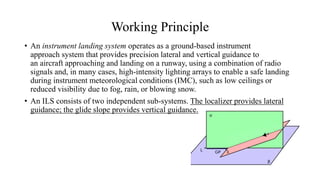
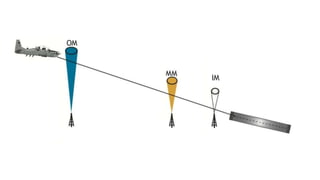
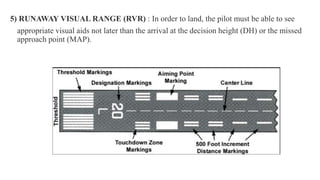
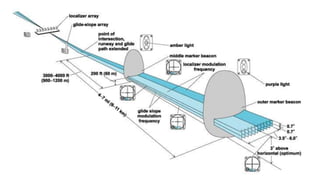
The document discusses the Instrument Landing System (ILS). The ILS provides precision guidance to aircraft for landing using radio signals and lighting. It consists of two subsystems - the localizer for lateral guidance and the glide slope for vertical guidance. There are also marker beacons, Distance Measuring Equipment, and approach lighting systems that aid pilots. The ILS allows aircraft to land in low visibility conditions down to 50 feet, increasing safety and efficiency compared to visual landings. It is the standard international system used at most airports worldwide.