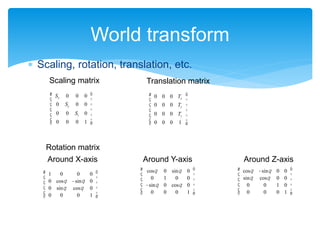
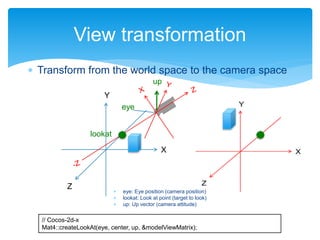
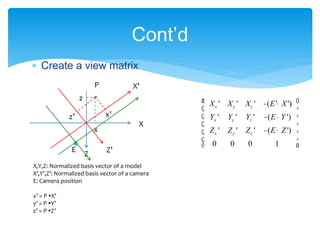
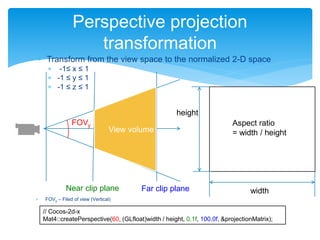
The document outlines the second day of an international 5-day graphics programming workshop focused on 3D geometry and transformations using Cocos2D-x. It covers topics such as camera usage, world and view transformations, projection, texture mapping, and the mathematics behind 3D graphics. The agenda includes practical work on dice modeling, shader programming, and managing the drawing order using depth buffers.



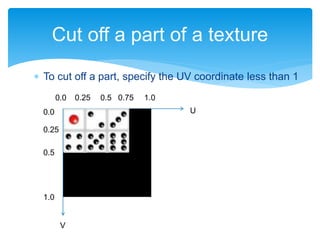

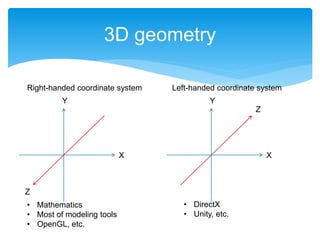
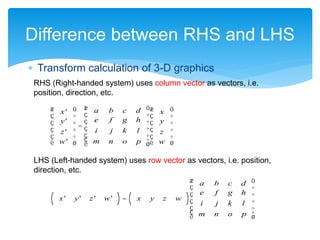
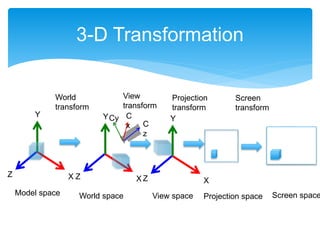
![ Draw a cubic dice not using a camera
Copy the whole project to a new project “WSSample2”
Create a cube vertices and draw
For lighting, prepare normal vectors (Nx,Ny,Nz)
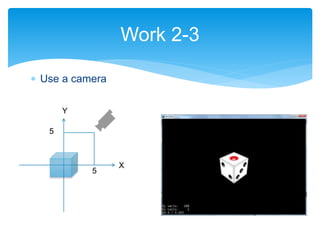
Work 2-2
GLfloat vertices[] = {
// x y z Nx Ny Nz R G B A U V
-1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // 1
-1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.25f,
1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.25f, 0.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.25f, 0.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.25f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.25f, 0.25f,
// snip…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graphicsworkshop2014-2-140729010959-phpapp02/85/Trident-International-Graphics-Workshop-2014-2-5-14-320.jpg)