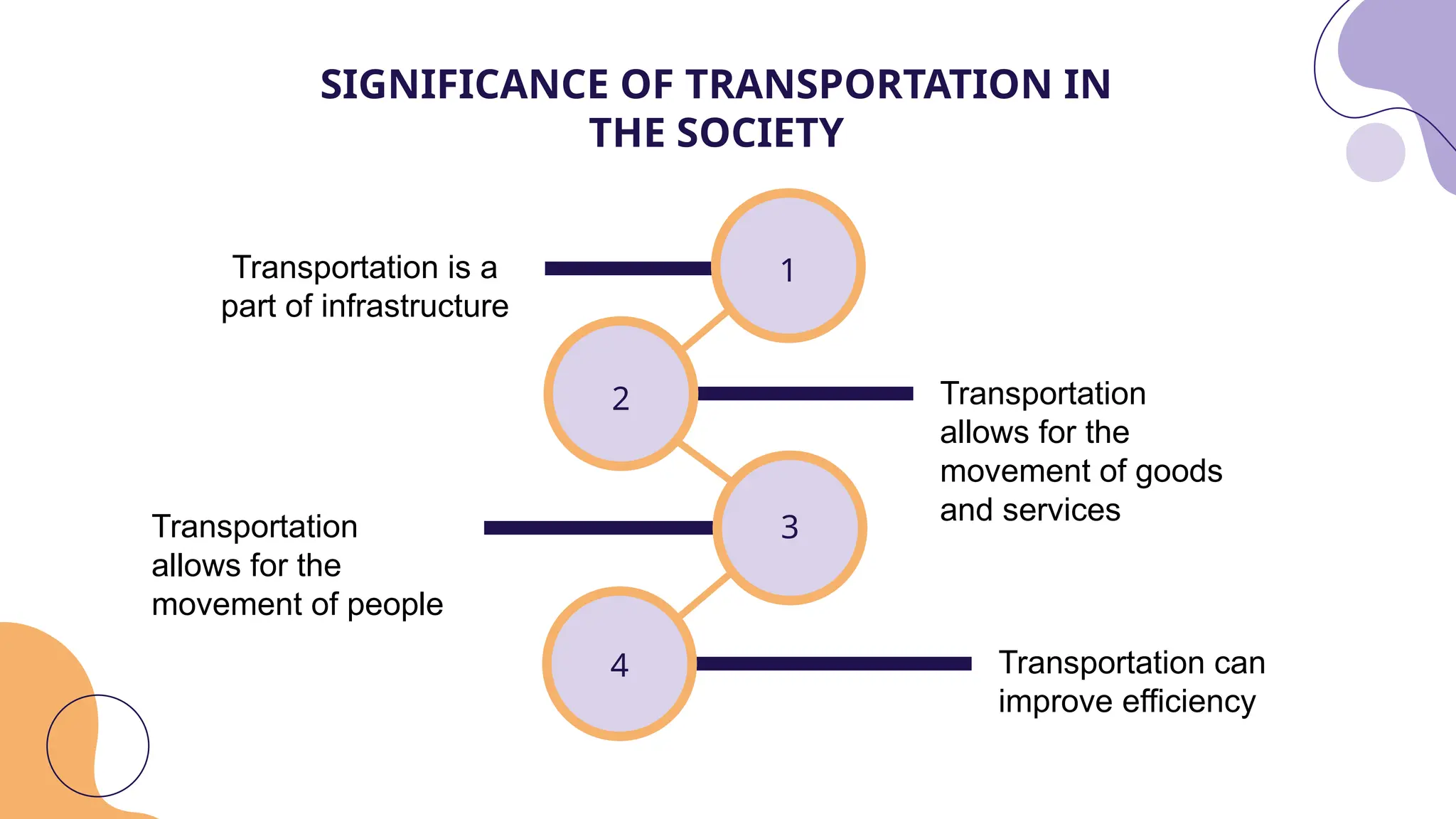
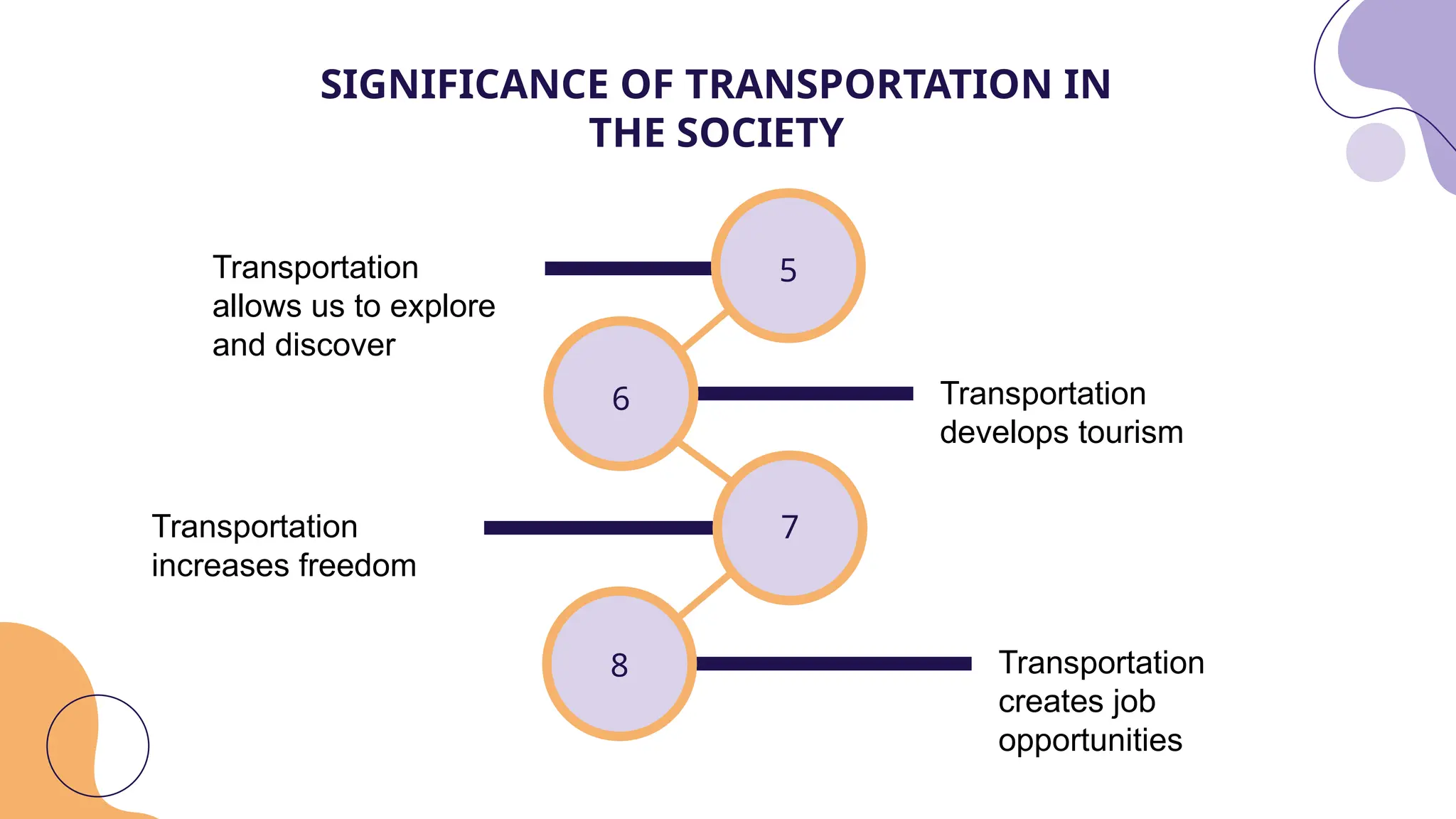
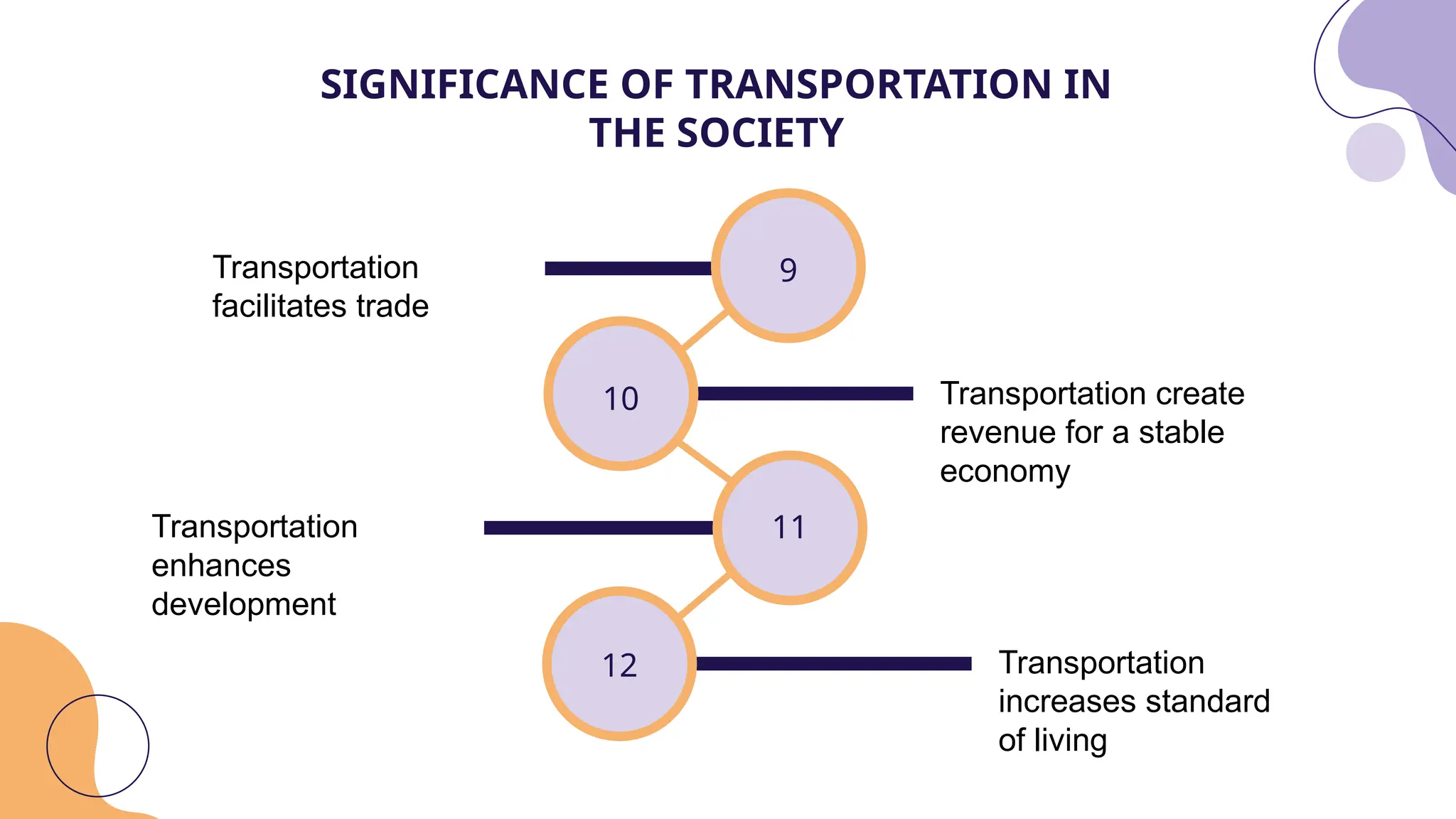
Transportation is crucial for modern society, facilitating the movement of people and goods while enhancing economic development and public safety. Transportation engineering, a branch of civil engineering, focuses on the planning, design, and maintenance of transportation systems to create smart and livable communities. Key aspects include transportation planning, geometric design, pavement analysis, and traffic engineering, each aiming to improve efficiency, safety, and environmental sustainability.