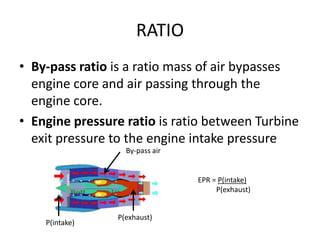
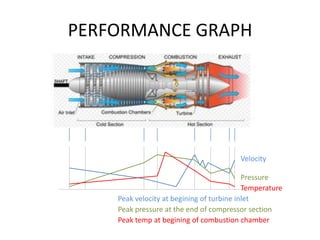
This document discusses various aspects of engine performance including:
- Thrust is generated through momentum thrust, net thrust accounts for momentum drag, and choked nozzles add pressure thrust.
- Thrust distribution varies across engine sections and can be calculated based on exit area, pressure, velocity and mass flow.
- Horsepower calculations relate thrust to aircraft speed or shaft power for different engine types.
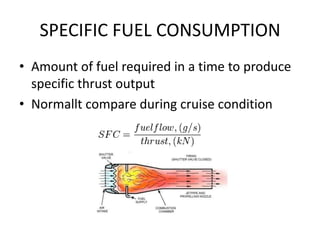
- Specific fuel consumption measures the fuel required to produce thrust during cruise conditions.