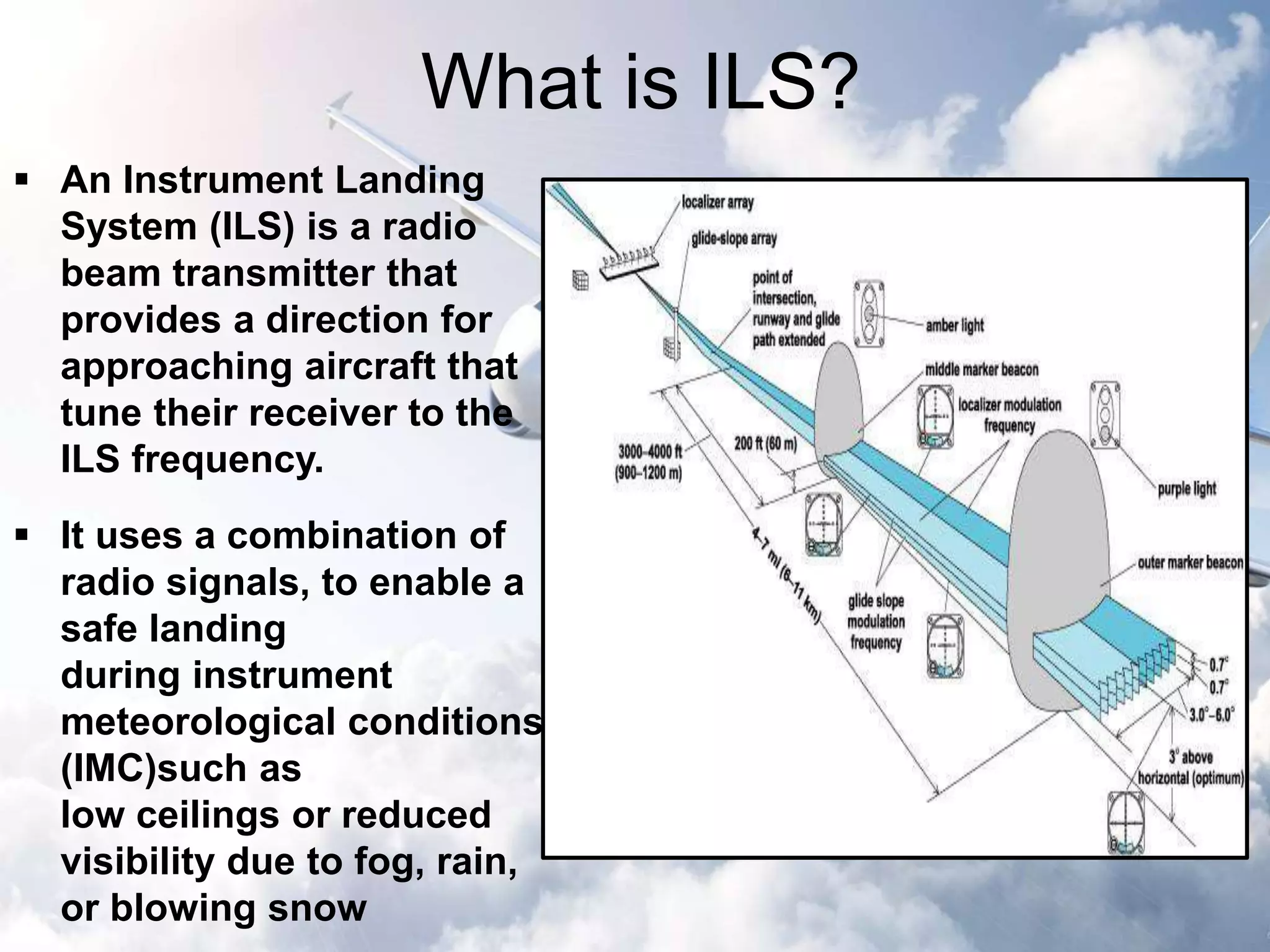
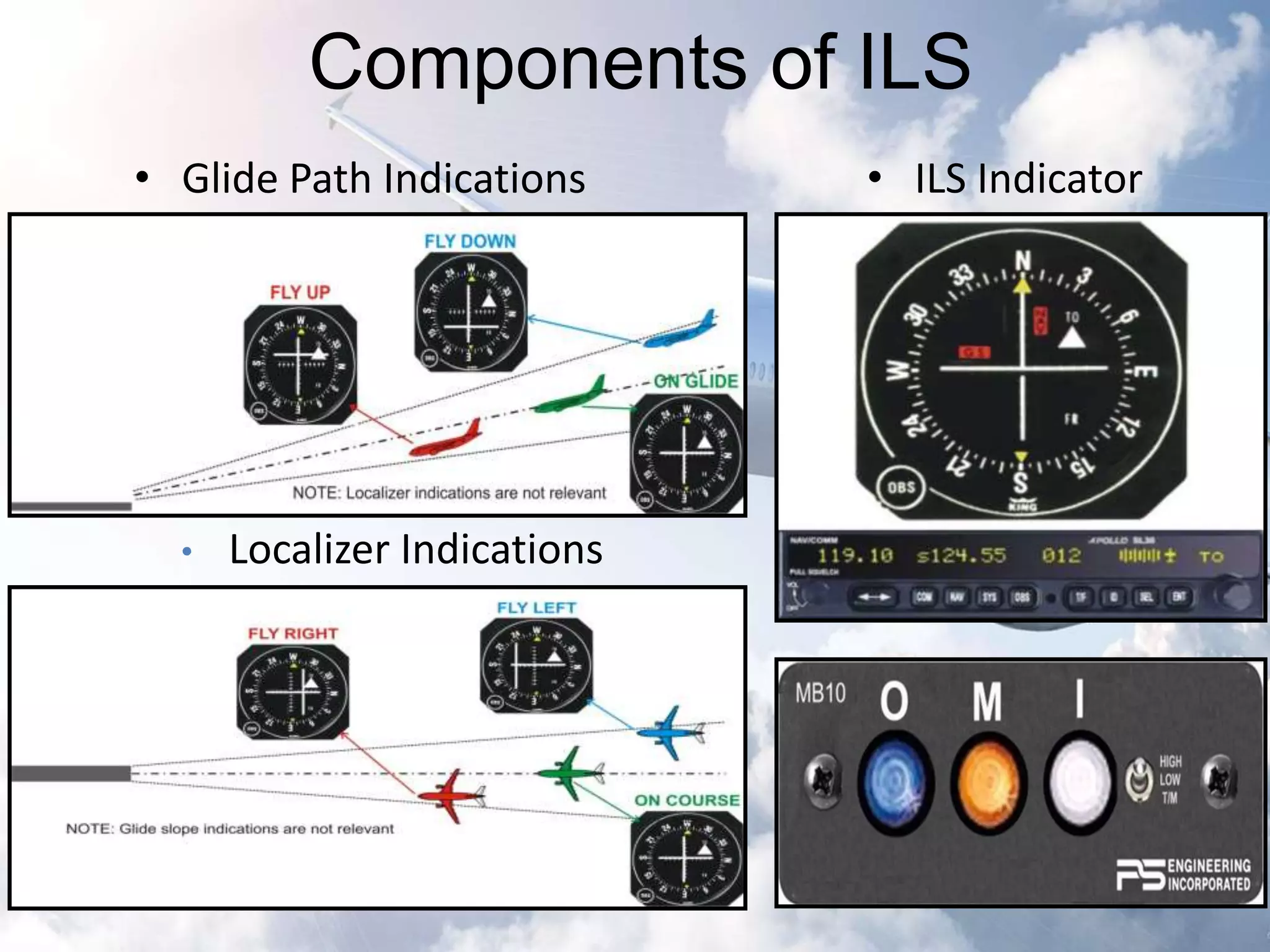
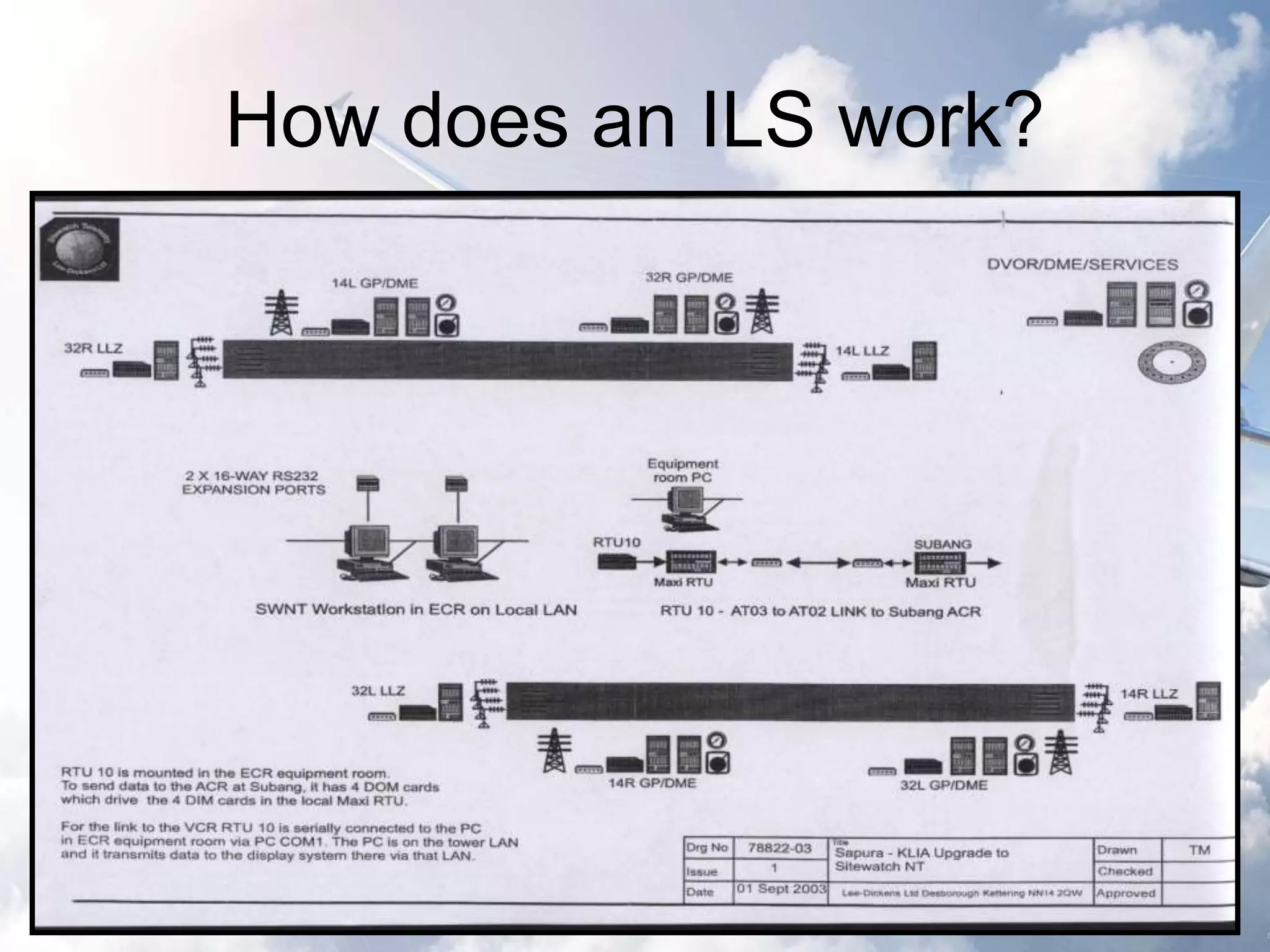
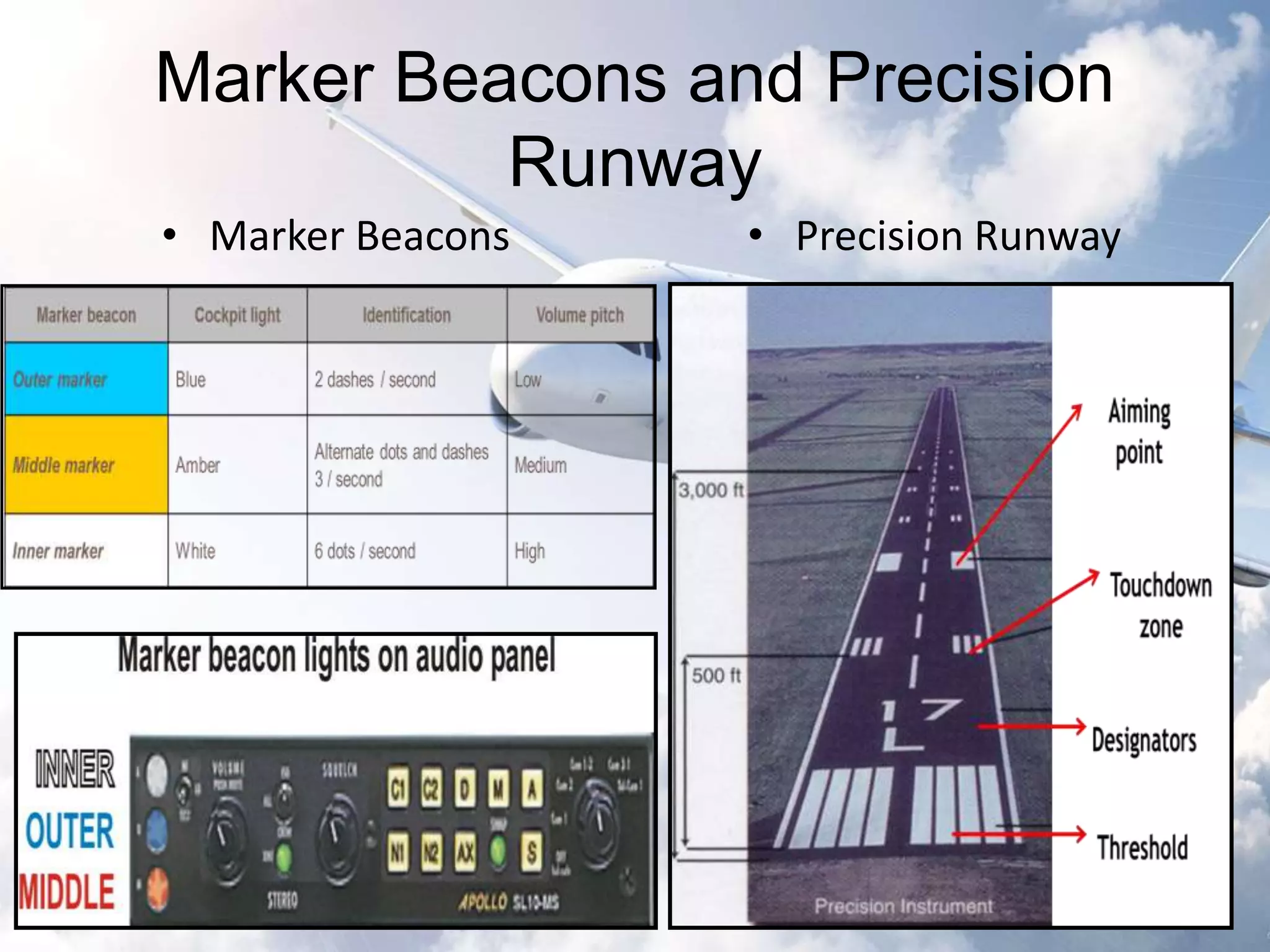
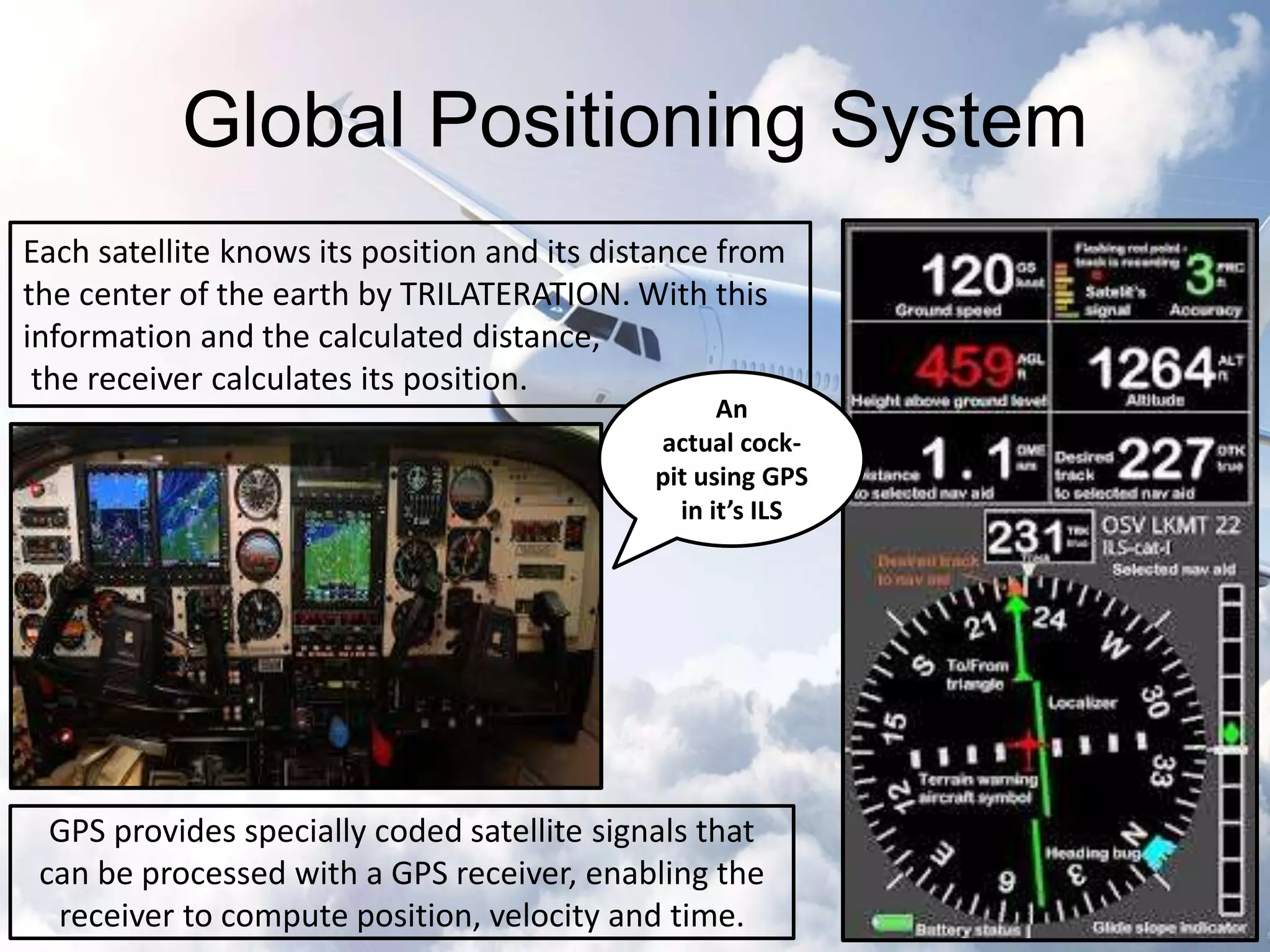
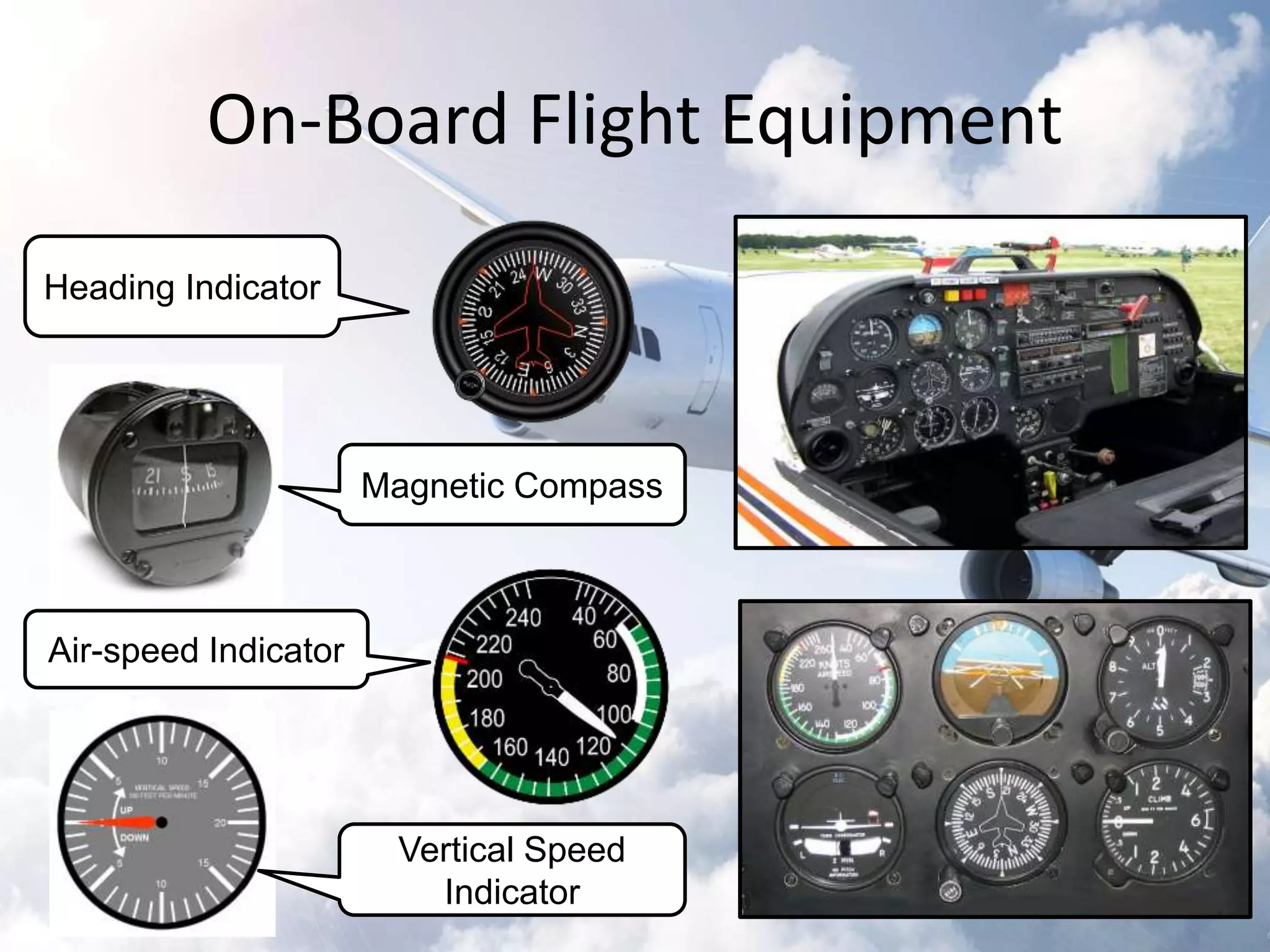
The document provides an overview of the Instrument Landing System (ILS), which is a radio beam transmitter aiding aircraft landings in poor visibility conditions. It details the history, components, and functioning of ILS, including its evolution since its first tests in 1929 and standardization by ICAO in 1949. Additionally, the document discusses associated technologies such as GPS and includes references to unfortunate incidents linked to ILS failures.