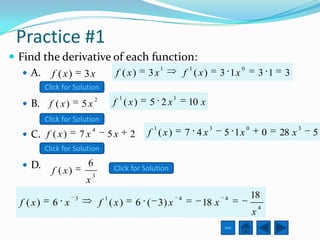
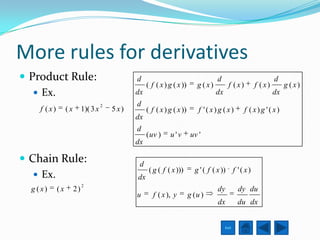
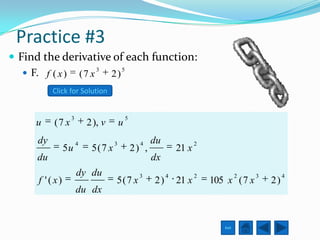
The document defines the derivative and discusses rules for computing derivatives. It introduces the derivative as describing the slope of a curve at a point. It then outlines several basic rules for determining derivatives, such as the power rule, sum rule, and rules for constants and combinations of functions. The document also discusses the product rule, chain rule, and applications of derivatives to motion and rates of change problems.