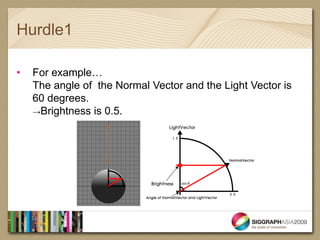
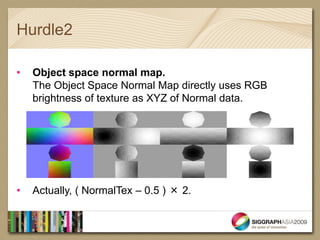
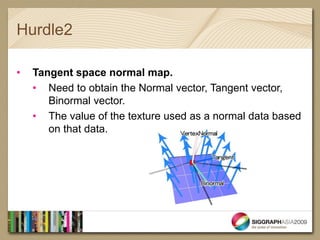
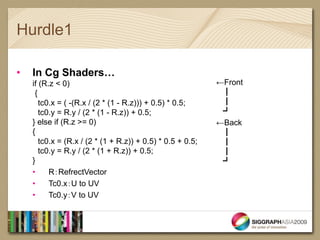
- The document introduces real-time shaders for artists working in Softimage and discusses three key hurdles for understanding shaders: 1) dot products and shading calculations, 2) normal mapping and environment mapping, and 3) shader blending techniques.
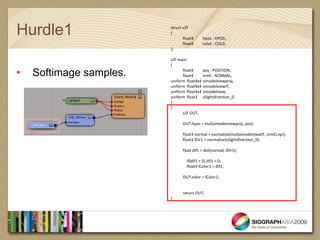
- It provides examples of shader code to illustrate dot products, normal mapping, and blurring textures.
- The goal is to help artists understand and use shaders through a tutorial on basic shader concepts and translating shader logic into Softimage.