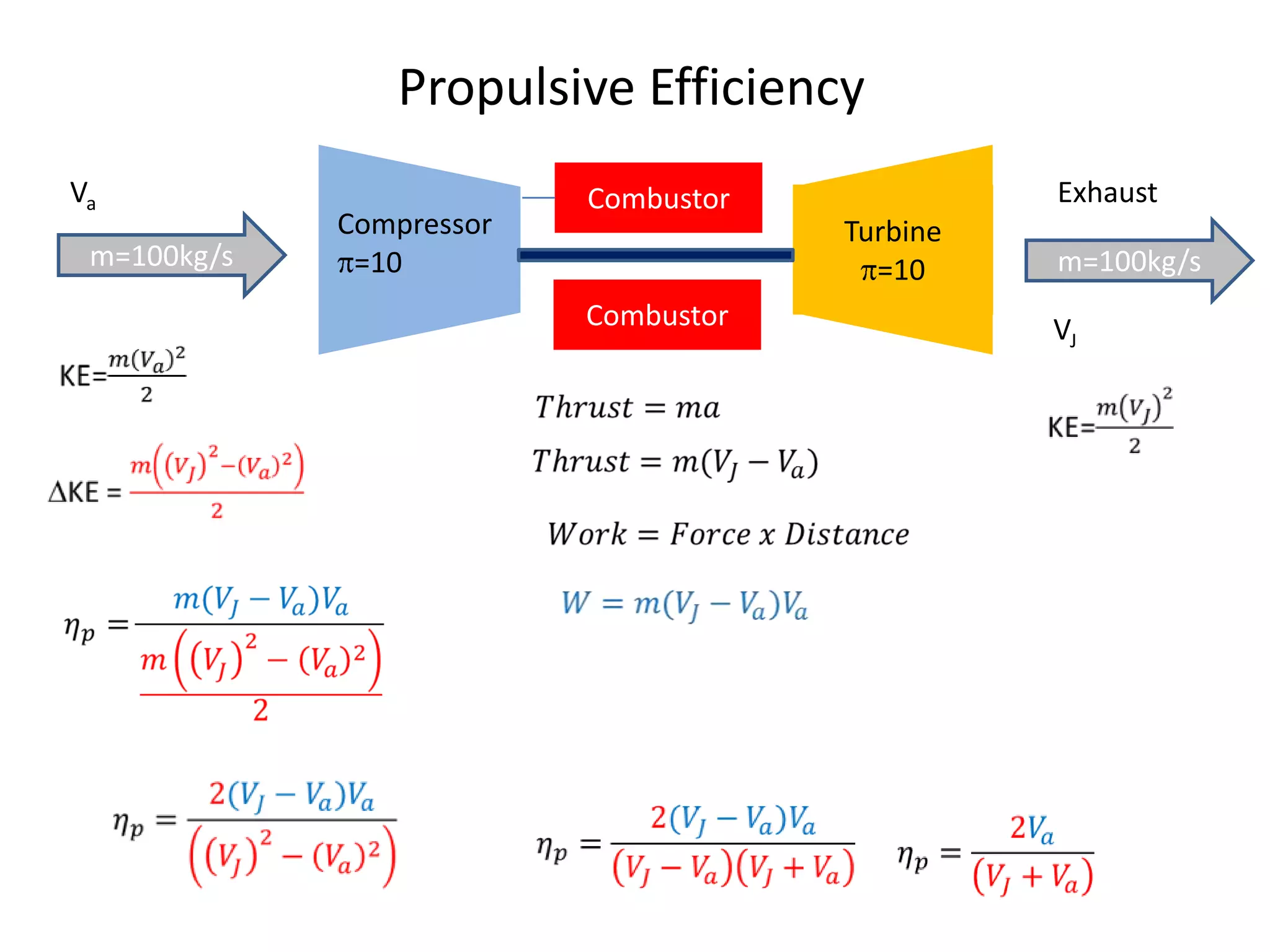
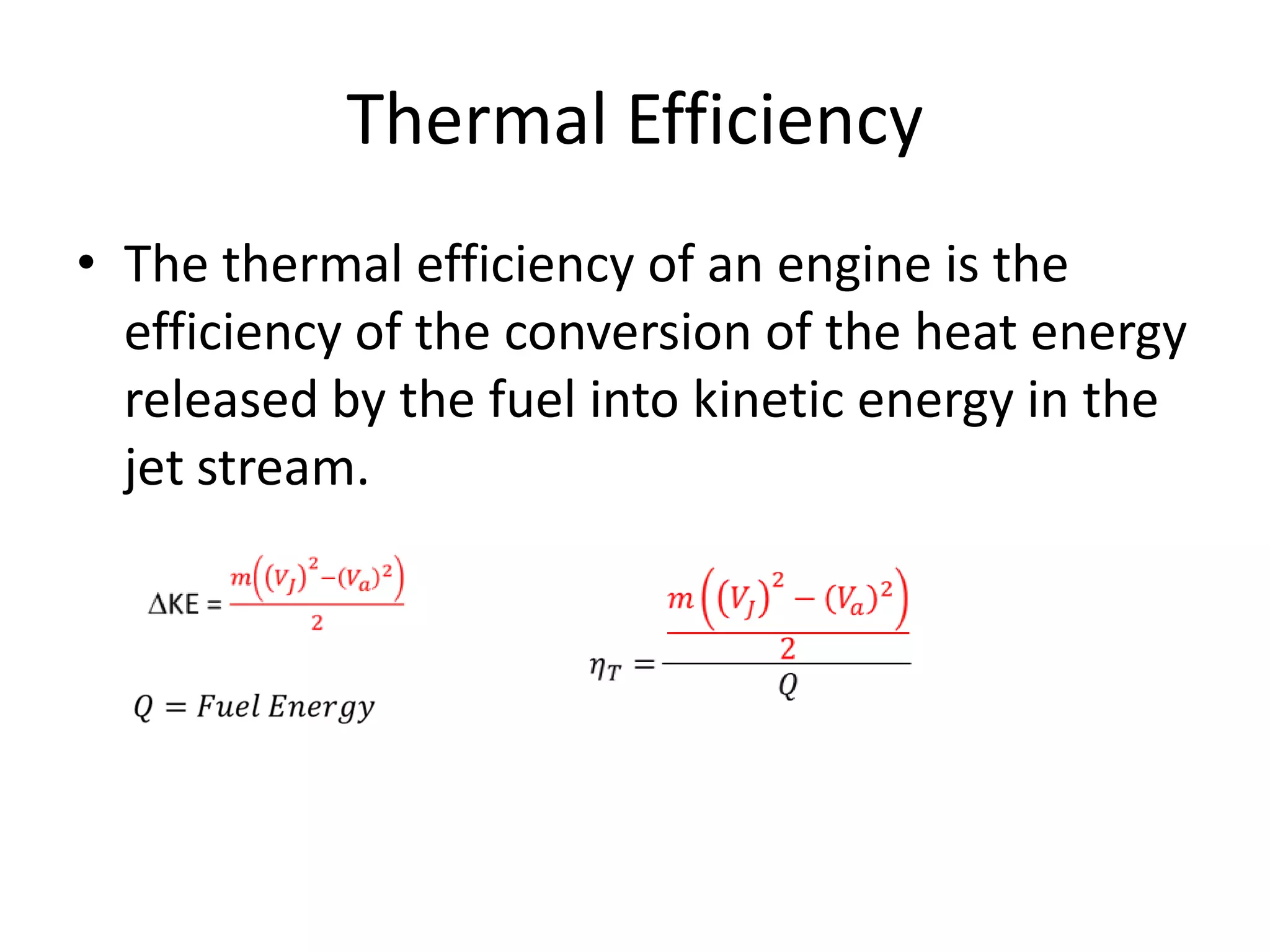
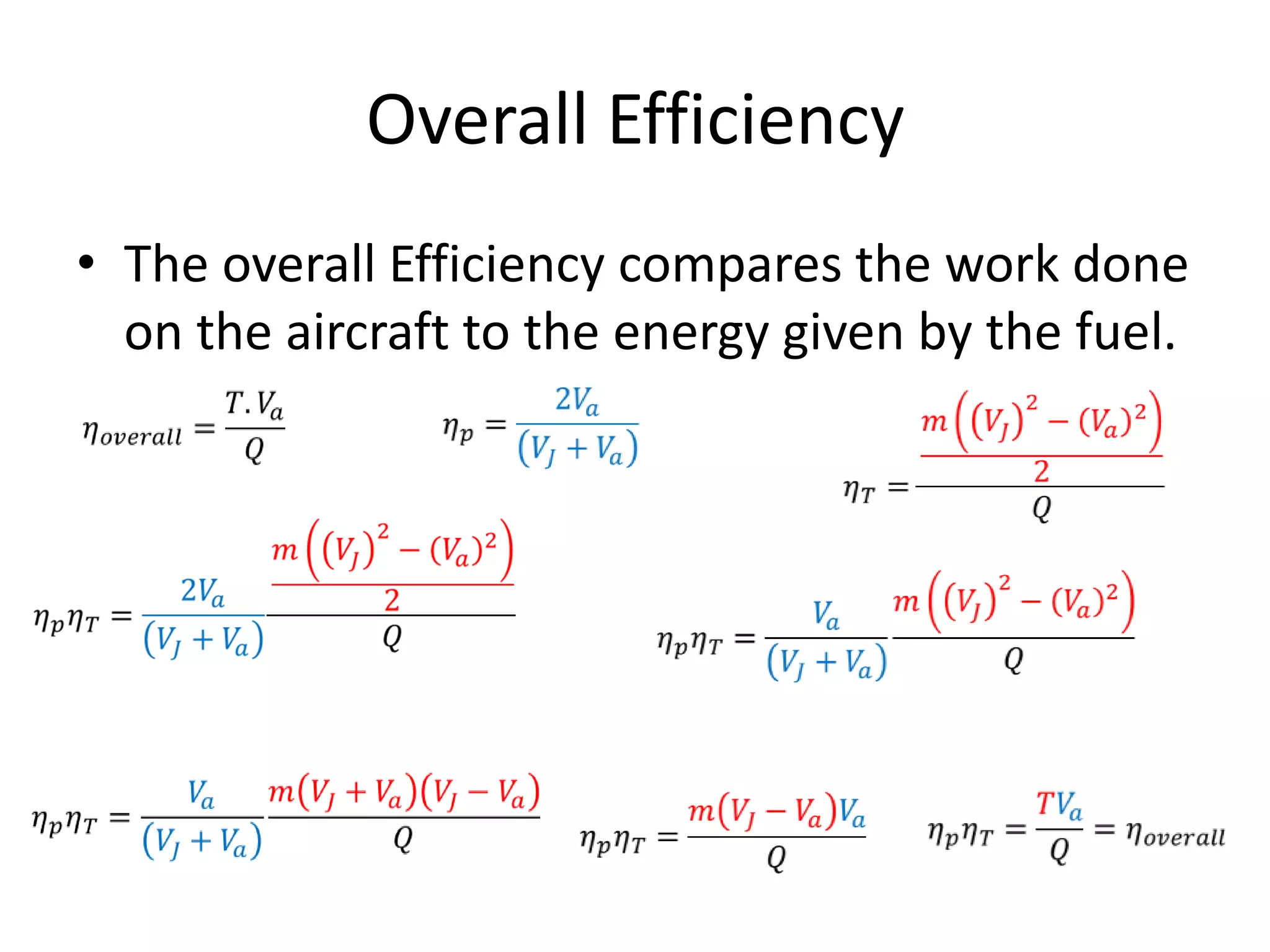
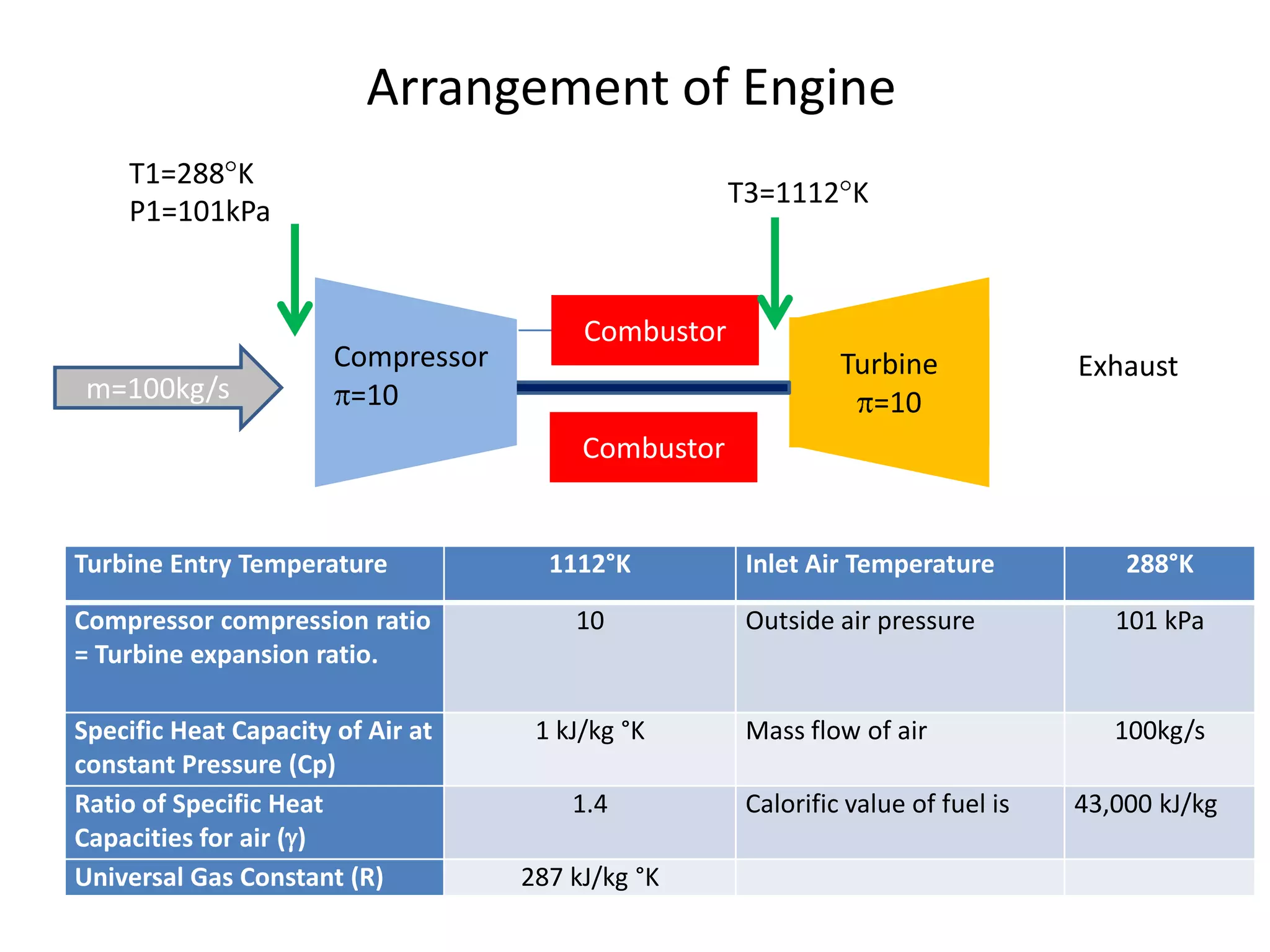
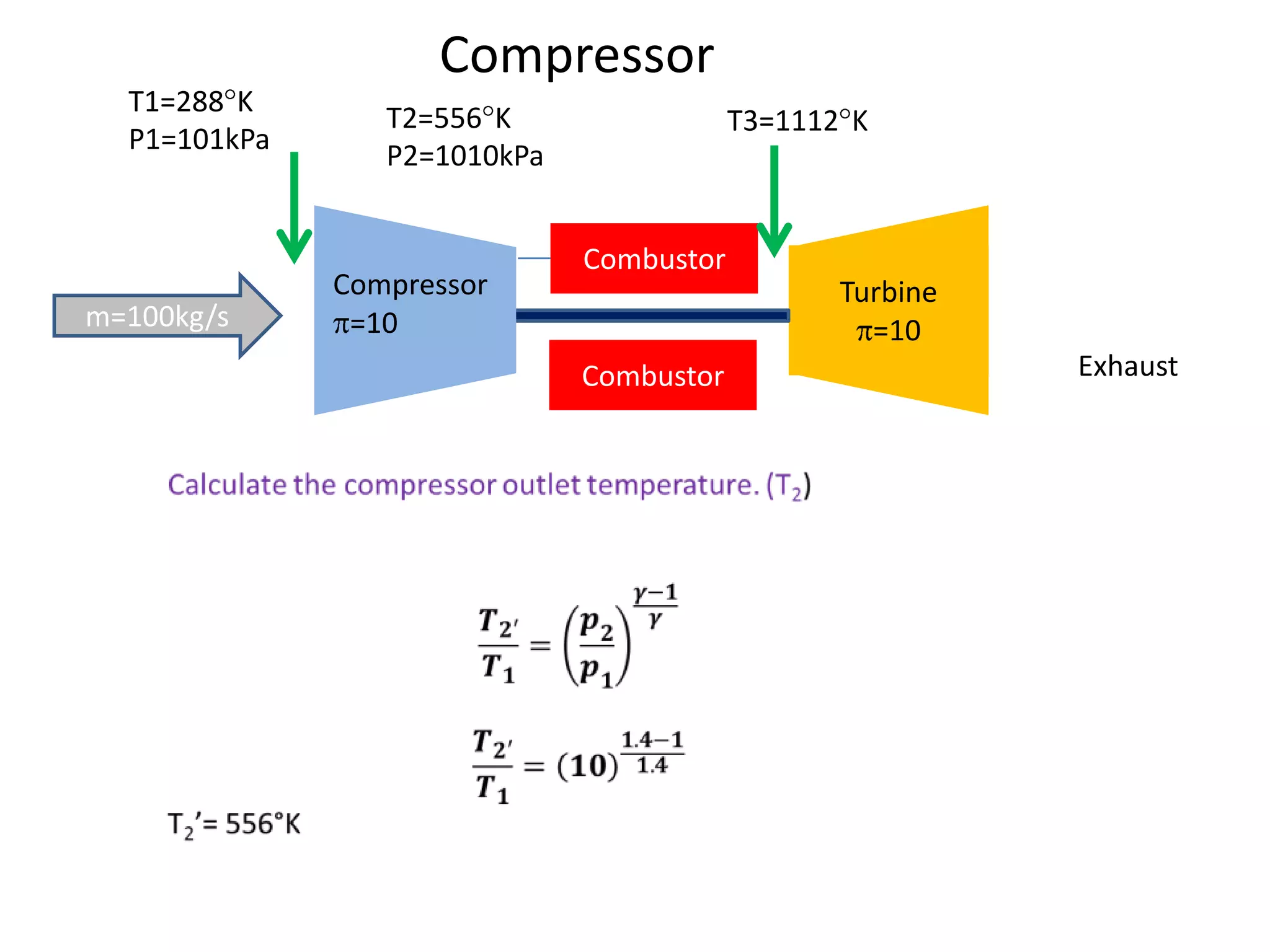
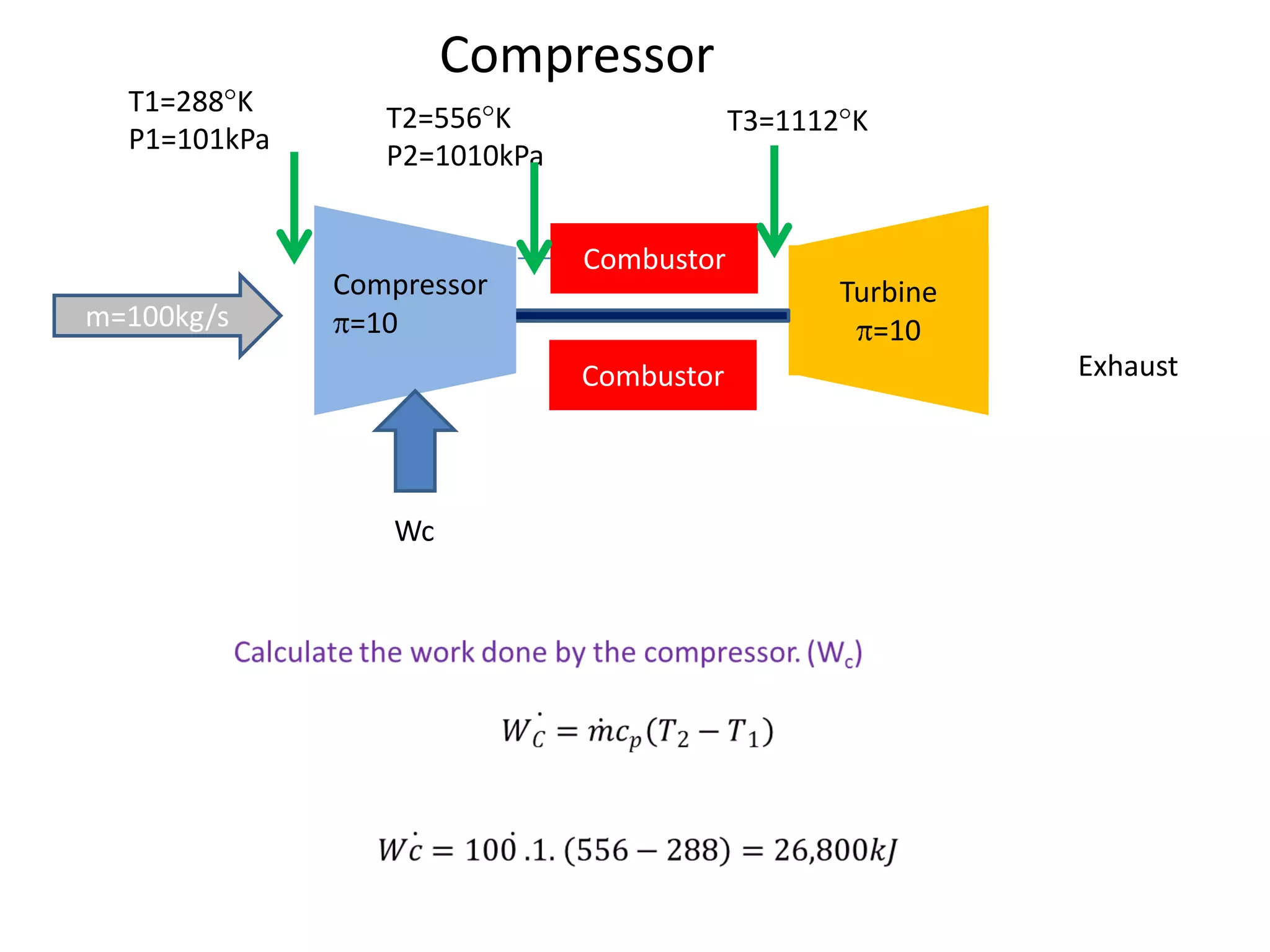
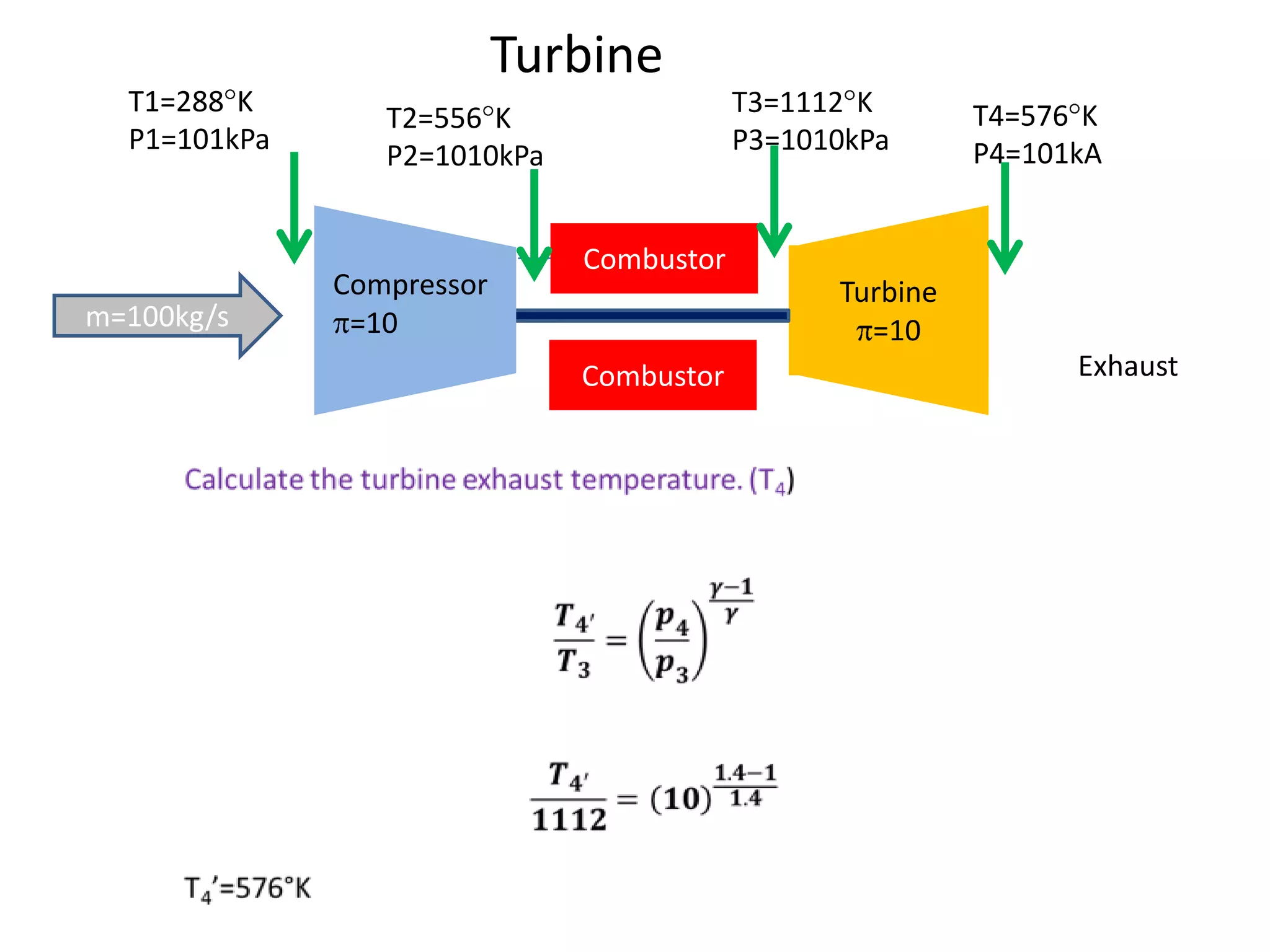
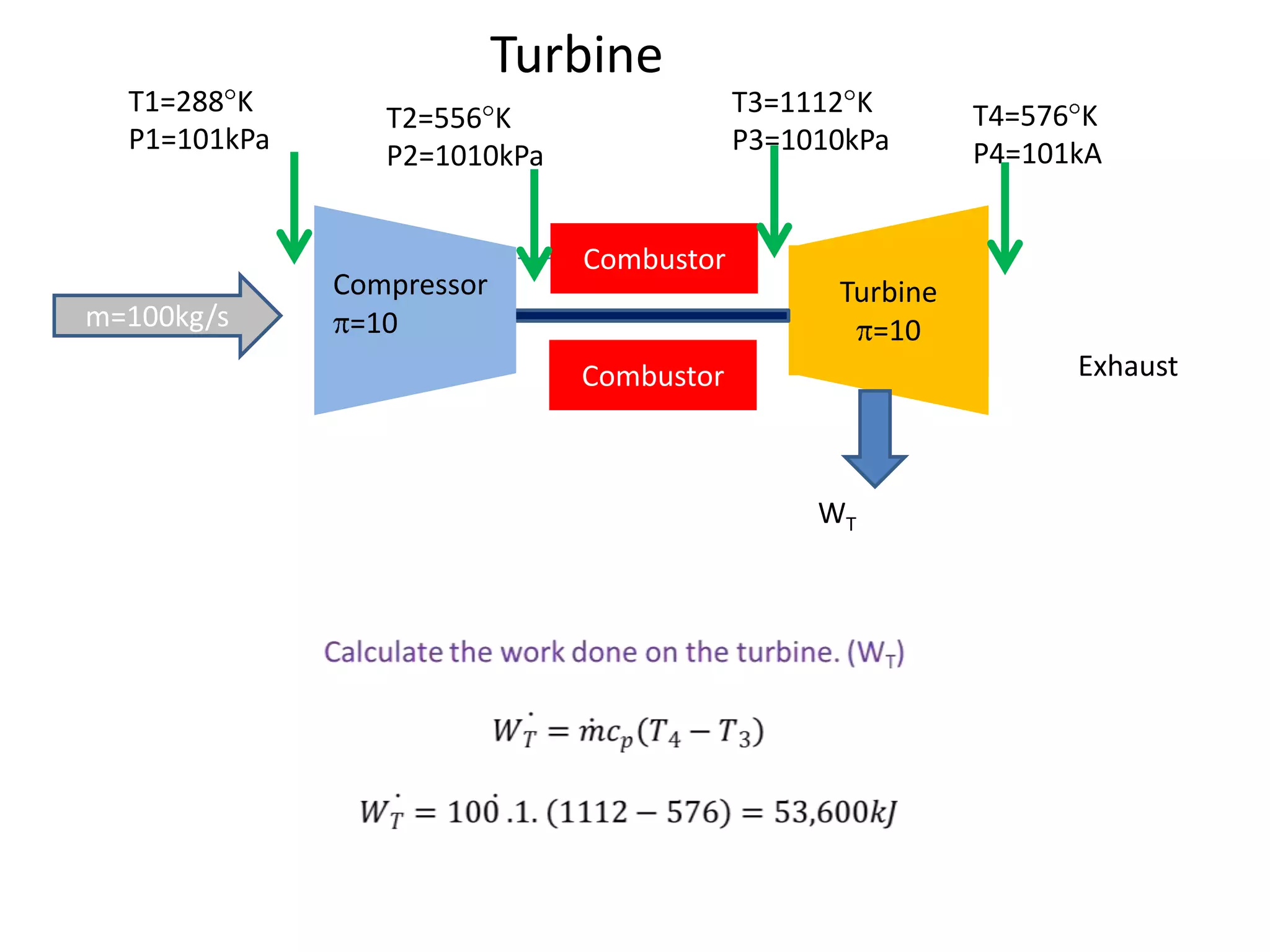
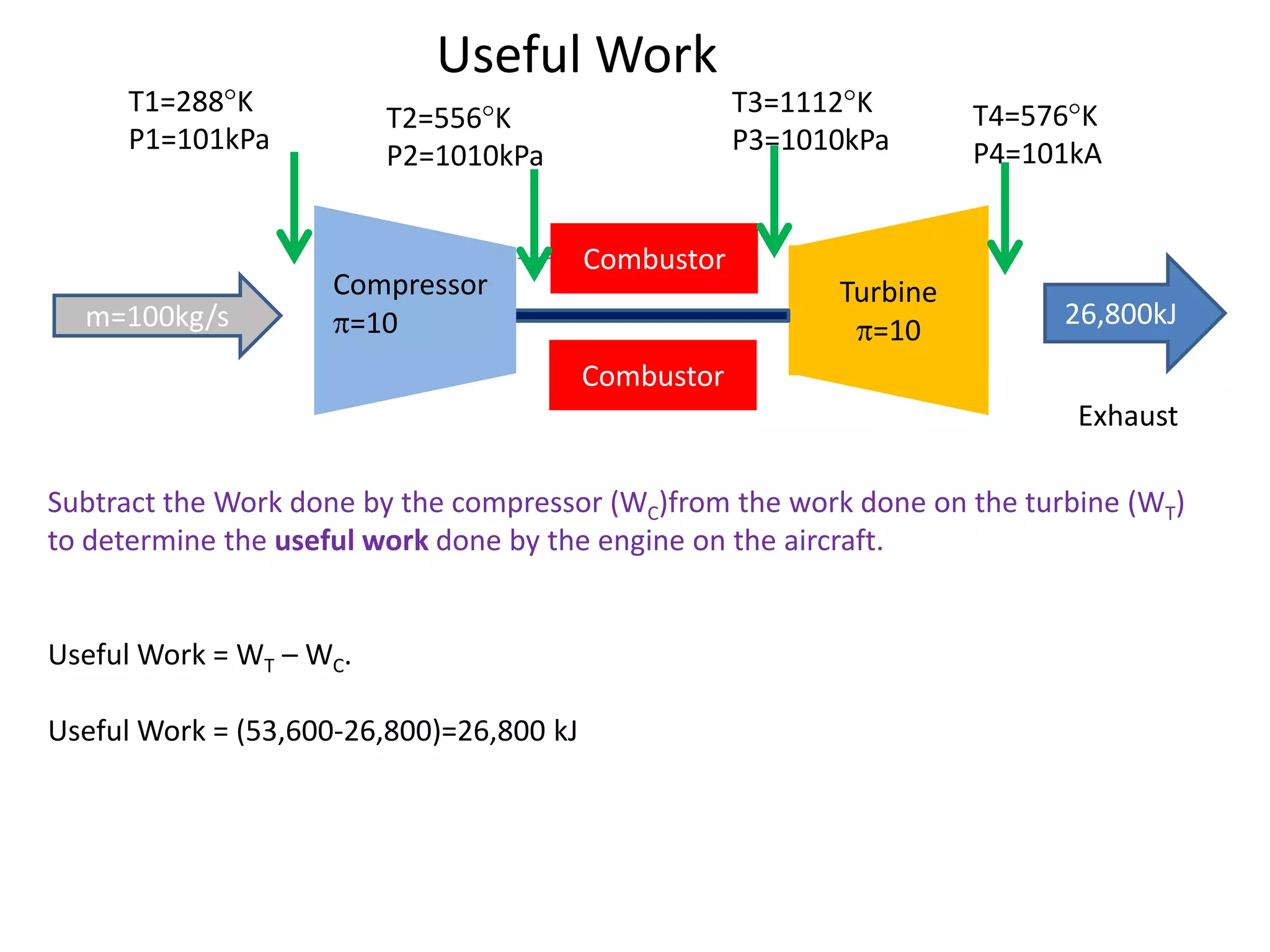
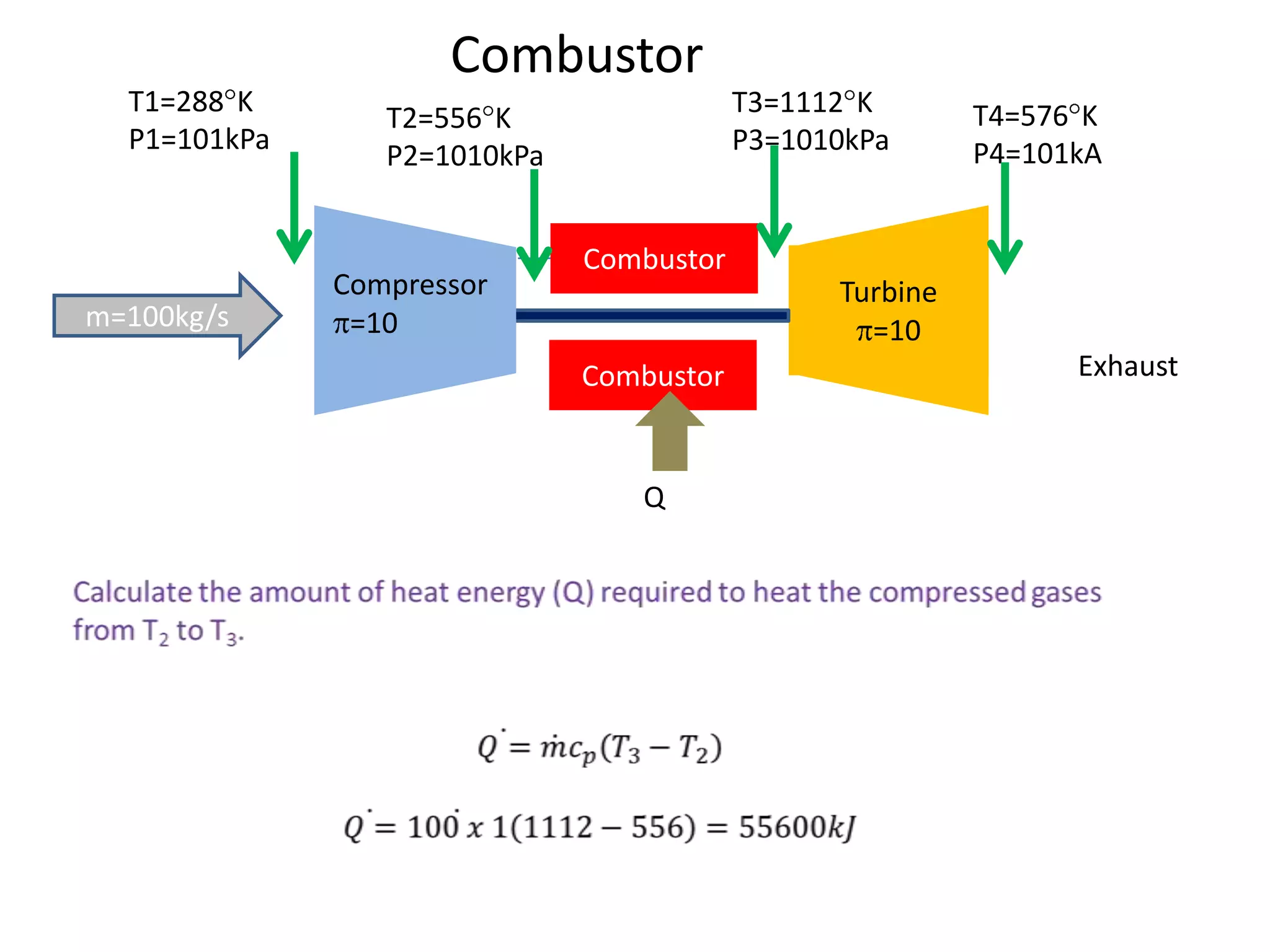
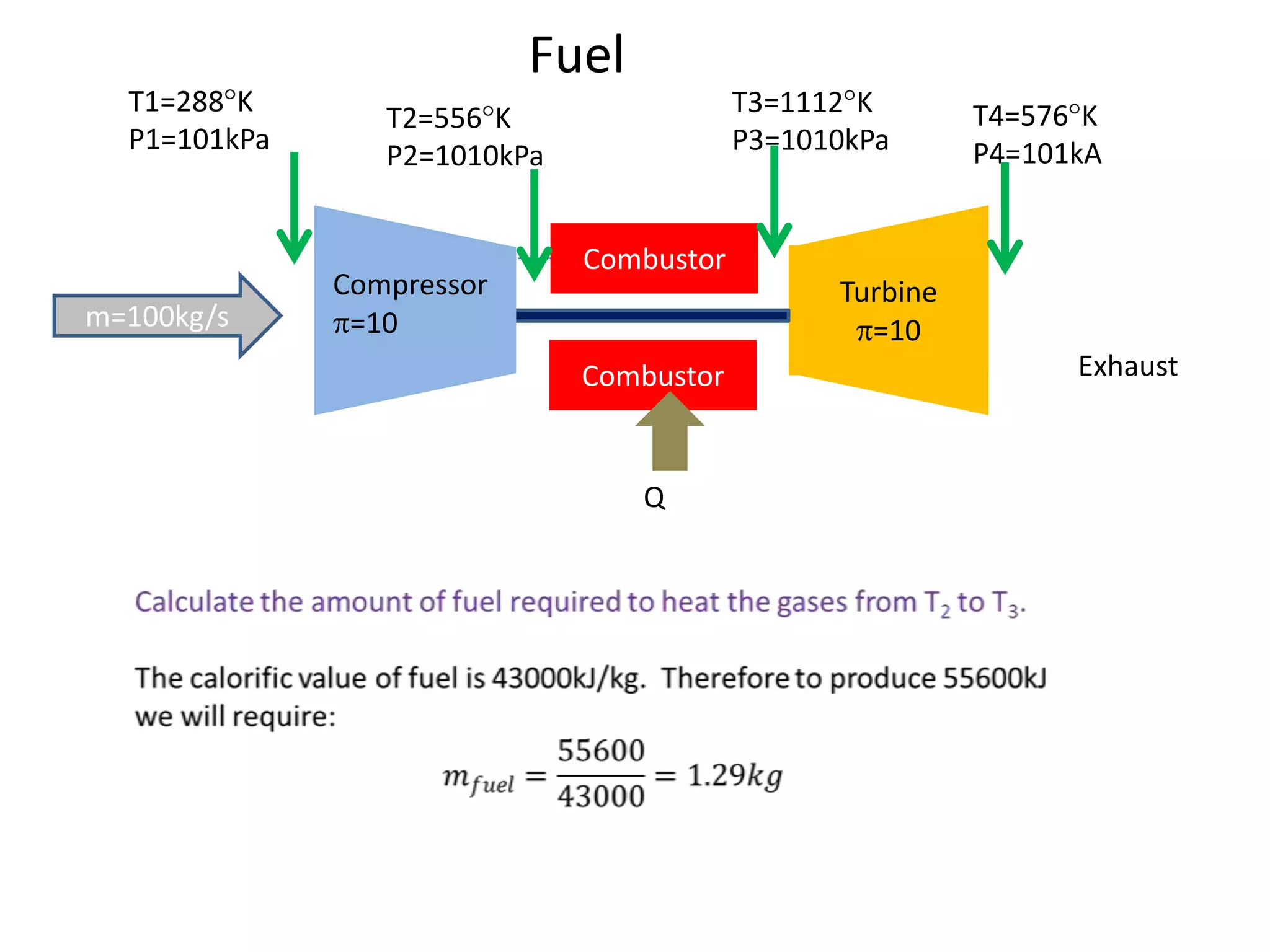
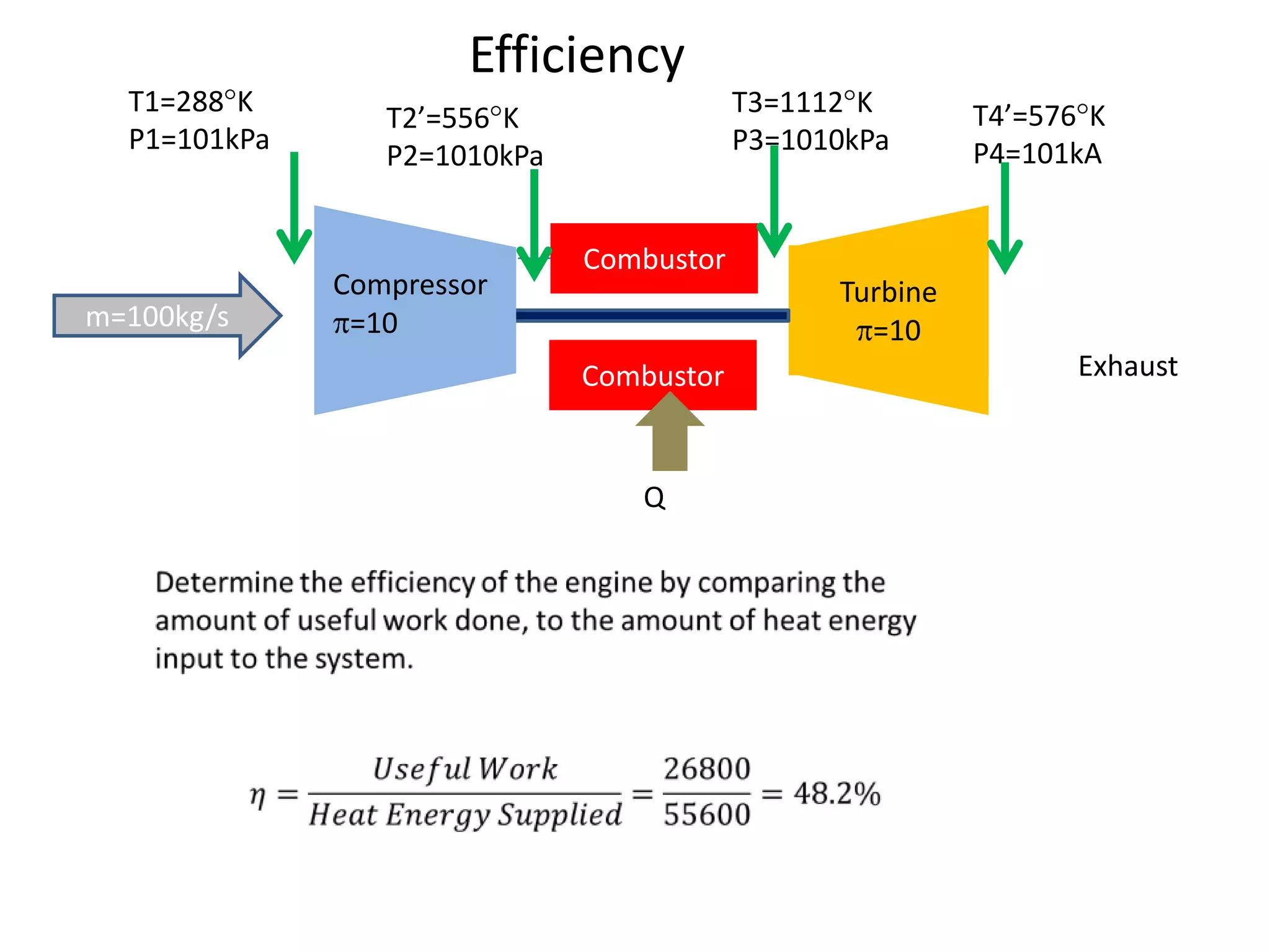
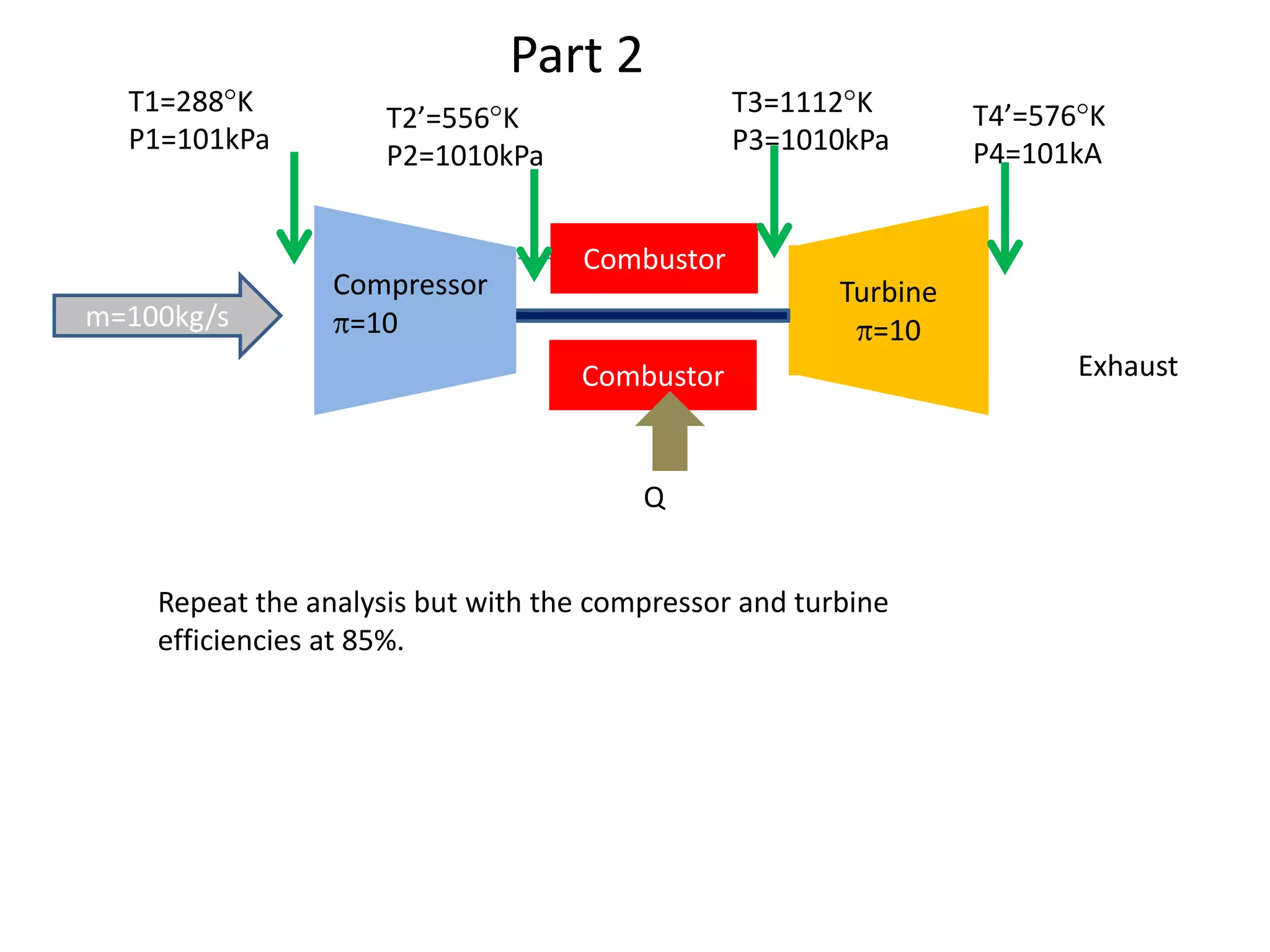
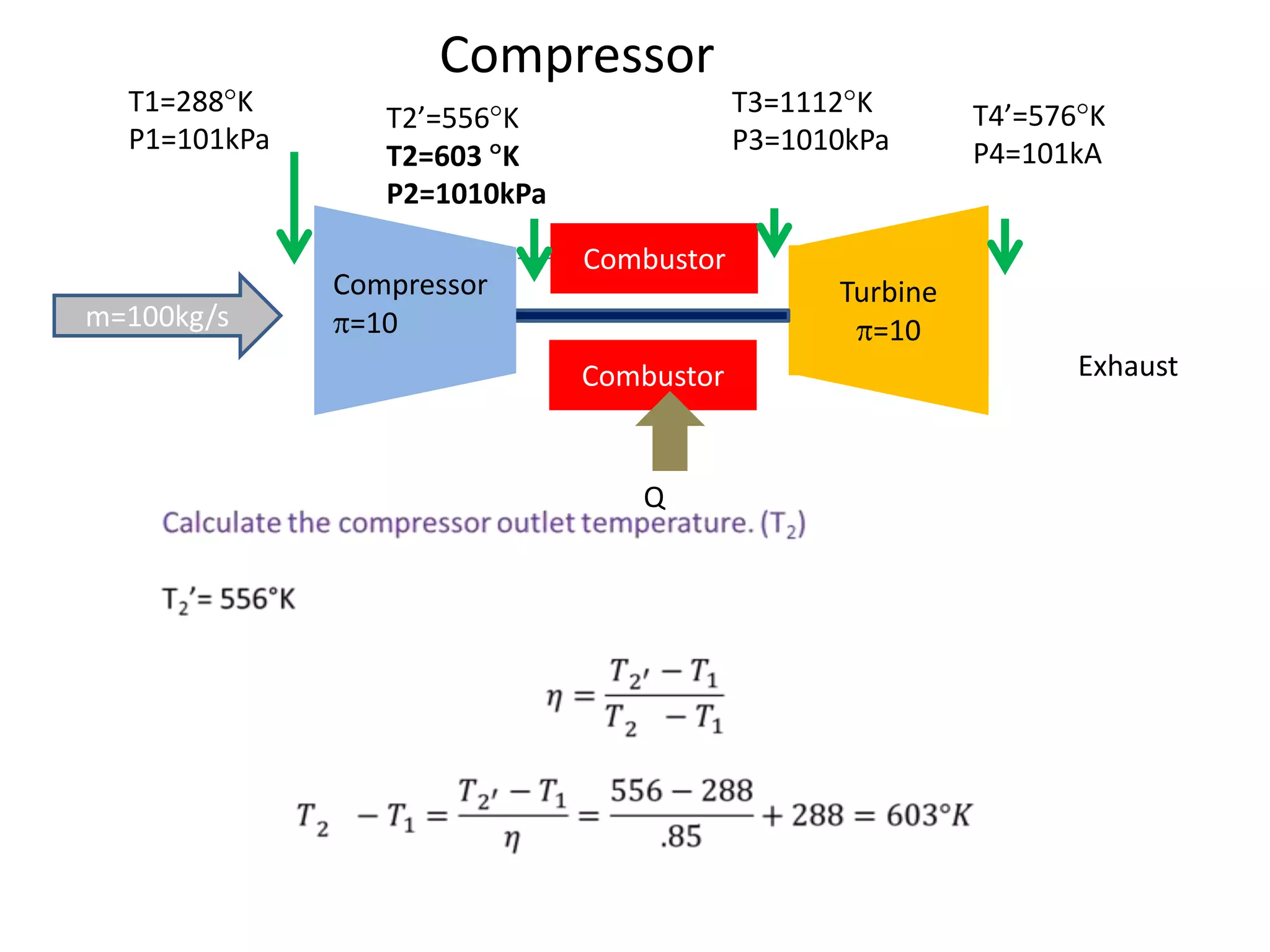
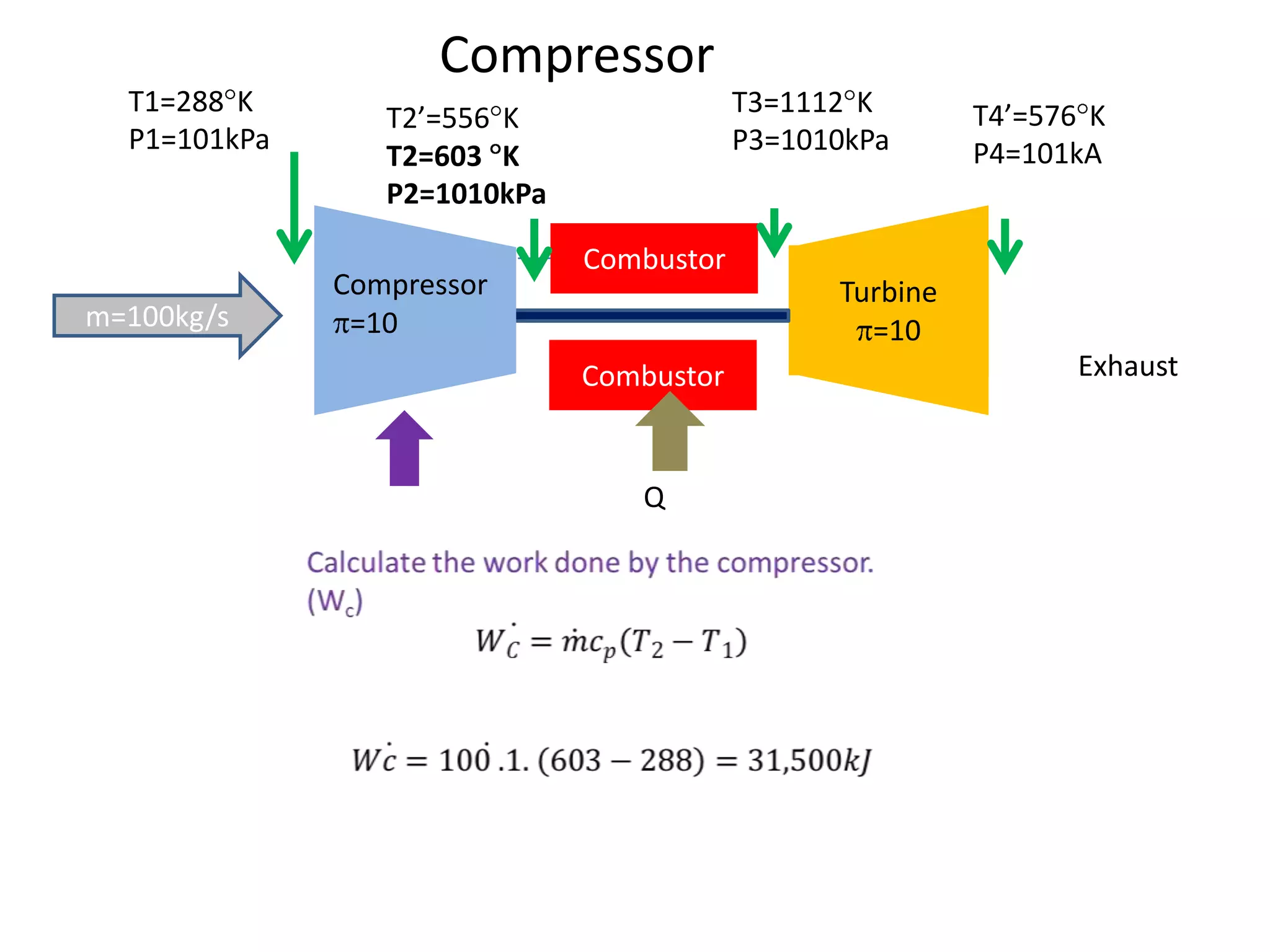
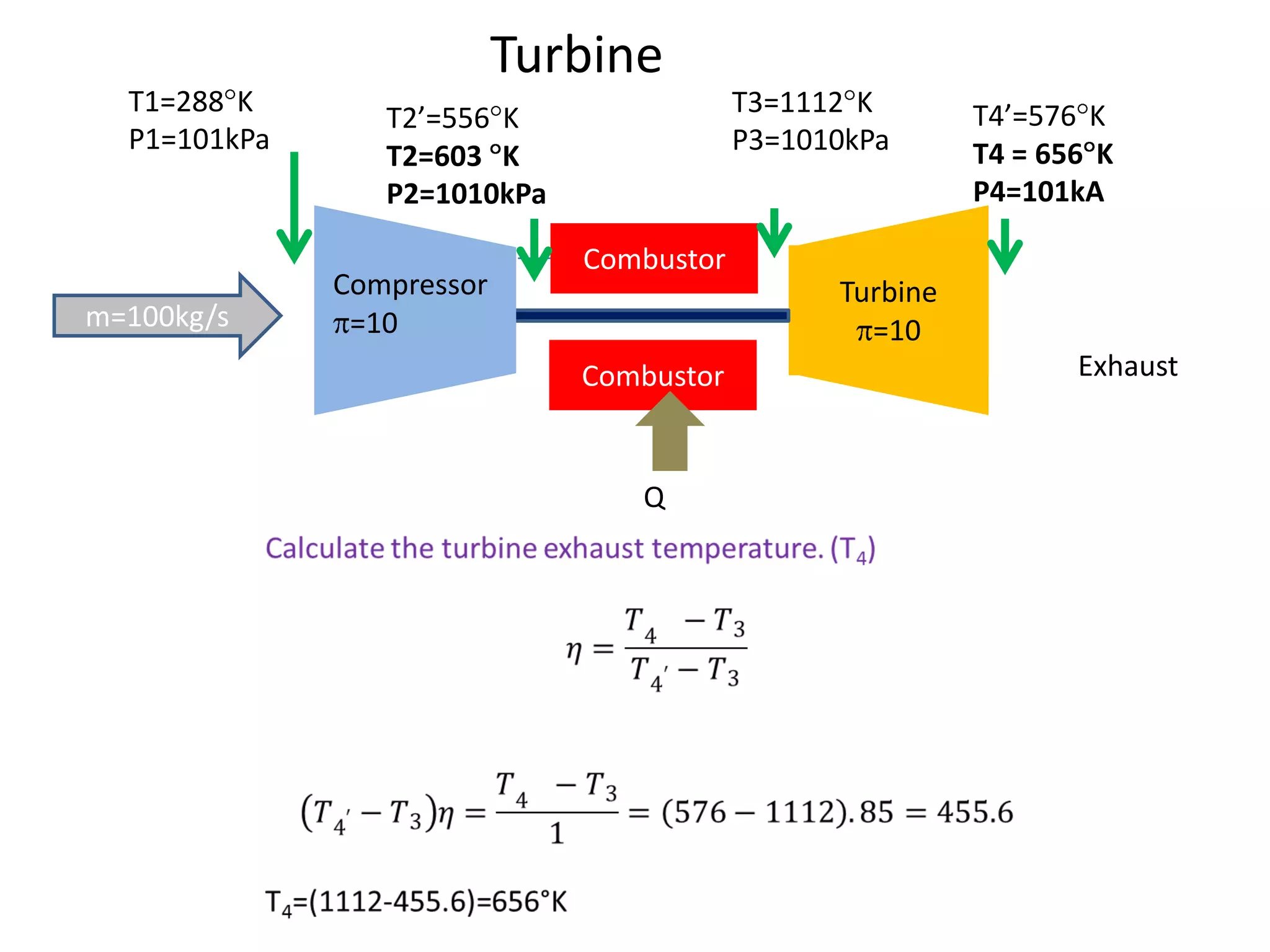
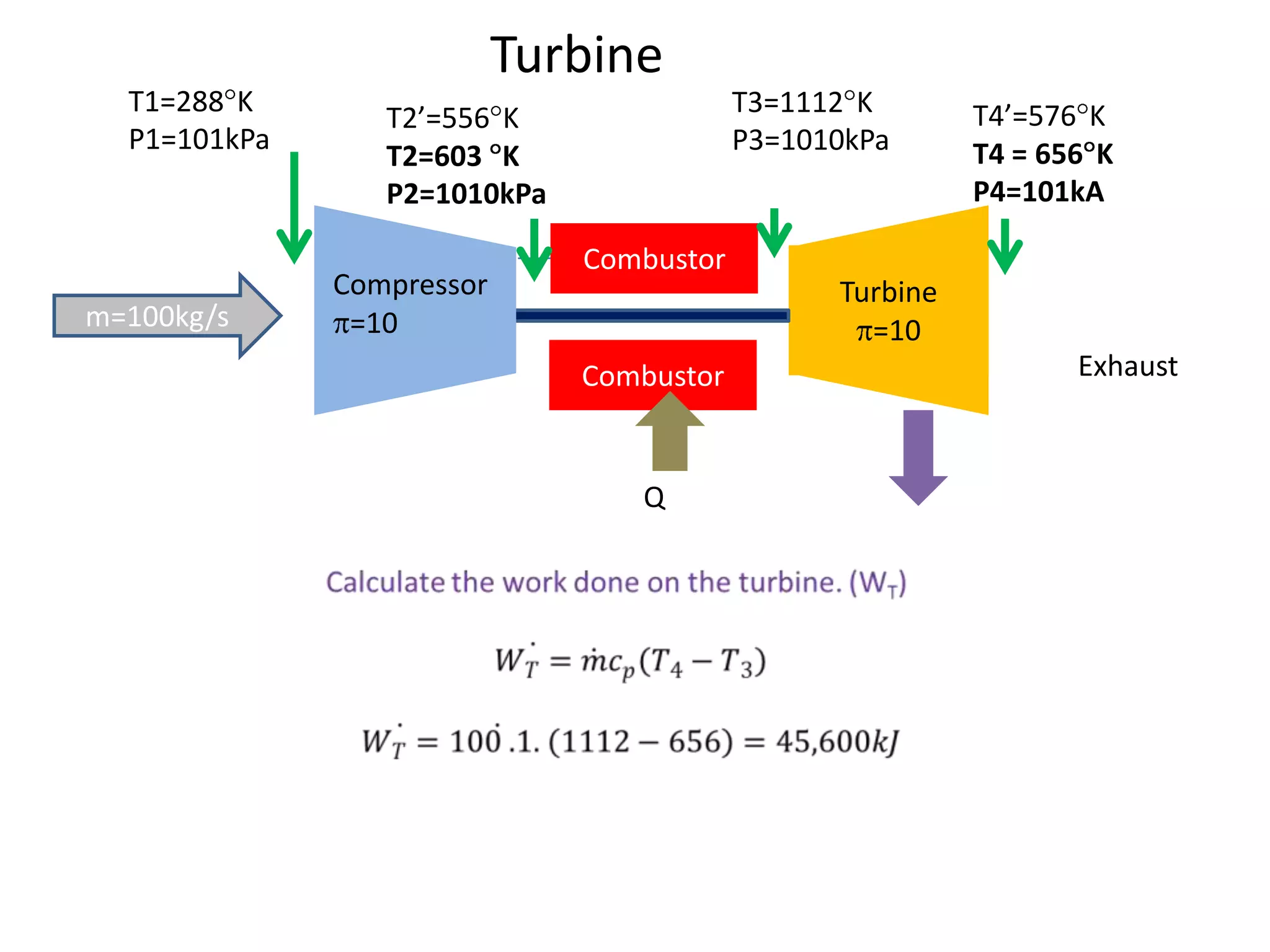
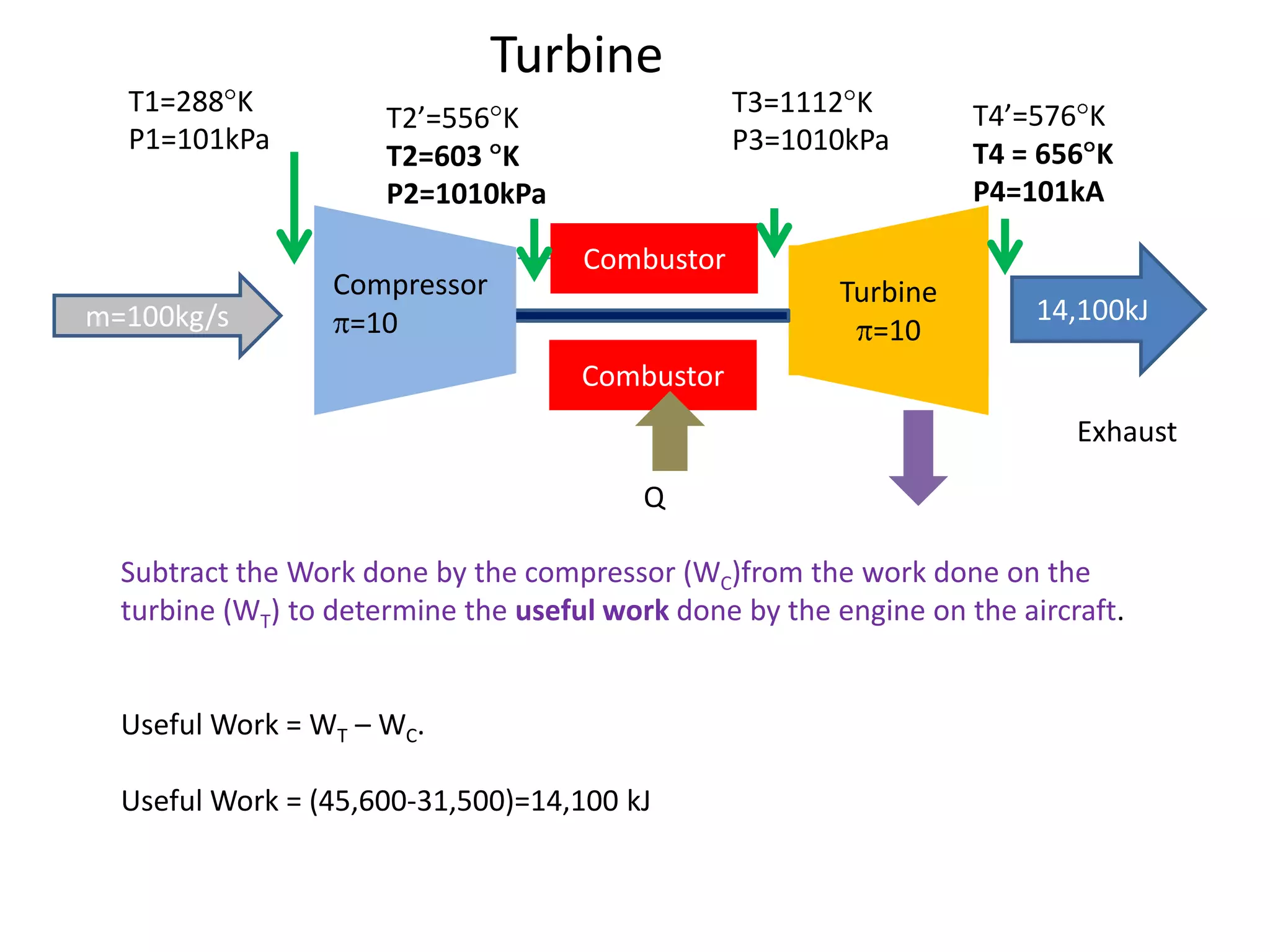
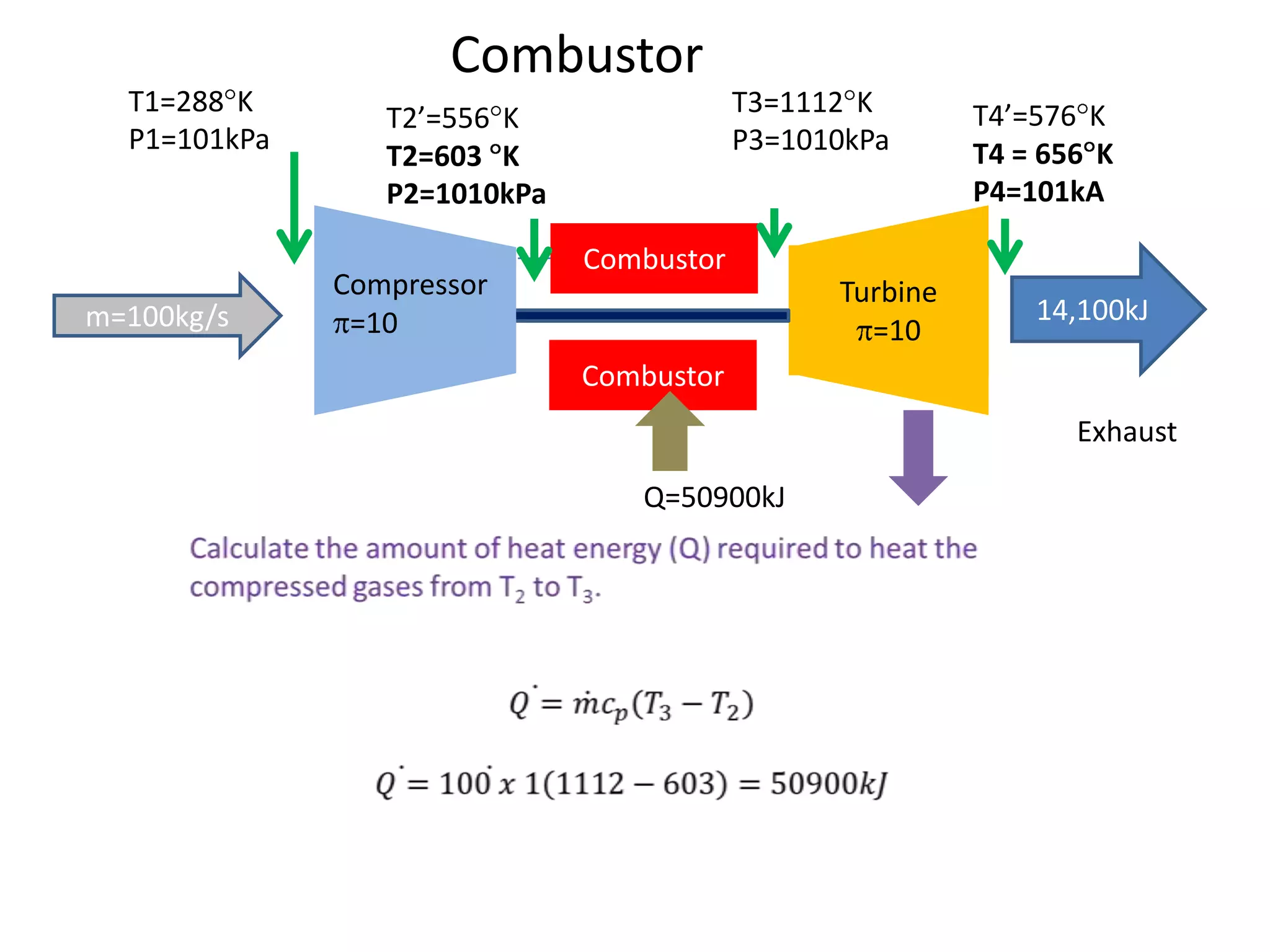
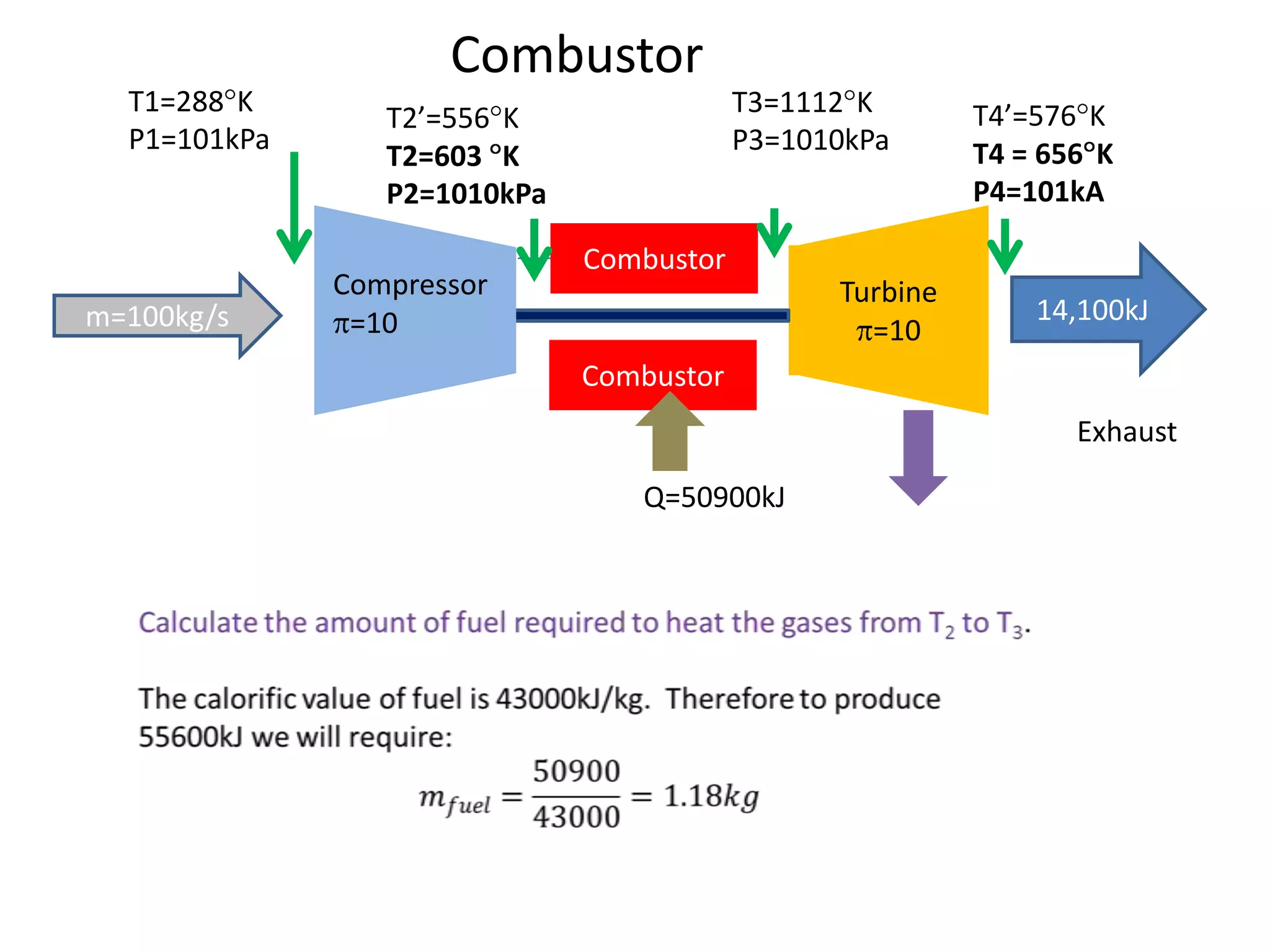
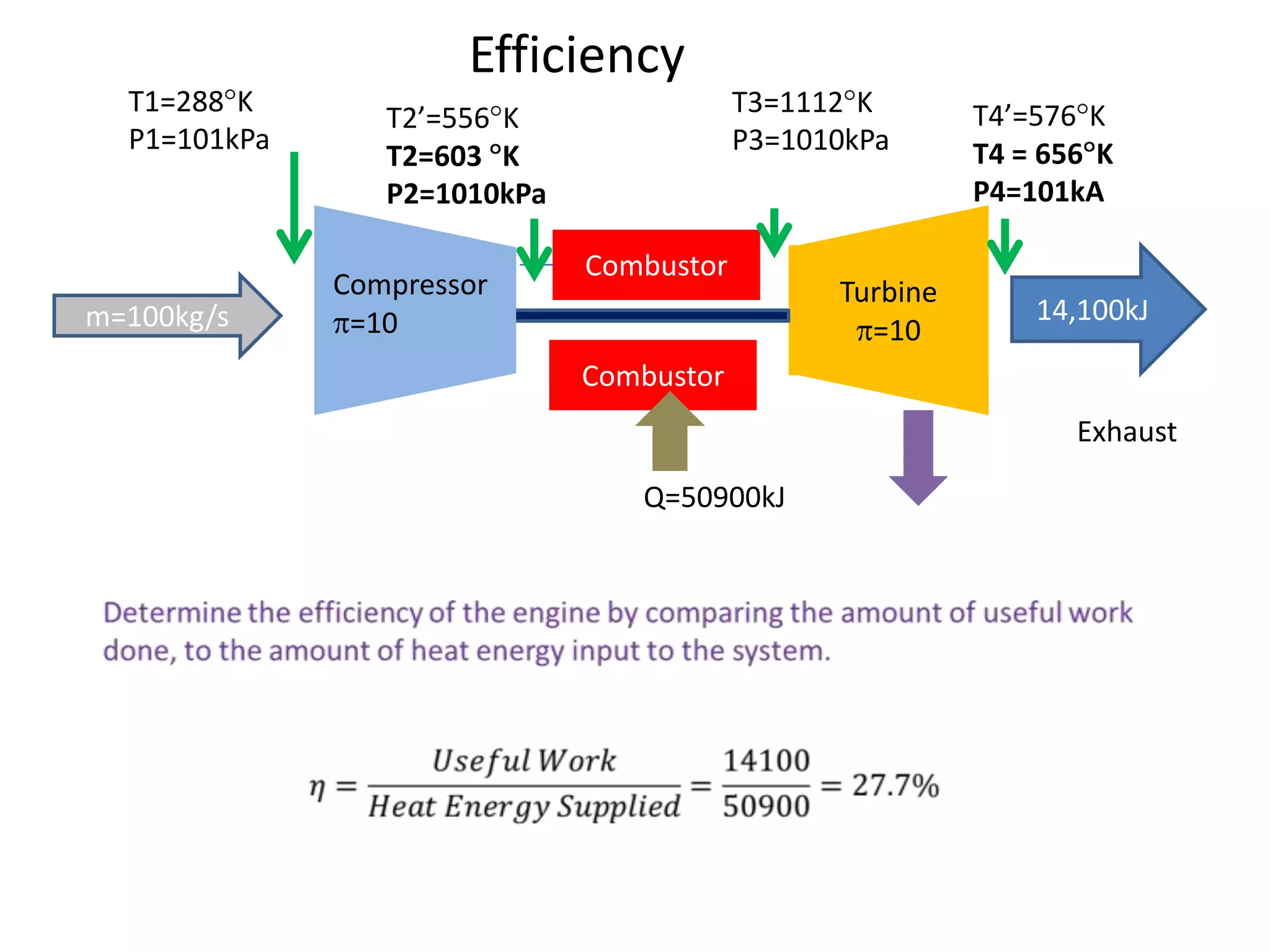
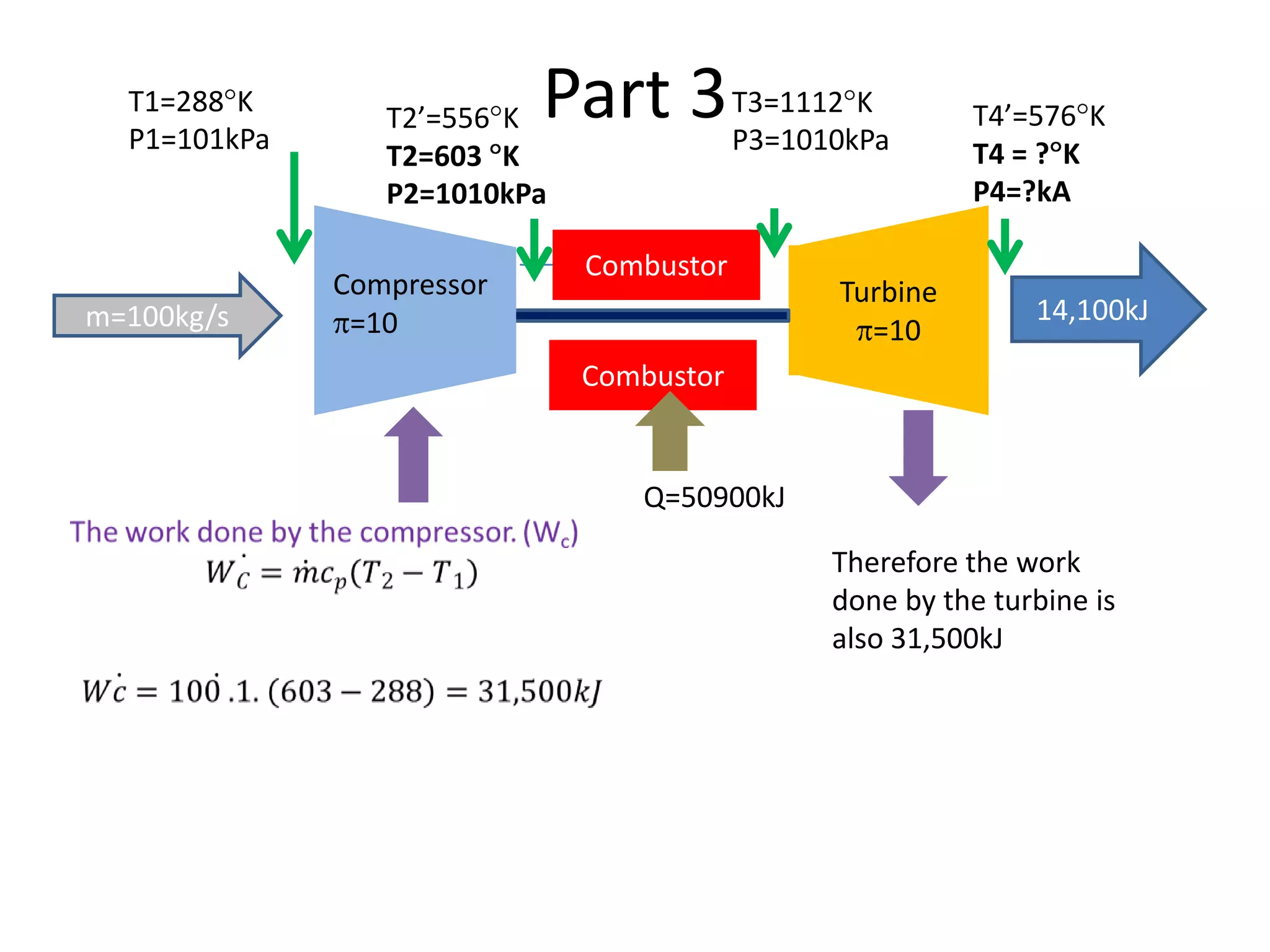
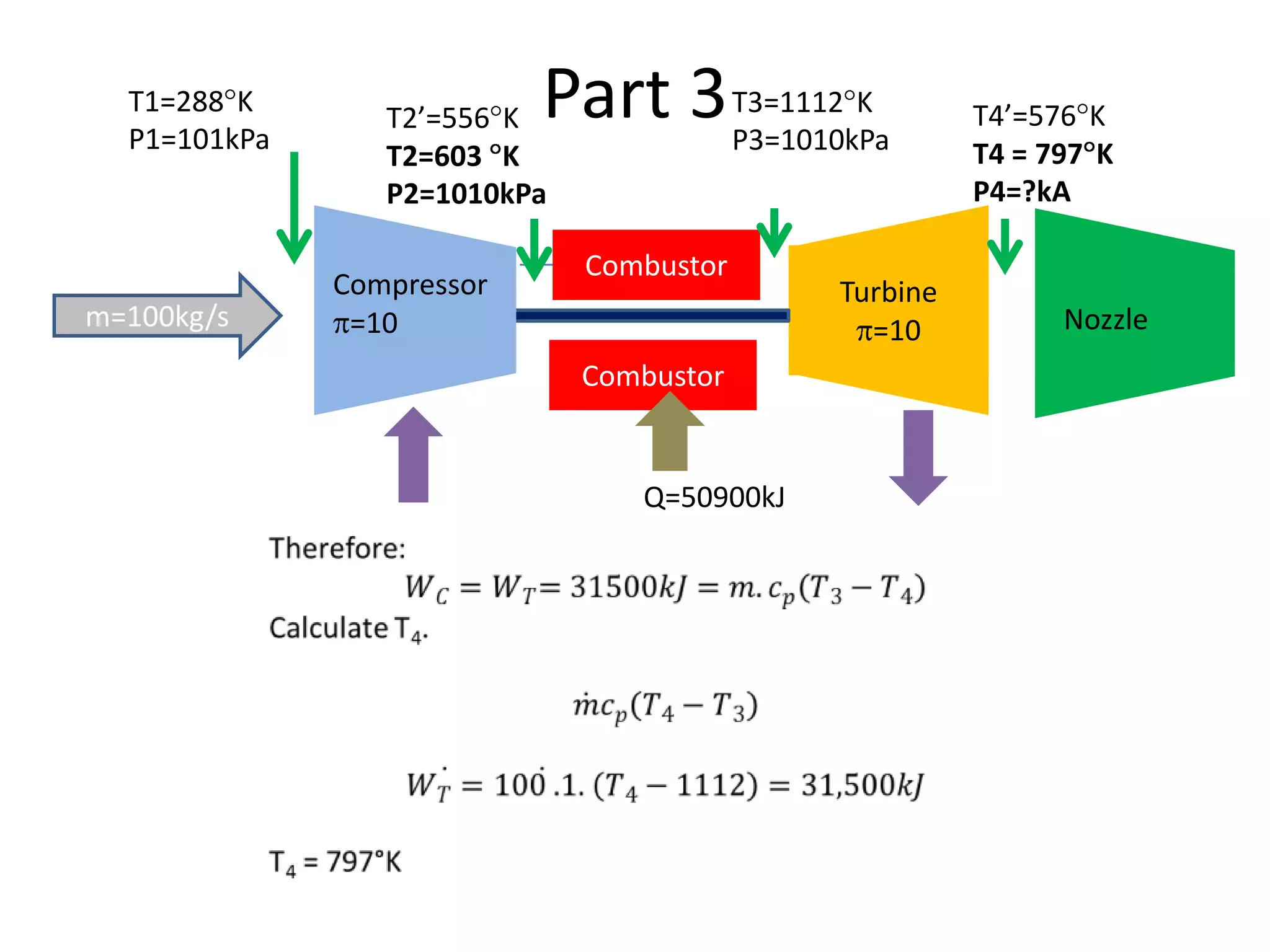
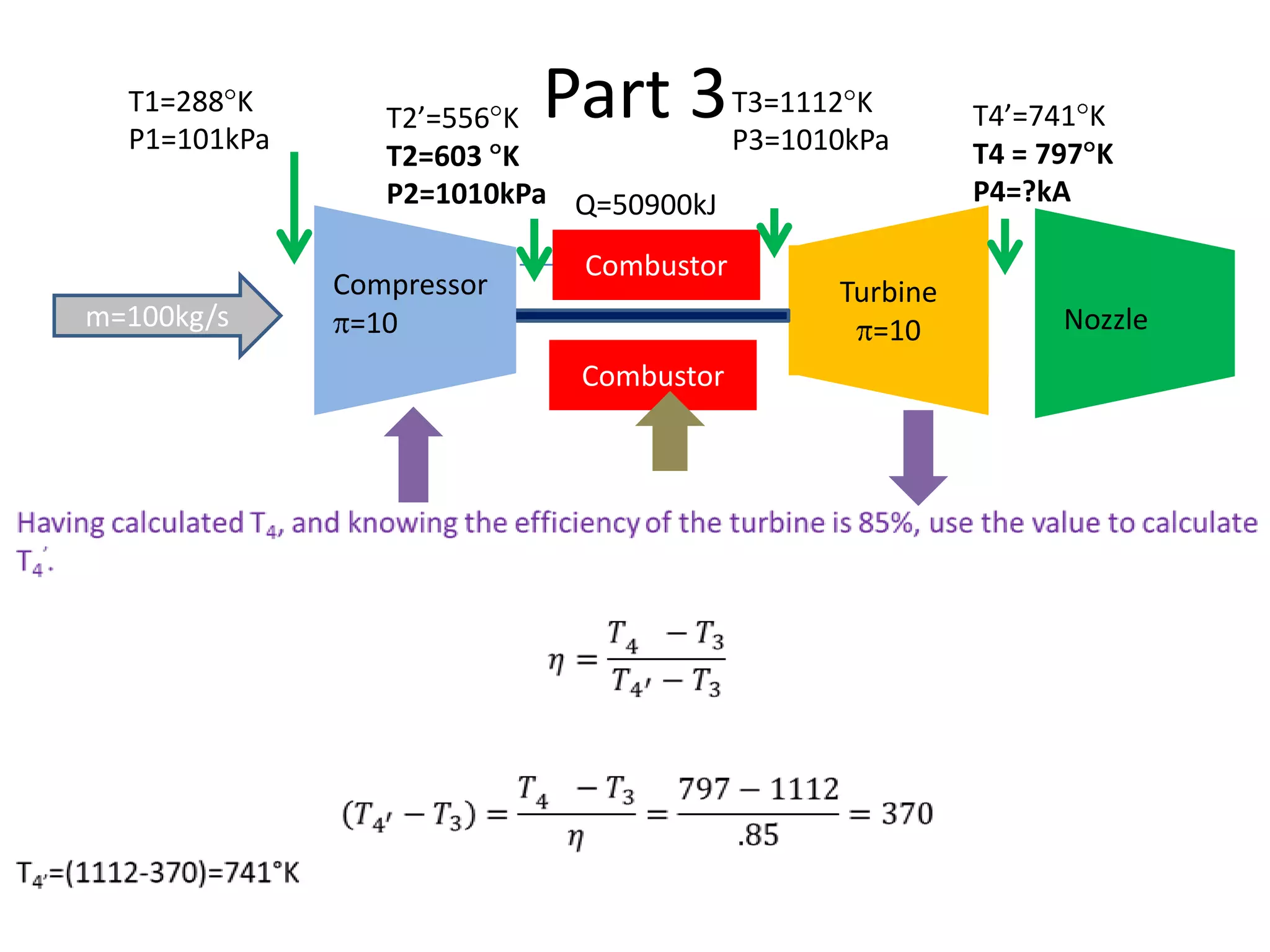
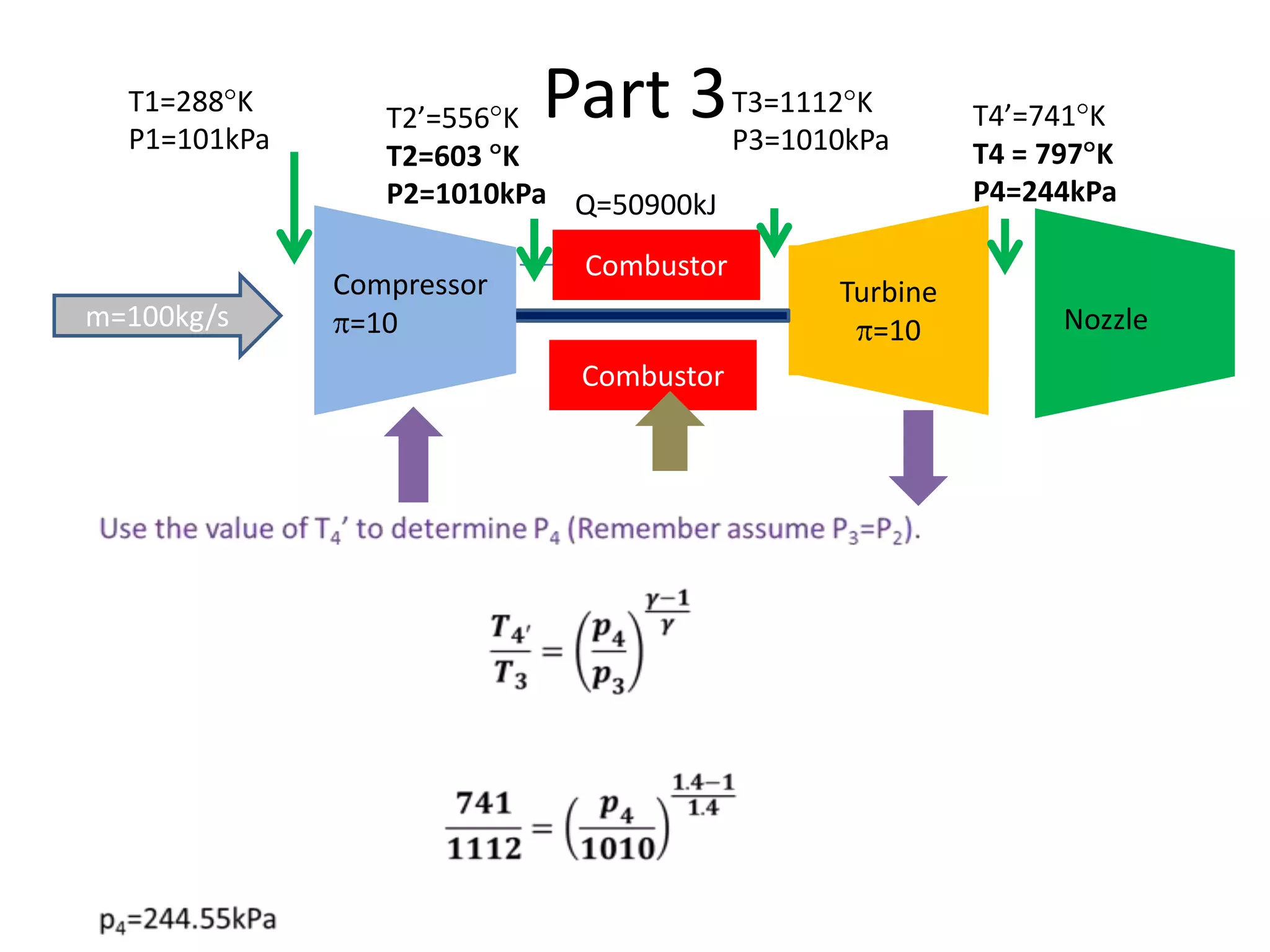
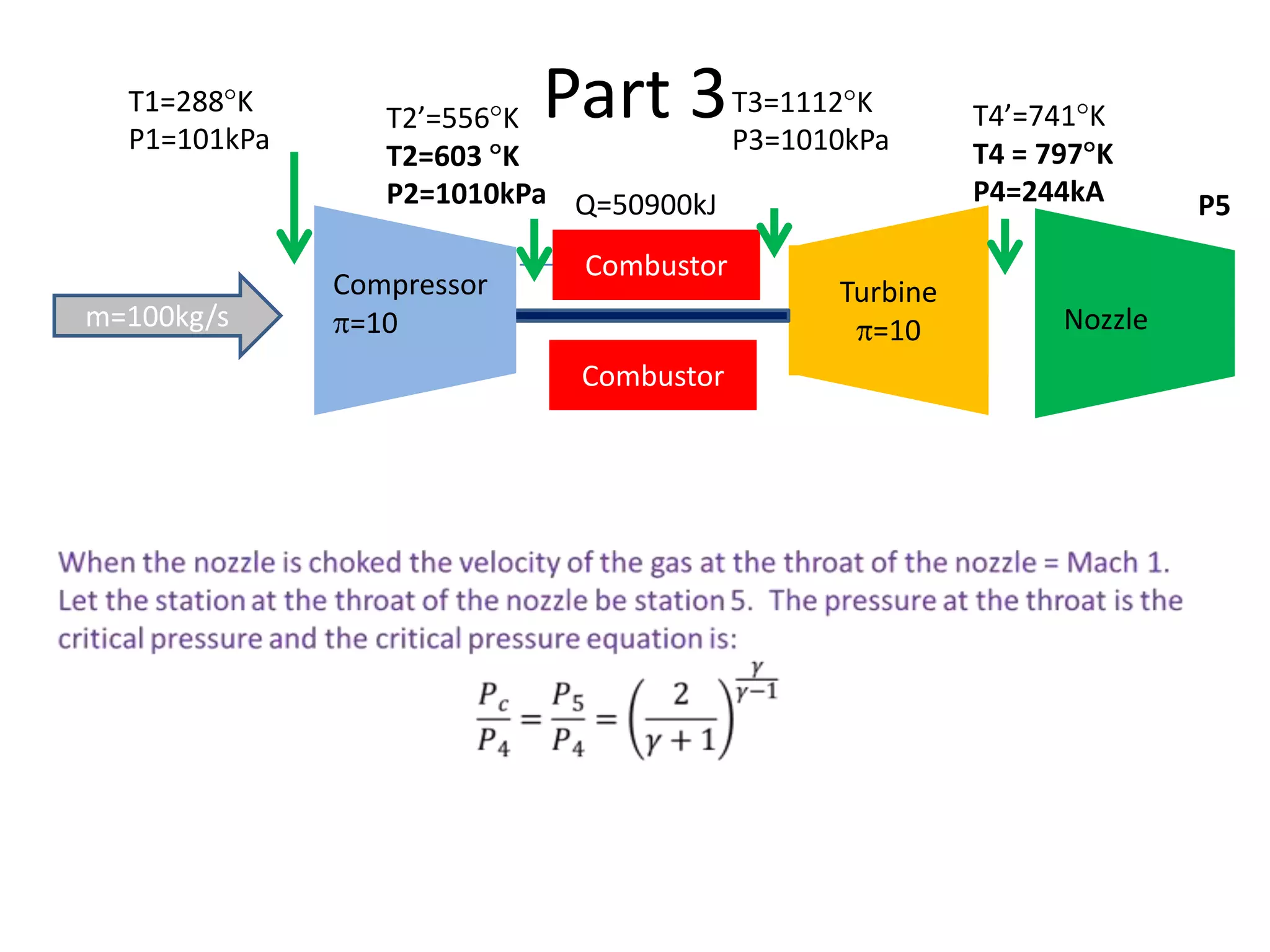
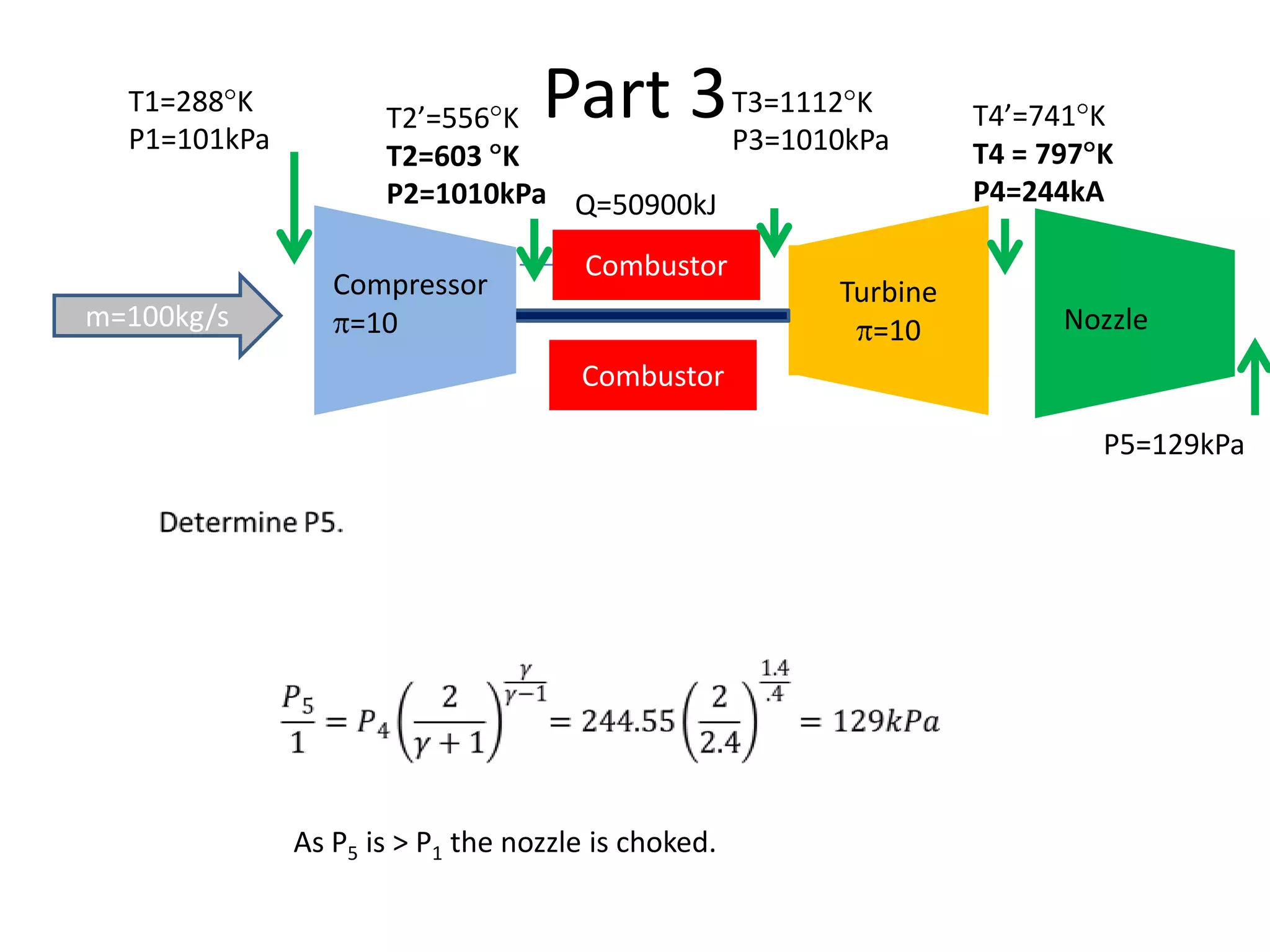
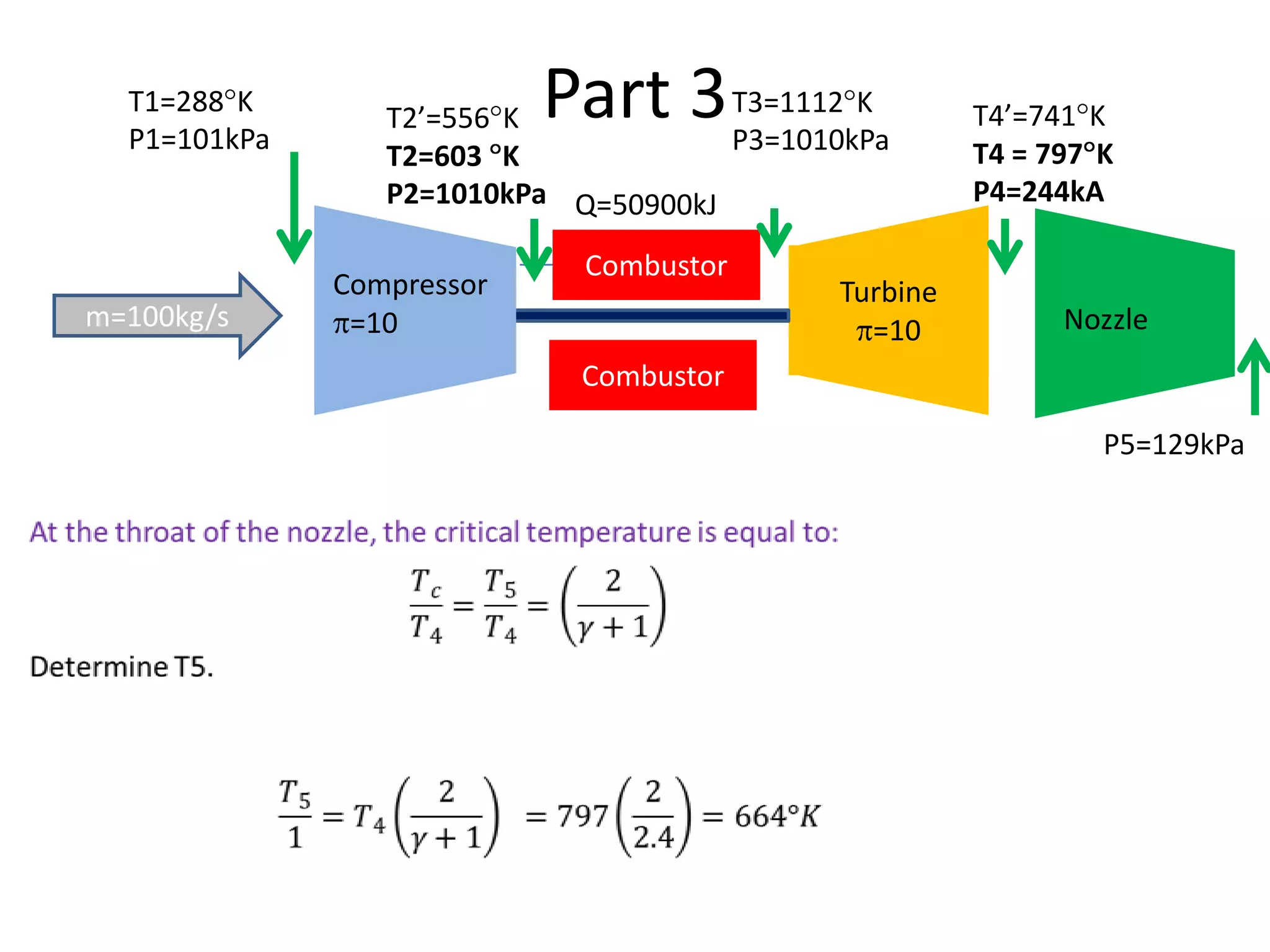
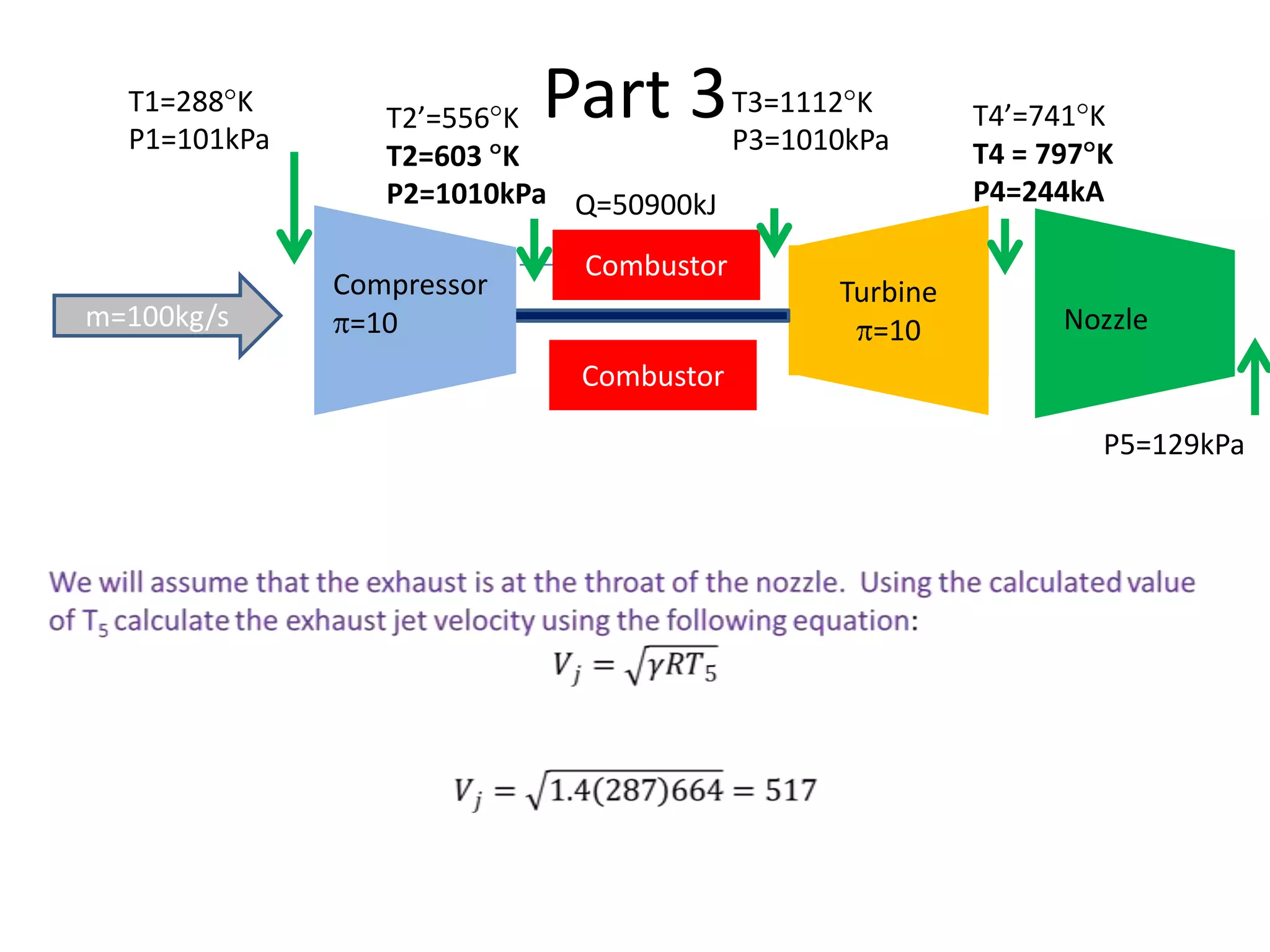
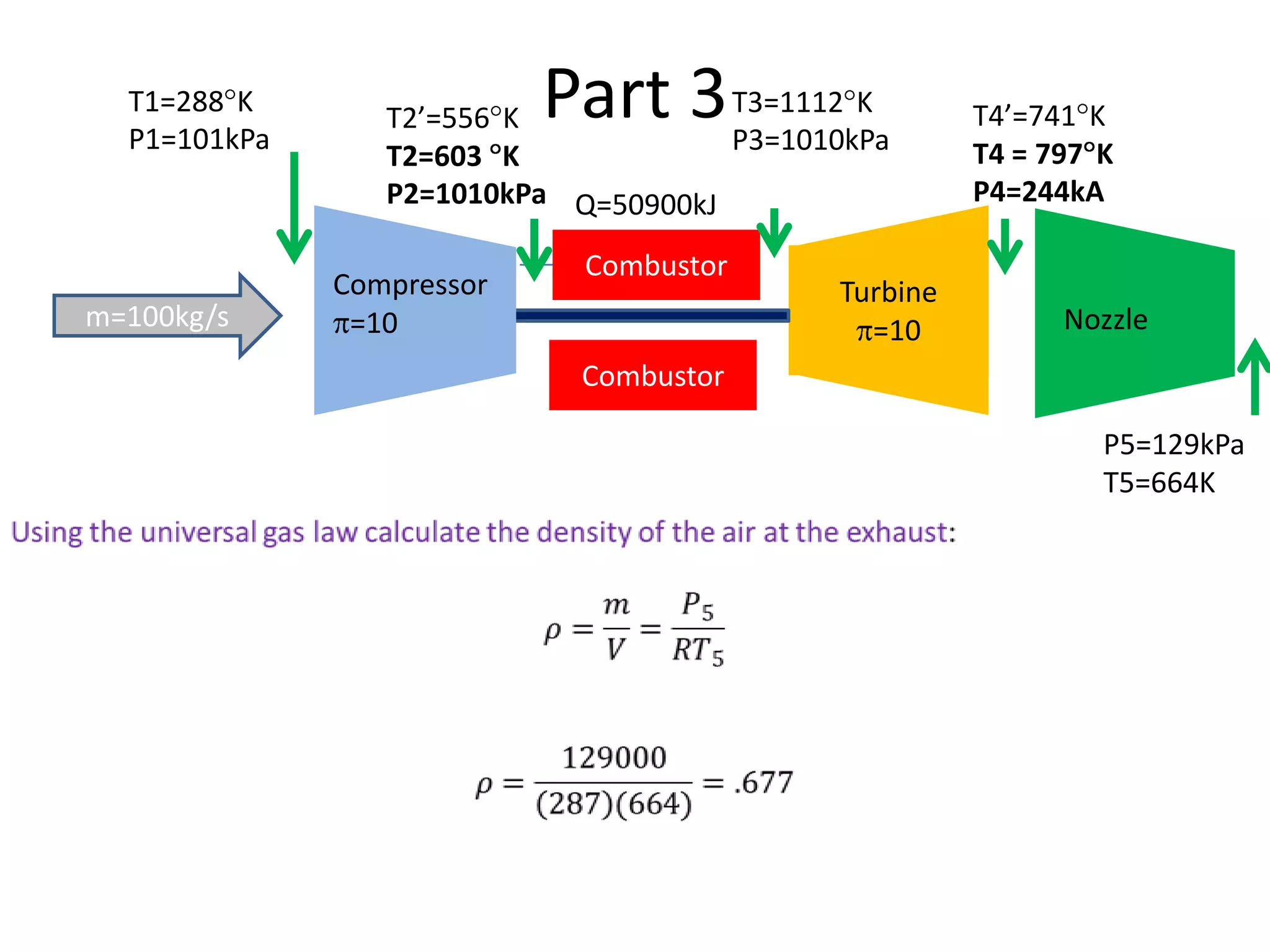
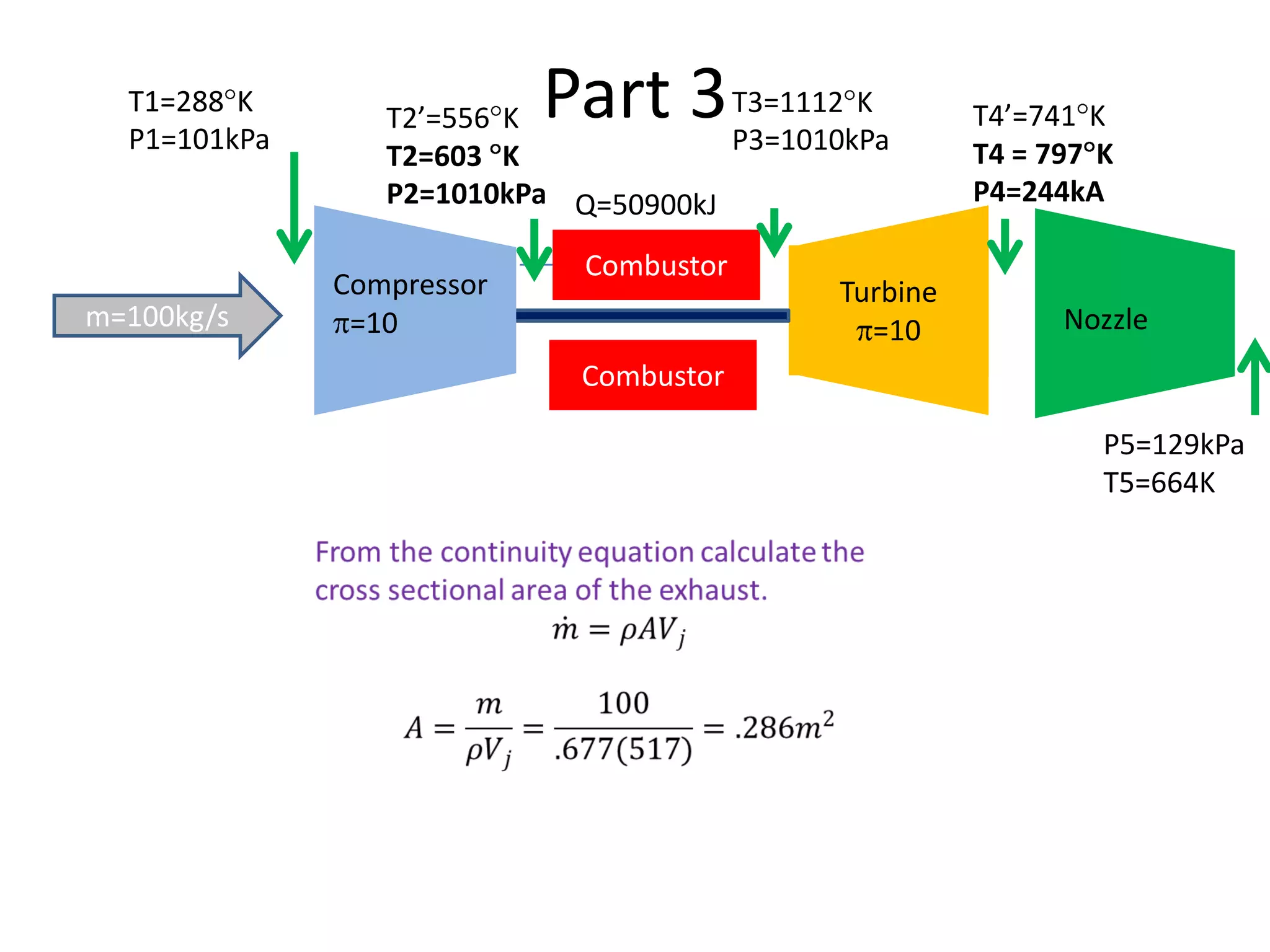
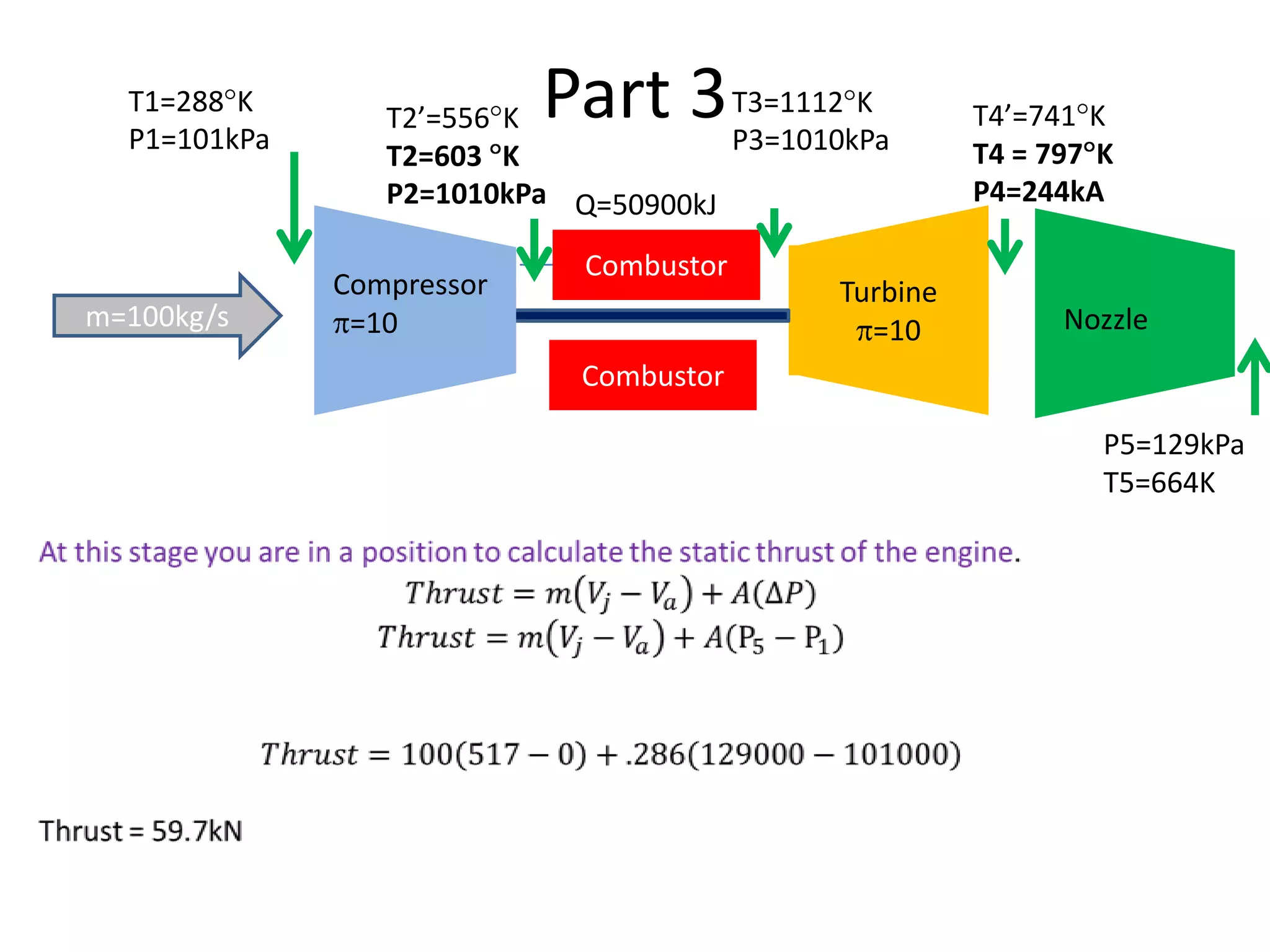
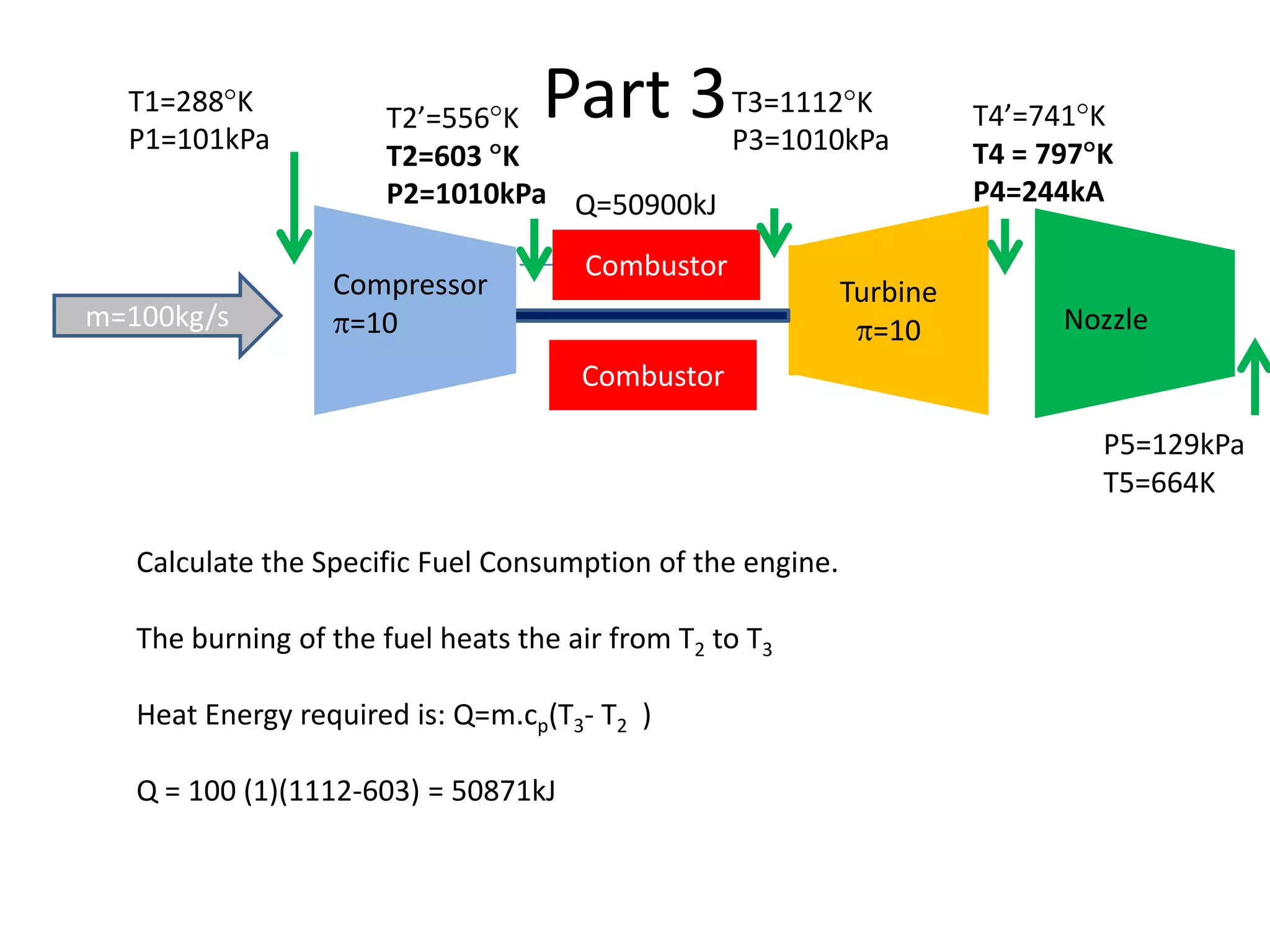
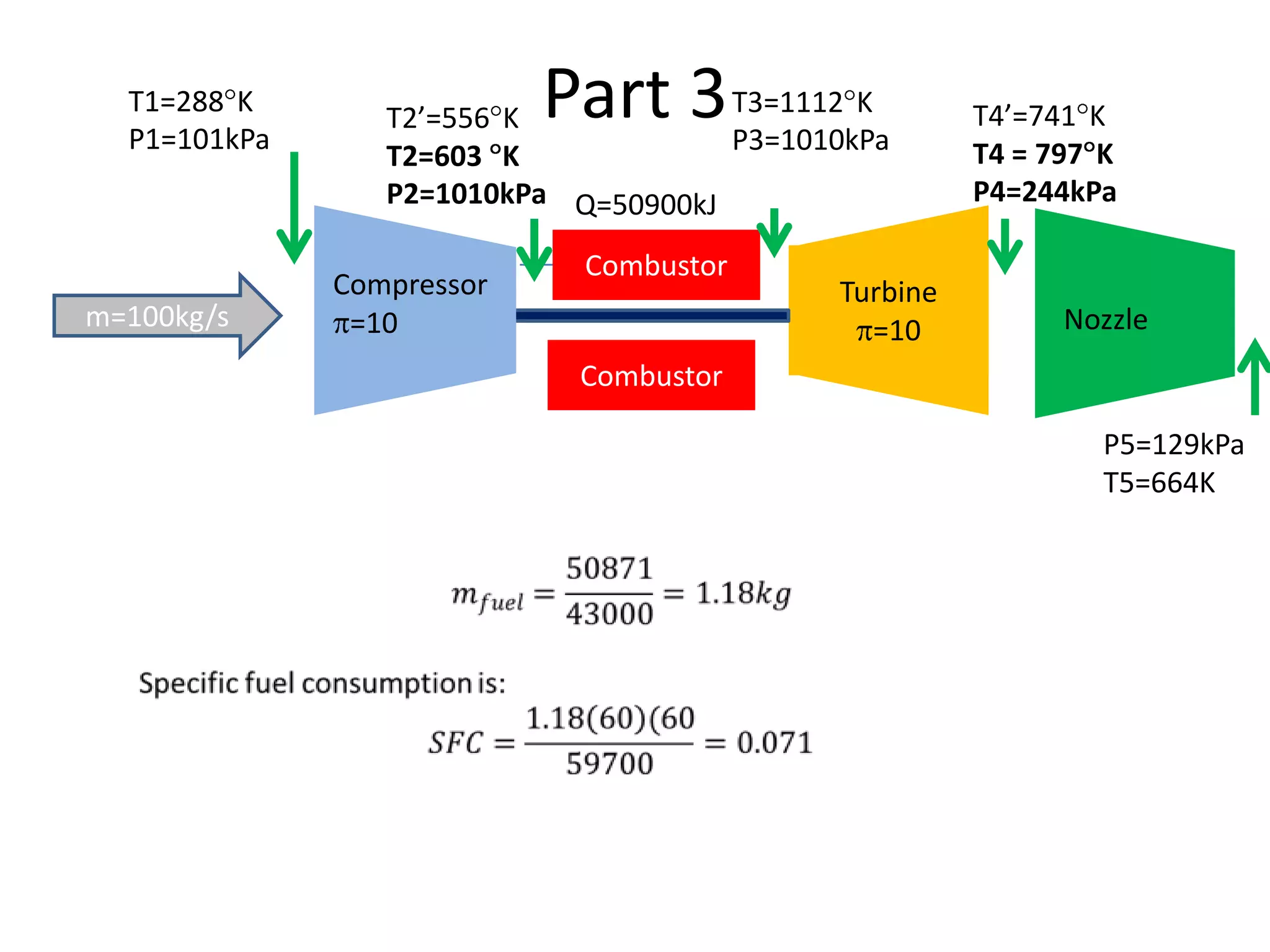
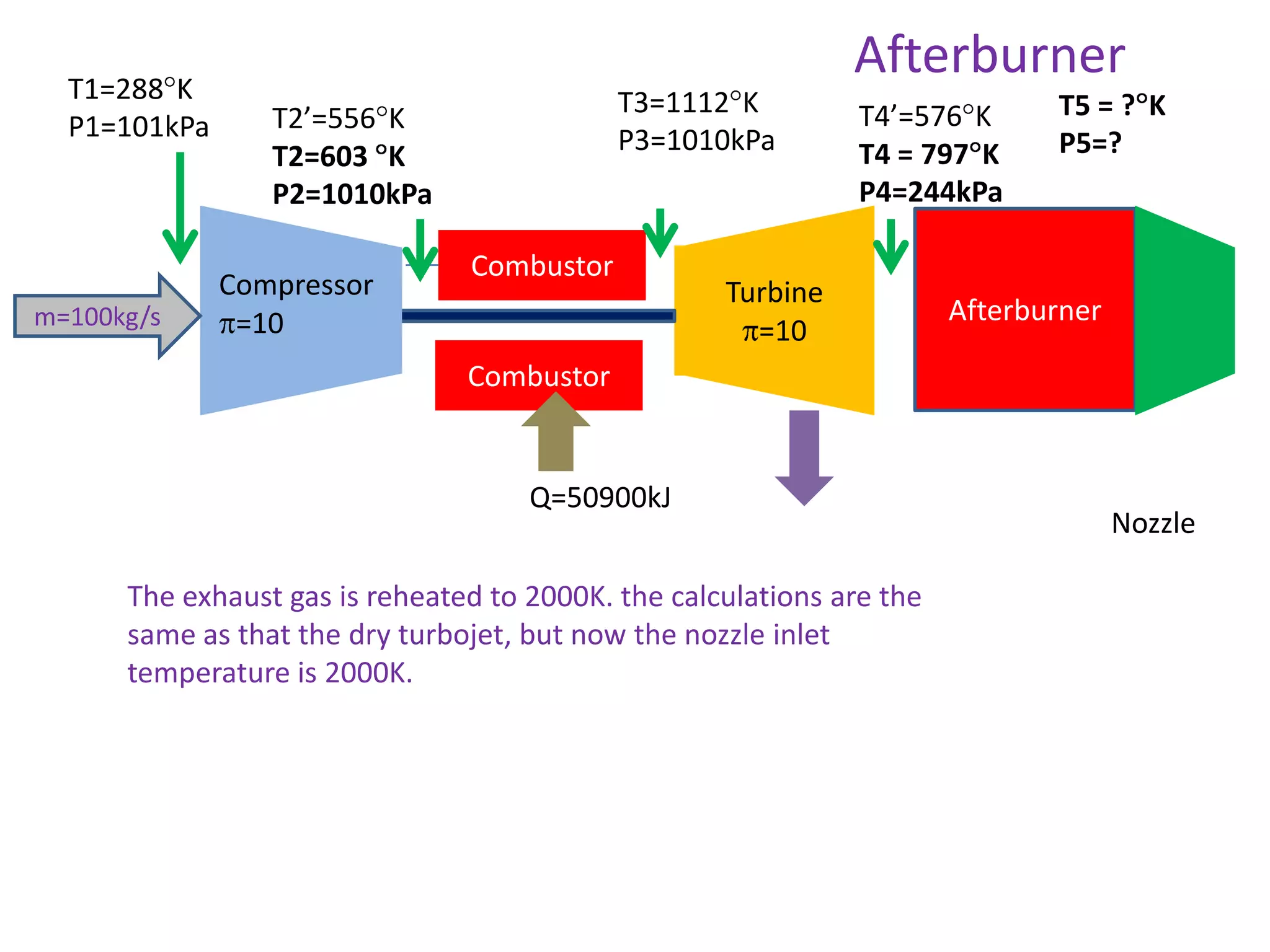
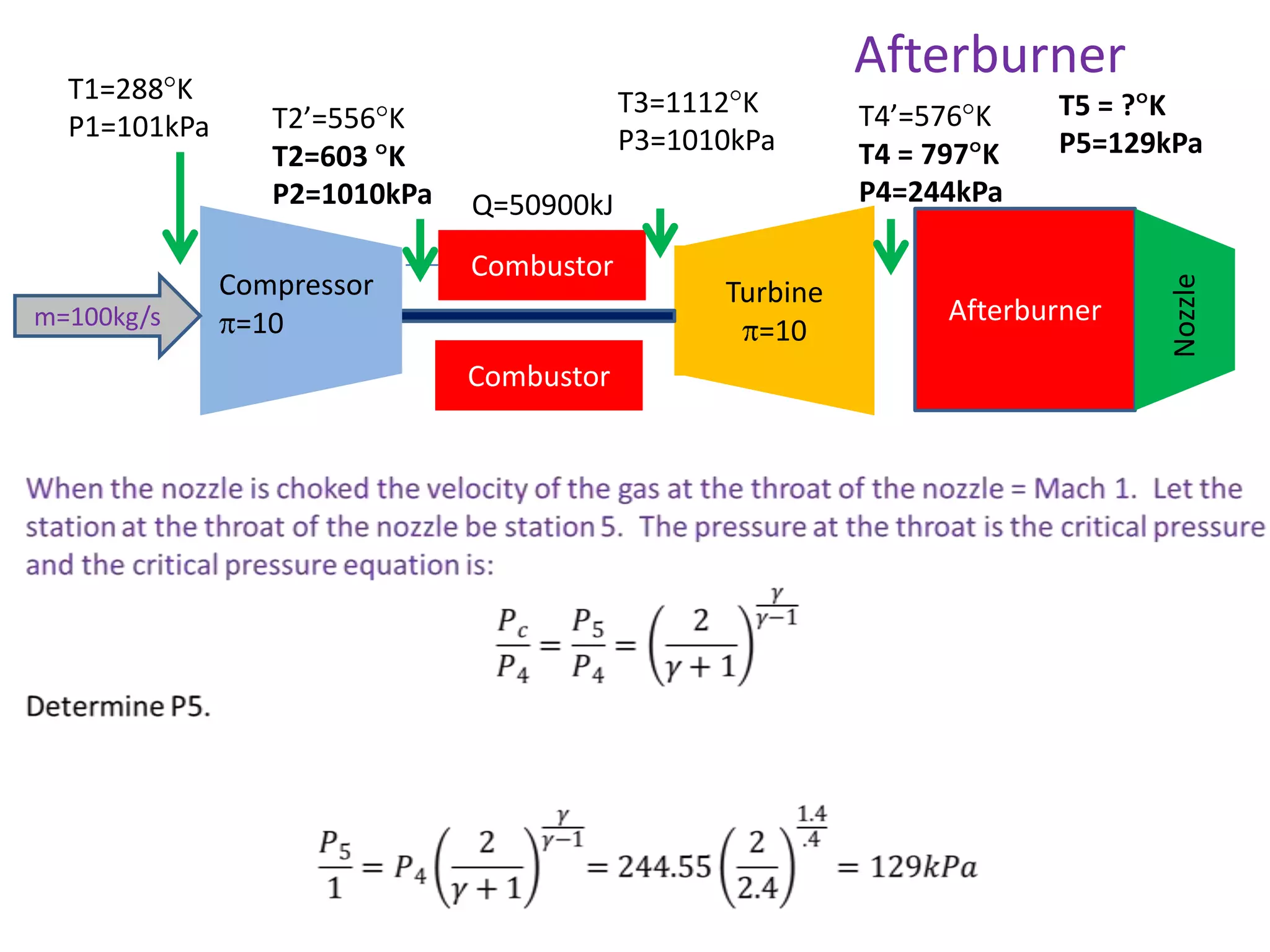
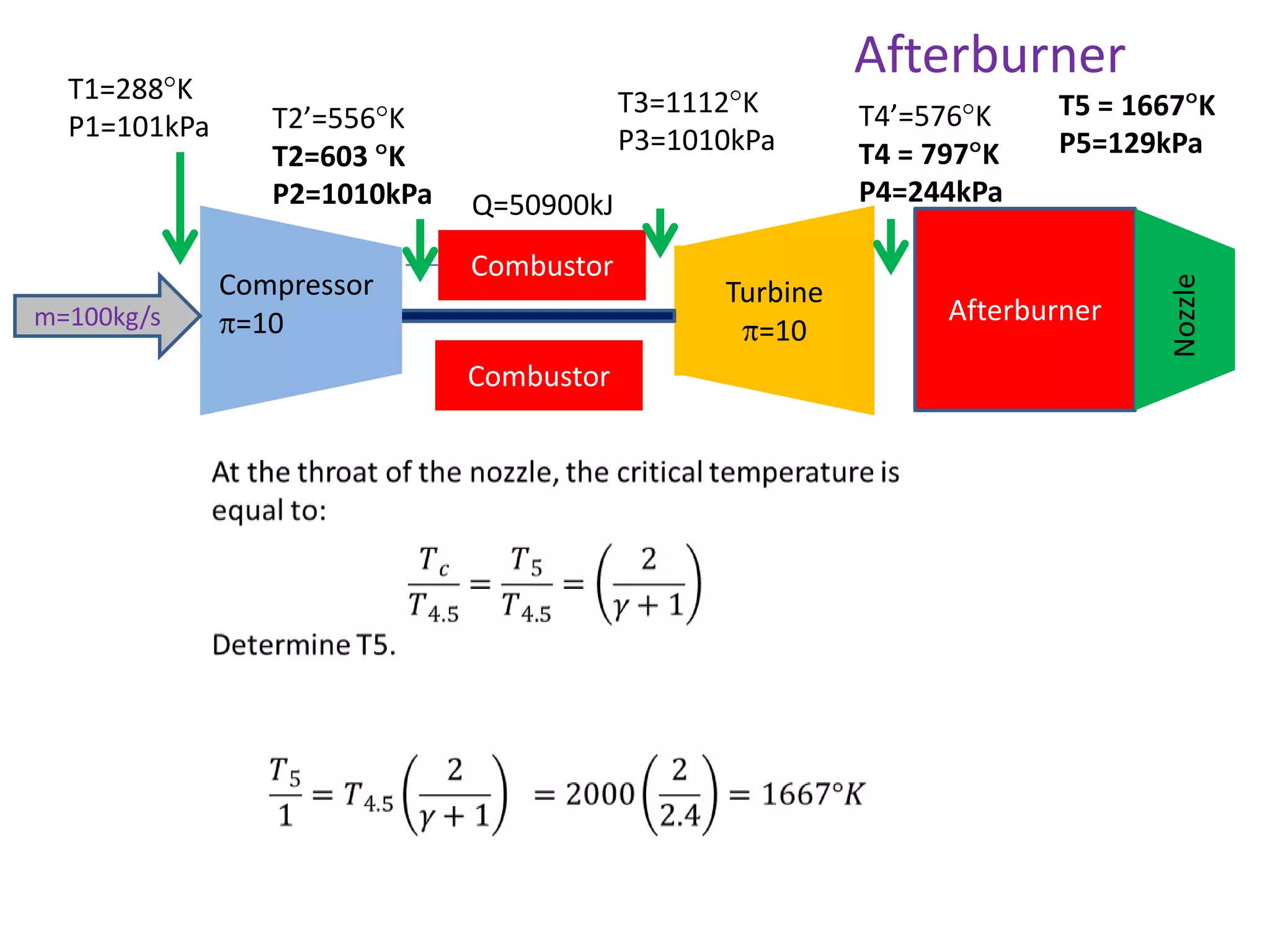
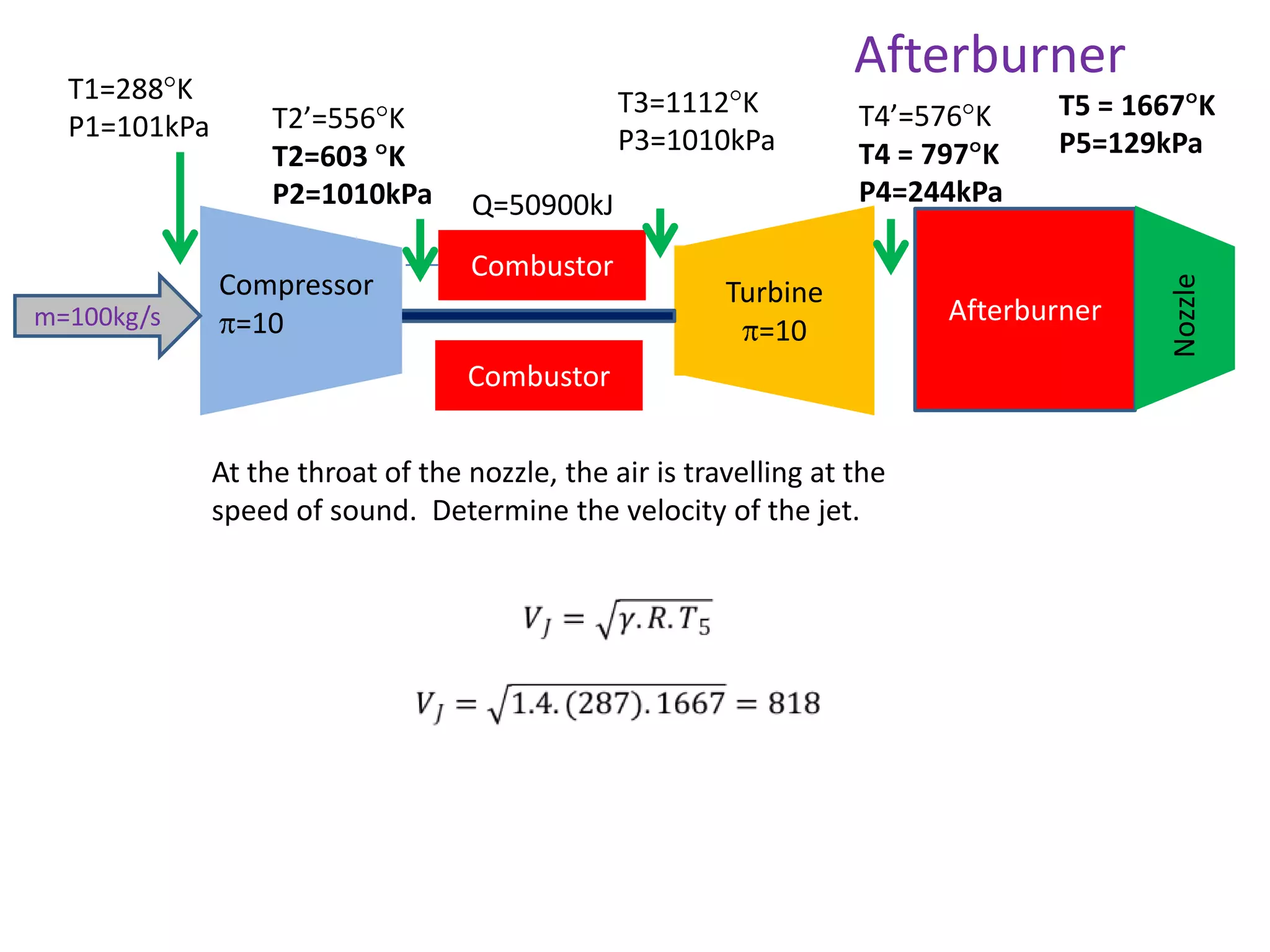
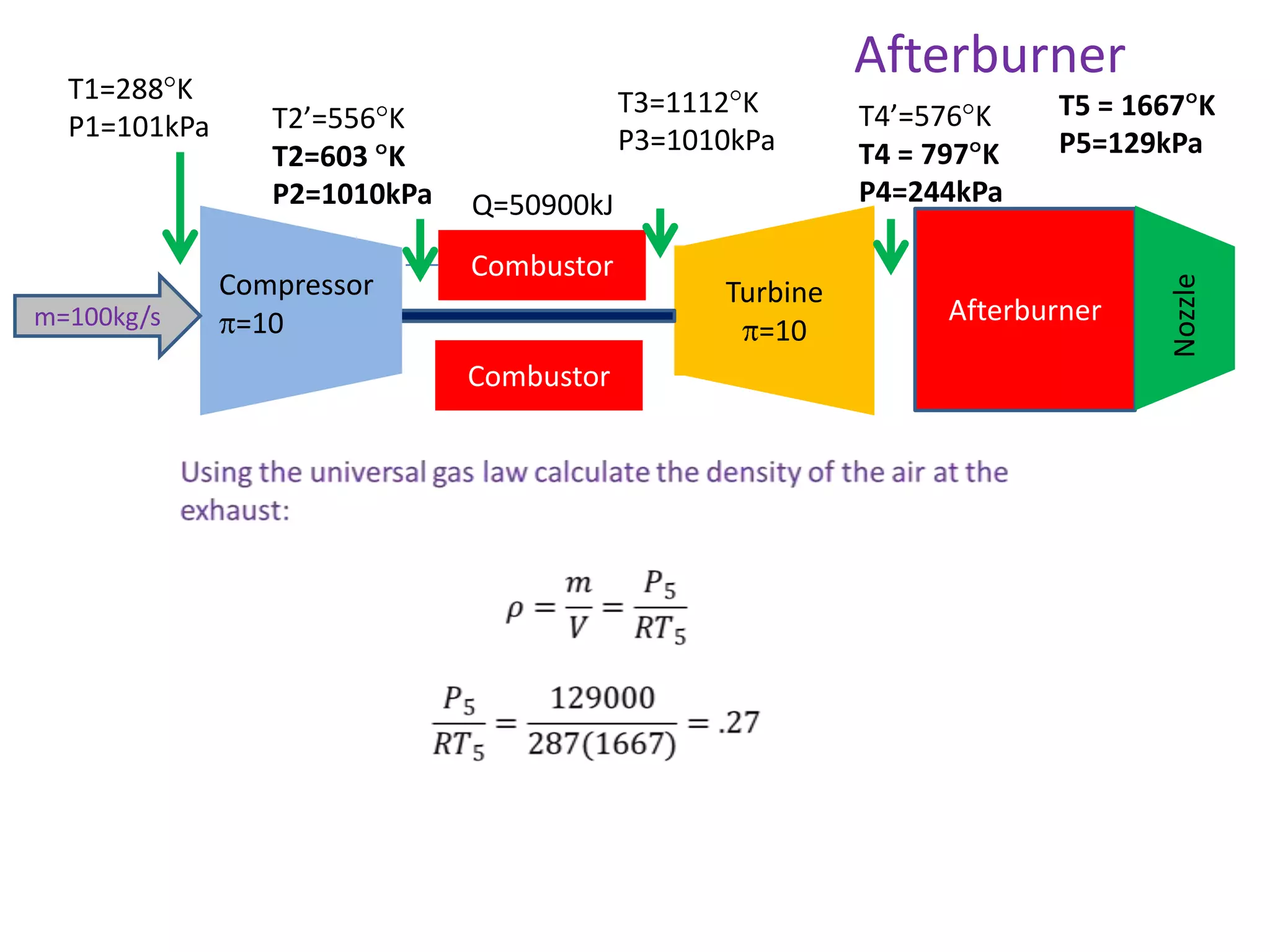
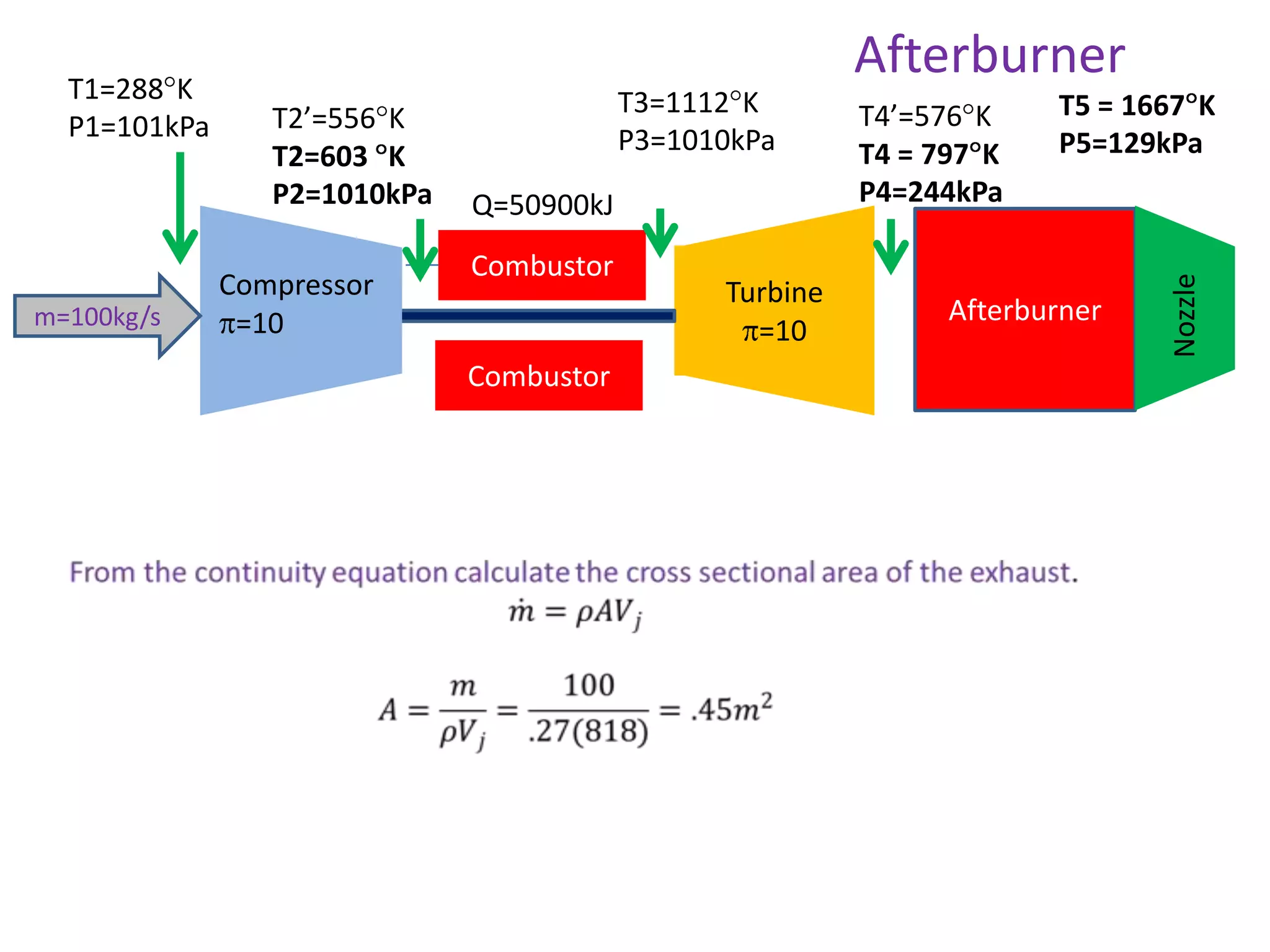
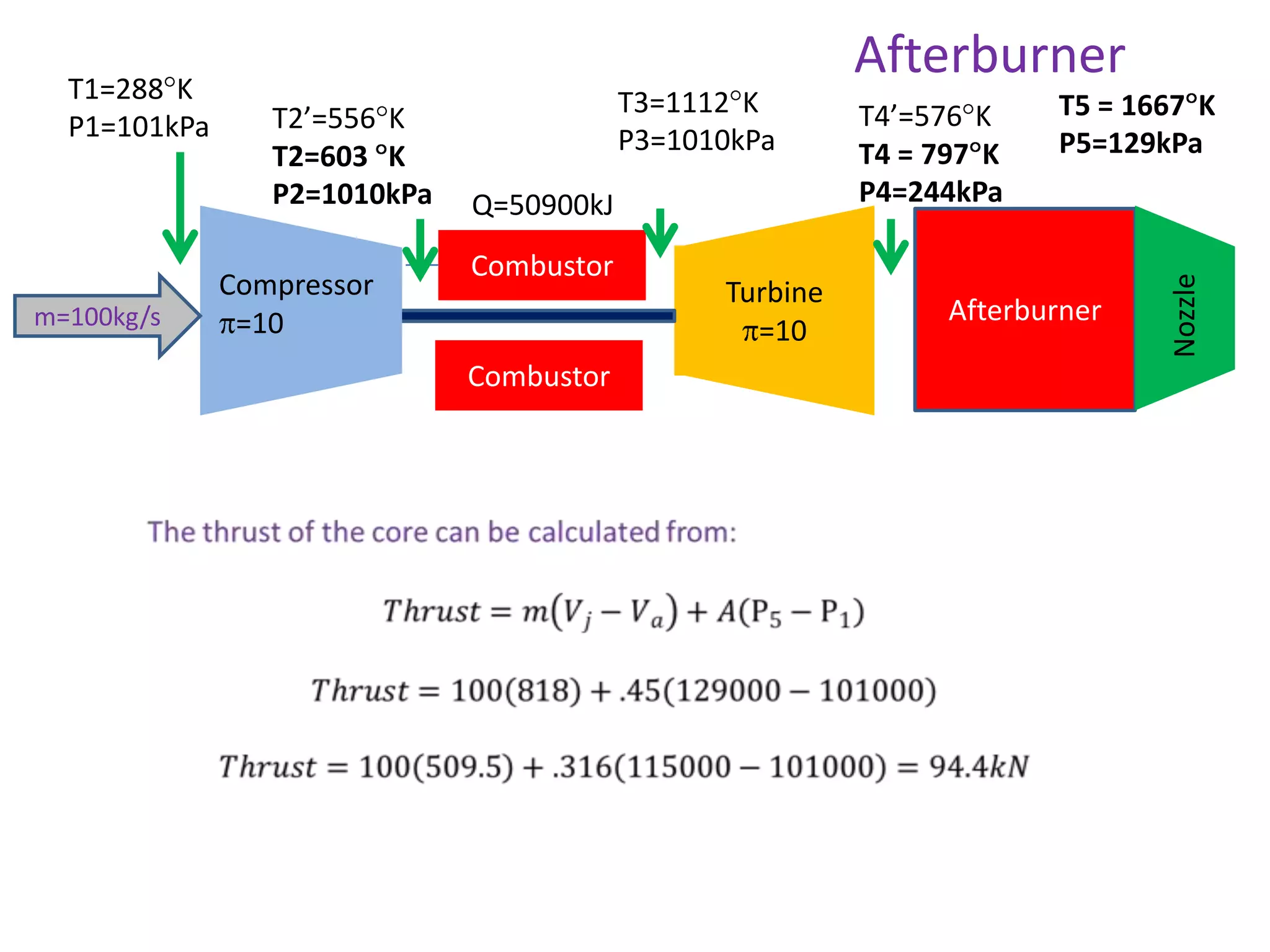
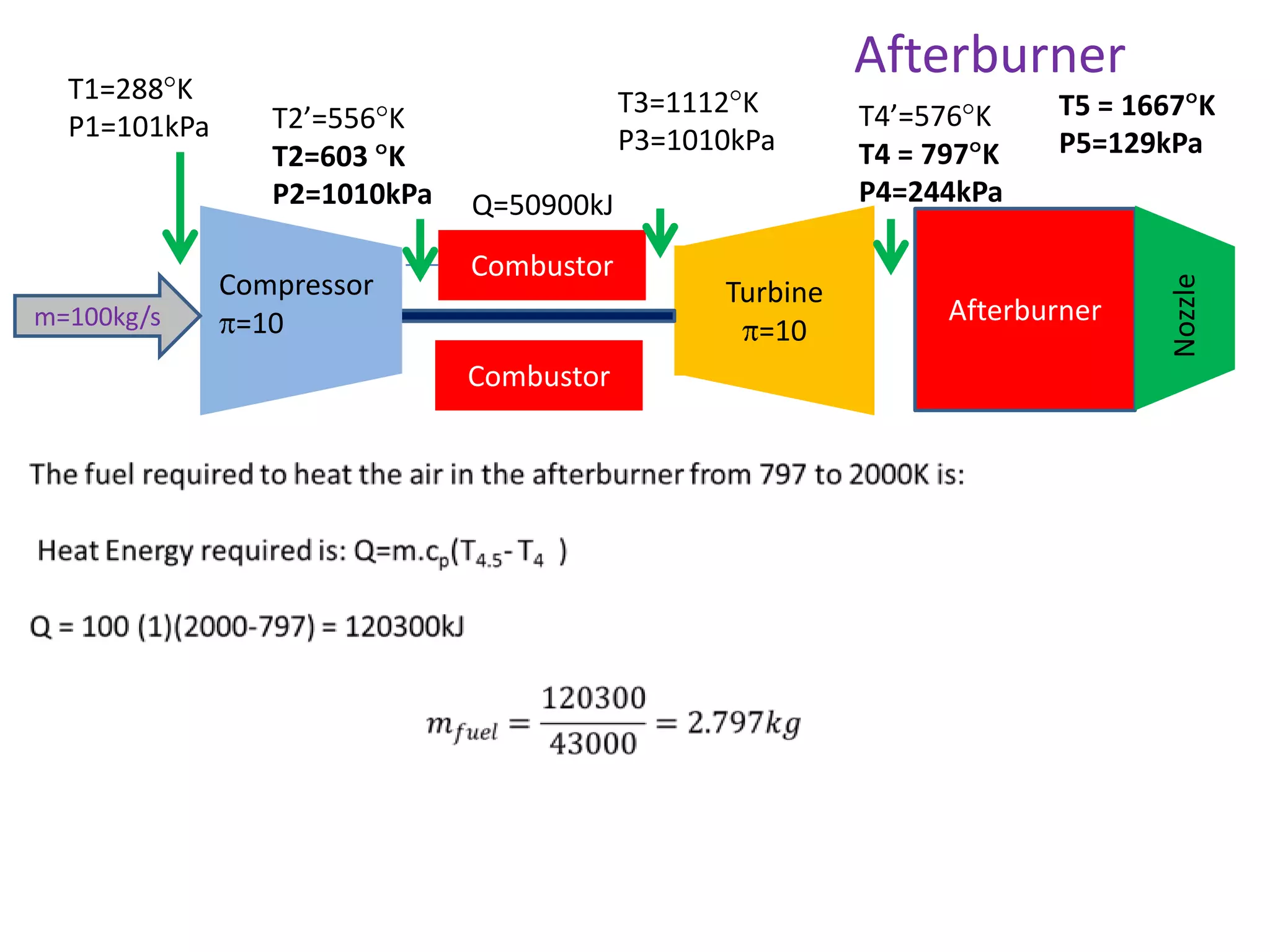
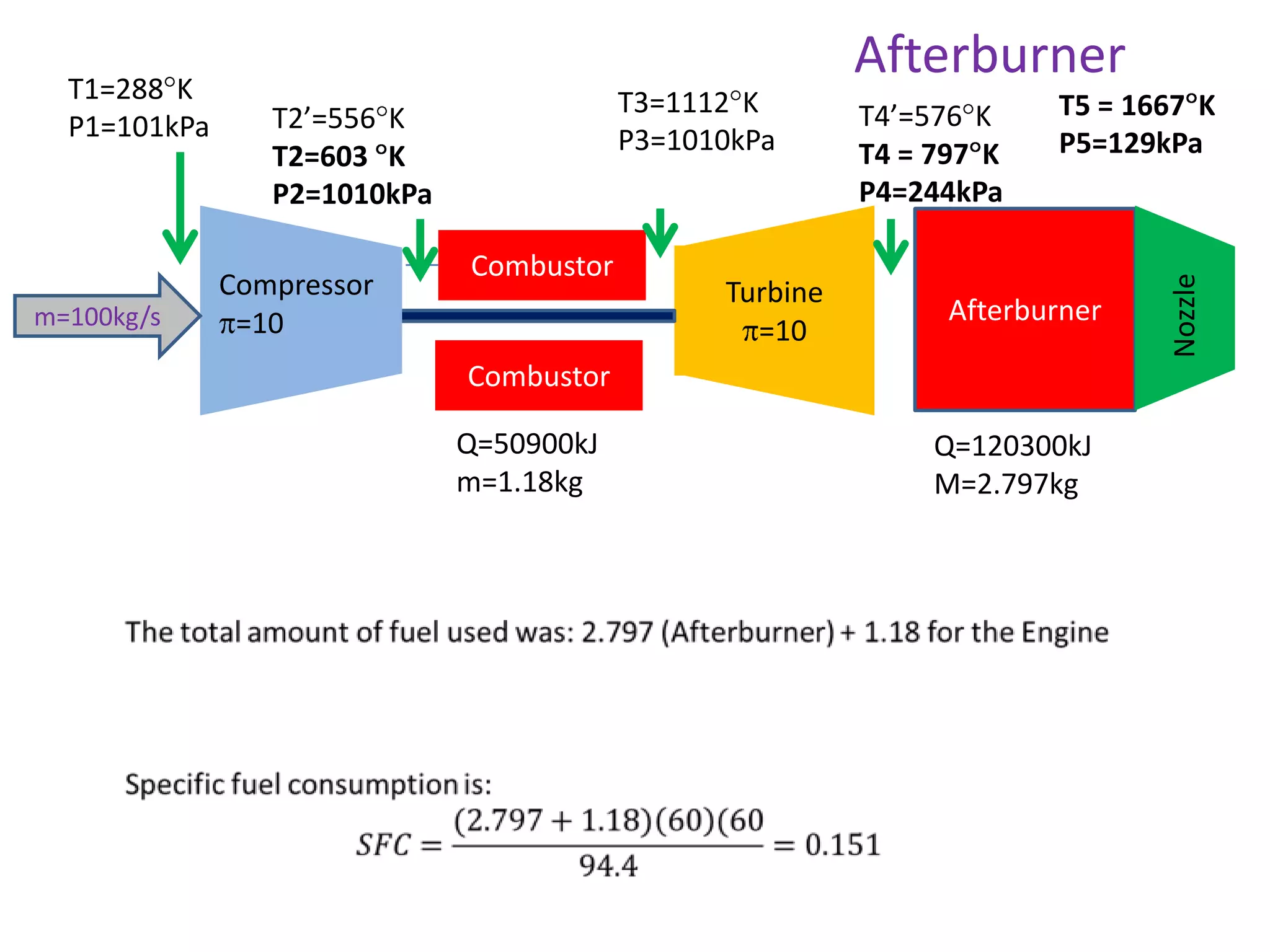
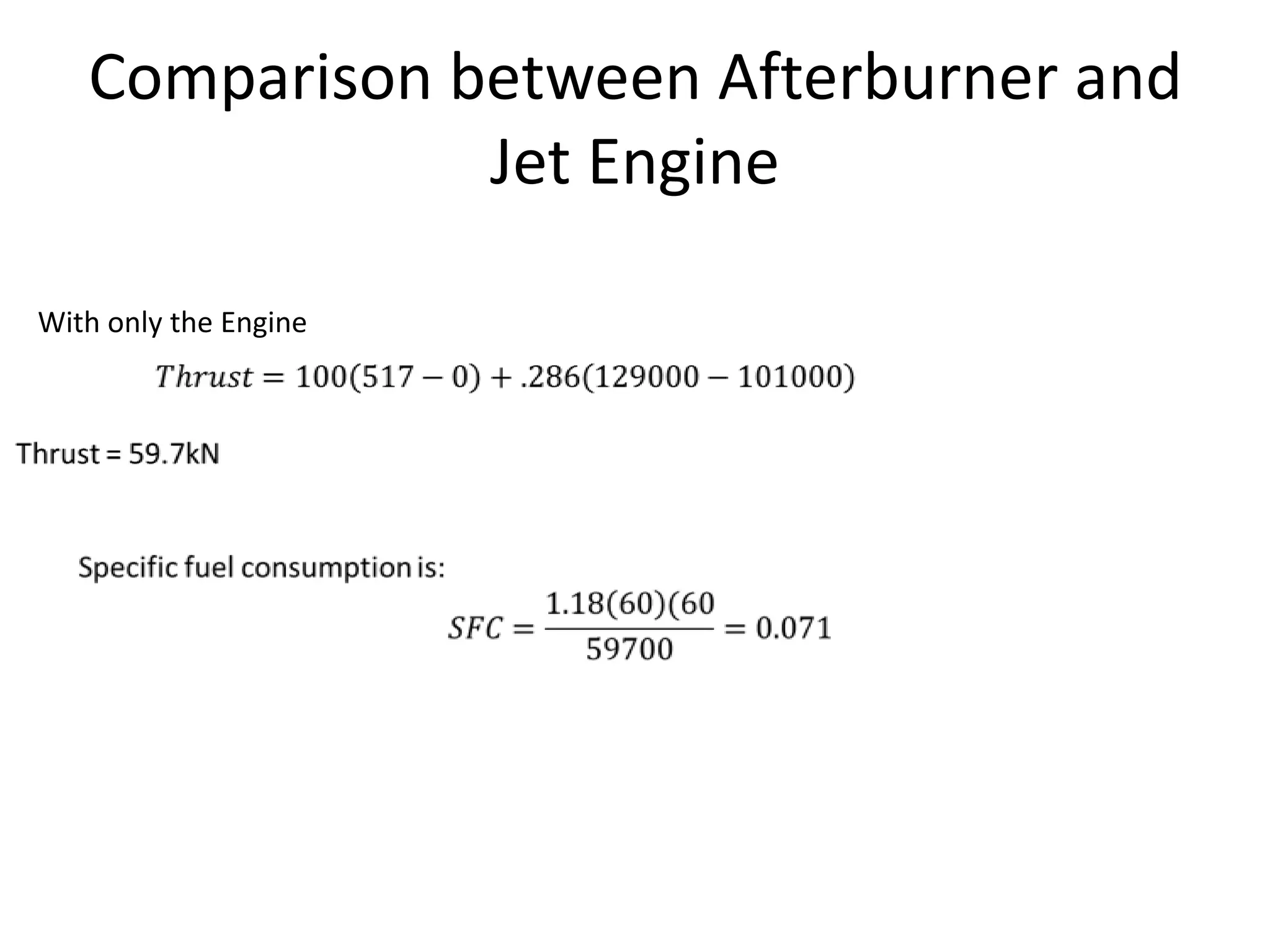
The document analyzes the ideal performance of a jet engine through three parts. It examines the propulsive, thermal, and overall efficiencies. The compressor compresses the air 10 times while the turbine expands it 10 times. With compressor and turbine efficiencies of 85%, the useful work is 14,100kJ. The combustion temperature is 1112K and heat supplied is 50,900kJ. The nozzle exhaust is choked with pressure of 129kPa and temperature of 664K. Specific fuel consumption is calculated based on the heat required to increase the air temperature. An afterburner is considered which further increases the exhaust temperature.