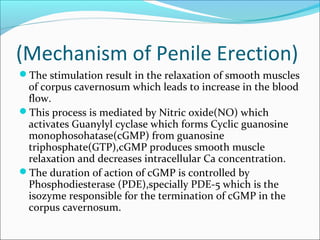
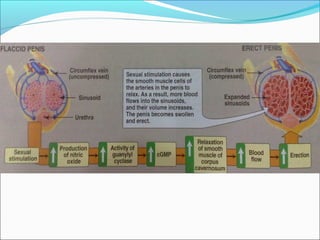
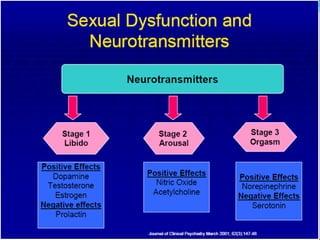
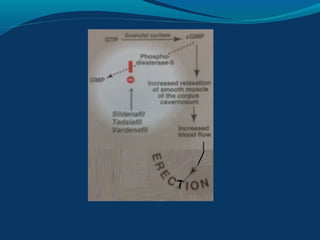
Sexual dysfunction can affect both men and women and has physiological, psychological, and social causes. It includes disorders like hypoactive sexual desire disorder and erectile dysfunction. Erectile dysfunction affects blood flow in the penis and is treated with drugs like sildenafil that inhibit PDE5. Female sexual dysfunction involves issues like low libido and vaginal dryness, treated with estrogen or testosterone therapy. Many drugs can cause sexual side effects, like SSRIs and beta blockers, by decreasing dopamine, nitric oxide, or testosterone levels.