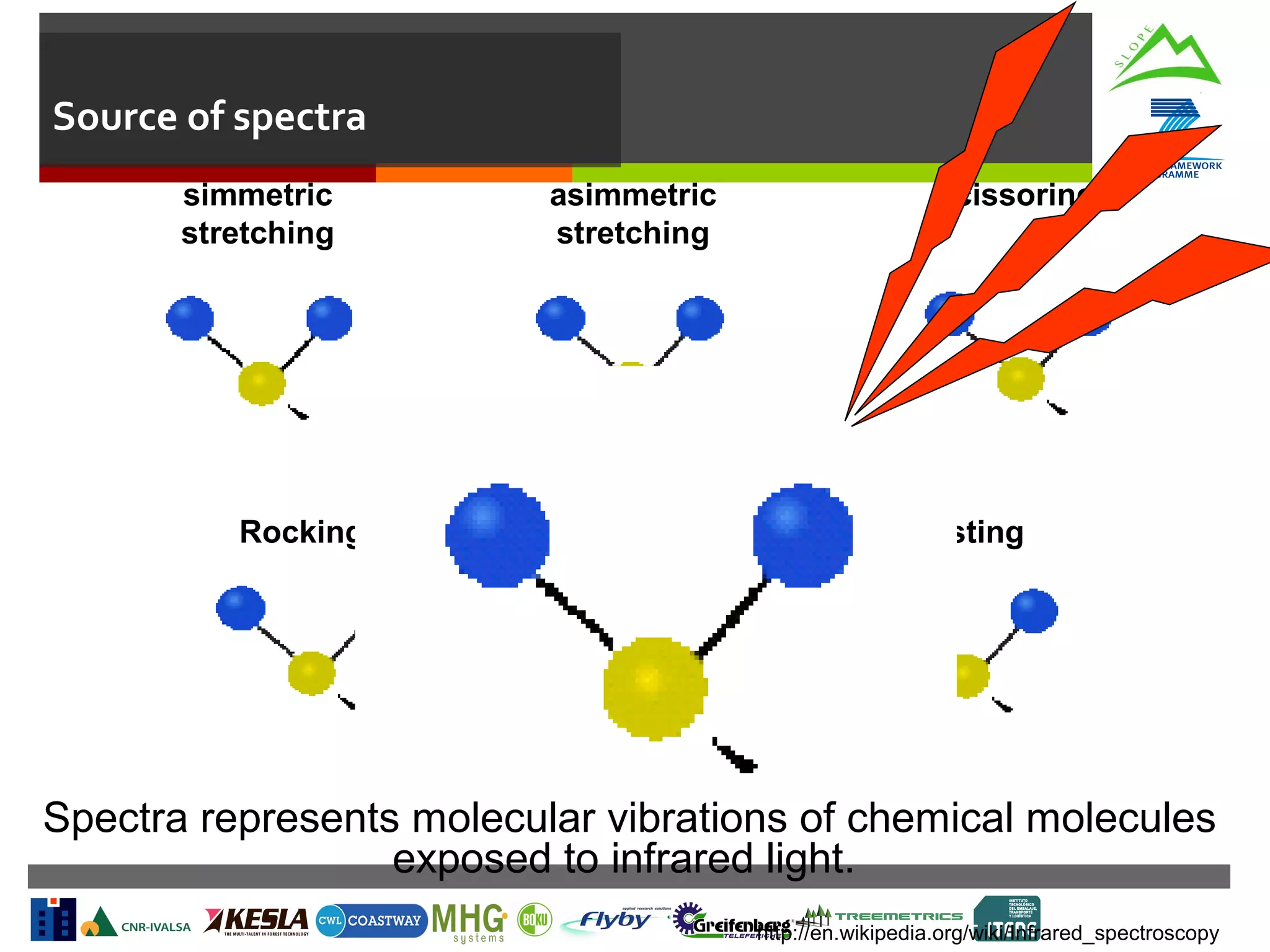
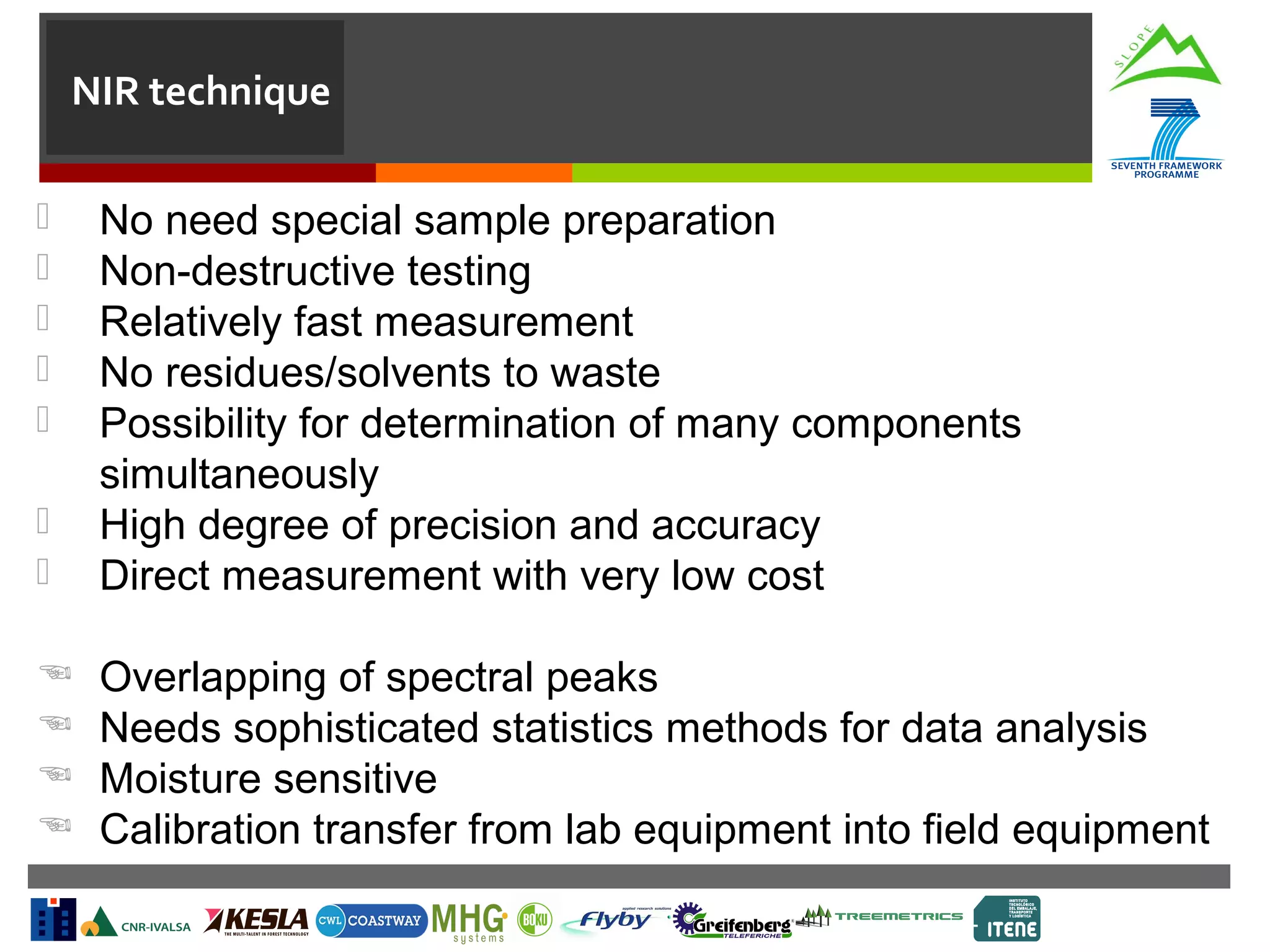
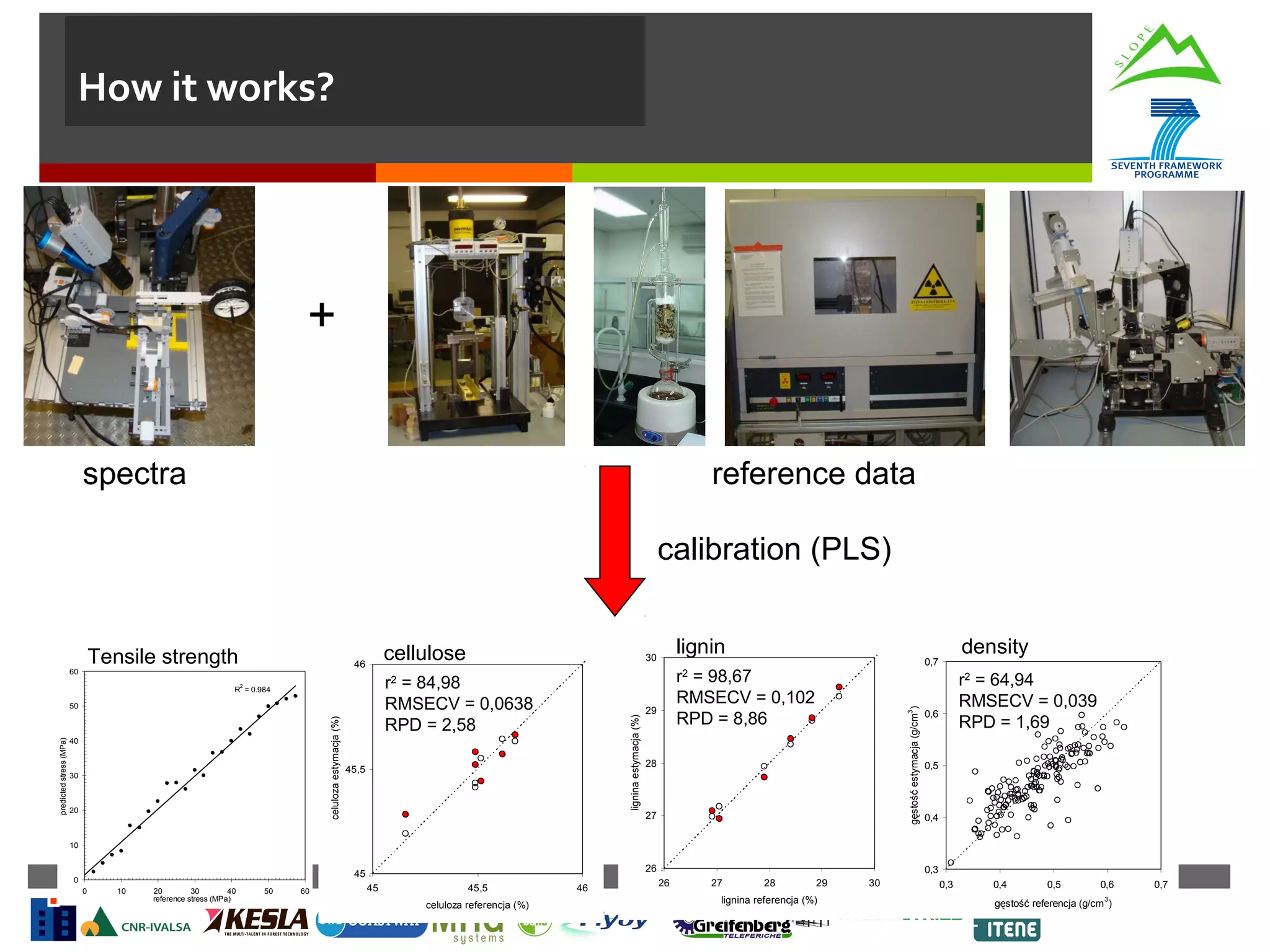
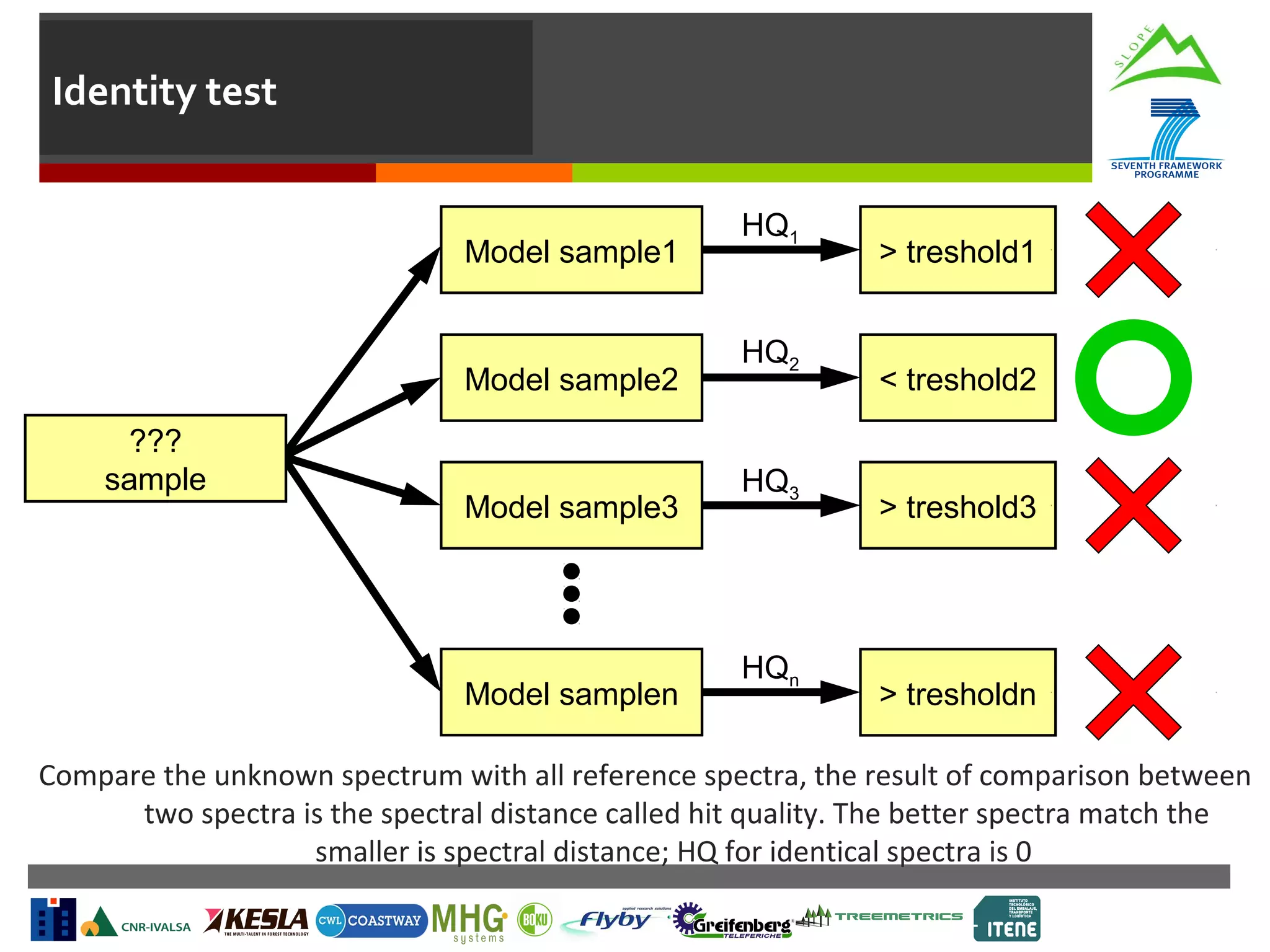
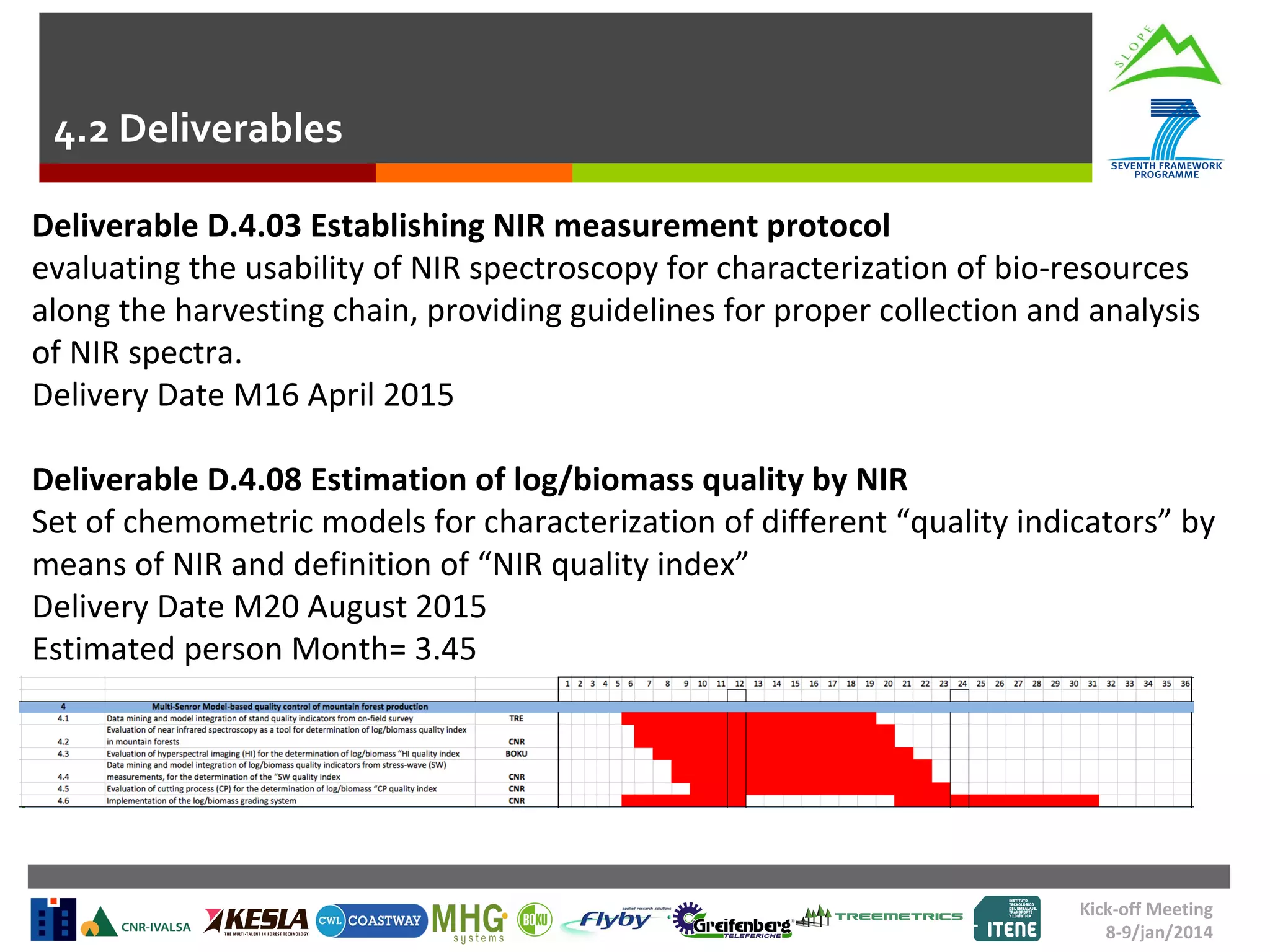
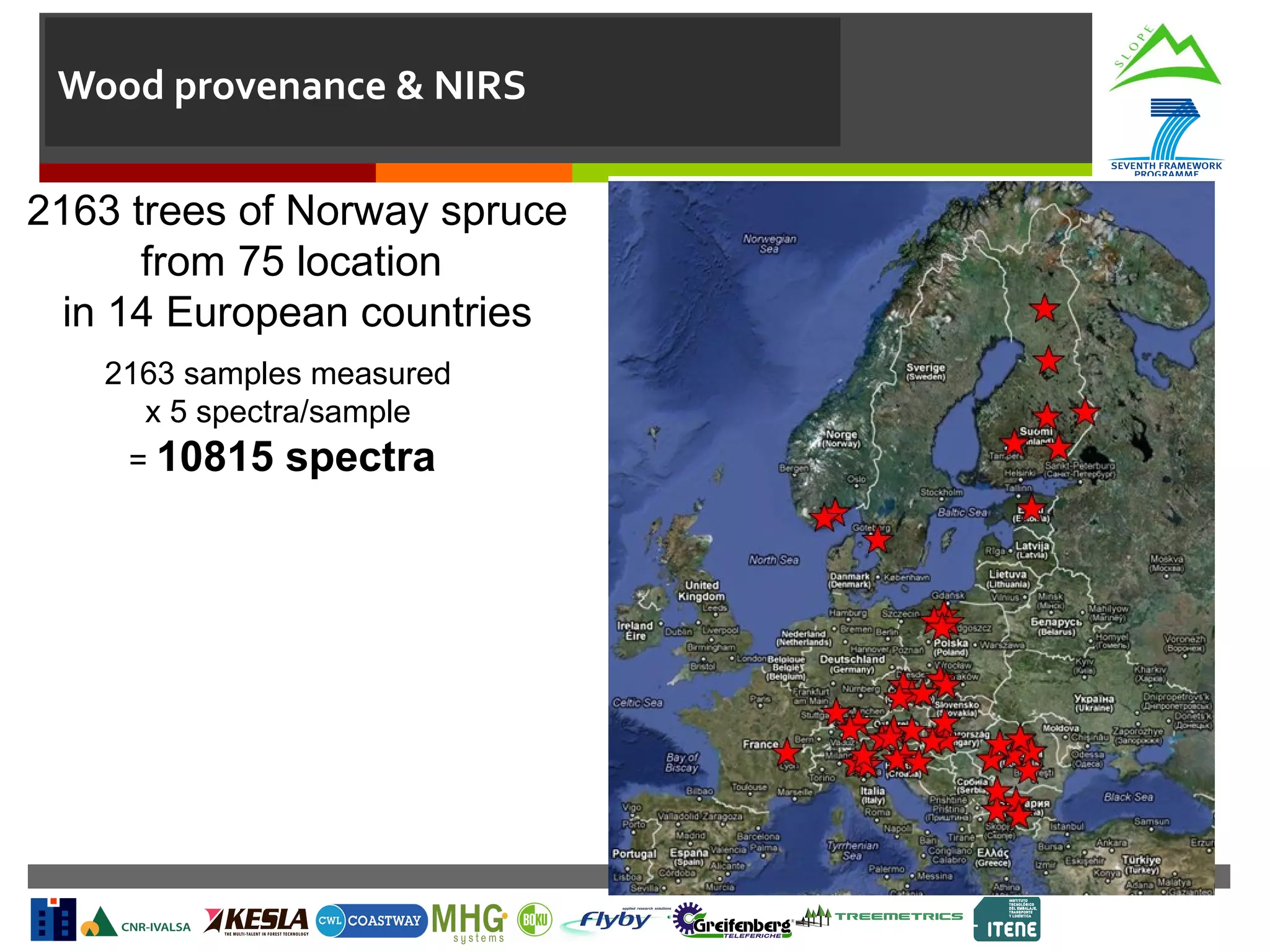
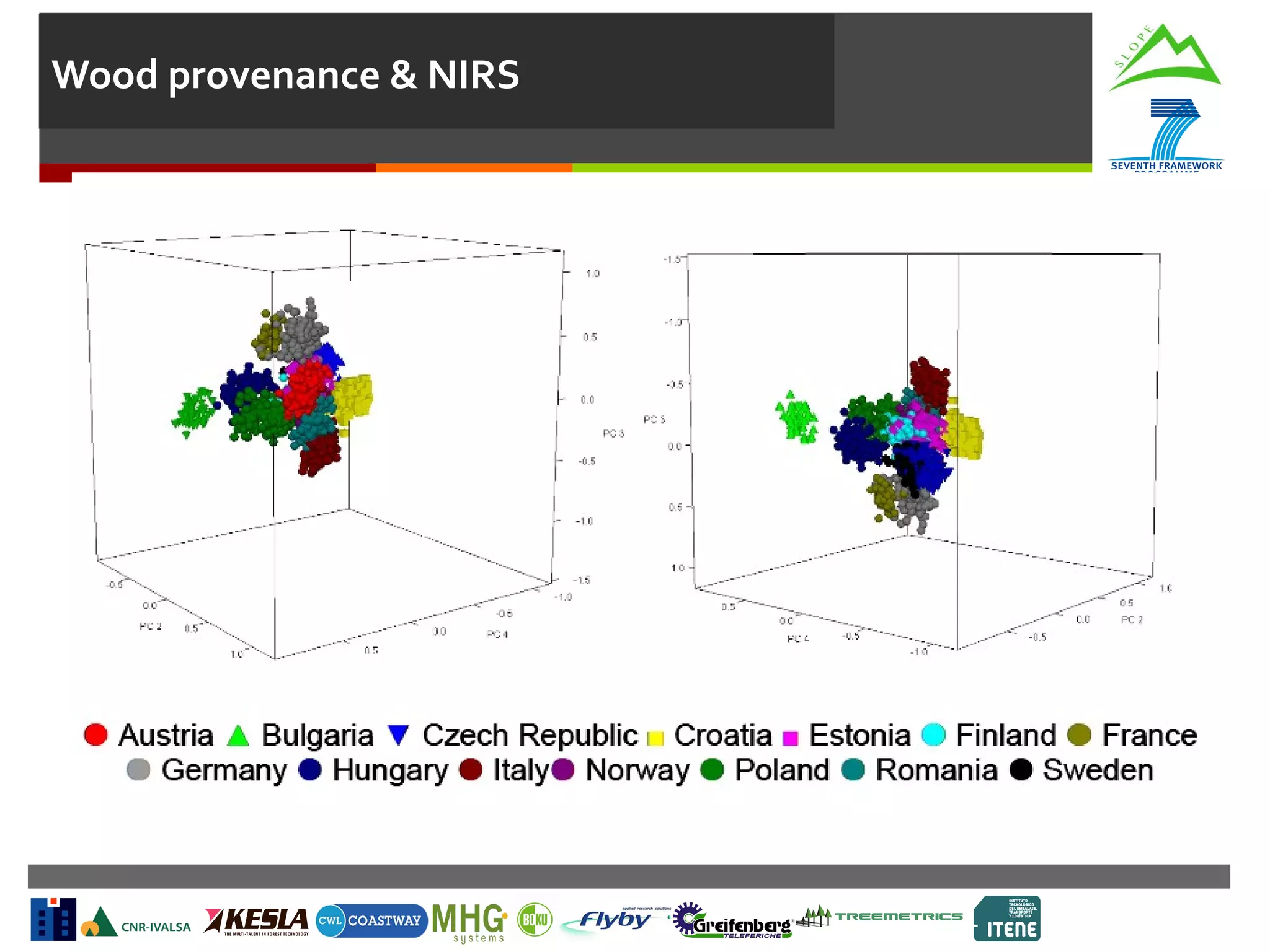
This document summarizes a task to evaluate near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy for determining log and biomass quality in mountain forests. Several organizations will work together on the task, led by CNR. CNR will coordinate, evaluate NIR spectroscopy along the harvesting chain, and develop a "NIR quality index." Boku will support CNR with lab measurements and calibration transfer. Other partners will help collect NIR spectra in the field. The objectives are to evaluate NIR spectroscopy for characterizing resources along the harvesting chain and provide guidelines for collection and analysis of NIR spectra. Activities will include feasibility studies, developing chemometric models to predict quality indicators from spectra, and transferring calibrations between lab and portable instruments. Del