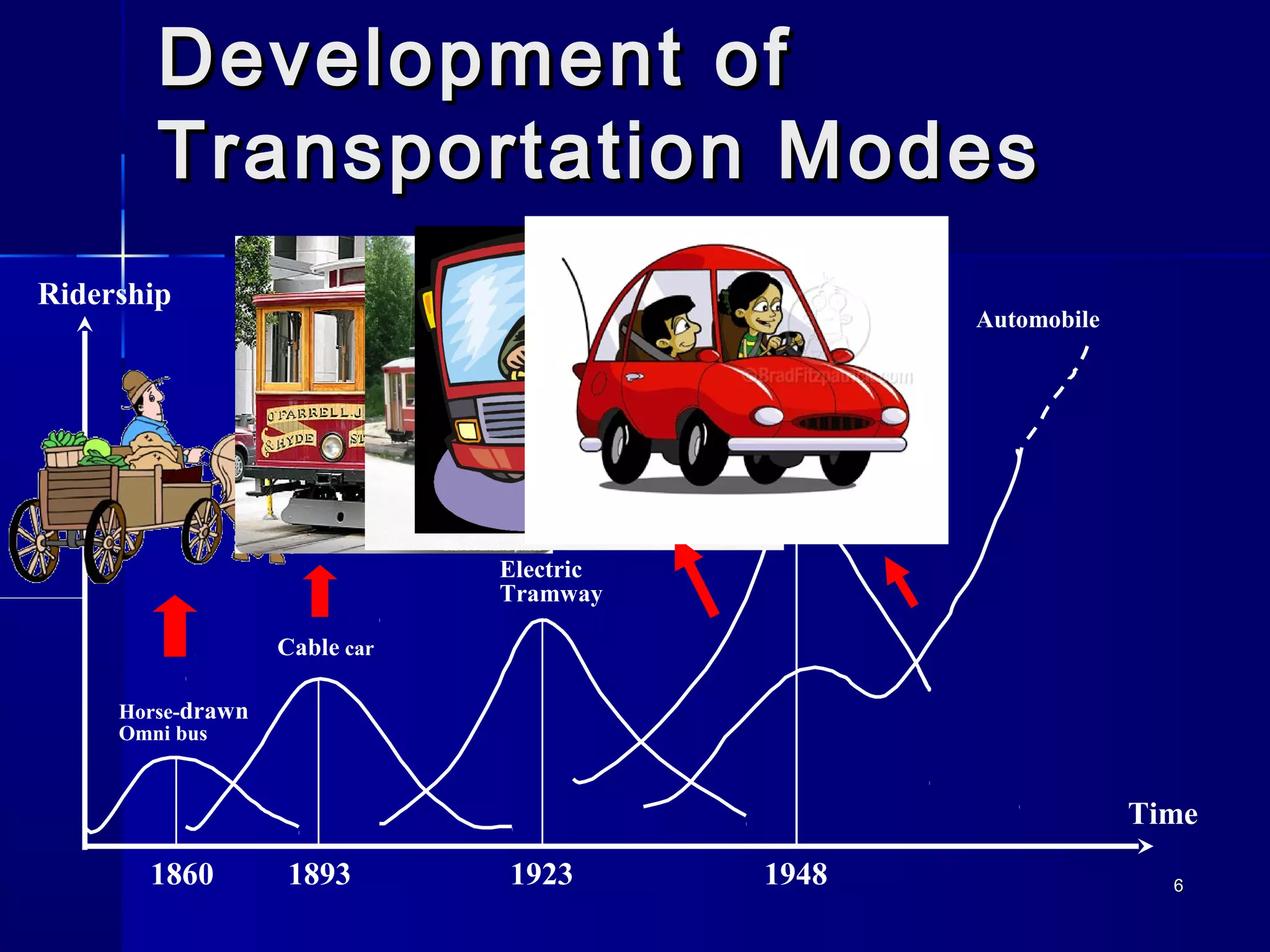
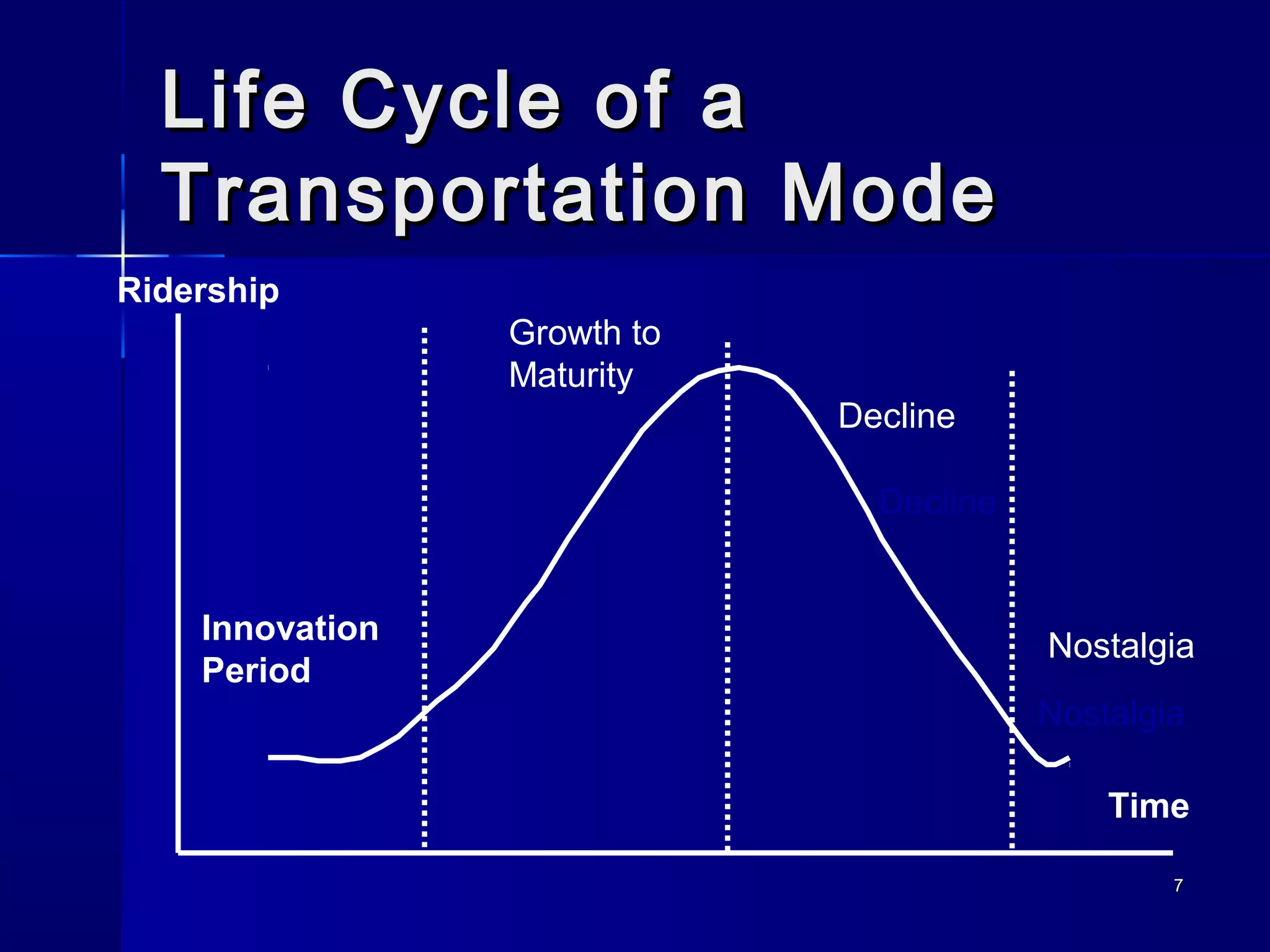
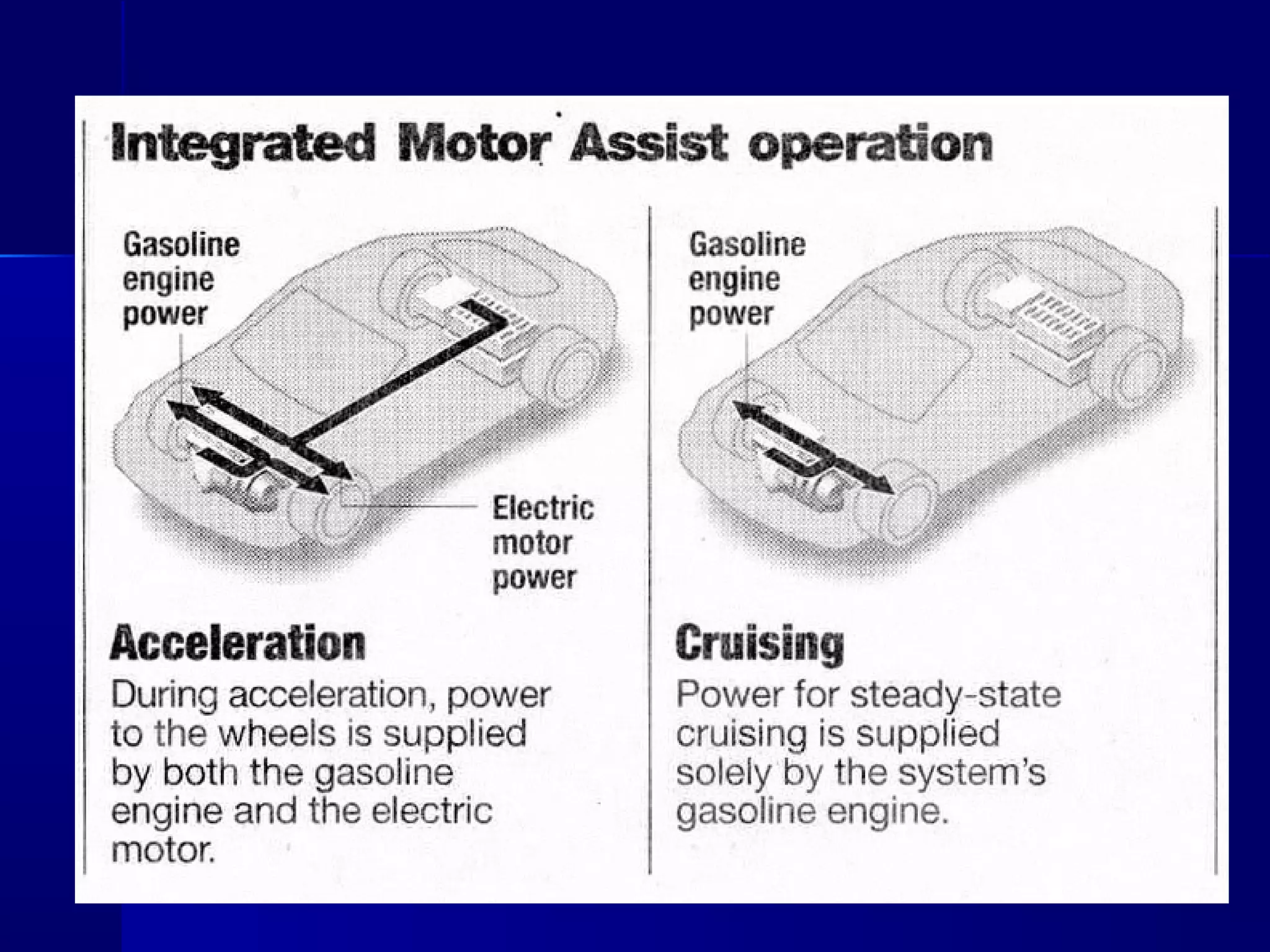
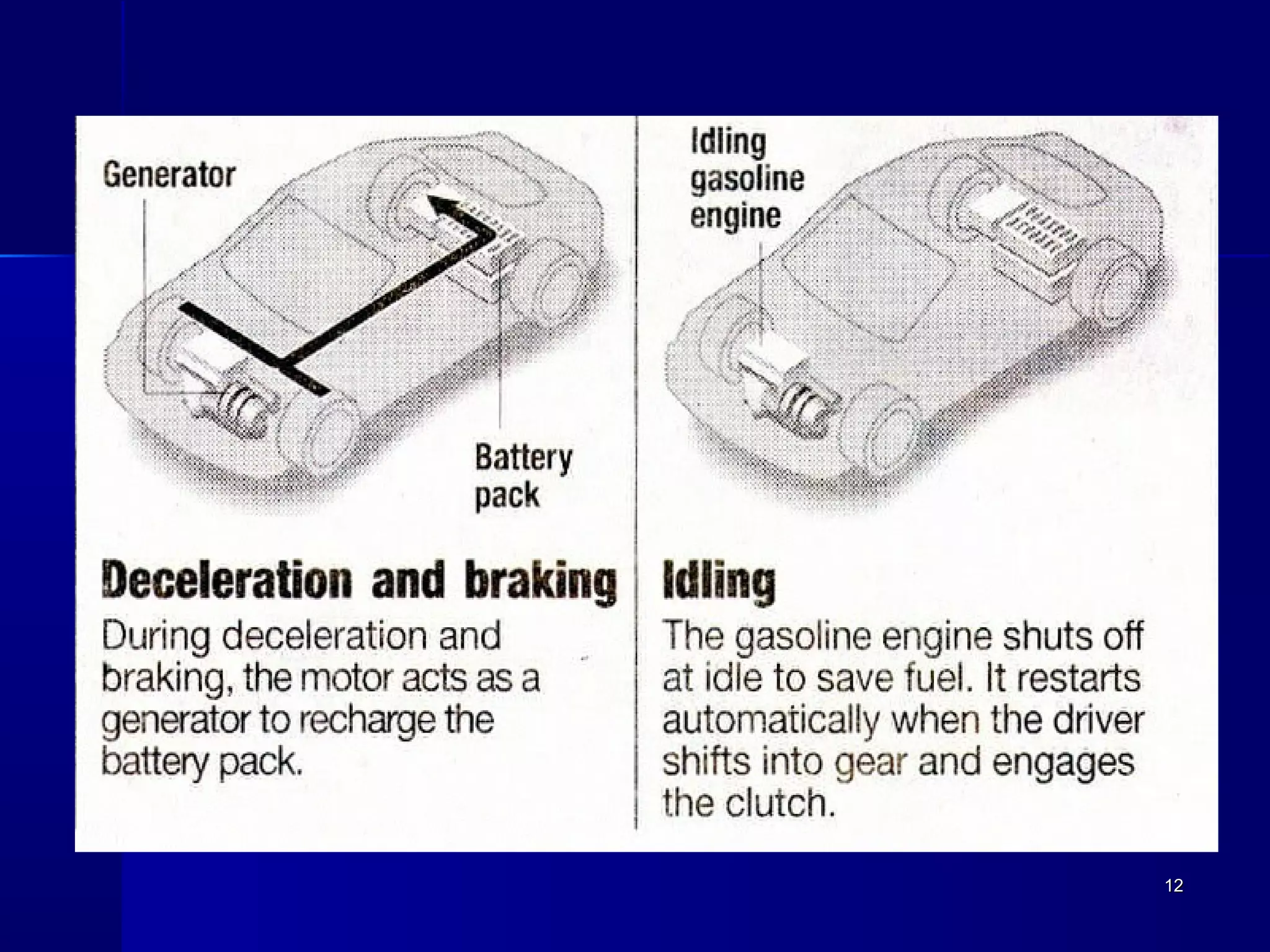
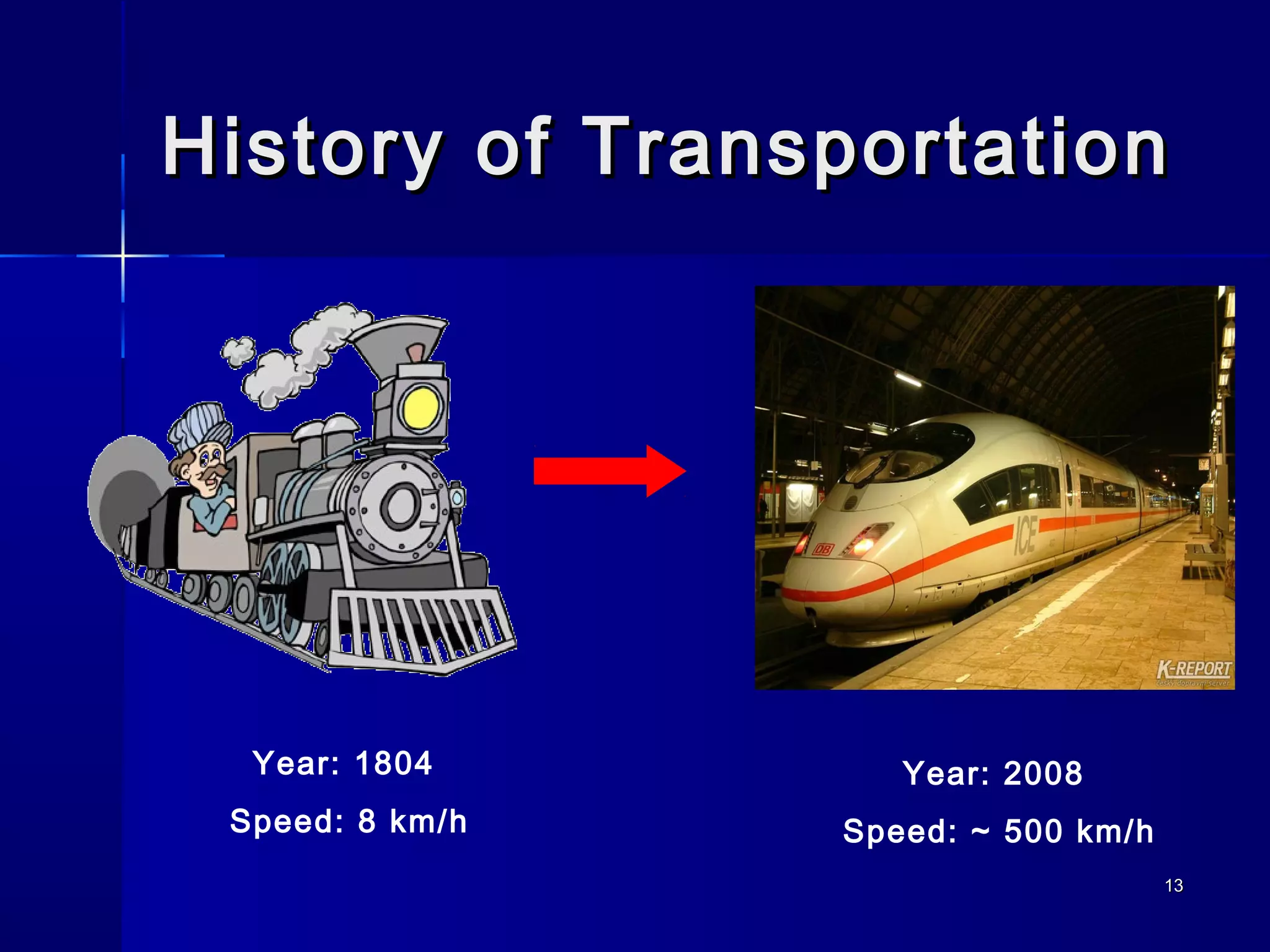
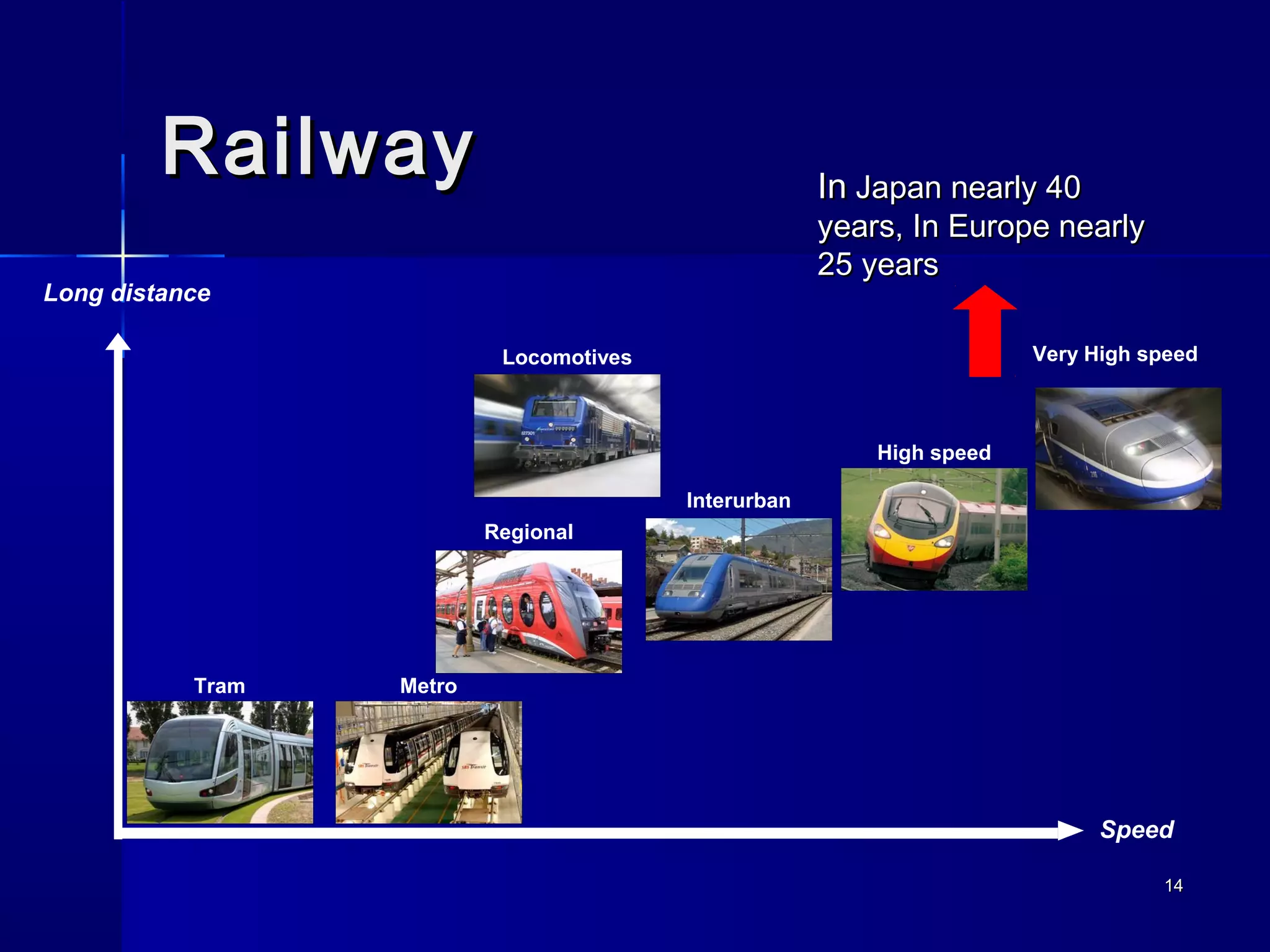
Transportation involves the movement of people and goods over time and space using various modes. It should be safe and environmentally friendly. The document discusses the history and development of different transportation modes like railways and cars. It also covers concepts in transportation engineering like transportation planning, traffic operations, and level of service analysis. The future of transportation focuses on more environmentally friendly options like hybrid vehicles.