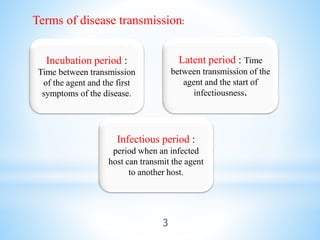
This document discusses incubation periods of diseases. It defines incubation period, latent period, and infectious period. It notes that incubation period is the time between transmission of an agent and first symptoms. Latent period is time between transmission and infectiousness, while infectious period is when an infected host can transmit. It lists factors that influence incubation periods like pathogen generation time and infective dose. It categorizes incubation periods as short (2-3 days for food poisoning and influenza), medium (10-21 days for measles and mumps), and long (weeks to years for hepatitis B and rabies). Finally, it discusses the importance of knowing incubation periods for tracing infections, determining quarantine periods, and prognosis.