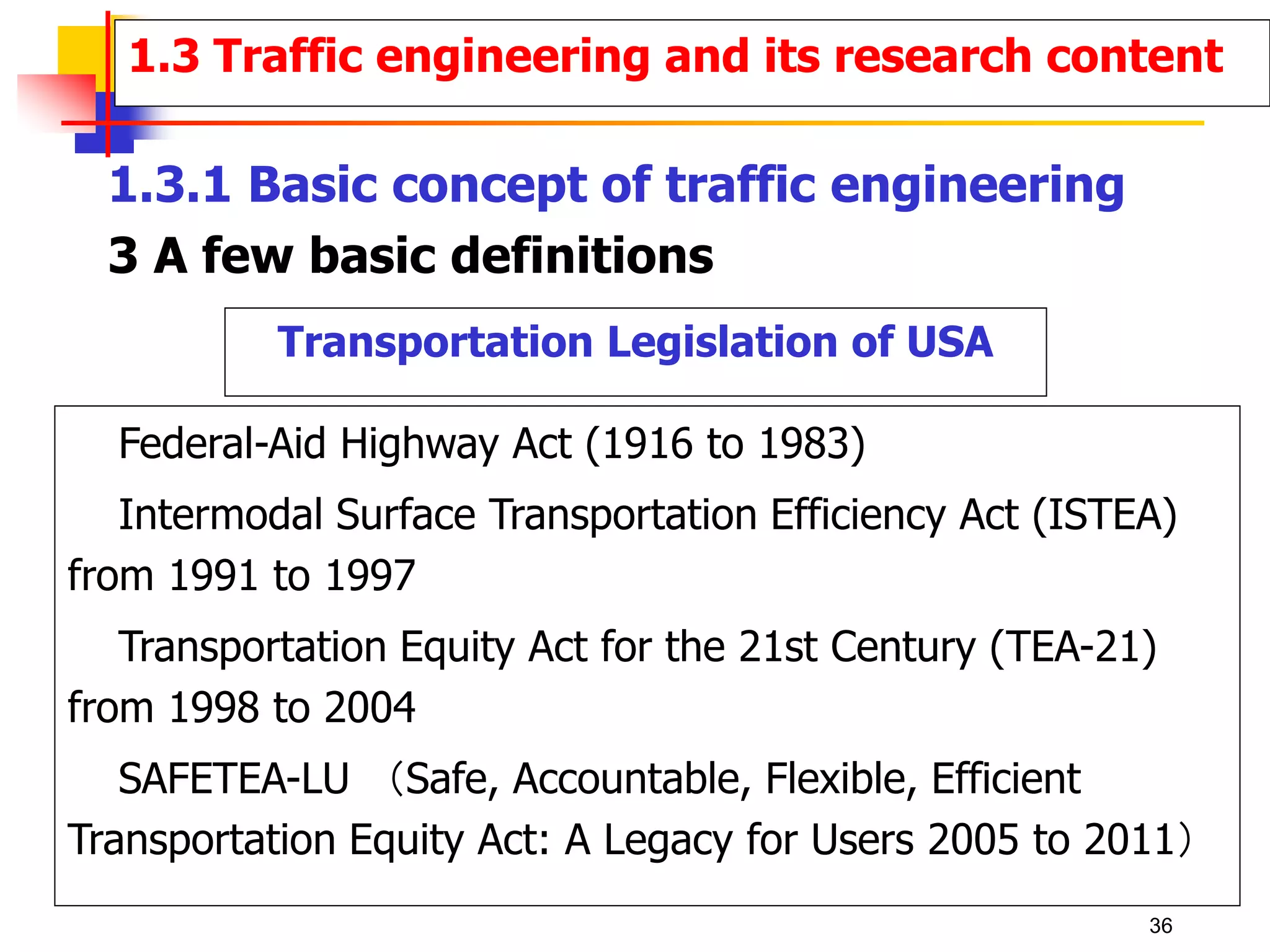
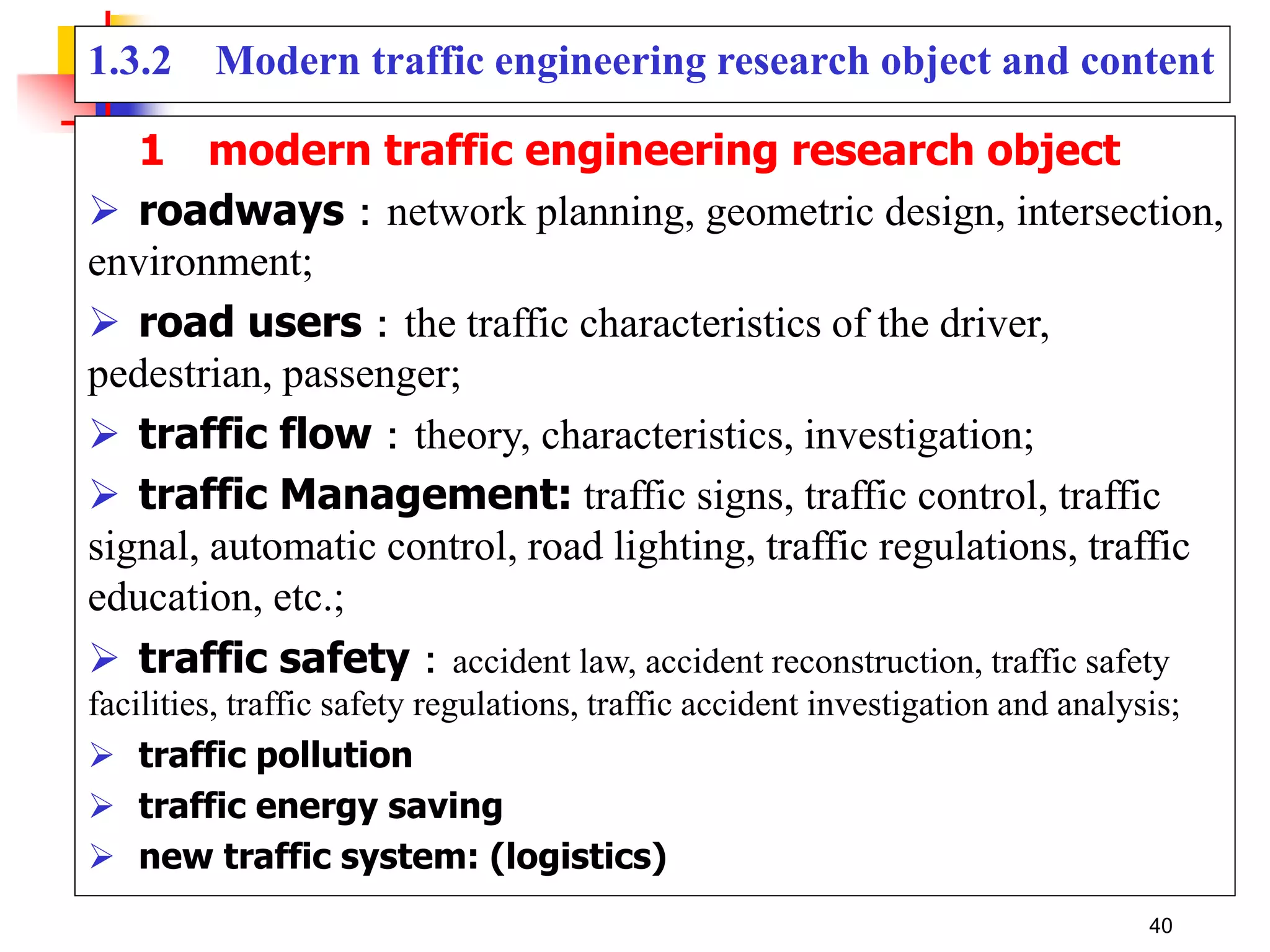
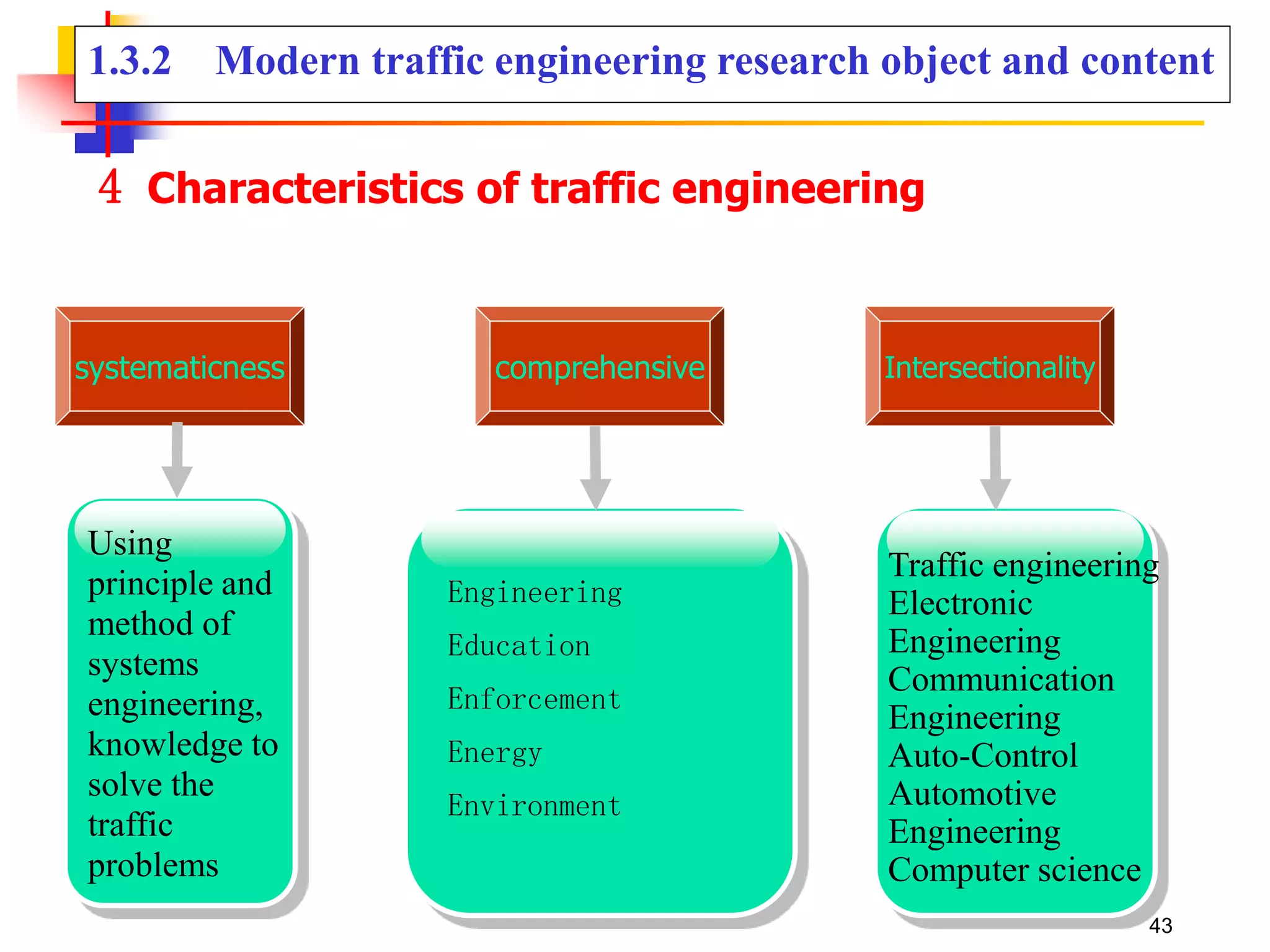
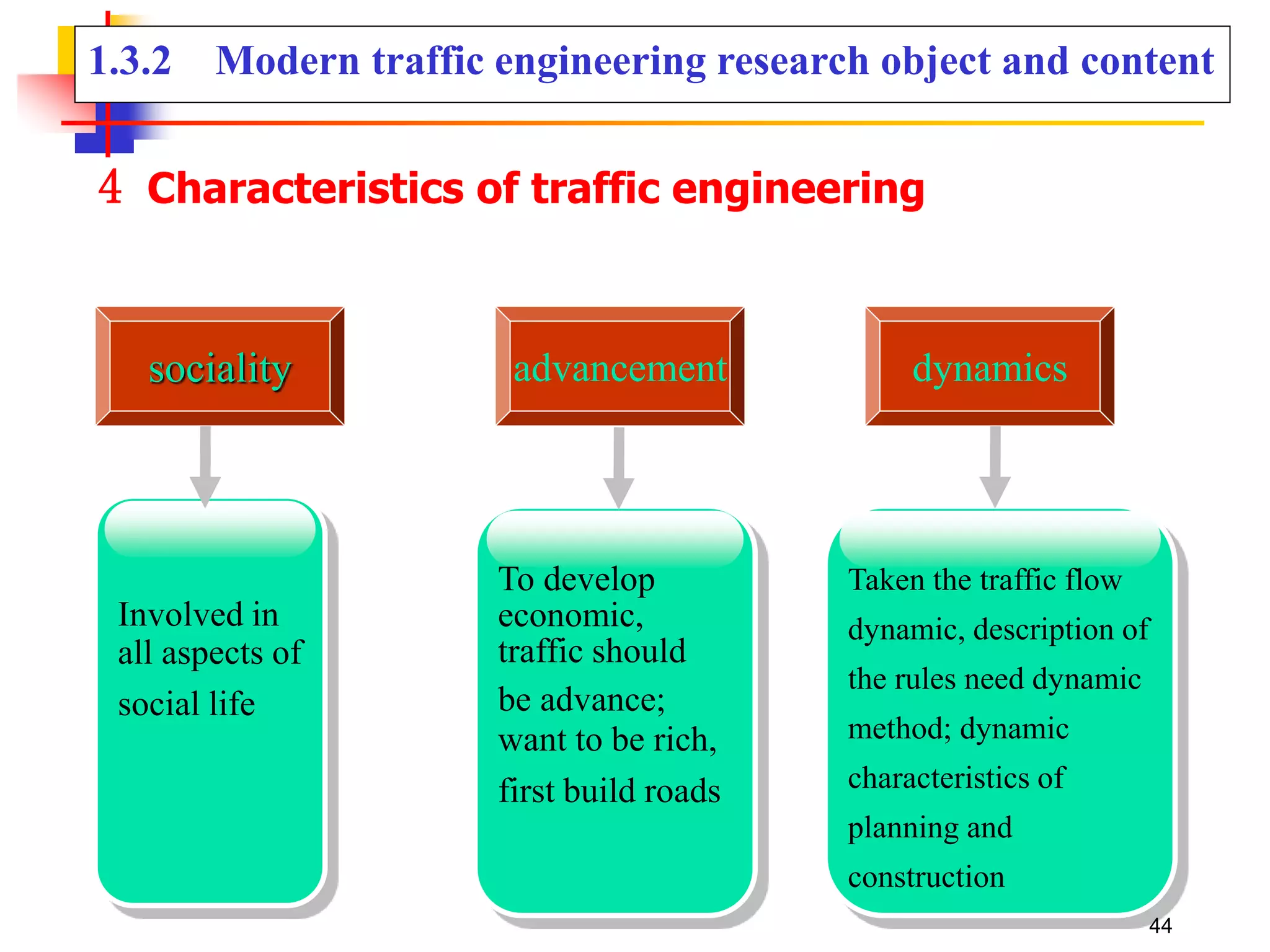
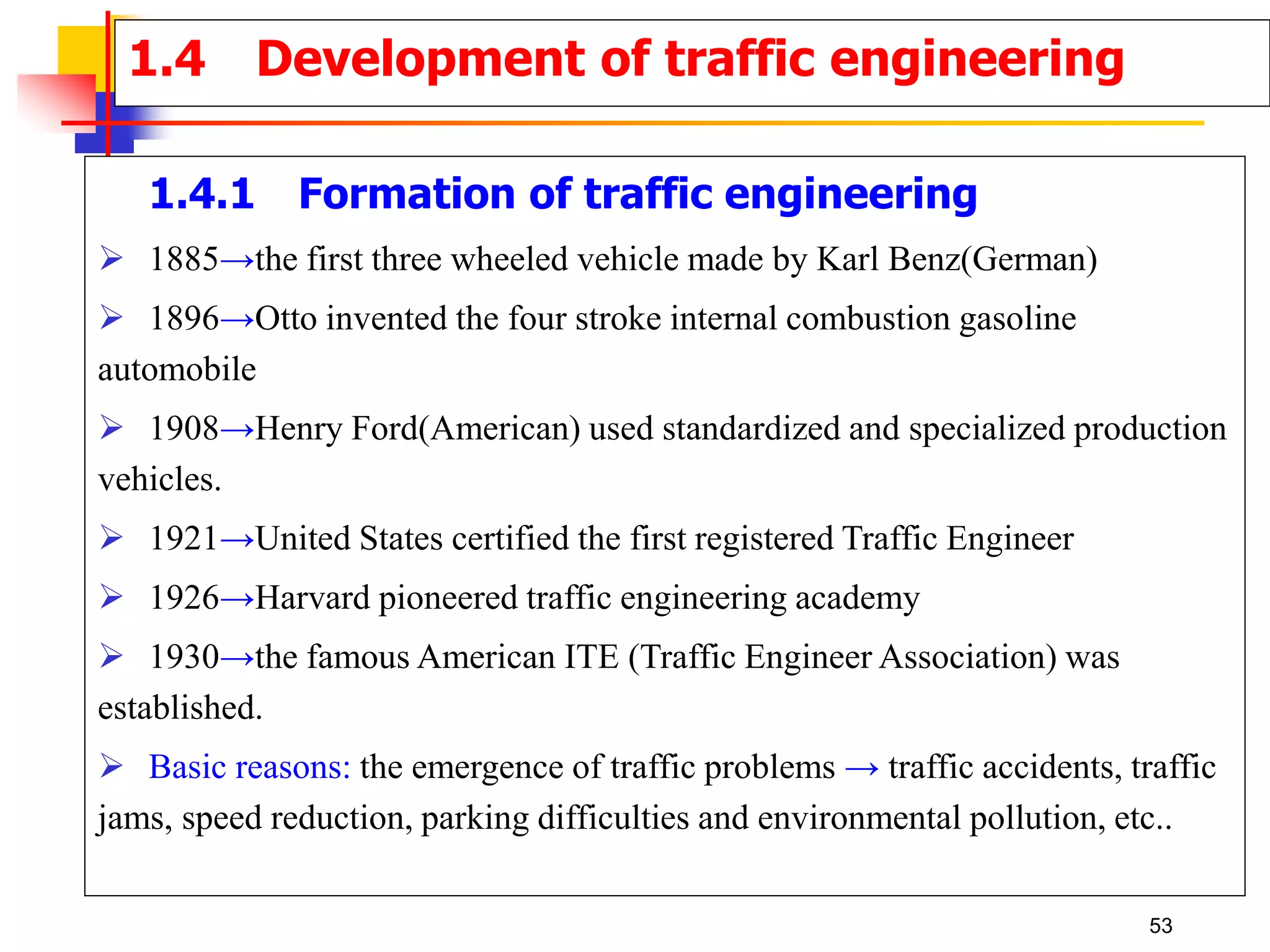
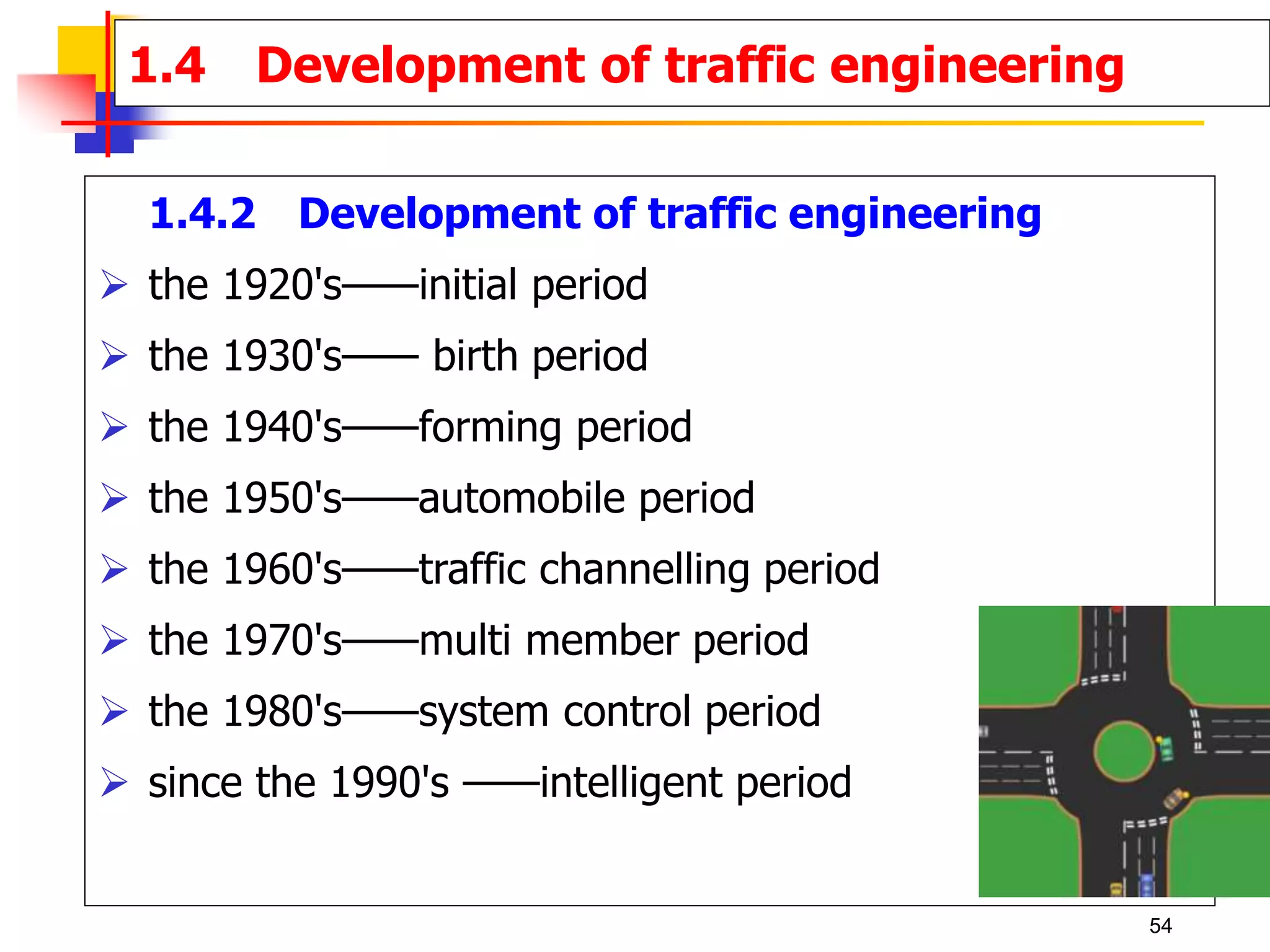
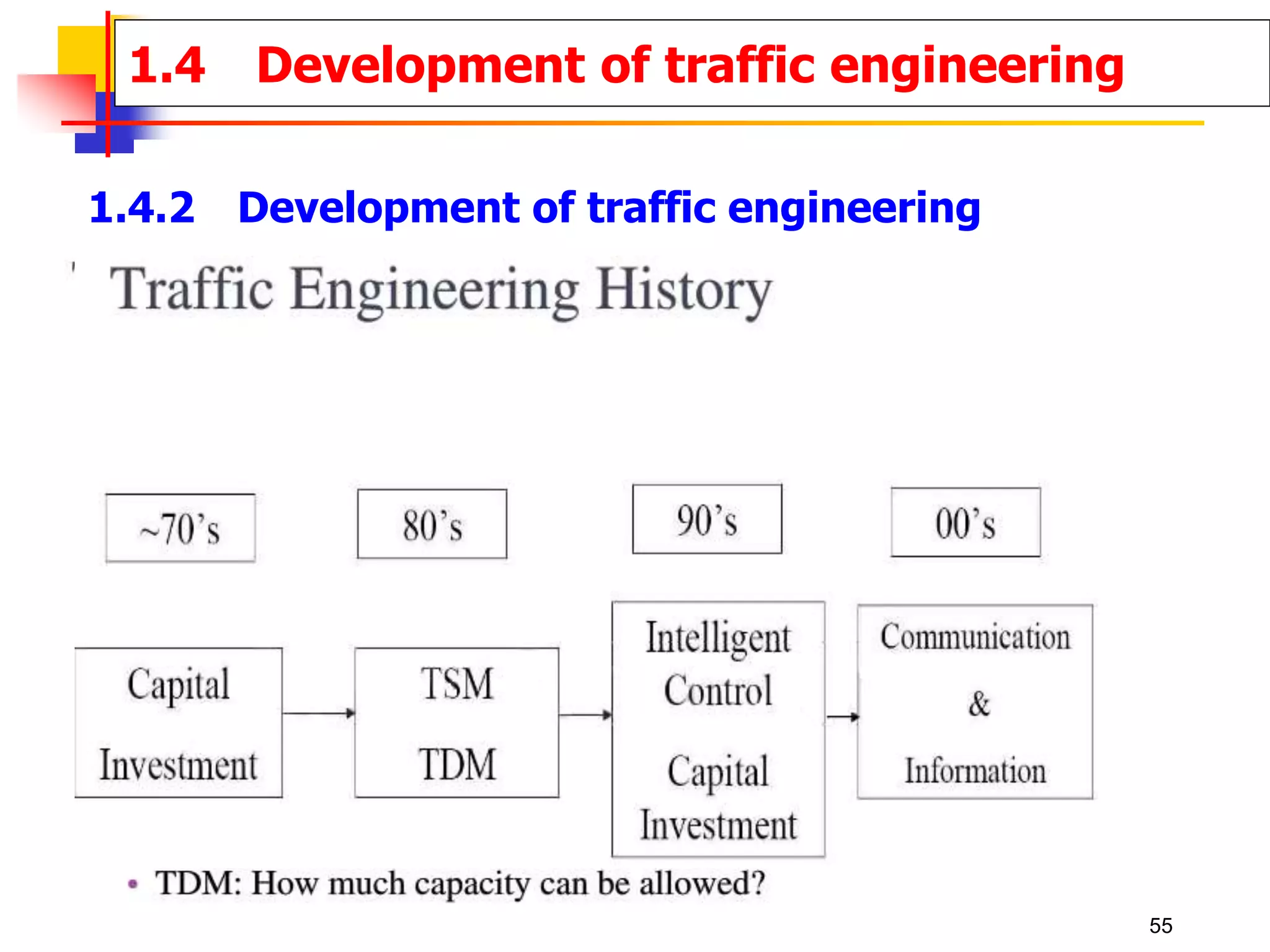
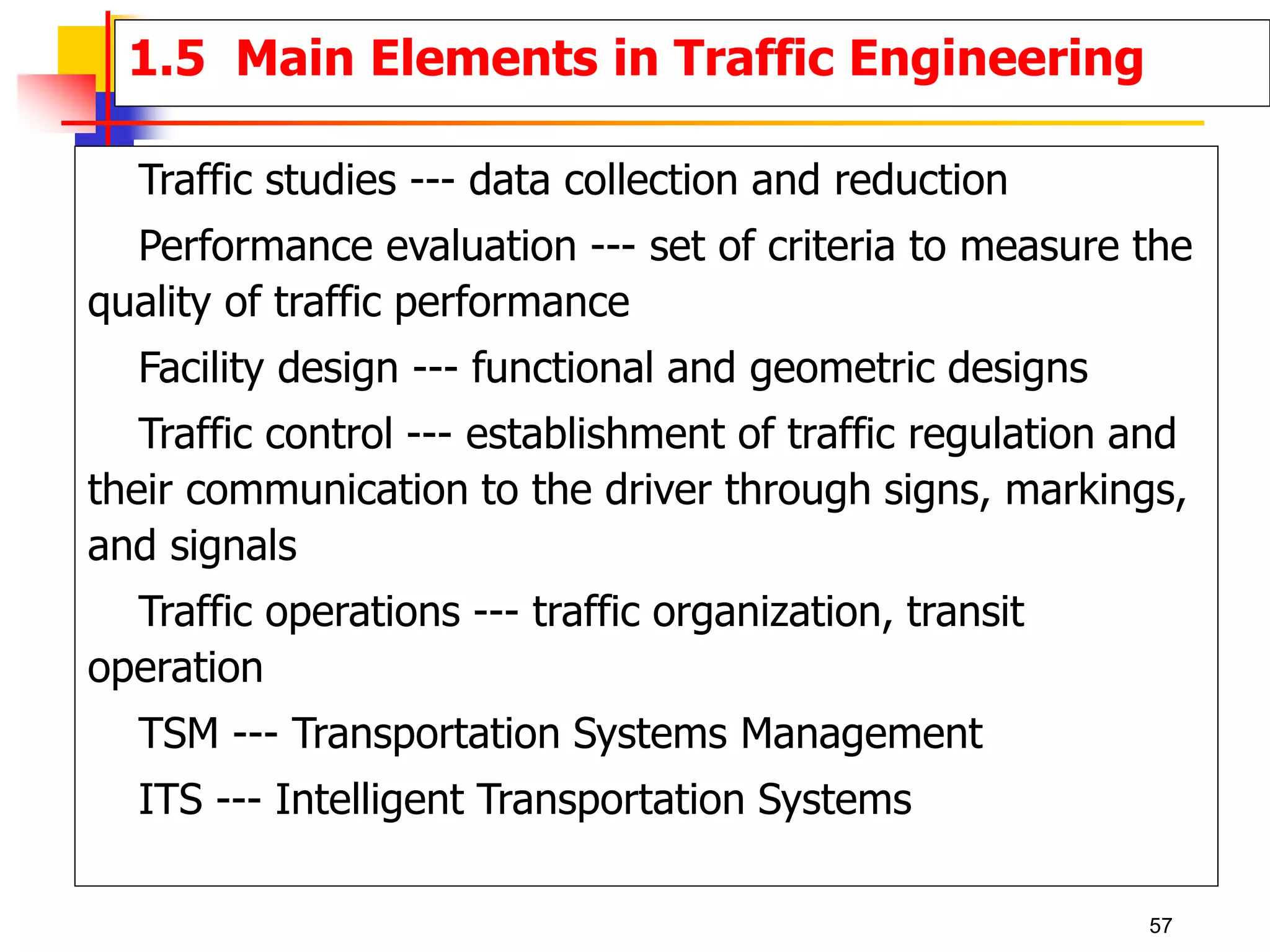
This document outlines the course content for a Traffic Engineering course. The course is 32 credit hours taught in English. It covers fundamentals of traffic flow, highway capacity analysis, and traffic control at signalized intersections. Students complete assignments on each topic and are provided supporting videos. The final grade is based on exam, homework, and group presentation scores. Reference textbooks include Traffic Engineering by Roger Roess and Principles of Highway Engineering and Traffic Analysis by Fred Mannering. The course also covers topics such as traffic stream characteristics, traffic planning, and traffic control.