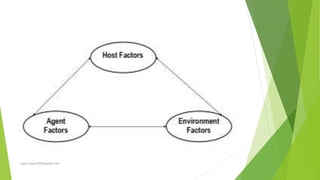
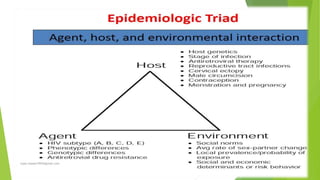
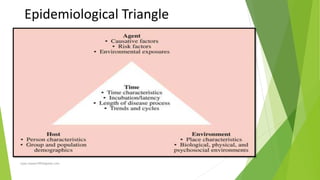
The epidemiological triad is a core concept in epidemiology that explores the interaction between an agent, host, and environment in the spread of diseases. This framework helps identify risk factors and develop preventive measures by emphasizing that the presence of disease relies on the interplay of these three components. Understanding these elements is essential for managing health issues ranging from infectious diseases to chronic conditions.